-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2017; 7(1): 1-5
doi:10.5923/j.chemistry.20170701.01

Synthesis of Acrylate Binder from Soft and Hard Monomers through Emulsion Polymerization to Introduce Mechanical Properties to the Applied Substrate
Md. Mostafizur Rahman, Shamim Al Azad, Muhammad Abu Taher, Shohel Ahmed, Ashique Ul Haque
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Wuhan Textile University, Wuhan, China
Correspondence to: Md. Mostafizur Rahman, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Wuhan Textile University, Wuhan, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

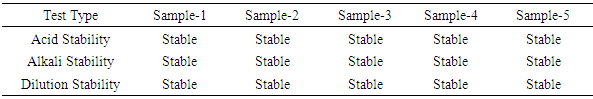
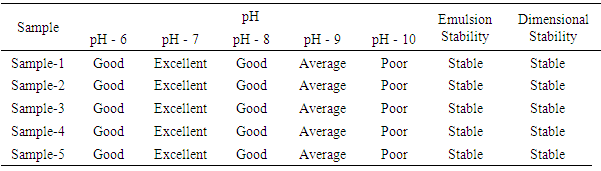
This work propose polyacrylate binders synthesized by emulsion polymerization. Emulsions used as pigment binders in formulations that have to deal with the challenge to assure an outstanding film configuration and exterior as well as good mechanical properties. To produce polyacrylate binder, homo and copolymers were synthesized by emulsion polymerization using different types of monomers. Emulsion polymerization is a type of radical polymerization that usually starts with an emulsion incorporating water, monomer, and surfactant. With increasing proportion of monomers in the formulation, lower conversion was observed which could be due to the lower reactivity of monomers for radical polymerization in the presence of these others monomers. It is ensured that monomers were put one by one to the reactor instead of putting quickly & the stirring speed was not more or less comparing with the standard. In accordance with recipe calculation and method of preparation, our sample shows pretty good tensile and tear strengths, good abrasion resistance and stiffness, excellent chemical resistance and water repellence as well as air permeability. In the area of testing, gel ratio and solid content percentage of soft polymer and hard polymer is tested. Also the dilution, acid, alkali and electrolyte resistance stability were checked.
Keywords: Polyacrylate, Binder, Pigment, Polymer, Emulsion, Cross linking agent
Cite this paper: Md. Mostafizur Rahman, Shamim Al Azad, Muhammad Abu Taher, Shohel Ahmed, Ashique Ul Haque, Synthesis of Acrylate Binder from Soft and Hard Monomers through Emulsion Polymerization to Introduce Mechanical Properties to the Applied Substrate, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2017, pp. 1-5. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20170701.01.
1. Introduction
- Binder is a film forming substance made up of long chain macromolecules, when applied to the textile with pigment, produces a three-dimensionally network [1]. The links are formed during some suitable fixing process, which usually consists of dry heat and change in pH value, bringing about either self-crosslinking or reaction with other suitable crosslinking agents [2]. Binder film in pigment printing is a three-dimensional structure where the third dimension is rather less important than the other two [3].Polyacrylate is a chemical class of acrylate polymers derived from the polymerization of acrylic acid esters and salts. Each acrylate monomer contains a vinyl group: a pair of double-bonded carbon atoms attached to the carbon of a carboxyl group. The choice of binders always depend upon the final fastness requirements as well as the cost requirements of the process [4]. Choosing a binder for pigment coloration is a complex but critical step in developing a recipe which it will meet very specific requirements [5].Pigment printing process is simple, energy saving, suitable for bright color, wide range of applications so that it have been widely used in printing and dyeing industries [6]. In Polyacrylate binder most of the polymer with emulsion adhesive can be divided according to their chemical structure, polyacrylate, butadiene, vinyl acetate, and polyurethane, where in the polyacrylate pressure-sensitive adhesive applications has a significant impact on the application performance of the adhesive [7]. Emulsified by one-step emulsification, can be coated on the surface of the latex particles to reduce the interfacial energy between the latex particles and water, and enhance the stability of the emulsion [8]. In pigment printing of textile fabrics, pigments with little or no chemical affinity for the fibers are bound physically to the fabric by a polymeric film-forming adhesive [9, 10]. Both mechanical properties of the binder and adhesive to pigment and fabric contribute to enhance fastness, good mechanical properties being advantageous in resisting deformation of the coating on rubbing [11, 12].
2. Experimental
- Materials:Hard Monomers: Hard monomers, characterized by high Tg values, includes Styrene (S.T), Methyl Meth Acrylate (MMA) were respectively supplied by Xiangcang Hongrun Co. Ltd.China, and Hubei Ocean Biotech Co. Ltd China.Soft Monomers: Soft monomers, characterized by low Tg values, includes n-butyl acrylate, 2-ethyl hexyl acrylate and iso-octyl acrylate. These monomers are longer chain alkyl acrylates and exhibit low water solubility. Ethyl Acrylate (EA) was supplied by Changshu Jinfeng Chemical Co. Ltd China. Butyl Acrylate (BA) was supplied by Hubei Ocean Biotech Co.Ltd China.Functional/Cross-linking Monomers: Functional monomer with various functional groups were acrylic acid and hydroxyethyl acrylate, which are very water-soluble. Acrylic Acid was supplied by Zhengzhou Sino Chemical Co. Ltd China. 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate was supplied by Haihang industry (Jinan) Co.Ltd. China.Emulsifier: Sodium Dodecyl sulfate (SDS) Emulsifier was supplied by Zhengzhou Fuhong Biotech Co. Ltd. China. Ammonium persulfate (APS), Deionized Water was used to emulsify the monomers. Ammonia is used to ensure the pH of water between 7-8.Method: All the monomers were emulsified with surfactants at room temperature with emulsifier OP-10 and K-12. Then 20% of total water was added and all the monomer one by one at 5 minutes of time interval were added. Then a run time about 30 minutes at room temperature was given with continuous stirring. A solution of Initiator was made by adding 0.25 gms of ammonia per sulphate in 20 ml of water. 1/6 parts of pre-emulsion is transferred in a 3 neck bottle; remaining 80% of total water was added, then temp was applied with continuous stirring. At temp 75°C, 1/3 parts of initiators was added in the pre-emulsion solutions and was run about 20 minutes. The process continued until the blue beam observed in the mixtures. When blue beam observed then remaining 5/6 parts of pre-emulsion and 2/3 parts of initiators were added into the reactor simultaneously one by one in 90 minutes of time intervals at 80°C temp. Then temperature was increased from 80°C to 85°C and continued it about 30 minutes. Stirring speed was slower. Process continued until sweet smell observed. When sweet smell is observed, temperature was decreased at 40°C, the solution was neutralized by adding (20%) ammonia water to the solutions mixtures until PH=7 is not achieved.Temperature of the solution decreased to room temperature and all the segments and residue were collected by filtration, the entire residue were washed and dried it at 105°C for 90 minutes.
3. Result and Discussion
- Gel Ratio: After completion of the reaction, all gels, rinse, and baked in an oven at 120°C for 2 hrs, cooled to room temperature in a desiccator, weighted.
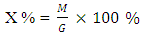 Where, X - The gel fraction; M - Weight of the gel;G - Monomer weight.5 samples were tested for this research where different results were found which may be due to the variation of chemical concentration as per specified chemicals in recipe. It is seen in the figure-1 that Gel Ratio is maximum for sample 5 which may be due to the more concentration of Acrylate binder. Gel ratio is minimum for sample 1 where Acrylate binder is used for 1 gram per liter. The similar effect is seen for other samples too. It could be noted that less the gel ratio better the product (binder) & higher the gel ratio poorer the product quality.Solid Content: approximately 5.5 gm of the sample were taken and weigh it accurately in a glass dish. Place it in the oven for 4 hours at 110°C. After cooling weight the dish accurately.
Where, X - The gel fraction; M - Weight of the gel;G - Monomer weight.5 samples were tested for this research where different results were found which may be due to the variation of chemical concentration as per specified chemicals in recipe. It is seen in the figure-1 that Gel Ratio is maximum for sample 5 which may be due to the more concentration of Acrylate binder. Gel ratio is minimum for sample 1 where Acrylate binder is used for 1 gram per liter. The similar effect is seen for other samples too. It could be noted that less the gel ratio better the product (binder) & higher the gel ratio poorer the product quality.Solid Content: approximately 5.5 gm of the sample were taken and weigh it accurately in a glass dish. Place it in the oven for 4 hours at 110°C. After cooling weight the dish accurately.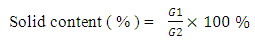 Where, G1 = Initial weight of sample.G2 = Oven dry weight of the sample.More Solid content percentage ensures that the product quality is good. Practically the % is found for 70% but 80% is considered as good binder. Normal treatment is performed at 60-80°C for 6-7 hours. Finally the solid content is found after the treatment of the polymer suspension at 140°C for 5 minute.Monomer Conversion rate: Draw l to 2 g emulsion to clean the weighing bottle, add 1 to 2 drops of a solution of hydroquinone, and baked in an oven at 120°C for 2h, cooled to room temperature in a desiccator.C% = [W (W2-W1) / G1 -Y] / G × 100 %Wherein: C- monomer conversion; W1 - Empty weighing bottle;W2 - Dried weighing bottle; W - Weight of the material; Y - The weight of non-volatile matter in the emulsion;G1- To learn the weight of the emulsion; G - The total weight of the monomer.More the monomer conversion rate the better the polymer product quality. The average monomer conversion rate found is more than 83% which ensures that the binder quality is good.Surface Tension Test:Lower the surface tensions better the product quality. As all most all the surface tensions are within 27% so the binder quality is good.Dilution Stability Test: The emulsion was diluted to a solid content of 3%, then the emulsion was poured into 30ml tubes after dilution, the liquid column height of 20cm, is placed 72 hrs, measuring the volume of supernatant and precipitate upper portion. No change found in the emulsion.Acid and Alkali Stability: In two test tubes were charged emulsion 5g sample tested, the two tubes were then added drop wise 1ml (1mol / L) hydrochloric acid and 1ml (1mol / L) solution of KOH. After shaking, the PH test and observe the emulsion is stable. Then the two tubes placed at room temperature for 24h, and then observe the stability of the emulsion. No change found, Emulsion is resistant to both acid and alkali.A polyacrylate binder for pigment printing according to claim, the Tg should be between 10-25°C. If Tg greater than 25°C; then polymer becomes hard, as a result hand feel is not good. Also if the Tg goes less than 10°C the polymer become soft but hand fell is sticky. We have taken the hard monomers 55%; soft monomers 42%; Functional/ cross-linking Monomers 3% and by applying Flory-Fox equation we have obtained the resultant Tg about 21°C.A polyacrylate binder for pigment printing according to claim, the silicone is methyl trichlorosilane and methyl phenyl dichlorosilaneare taken 12% of the total monomers will increase the mechanical properties, thermal oxidation, and water resistance, excellent in weathering resistance, pretty good stain resistance, and good air permeability. It also increase the cross linking between polymer chain.A polyacrylate binder for pigment printing according to claim, de-ionized water will control the conductivity of the latex. A polyacrylate binder for pigment printing according to claim, ammonia water (5-7% of total deionized water) will adjust the pH 7-8.Illustrated Properties: These binders offer the greatest durability, color stability, and dry/wet performance. Strong thickening ability, good water cohesive property. Good Evenness of the fabric. Good printing effect with precise printing edge. Toxic free like APEO and Formaldehyde. Heat and oil resistance. Excellent pigment stabilization with color constancy. Acrylic binders have the widest range of fabric hand properties.
Where, G1 = Initial weight of sample.G2 = Oven dry weight of the sample.More Solid content percentage ensures that the product quality is good. Practically the % is found for 70% but 80% is considered as good binder. Normal treatment is performed at 60-80°C for 6-7 hours. Finally the solid content is found after the treatment of the polymer suspension at 140°C for 5 minute.Monomer Conversion rate: Draw l to 2 g emulsion to clean the weighing bottle, add 1 to 2 drops of a solution of hydroquinone, and baked in an oven at 120°C for 2h, cooled to room temperature in a desiccator.C% = [W (W2-W1) / G1 -Y] / G × 100 %Wherein: C- monomer conversion; W1 - Empty weighing bottle;W2 - Dried weighing bottle; W - Weight of the material; Y - The weight of non-volatile matter in the emulsion;G1- To learn the weight of the emulsion; G - The total weight of the monomer.More the monomer conversion rate the better the polymer product quality. The average monomer conversion rate found is more than 83% which ensures that the binder quality is good.Surface Tension Test:Lower the surface tensions better the product quality. As all most all the surface tensions are within 27% so the binder quality is good.Dilution Stability Test: The emulsion was diluted to a solid content of 3%, then the emulsion was poured into 30ml tubes after dilution, the liquid column height of 20cm, is placed 72 hrs, measuring the volume of supernatant and precipitate upper portion. No change found in the emulsion.Acid and Alkali Stability: In two test tubes were charged emulsion 5g sample tested, the two tubes were then added drop wise 1ml (1mol / L) hydrochloric acid and 1ml (1mol / L) solution of KOH. After shaking, the PH test and observe the emulsion is stable. Then the two tubes placed at room temperature for 24h, and then observe the stability of the emulsion. No change found, Emulsion is resistant to both acid and alkali.A polyacrylate binder for pigment printing according to claim, the Tg should be between 10-25°C. If Tg greater than 25°C; then polymer becomes hard, as a result hand feel is not good. Also if the Tg goes less than 10°C the polymer become soft but hand fell is sticky. We have taken the hard monomers 55%; soft monomers 42%; Functional/ cross-linking Monomers 3% and by applying Flory-Fox equation we have obtained the resultant Tg about 21°C.A polyacrylate binder for pigment printing according to claim, the silicone is methyl trichlorosilane and methyl phenyl dichlorosilaneare taken 12% of the total monomers will increase the mechanical properties, thermal oxidation, and water resistance, excellent in weathering resistance, pretty good stain resistance, and good air permeability. It also increase the cross linking between polymer chain.A polyacrylate binder for pigment printing according to claim, de-ionized water will control the conductivity of the latex. A polyacrylate binder for pigment printing according to claim, ammonia water (5-7% of total deionized water) will adjust the pH 7-8.Illustrated Properties: These binders offer the greatest durability, color stability, and dry/wet performance. Strong thickening ability, good water cohesive property. Good Evenness of the fabric. Good printing effect with precise printing edge. Toxic free like APEO and Formaldehyde. Heat and oil resistance. Excellent pigment stabilization with color constancy. Acrylic binders have the widest range of fabric hand properties.  | Figure 1. Preparation Process of polyacrylate Binder |
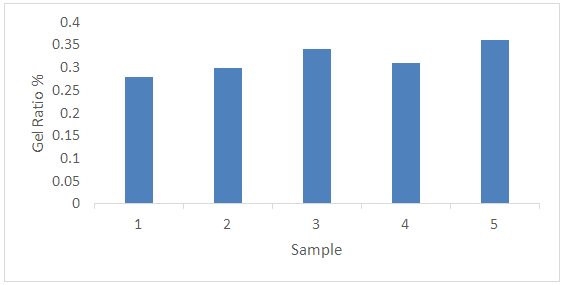 | Figure 2. Gel Ratio (%) of Prepared Binder Sample |
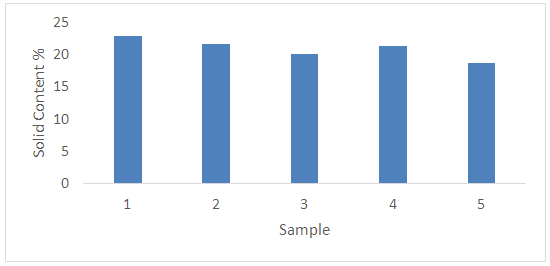 | Figure 3. Solid content (%) of Prepared Binder Sample |
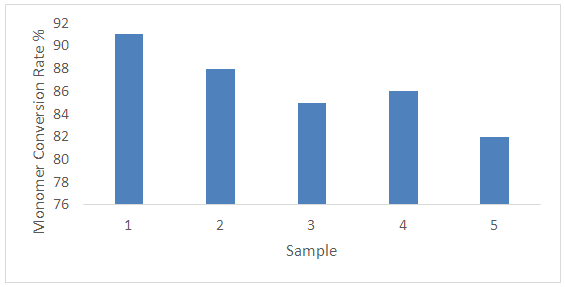 | Figure 4. Monomer Conversation Rate (%) of Prepared Binder Sample |
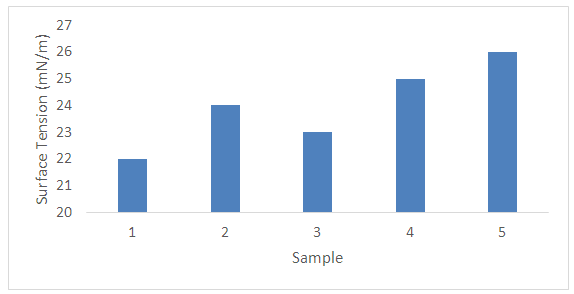 | Figure 5. Surface Tension (nM/m) of Prepared Binder Sample |
|
|
4. Conclusions
- By this work it is clear that, the emulsion polymerization technique need soft, hard and functional monomers. It is observed that, emulsion polymerization is a type of radical polymerization that usually starts with an emulsion incorporating water, monomer, and surfactant. With increasing proportion of monomers in the formulation, lower conversion was observed which could be due to the lower reactivity of monomers for radical polymerization in the presence of these others monomers. In the area of testing result it is found that, gel ratio and solid content percentage of soft polymer is less than the hard polymer but on the other hand conversion ratio percentage is more on hard polymer than the soft polymer. Also the dilution, acid, alkali and electrolyte resistance stability for both polymers are stable. It is advised, to get the better result on gel ratio, solid content and conversion ratio, be aware of the required temperature on every stage. Add monomer one by one to the reactor instead of putting monomers quickly & must be aware of the stirring speed which should not be more, less comparing with the standard. More study for the utilization of monomers in polymer synthesis is needed, on which successful optimization, would give a cost-effective alternative to various commercial areas.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML