-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2018; 8(1): 8-12
doi:10.5923/j.chemistry.20180801.02

A Complete and Sustained Clemmensen Reduction Mechanism
Francisco Sánchez-Viesca, Martha Berros, Reina Gómez
Department of Organic Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico City (CDMX), México
Correspondence to: Francisco Sánchez-Viesca, Department of Organic Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico City (CDMX), México.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The mechanism for the Clemmensen reduction is not yet fully understood and there are two principal proposals: the ‘Carbanionic Mechanism’ and the ‘Carbenoid Mechanism’. After a critical review, we present a complete and coherent reaction mechanism that involves the formation of a free carbene as well as a zinc carbene and two different carbanionic species as intermediates. This point of view is based on well known reactivities and eliminates all the wrong, dubious or hindered intermediates suggested in previous proposals.
Keywords: Carbanions, Carbenes, Carbonyl deoxygenation, Ionic sequence, Organometallic intermediates
Cite this paper: Francisco Sánchez-Viesca, Martha Berros, Reina Gómez, A Complete and Sustained Clemmensen Reduction Mechanism, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 8 No. 1, 2018, pp. 8-12. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20180801.02.
1. Introduction
- The Clemmensen reduction of carbonyl compounds to alkane analogs by means of amalgamated zinc and hydrochloric has been studied with many substrates. Aliphatic and aromatic compounds have been employed and have shown different chemical deportments. Thus, the original reaction giving methylene analogs is not strictly followed by the aryl derivatives since other products are also formed.Other point of interest has been the reaction mechanism because with the aliphatic compounds the reduction does not go through the alcohol. There is not a detailed presentation on this subject. We present a complete and clear reaction mechanism, with the respective comment in each step.Our sequence is a unified theory of the carbanionic mechanism and the carbenoid proposal. There must not be two very different mechanisms in order to explain the same reaction, but a complete and coherent one. This way the two theories are conciliated.This will also fill a gap in Chemical Education.
2. Early Approaches and Modern Theories
- The Clemmensen reaction consists in the reduction of a carbonyl compound to a methyl or methylene group by means of zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid. There are two reviews [1, 2] and general information [3-8].We will comment only pertinent studies that are subsequent to the 1942 review.Brewster [9] studied the Clemmensen reduction. He considers the solid metal as an “electron pump”, this mechanical simile can be misleading since zinc has been interpreted by other authors as a source of free electrons in the reaction medium. He represents the metal as - (:M)x+. This is inadmissible because there is no reason to polarize the reagent. There is no such dipole in Zn0.In other communication [10], Brewster studied the reduction of some sterically hindered ketones and proposes as intermediary the structure in Figure 1. This is in contradiction with his previous paper in which he considers there is no carbonium ion. If so, how the proposed intermediate can be formed?
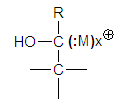 | Figure 1. Brewster’s outmoded representation of a reaction intermediate |
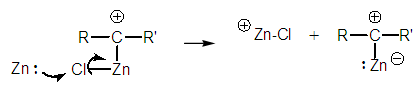 | Figure 2. Unfeasible electrophilic reaction |
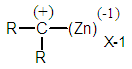 | Figure 3. A variant of the previously rejected intermediate |
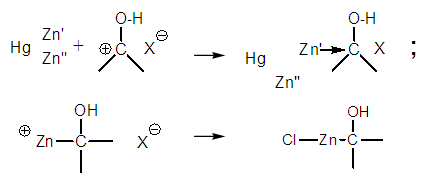 | Figure 4. Incorrect and corrected structure after reaction with zinc |
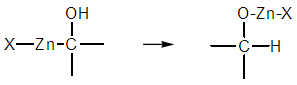 | Figure 5. Arbitrary twofold atom tranfer |
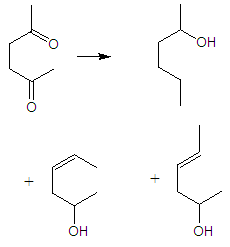 | Figure 6. An example of I,4 diketone reduction by Clemmensen reaction |
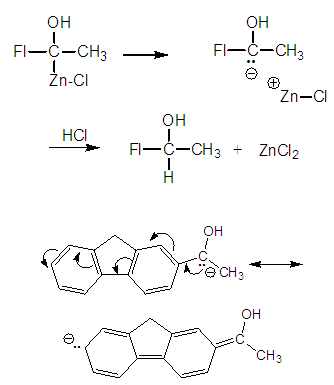 | Figure 7. Formation of methyl-2-fluorylcarbinol and carbanion stabilization |
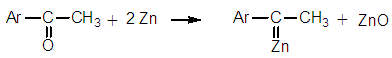 | Figure 8. Main reaction of the so-called ‘Carbenoid mechanism’ |
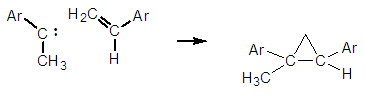 | Figure 9. Formation of a cyclopropane derivative with capturing styrene |
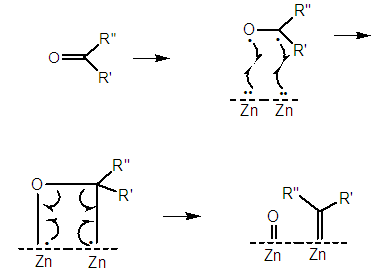 | Figure 10. Supposed formation of zinc oxide and a zinc-carbene |
3. Discussion
- Instead of two different reaction mechanisms, the ‘Carbanionic’ and the ‘Carbenoid’, we present a complete mechanism that includes the formation of both species. This has been possible considering the formation of sigma bonded organometallic intermediates, Figure 11.
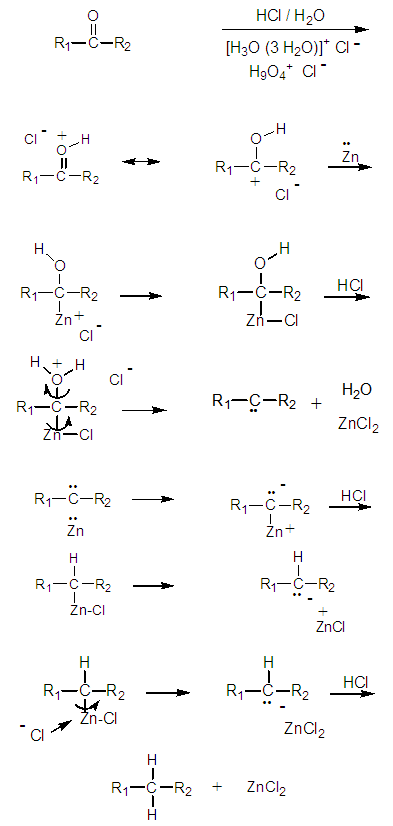 | Figure 11. Complete reaction mechanism of the Clemmensen reduction |
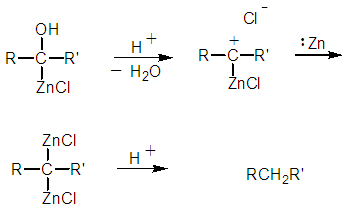 | Figure 12a. Improbable protolysis to the hydrocarbon |
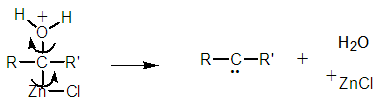 | Figure 12b. The required carbene formation via a concerted reaction mechanism |
4. Conclusions
- • We present a complete and coherent reaction mechanism for the Clemmensen reduction in order to explain the deoxygenation of a carbonyl group to a methylene.• The sequence is fully commented and is based on facts and well known reactivities.• This reaction mechanism includes the intermediates proposed by the two actual theories: the ‘Carbanionic Mechanism’ and the ‘Carbenoid Mechanism’.• The unification of both theories has been possible postulating certain organometallic links instead of free electrons reduction or direct formation of a zinc-carbene.• The finding that both carbenes and carbanions are formed in the same reaction sequence eliminates the disagreement on the Clemmensen reduction mechanism.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML