-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2016; 6(5): 145-147
doi:10.5923/j.chemistry.20160605.04

Synthesis of Mesoporous Tin Oxide with Cationic Surfactant as a Template in Aqueous Media
M. Y. Ahmad, M. Z. Abu Bakar, J. Jusliha
School of Chemical Engineering, University Science Malaysia, Penang, Malaysia
Correspondence to: M. Y. Ahmad, School of Chemical Engineering, University Science Malaysia, Penang, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Mesoporous tin oxide (SnO2) with high surface area was synthesized in alkaline condition. The synthesis of the product was achieved using cationic surfactant (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide: CTAB) as template and hydrated tin chloride (SnCl4.5H2O) as inorganic precursor. Mesoporous SnO2 was characterized by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and N2 adsorption-desorption experiment. The BET surface area of the sample calcined at 400°C is 164.9 m2/g, with an average pore diameter of 4.1 nm.
Keywords: Mesoporous tin oxide, Cationic surfactant, Hydrated tin chloride, High surface area
Cite this paper: M. Y. Ahmad, M. Z. Abu Bakar, J. Jusliha, Synthesis of Mesoporous Tin Oxide with Cationic Surfactant as a Template in Aqueous Media, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 6 No. 5, 2016, pp. 145-147. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20160605.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Since the successful synthesis of MCM-41 [1], a number of mesoporous materials have been synthesized [2], employing the supramolecular assembly of surfactant molecules as templates. Mesoporous materials have attracted much interest, due to their large surface areas and narrow pores size distributions, which make them ideal candidates for catalyst, molecular sieve, and electrodes in solid-state ionic devices [3].Tin oxide (SnO2) is an n-type semiconductor with a wide energy band gap. SnO2 is known as one of the promising metal oxides to be used as a catalyst, gas sensor, lithium ion batteries, and optical electronic devices [4]. Previously, several approaches using supramolecular templating mechanism have been reported for the preparation of mesoporous SnO2 [5-8]. However, the mesoporous SnO2 powders prepared so far are not always thermally stable and the poor thermally stability restricts their performance, especially in gas sensor field which have to be operated at elevated temperature [9].In this paper, preparation of mesoporous SnO2 using SnCl4.5H2O as inorganic precursor, with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) as a template under alkaline condition was reported based on the modified Guo et al. [7] worked. This method of synthesizing mesostructured SnO2 is much faster than previous worked and can produce high surface area of SnO2, to the based on our knowledge. The as-synthesized product and its corresponding resultants calcined at different temperature were characterized.
2. Experimental
2.1. Synthesis
- The mesoporous SnO2 were synthesized based on supramolecular templating mechanism by using cationic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, (CTAB) as template and chemical materials (SnCl4.5H2O and NH4OH) as inorganic precursor and alkali source, respectively. The procedure was as follows: 1.6 g of CTAB was mixed with 100 ml of deionized water until a homogenous solution was obtained. A Sn4+ solution of 5 g SnCl4.5H2O diluted with 100 ml deionized water was then added into the CTAB solution. 1 M of NH4OH was introduced into the above mix solution under stirring till the pH value of the mixture was adjusted to 10 to promote hydrolysis process. After stirring for 3 h, the sol was aged for 3 days. The resulted white slurry was centrifuged and washed by deionized water for few times, and then dried overnight by using freeze dryer. The mesoporous SnO2 were obtained by calcining the as-synthesized powders in a furnace at 400°C and 500°C for 2 h, respectively, and doted as Sn-400 and Sn-500. For the purpose of comparison, the commercial SnO2 is selected and doted as Sn-C.
2.2. Characterization
- The sample was characterized by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA, Parkin Elmer Pyris7) to analyse the amount of weight loss in the sample with a temperature increasing rate of 10°C/min. The phase transition and crystallite size of SnO2 were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Philips PW 1710) using Cu Kα radiation (0.15418 nm). Specific surface area and pore size distribution were measured by a BET method using N2 sorption isotherm (Micromeritics, ASAP 2020).
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Analysis
- Figure 1 shows the TGA curve of the as-synthesized sample under N2. At Stage I, the weight loss of water in the sample at the lower temperature range (<160°C) was about 6%. For stage II, the weight loss due to the surfactant begins at 160°C and it was greatly removed at about 320°C. From temperature 340°C to 800°C (Stage III), removal of carbon and little residual surfactant was occurred [10].
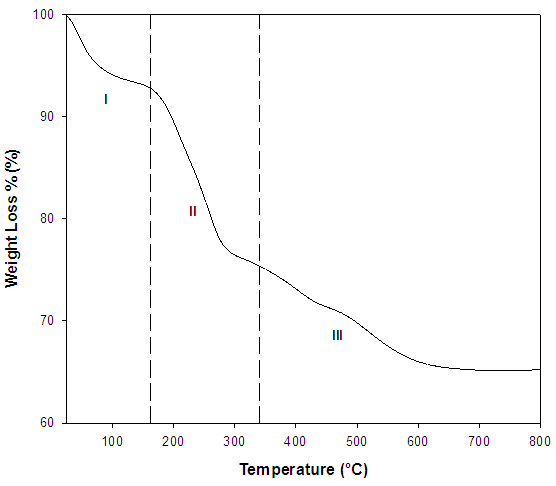 | Figure 1. TGA curve of the as-synthesized sample |
3.2. XRD Analysis
- XRD patterns are shown in Figure 2 for the commercial and synthesized mesoporous SnO2. It can be seen from the XRD patterns that all the samples are well crystallized and all diffraction peaks can be well indexed to the cassiterite tetragonal structure of SnO2 (JCPDS 41-1445). As observed from Figure 2, the diffraction peaks of the Sn-400 and Sn-500 are apparently broader than the peaks of the Sn-C, indicating the synthesized SnO2 sample have smaller particle size.
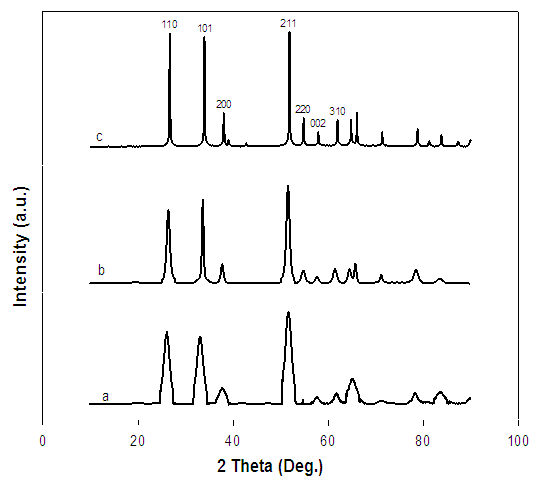 | Figure 2. XRD patterns of Sn-400 (a), Sn-500 (b), and Sn-C (c) |
3.3. N2 Adsorption and Desorption
- Figure 3 shows the N2 adsorption isotherms for sample Sn-400 and Sn-500. Both curve illustrates the sample have similar type IV adsorption isotherm with are typical for mesoporous materials [12]. The adsorption amount of N2 on Sn-500 is much smaller than on Sn-400, indicating that Sn-500 has a much lower surface area than Sn-400 [13]. Sn-400 has a BET surface area of 164.9 m2/g which is higher than Sn-500 (74.7 m2/g). Both curves also show a H2 type of hysteresis loops according to the IUPAC classifications. Both isotherms show a strong hysteresis loop in the P/P0 region from 0.5 to 0.7 and 0.7 to 0.9 for sample Sn-400 and Sn-500 respectively. This is related to the formation of bottleneck in the channels with the mesostructure framework collapse in the process of calcination [11, 14, 15].
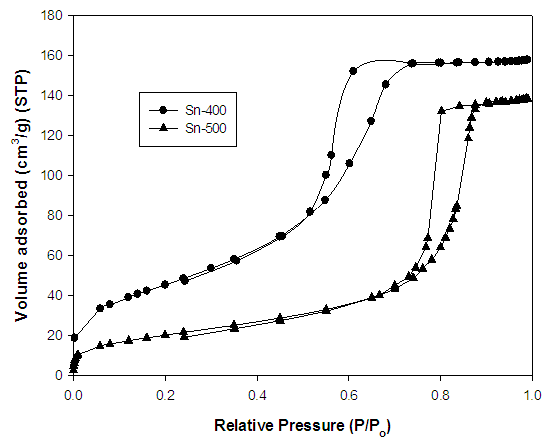 | Figure 3. N2 adsorption isotherm of mesoporous SnO2 |
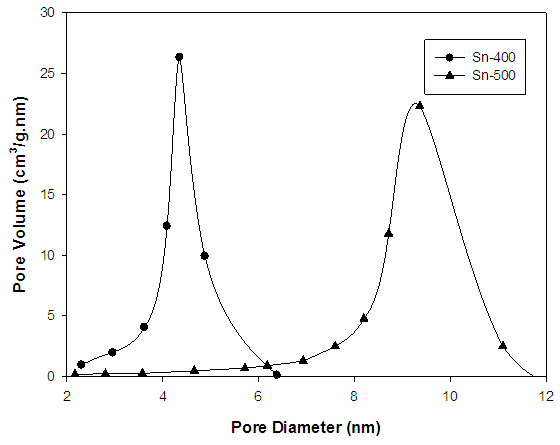 | Figure 4. Pore size distribution of mesoporous SnO2 |
4. Conclusions
- In conclusion, the mesostructured tin oxide has been synthesized, employing cetyltrimethylammonium bromide as template and SnCl4.5H2O as inorganic precurosor under alkaline condition. Sample with being calcined at 400°C (Sn-400) has high specific surface area which is 164.9 m2/g and has an average pore diameter of 4.1 nm and narrow pore size distribution.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors gratefully acknowledge School of Chemical Engineering, Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for providing the instrumental facilities.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML