-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2017; 7(5): 153-162
doi:10.5923/j.chemistry.20170705.01

Geochemical Characterization of the Black Shale from the Ama Fatma Coastal Site in the Southwest of Morocco
Samira El Aouidi1, Said Fakhi2, Abdelmourhit Laissaoui1, Omar Ait Malek3, Moncef Benmansour1, Ayoub Ayach2, Youness El Batal3, Malika Aadjour3, Mounia Tahri1, Adil El Yahyaoui1, Azouz Benkdad1
1Centre National de l’Energie, des Sciences et des Techniques Nucléaires (CNESTEN), Rabat, Morocco
2Hassan II University of Casablanca, Engineering and Materials Laboratory (LIMA), Thermostructural Materials, Polymers and Radiochemistry Team (TMPR), Faculty of Sciences Ben M'Sik Casablanca, Morocco
3Hassan II University of Casablanca, Geodynamics of Old Chains Laboratory, Faculty of Sciences Ben M'Sik Casablanca, Morocco
Correspondence to: Samira El Aouidi, Centre National de l’Energie, des Sciences et des Techniques Nucléaires (CNESTEN), Rabat, Morocco.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Application of natural geological materials as traps of stable and radioactive metals is part of the overall Moroccan vision for the treatment of radioactive wastes. In this context, the present work focuses on the geochemical characterization of a series of natural black shale samples collected for the Ama Fatma coastal site located in the Moroccan basin of Tarfaya-Boujdour. Major and trace elements were determined by using X-Ray fluorescence and Inductively Coupled Plasma – Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Among the major elements determined, CaO was the most abundant component followed by silicon and iron oxides. Comparison between the obtained results and the geochemical standards indicated that Al, K, Ti, Mg were present in similar concentrations, Ca, Fe, P, and Mg were higher while Si was much lower. The mineralogical composition, determined by X-ray diffraction, showed that the samples were composed essentially of calcite (up to 70%). The predominance of carbonates in the sedimentary environment revealed that the deposition occurred in open marine settings. On the other hand, correlation analysis was carried out in an attempt to establish the elements association and origin, while element ratios were used as indicators of redox conditions, suggesting that the black shale were deposited during anoxic conditions.
Keywords: Black shale, Ama Fatma, Morocco, Major and trace elements, Mineralogy, Enrichment factor, Redox reconstruction
Cite this paper: Samira El Aouidi, Said Fakhi, Abdelmourhit Laissaoui, Omar Ait Malek, Moncef Benmansour, Ayoub Ayach, Youness El Batal, Malika Aadjour, Mounia Tahri, Adil El Yahyaoui, Azouz Benkdad, Geochemical Characterization of the Black Shale from the Ama Fatma Coastal Site in the Southwest of Morocco, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 7 No. 5, 2017, pp. 153-162. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20170705.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Shale rocks are sedimentary formations which belong to the category of mudstones because they result from the compaction of mud mineral particles over very large timescales. During the last decades, and besides being a potential source of non-conventional hydrocarbons (Dyni and Qian 2006), black shalerocks have been explored to prove their suitability as geological media for long term radioactive waste disposal (Frank et al. 2010; Christopher 2014). Indeed, their specific properties such as low permeability, self-sealing, the prevailing chemically reducing conditions and their high capacity of sorption make the shale formations ideal candidates to permanently host high level radioactive wastes repositories.Morocco has three major black shale deposits, namely Tanger, Tarfaya and Timahdit belonging to the Upper Cretaceous, 70 Myrs, which represent about 15% of known black shale reserves in the world (Ambles et al. 1988). Many studies have been carried on these black shale, among them chemical characterization of kerogen (Ambles et al. 1988) and composition and physicochemical properties (Saoiabi et al. 2001). The main chemical studies concerning the black shale from Timahdit involved its pyrolysis (Nuttall et al. 1983) and its thermal degradation (Alaoui-Sosse et al. 1988). On the other hand, black shale from the Tarfaya basin were explored for their geochemical characterization (Kolonica et al. 2002), and the work was aimed at producing new adsorbents and testing them for their potential in trapping of radionuclides such as U and Th isotopes (Bekri et al. 1991; Khouya et al. 2002; Galindo et al. 2007). The Ama Fatma is located in the basin of Tarfaya-Boujdour. The basin corresponds to the section of the Atlantic margin between the town of Tarfaya in the north and that of Boujdour in the south. It is limited in the west by the Atlantic Ocean and in the east by the Republic of Mauritania (Figure 1). This area is located on the road leading to Tarfaya, about 80 km north of the city. This section begins with black shale thicker than 2 m (Figure 2) (El Batal 2014), alternating with grayish to blackish limestones, The Ama Fatma cut has been dated thanks to numerous ammonites, it is of lower Turonian age. The black shale of Ama Fatma, which is the subject of the present study, has been found to be rich enough of organic matter chemically linked to a mineral matrix (Khouya 2002). Organic deposits were previously interpreted as the result of early coastal upwellings (Einsele and Wiedmann 1982).
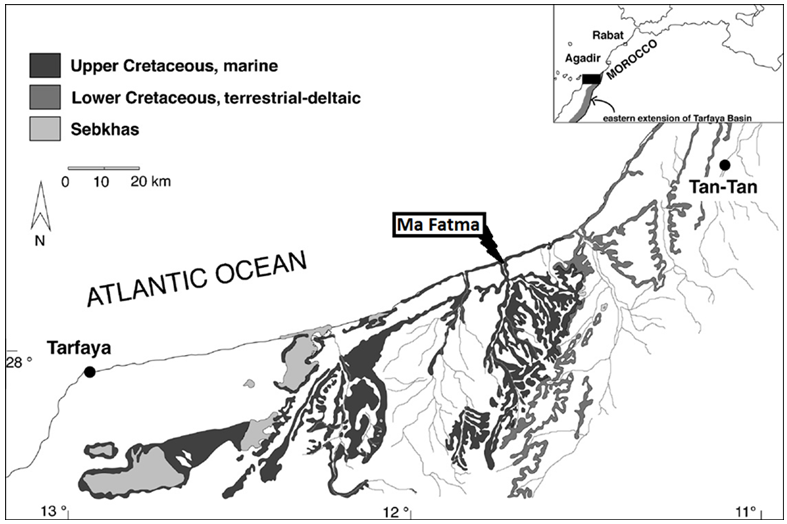 | Figure 1. A sketched map of the study area showing its main geological features (Gebhardt and Zorn 2008) |
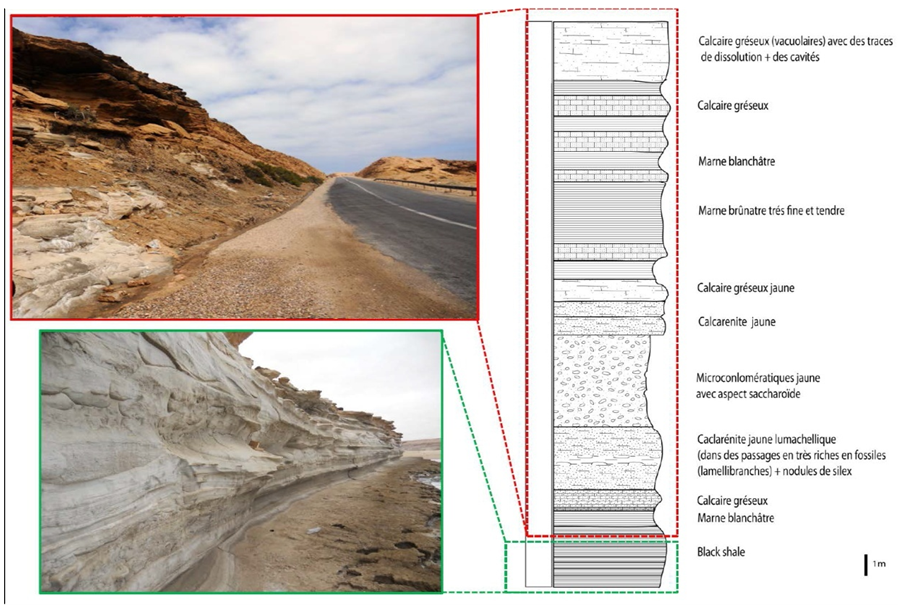 | Figure 2. Pictures and schematic profile showing the stratigraphic layers of the studied location (El Batal 2014) |
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Characterization
- Prior to characterization and geochemical analyses, the collected black shale samples (El Batal 2014) were ground to fine powder using electric grinder. The mineralogy of the samples was determined in the National Center of Scientific and Technical Research (CNRST) by X-ray diffractometry using The X’Pert Pro MPD PAnalytical 2-circle diffractometer installed equipped with a thêta-thêta goniometer, a rapid X’Celerator detector, a sample changer and a high temperature chamber. Particle size distributions were determined in the National Center for Energy Sciences and Nuclear Techniques (CNESTEN- Morocco) in the homogenized sub-samples using a wet Laser Diffraction equipment (Malvern Mastersizer 2000) using the Hydro 2000G dispersion Unit. The particle size distribution range is 0.02–2000 µm. A small amount of sample (1g) was introduced in the dispersion unit containing demineralized water, used as dispersant, and then measured after a brief time (10s) of ultrasound application to disperse any agglomerates.
2.2. Determination of Major and Traces Elements
- Major elements data were obtained by using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) S1 Turbo SD spectrometer. For trace elements determination, 50 mg of the fine fraction of each sample was weighed into acid-cleaned Teflon vessels, and 3 ml of HNO3 Supra pure and 5 ml of HF were added. The mixture was allowed to react overnight and then subjected to microwave digestion Speed Wave Four (Berghof technologies). The obtained solubilized samples were analyzed by ICP-MS using a Thermo Scientific XSERIES 2.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Black Shale Characterization
- From Table 1, the granulometric distribution showed a predominance of sand (50.42 – 83.76%), followed by silt (16.13 – 30.18%) and then clays with contents ranging from 0.1% to 19.40% with the highest value recorded at the upper layer, S1(9). Consequently, the black shale samples, subject of this study, have predominantly a sandy loam texture.
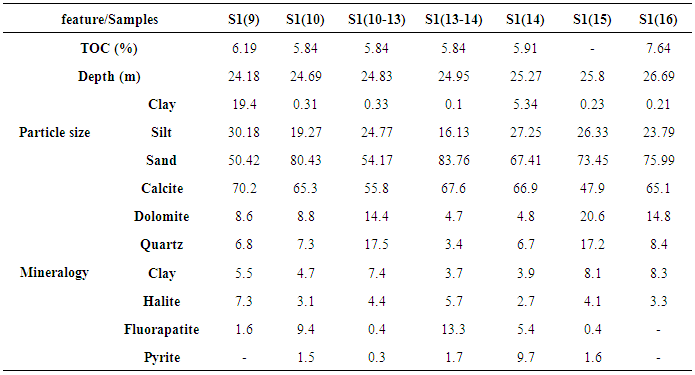 | Table 1. Particle size and mineralogical composition of the black shale from the Ama Fatma site.TOC contents were determined by El Batal (2014) |
3.2. Major Elements Geochemistry
- Major elements were analyzed in our sample in order to use them in conjunction with the mineralogical data to establish the element/mineral association. Although elements associations could vary from one sample to another, a correlation analysis would indicate the general trends (Fu et al. 2010a). Major elements concentrations are presented in Table 2. CaO, whose concentration varied between 27.5 – 71.05%, was the most abundant in our samples, followed in importance by silicon and iron oxides, SiO2 (3,09-22,4%) and Fe2O3 (4,50-15,77%), while Al2O3 (0,53 - 8% ), Na2O (1,52-4,06%) and MgO (1,09-4,51%) were less abundant. Other elements such as P2O5, K2O, TiO2 and MnO were present in weak concentrations, often less than 1%. The average concentrations of Al2O3, K2O, TiO2 and MgO were similar to those reported for the widely used geochemical standards; the Upper Continental Crust (UCC; Taylor and McLennan 1985), Post Archean Australian Shale (PAAS; Taylor and McLennan 1985) and North American Shale Composite (NASC; Gromet et al. 1984). On the other hand, CaO, Fe2O3, P2O5 and MnO exhibited higher concentrations compared to these standards, while SiO2 was much lower. Exceptionally, CaO (27.5 – 71.05%), higher by one order of magnitude than the geochemical standards, indicated a predominance of carbonates in the sedimentary environment of the Ama Fatma site, which should be associated to the abundant bivalve and gastropods fossilized remains. In addition, carbonate precipitation occurs normally in open marine environments characterized by weak clastic inputs in the water. Therefore, the high carbonate content in the black shale of Ama Fatma reveals that deposition occurred in an open marine setting, as reported in previous research for similar environment (Armenteros and Huerta 2006).
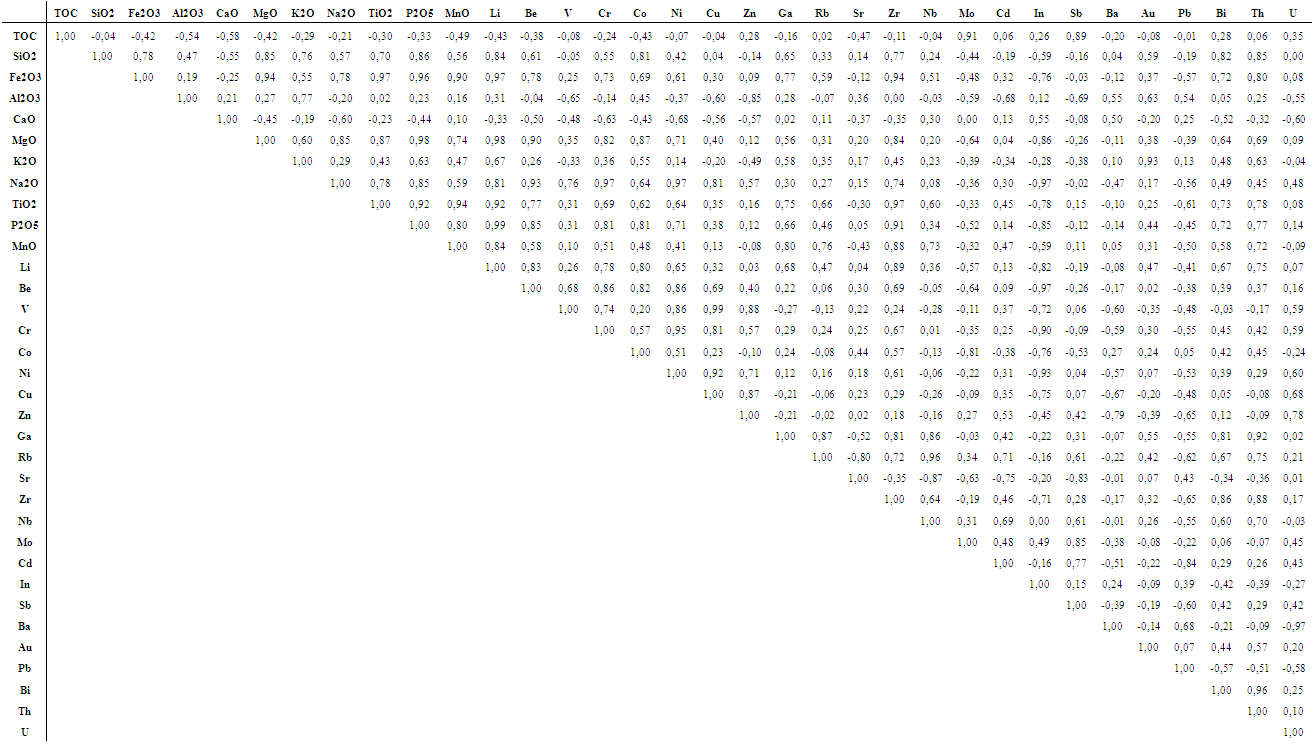 | Table 4. Pearson’s correlations among major and trace elements |
3.3. Uraniumand Thorium
- U and Th concentrations found in the black shale from Ama Fatma were ranging from 4.09 to 17.84 ppm and from 1.29 to 4.48 ppm with depth averaged values of 13.2 ppm and 2.48 ppm, respectively. U levels are much higher than those reported for the geological standards (UCC, PAAS and NASC) while Th levels are lower. This ultimate was found to be significantly and positively correlated to SiO2, Fe2O3, MgO, K2O, TiO2, P2O5, and MnO, and not correlated to TOC and CaO indicating that thorium is pre-dominantly of detrital origin. The weak correlation between U and TOC, and the non-correlation with SiO2 and Fe2O3 might be due to the relatively high content of OM which could influence the oxidation state of U, and consequently its solubility/mobility. In addition, organic matter may possibly compete with U in the sorption processes onto mineral surfaces, such as Fe- and Si- oxides and hydroxides (Cumberland et al. 2016).
3.4. Trace Elements Geochemistry and Enrichment
- From trace elements abundances given in Table 3, Li, Cr, Cu, In, Sb were found to be of the same range of concentrations of the averages reported for geological standards (UCC, PAAS and NASC), while elements such as Ga, Rb, Zr, Nb, Ba and Th are lower. In contrast, Be, V, Co, Ni, Zn, Sr, Mo, Cd, Pb, Bi and U presented concentrations higher, to much higher, than the standards. On the other hand, all trace elements, except for Mo and Sb, did not appear to be associated to organic matter as can be seen in the correlation table. The negative correlations of some heavy metal elements with CaO could be attributed to the adsorption mainly on clay and/or MnO minerals. Secondly, the heavy metals may enter the calcium lattice defects and, therefore, constitute metal carbonate (Aziz HA et al. 2008).Element enrichments in our black shale samples were estimated by using the Enrichment Factor (EF) defined as follows (Brumsack 2006):
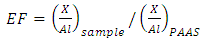 | (1) |
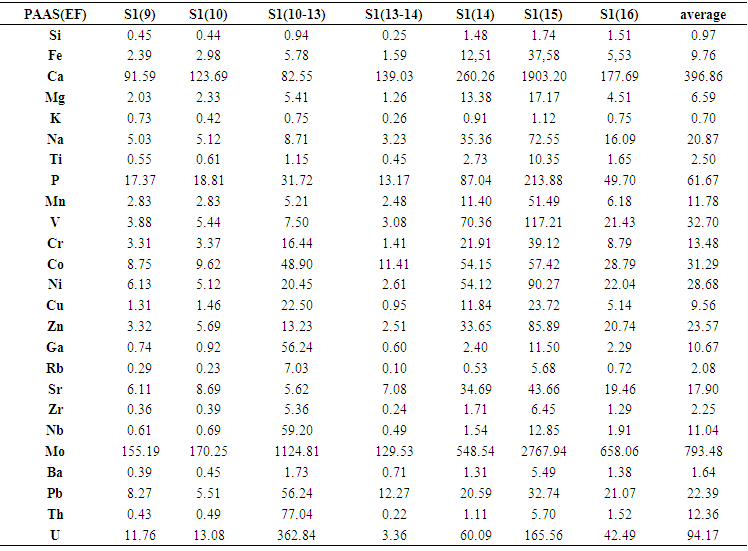 | Table 5. Mean enrichment factor (EF) of selected trace elements in the Ama Fatma black shale section. EF = (X/Al) sample/(X/Al) PAAS |
3.5. Redox Conditions Reconstruction
- Trace elements ratios are widely used as proxies for establishing the redox conditions of the depositional environment in old and modern sedimentary systems (Calvert and Pedersen 1993; Jones and Manning 1994; Wignall 1994; Crusius et al. 1996; Dean et al. 1997, 1999; Yarincik et al. 2000; Morford et al. 2001; Pailler et al. 2002). Indeed, previous studies have used ratios such as V/(V + Ni), V/Cr and U/Th to reconstruct redox conditions under which the geological formations occurred (Hatch and Leventhal 1992; Jones and Manning 1994; Rimmer et al. 2004). In Figure 3, the vertical profiles of the above mentioned ratios are plotted.
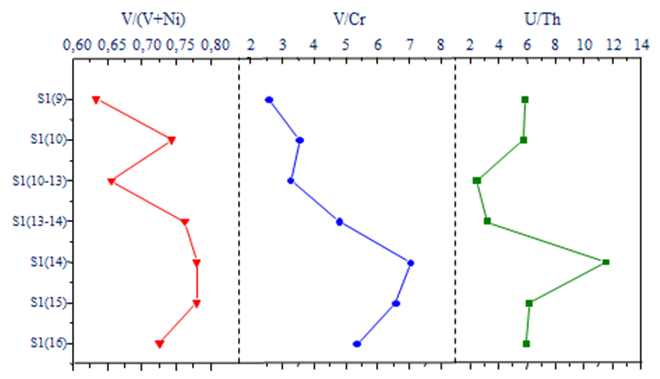 | Figure 3. Vertical profiles of V/(V+Ni), V/Cr and U/Th in black shale form the Ama Fatma site |
4. Conclusions
- In the present work, the geochemical characterization of the black shale from the Ama Fatma coastal site was investigated as a preliminary step for the use of this geological matrix in the storage of radioactive wastes. The results showed that:1. Particle size distribution in black shale are dominated by sand followed by silt and then clays, giving our black shale a sandy loam texture;2. The mineralogical composition of Ama Fatma black shale is dominated by calcite with a low fraction of dolomite, Quartz, clays, halite, fluorapatite and pyrite;3. Major element distributions showed higher concentration of CaO followed by SiO2 and Fe2O3, while the other elements were less abundant;4. The high carbonate content in the Ama Fatma black shale reveals that deposition occurred in an open marine setting;5. The correlation among major elements of our samples indicates that these oxides are associated to the terrigenous fractions and associated minerals;6. U and Th concentrations were found to be controlled by organic matter content and detrital component;7. Trace elements distribution show a high enrichment in Mo, U, Co, Ni, V, Zn and Pb indicating that the Ama Fatma bituminous shale was deposited under euxinic conditions;8. The high enrichment in V and Ni suggested that our bituminous shale are associated with type I and II kerogen;9. Trace elements ratios revealed an anoxic condition deposition of our studied oil shale.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This work has been carried out within the framework of the UMR between the University Hassan 2 - Casablanca and the National Center for Energy, Nuclear Science and Technology, and in the framework of the collaboration held between the Faculty of Sciences-Rabat and the University of Seville - Spain.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML