-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2023; 13(4): 107-113
doi:10.5923/j.chemistry.20231304.03

Challenges in Classifying Secondary and Tertiary Amides: A Critical Examination of IUPAC Guidelines
Sumeyra Yumak
Science Department, BMCC, CUNY, New York, NY, USA
Correspondence to: Sumeyra Yumak , Science Department, BMCC, CUNY, New York, NY, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Organic compounds are organized into classes or families based on their functional groups, which consist of specific groups of atoms. Similar physical and chemical properties are exhibited by compounds containing the same functional group. The classification of organic compounds according to their structure, compound naming, chemical reaction prediction, and product structure depiction is facilitated through the identification of functional groups. The amide functional group is extensively utilized in both synthetic organic chemistry and bioorganic chemistry, making it one of the most prevalent components. Its significance within the molecular sciences is profound, notably serving as the essential bond that forms the backbone of peptides, proteins, and a multitude of other biomolecules. In this study, we identify discrepancies in IUPAC's amide classification rules over the years and their lack of acceptance within the scientific community. We draw evidence from various sources, including textbooks, peer-reviewed articles, and online chemistry resources, to illustrate a lack of uniform adherence to IUPAC's amide classifications, despite complete agreement among these sources. These findings emphasize the necessity for IUPAC to reconsider these recommendations, not only to alleviate potential challenges for students and scientists but also to align with well-established scientific practices.
Keywords: Functional Groups, Amide classification, IUPAC
Cite this paper: Sumeyra Yumak , Challenges in Classifying Secondary and Tertiary Amides: A Critical Examination of IUPAC Guidelines, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 13 No. 4, 2023, pp. 107-113. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20231304.03.
1. Introduction and Background
- Within the context of first- and second-semester undergraduate introductory organic chemistry courses, functional groups within organic compounds assume a paramount role. The nomenclature of organic compounds holds equal importance in the broader curriculum encompassing introductory organic chemistry and general chemistry. The process of naming organic compounds frequently initiates with branched alkanes and progressively incorporates substituents and functional groups [1]. Consequently, it is imperative that students possess the ability to accurately categorize functional groups to ensure precise nomenclature of organic chemical compounds. A deficiency in comprehending organic compound nomenclature can give rise to challenges in grasping other aspects of organic chemistry. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established a comprehensive set of nomenclature rules, providing the necessary framework for naming and depicting molecules and functional groups [2,3].The functional group constitutes either an individual atom or a cluster of atoms exhibiting consistent chemical traits across diverse compounds. This structural element imparts distinct physical and chemical attributes to specific families of organic compounds [4]. Functional groups, at the core of organic chemistry, medicinal chemistry, toxicity assessment, and the various facets of spectroscopy, serve as the foundational concept. Within these domains, functional groups play a pivotal role by enabling specific interactions with target proteins, often through the establishment of hydrogen bonds and other less robust interactions. Additionally, functional groups significantly shape the metabolic stability and overall bioavailability of molecules, either through stereoelectronic or electrostatic considerations. Abundant scientific literature, including numerous research papers and books, is dedicated to elucidating the properties and reactivity of specific functional groups. The renowned book series titled "Chemistry of Functional Groups" provides a comprehensive exploration of various categories of organic molecules and encompasses an extensive library of over 100 volumes [5].In high school and college-level chemistry courses, it is common practice for textbooks to introduce functional groups through a table. This table typically includes information such as the class, structure, characteristics, and a representative example (refer to Figure 1) [6]. Students are generally tasked with mastering the content presented in this chart.
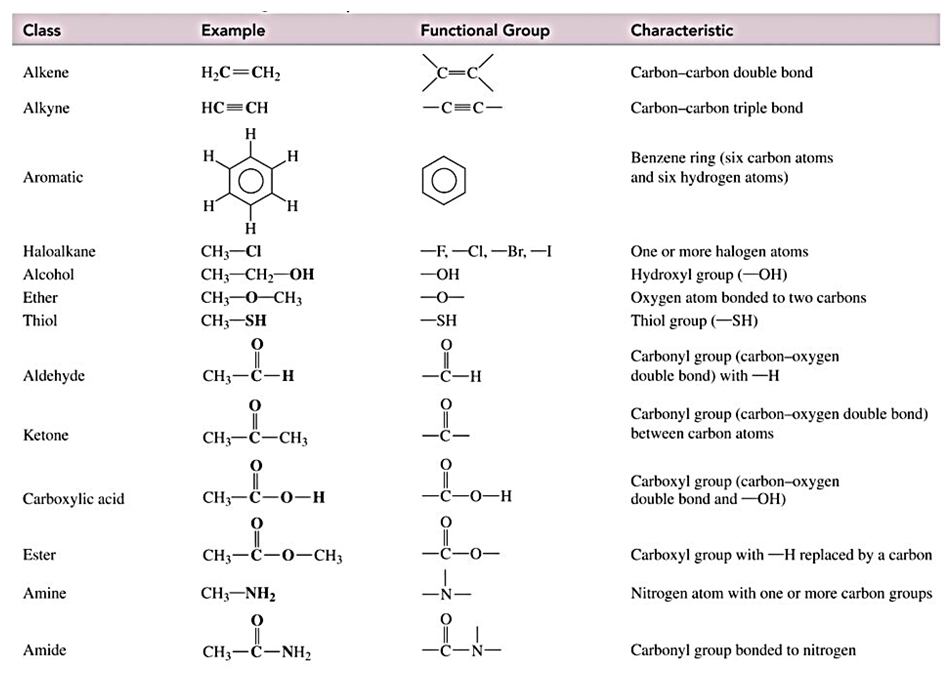 | Figure 1. The most common functional groups |
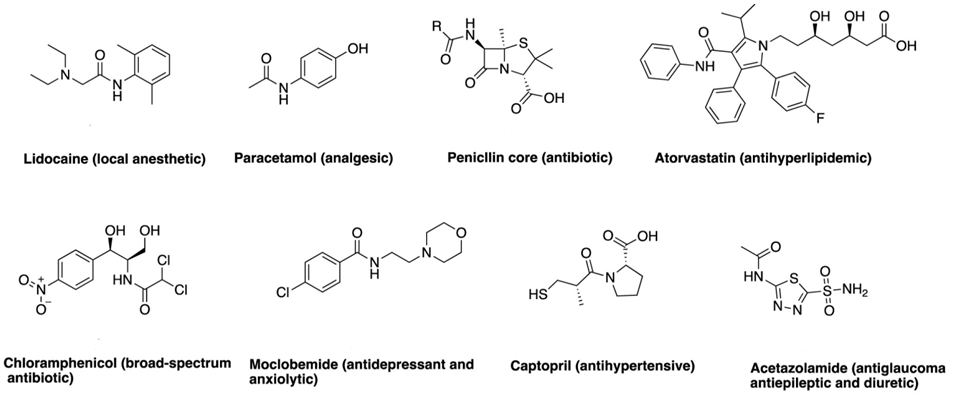 | Figure 2. Amide-Based Drug Structures and Functions |
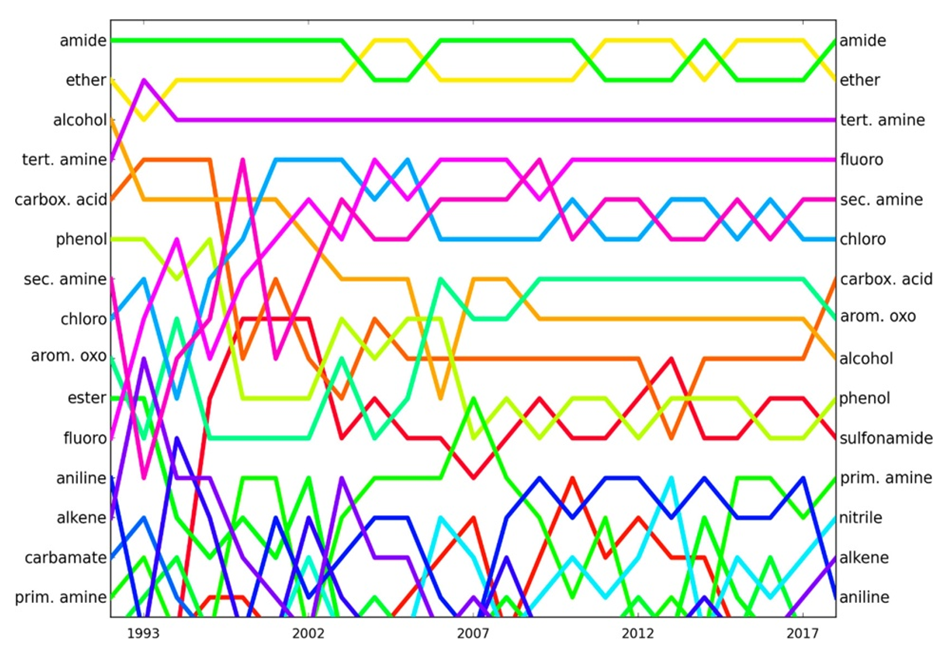 | Figure 3. Evolution of the popularity ranking of functional groups over time |
2. Study and Results
- Our investigation draws upon a range of sources, including chemistry textbooks, peer-reviewed journal articles, and online chemistry tutoring websites, to substantiate the assertion that IUPAC's recommendations regarding amide classifications are not consistently adhered to. Our findings underscore the need for IUPAC to reconsider these recommendations in order to prevent potential confusion among students and scientists.In a typical chemistry textbook [23], amides are classified as follows (Figure 4) [23]: “The N atom of an amide may be bonded to other hydrogen atoms or alkyl groups. Amides are classified as 1°, 2°, or 3° depending on the number of carbon atoms bonded directly to the nitrogen atom.” 1°, 2°, and 3° mean primary amide, secondary amide, and tertiary amide, respectively.
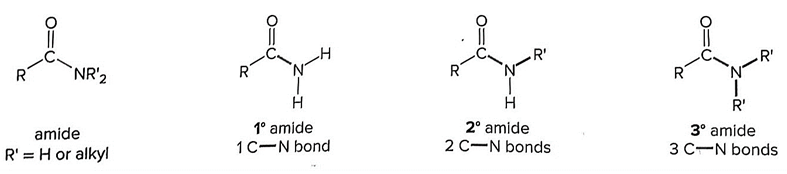 | Figure 4. Classification of Amides as primary, secondary, and tertiary amides |
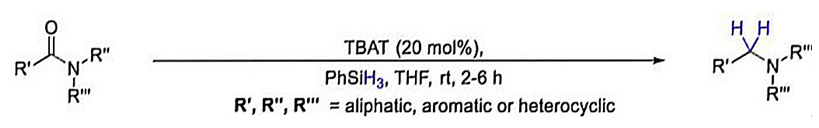 | Figure 5. A tertiary amide in a reduction reaction |
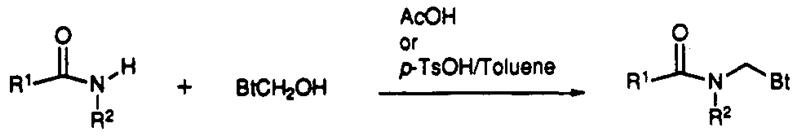 | Figure 6. The conversion of secondary into tertiary amides |
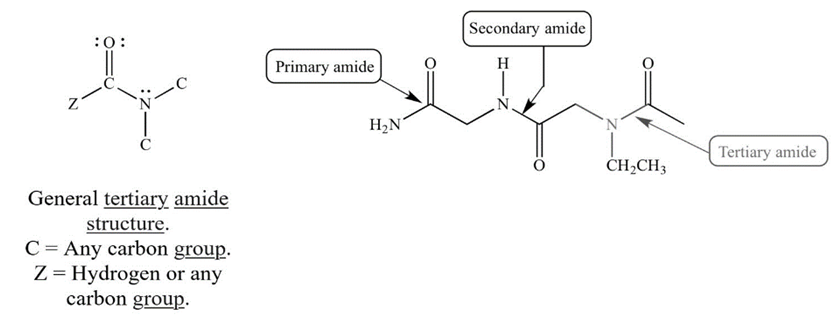 | Figure 7. Amide Classification taken from UCLA Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry |
3. Discussion
- Organic chemistry connects the chemical structures of everyday substances with their practical properties. This knowledge is essential for distinguishing between plastics, understanding food additives, and linking drug names to active ingredients. Unlike other sciences that use widely understandable language, chemistry relies on complex symbols and formulas. Therefore, organic chemistry nomenclature is crucial in translating these symbols, making it a vital skill for students at all levels, although it is often a challenge. The amide functional group holds immense significance in the field of molecular sciences. It serves as the foundational linkage in the structural framework of peptides, proteins, and various biomolecules. In the realm of medicine, amide-forming reactions represent a cornerstone of the pharmaceutical industry. Over the past century, our understanding of the properties of the amide functional group has evolved, further underlining its crucial role in drug design and development.IUPAC is globally recognized as the primary authority in chemical nomenclature and terminology. Nevertheless, its classification of amides has displayed inconsistency over time and lacks recognition and adherence within the scientific community. Over the years, IUPAC's approach to amide classification has displayed inconsistency, as observed across various editions of their guidelines. In the 1979 Blue Book edition, IUPAC introduced a classification system that labeled compounds with one, two, or three acyl groups attached to nitrogen as "amide," "primary amide," "secondary amide," and "tertiary amide," respectively. However, this approach underwent revision in the 1993 edition, where amide classification was entirely omitted, and the use of terms such as primary, secondary, and tertiary amides for mono-, di-, and triacyl derivatives of ammonia was discouraged. The 2013 edition reinstated the 1979 classification system, and in 2022, a newly updated eBook edition of the guidelines removed the specific classification of primary, secondary, and tertiary amides altogether. IUPAC recommends against classifying amides based on the number of carbon atoms or alkyl groups connected to the nitrogen atom. Nonetheless, our investigation, drawing evidence from textbooks, peer-reviewed articles, and online chemistry sources, indicates that amides continue to be consistently classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary amides, based on the number of carbon atoms connected to the nitrogen in the amide functional groups, in contrast to IUPAC's recommendations.In light of the extensive examination of amide classification rules presented in this study, supported by substantial evidence from various sources including chemistry textbooks, peer-reviewed journal articles, and online resources, a resounding consensus within the scientific community emerges. This consensus consistently disregards IUPAC's fluctuating amide classification recommendations over time, firmly advocating for the classification of amides based on the number of carbon atoms bonded to the nitrogen atom. The compelling body of evidence presented here underscores the case for IUPAC to reevaluate and overhaul its existing amide classification guidelines. Given the robust and unequivocal nature of this evidence, we strongly recommend that IUPAC consider aligning its amide classification recommendations with the well-established and widely accepted practice of classifying amides based on the number of carbon atoms attached to the nitrogen atom, rather than the number of acyl groups connected to the nitrogen. IUPAC can easily implement this update in the latest ebook version of the Blue Book for current and future editions. Such alignment would not only alleviate potential confusion among students, researchers, and professionals but also enhance the practical relevance of IUPAC's nomenclature guidelines, ensuring their continued resonance with the conventions observed by the broader scientific community. This harmonious approach will pave the way for a more streamlined and universally accepted amide classification system.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML