| [1] | Arshlan-Alaton (2007). Degradation of commercial textile biocide with Advanced Oxidation Processes and Ozone. J. Environ Manag. 82(2), 145-154. |
| [2] | Visinescu C. M, Sanjines R., Levy F, and Parvulescu V. I. (2005) “Photocatalytic degradation of acetone by Ni-doped titania thin films prepared by dc reactive sputtering,” Appl. Catal. B- Environmental, vol. 60, no. 3–4, pp. 155–162, 2005. |
| [3] | Forgacs E, Cserhati T, Oros G (2004) Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environ Int 30: 953–971. |
| [4] | Ganesh, I., Gupta A.K., Kumar, P.., Sekhar, P.S.C., Radha, K., Padmanabham, G. and Sundararajan, G. 2012. “Preparation and characterization of Ni-doped TiO2 materials for photocurrent and photocatalytic applications”, Science World journal, in press. |
| [5] | Gomathi DL, Girish KS, Mohan RK, Munikrishnappa C (2009) Photo degradation of methyl orange an azo dye by advanced Fenton process using zero valent metallic iron: influence of various reaction parameters and its degradation mechanism. J Hazard Mater 164: 459–467. |
| [6] | Han F, Kambala VSR, Srinivasan M, Rajarathnam D, Naidu R (2009) Tailored titanium dioxide photocatalysts for the degradation of organic dyes in wastewater treatment: a review. Appl Catal A 359:25–40. |
| [7] | Liu, X.H., He, X.B., Fu, Y.B. 2008. Effects of doping cobalt on the structures and performances of TiO2 photocatalyst, Acta Chimica Sinica, 66 1725–1730. |
| [8] | Ahmed M. A. (2012). “Synthesis and structural features of mesoporous NiO/TiO2 nanocomposites prepared by sol–gel method for photodegradation of methylene blue dye,” J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem., vol. 238, no. 0, pp. 63–70, 2012. |
| [9] | Ahmed M. A., El-Katori E. E., and Gharni Z. H. (2018) “Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye using Fe2O3/TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method,” J. Alloys Compd., vol. 553, pp. 19–29, 2013. |
| [10] | Martı´nez Huitle CA, Brillas E (2009) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: a general review. Appl Catal B 87: 105–145. |
| [11] | O ¨ zcan A, Oturan MA, Oturan N, Sahin Y (2009). Removal of acid orange 7 from water by electrochemically generated Fenton’s reagent. J Hazard Mater 163:1213–1220. |
| [12] | Pouran S.R, Aziz A.A, David W.M.A.W, Shafeeyan M.S (2015). Effect of Niobium and Molybdenum impregnation on adsorption capacity and fenton catalytic activity of magnetic RSC Adv. 5(106), 87535-87549. |
| [13] | Rawal S.B, Ojha D.P, Choi Y.S, Lee W.I (2014). Coupling of W-doped SnO2 and TiO2 for effluent visible-light photocatalysis. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 35(3), 913-918. |
| [14] | Yan-Hua Peng, Gui-Fang Huang, Wei-Qing Huang (2012). Visible-light absorption and photocatalytic activity of Cr- doped TiO2 nanocrystal films. International journal of Advanced powder Technology, 23(1) 8-12. |
| [15] | Zhang W, Yang B, Chen J (2012). Effect of calcination temperature on preparation of boron doped TiO2 by sol-gel method. Int. J. Photoenergy. |
| [16] | Akpan, U.G. and Hameed, B.H., (2009). Parameters affecting the photocatalyti degradation of dyes using TiO2-based photocatalysis: A review, joural of Hazardeous material, 170 pp 520-529. |
| [17] | Baran, W., Makowski, A., Wardas, W (2008). The effect of Uv radiation absorption of cationic and anionic dye solutions on their photocatalytic degradation in the presence of TiO2, dyes pigment. 76; pp 226-230. |
| [18] | Xiao, Q. Zhang, J. Xiao, C. Si, Z. and Tan, X. (2008). Solar photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue in carbon-doped TiO2 nanoparticles suspension,” Solar Energy, vol. 82, no. 8, pp. 706–713. |
| [19] | Akpan, U.G. and Hameed, B.H., (2009). Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2-based photocatalysis: A review, joural of Hazardeous material, 170 pp 520-529. |
| [20] | Fox, M.A and Dulay, M.T. (1993). Heterogeneous photocatalysis. Chemistry. Reviewed. 93; pp 341-357. |
| [21] | Goncalves, M.S.T., Oliveira-Campos, A.M.F., Pinto, E.M.M.S., Plasencia, P.M.S., Queiroz, M.J.R.P. (1999). Photochemical treatment of solution of azo dyes containing TiO2. Chemosphere 39, pp. 781-786. |
| [22] | Tang, W.Z. An, H. (1995). Photocatalytic degradation kinetics and mechanism of acidv blue 40 by TiO2/UV in aqueous solution, Chemosphere 31pp 4171–4183. |
| [23] | Konstantinou, K.I, and Albanis, T.A. (2004). “TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solutions: Kinetic and mechanistic investigation n: A review; Journal of applied catalysis B: Environmental, vol. 49, pp. 1-14. |
| [24] | Saquid, M., Muneer, M. (2008). Dyes pigments 56; pp. 49. |
| [25] | Sun, H. Wang, S. Ang, H.M. Tad´e, M.O. and Li, Q. (2010). Halogen element modified titanium dioxide for visible light photocatalysis, Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 162, no. 2, pp. 437–447. |
| [26] | Liu A. R., Wang, S. M. Zhao, Y. R. and Zheng, Z. (2006) “Lowtemperature preparation of nanocrystalline TiO2 photocatalyst with a very large specific surface area,” Materials Chemistry and Physics, vol. 99, no. 1, pp. 131–134, ISRN Materials Science 15. |
| [27] | Baran, W., Makowski, A., Wardas, W (2008). The effect of Uv radiation absorption of cationic and anionic dye solutions on their photocatalytic degradation in the presence of TiO2, dyes pigment. 76; pp 226-230. |
| [28] | Akpan, U.G. and Hameed, B.H., (2009). Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2-based photocatalysis: A review, joural of Hazardeous material, 170 pp 520-529. |
| [29] | Devi, L. G. Murthy, B. N. and Kumar, S. G. (2010). Photocatalytic activity of TiO2 doped with Zn2+ and V5+ transition metal ions: influence of crystallite size and dopant electronic configuration on photocatalytic activity,” Materials Science and Engineering B, vol. 166, no. 1, pp. 1–6. |


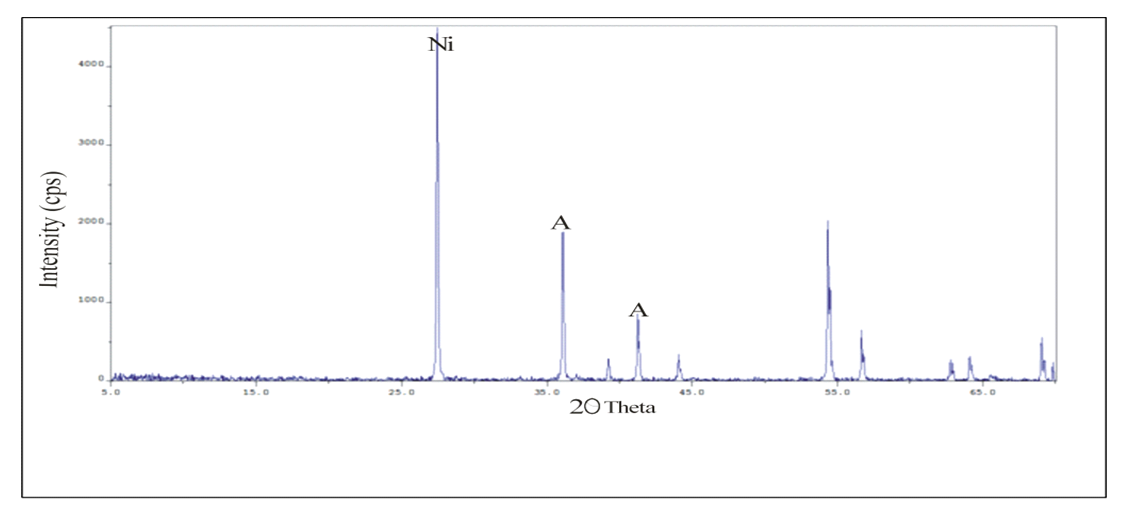
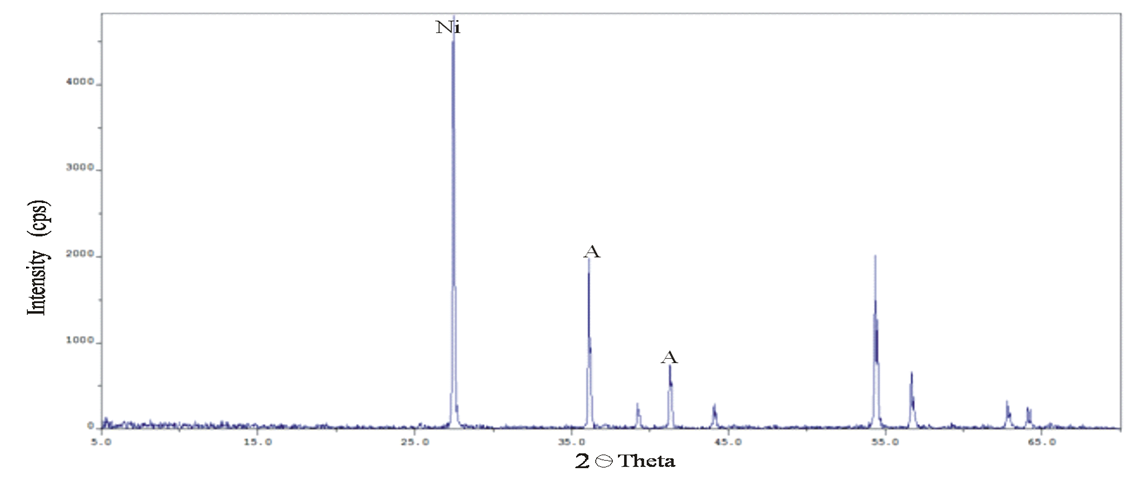
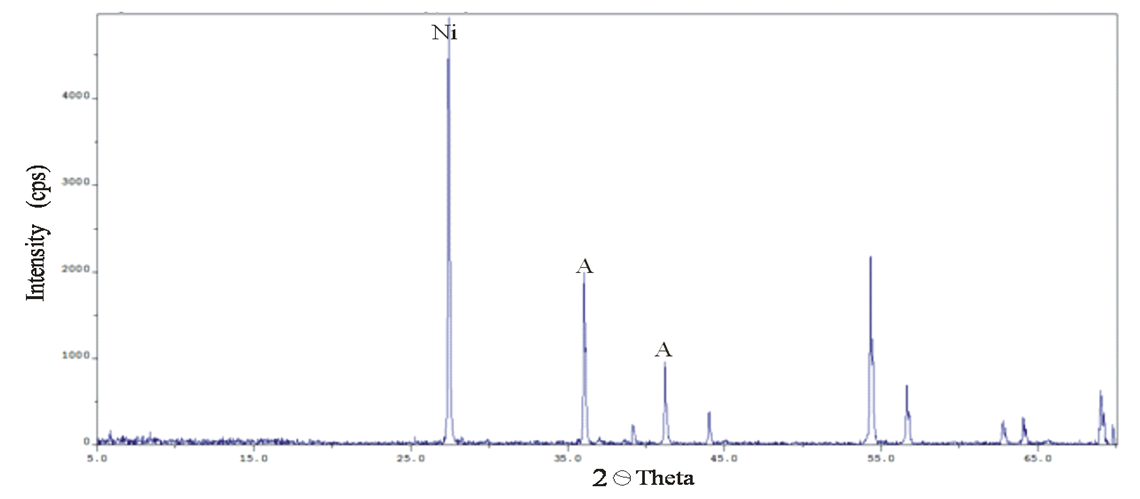
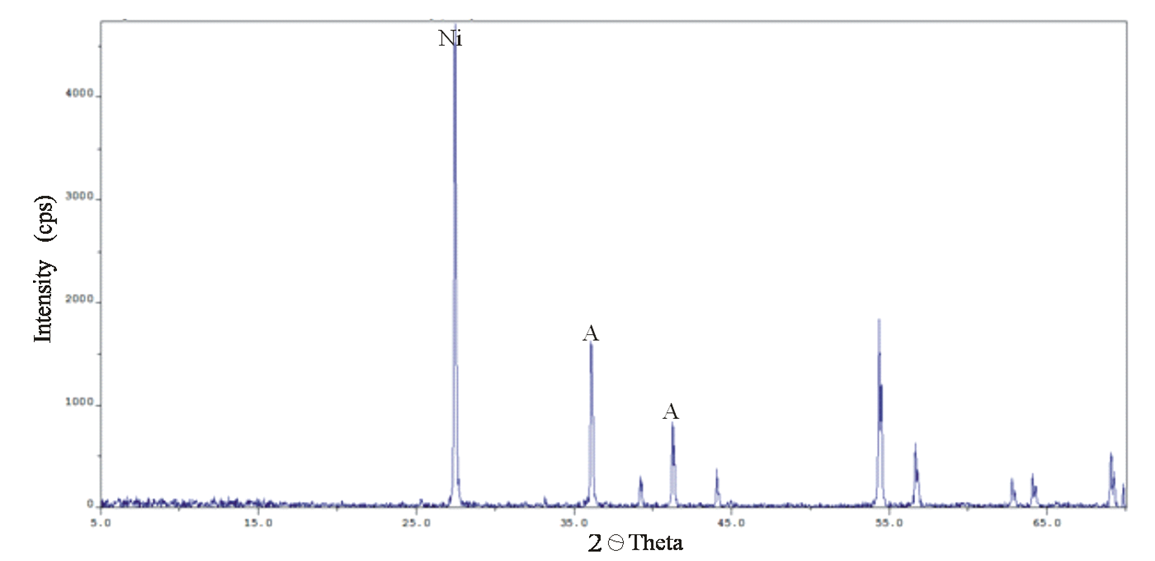



 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML