-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2016; 6(3): 65-73
doi:10.5923/j.chemistry.20160603.01

Precursors Influencing Tropospheric Ozone Formation and Apportionment in Three Districts of Ilupeju Industrial Estate, Lagos
Azeez L.1, Oyedeji O. A.2, Adewuyi S. O.3, Tijani K. O.4, Adebisi S. A.1, Olaogun M. A.5
1Analytical, Environmental and Nutritional Research Laboratory, Department of Chemical Sciences, Osun State University, Osogbo, Nigeria
2Department of Science Laboratory Technology, The Federal Polytechnic Ilaro, Nigeria
3Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Ogbomoso, Nigeria
4Department of Chemical Sciences, Fountain University, Osogbo, Nigeria
5Environmental Chemistry Unit, Environmental Accord Nigeria, Limited, Gbagada, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Azeez L., Analytical, Environmental and Nutritional Research Laboratory, Department of Chemical Sciences, Osun State University, Osogbo, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study determined concentrations of toxic pollutants, volatile organic compounds and meteorological parameters in three sampling locations (SL1, SL2 and SL3) at Ilupeju industrial Estate. Average concentrations of toxic pollutants; CO (14.70 ppm), NO2 (0.88 ppm), and SO2 (0.55 ppm) and O3 (17.67 ppb) were determined. These had high correlation with temperature, wind speed, pressure and relative humidity. In terms of air quality, unhealthy air quality was obtained for CO, NO2 and SO2 while O3 gave a good air quality. Seventeen VOCs species belonging to alkane, alkene, aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons were determined. m/p - xylene was the most abundant species accounting for 16.28%, 11.66% and 14.06% at SL1, SL2 and SL3 respectively. Different ratios such as toluene/m,p – xylene, Σ Xylene/CO, trichloroethene/CO and tetrachloroethene/CO indicated solvent related emissions from these locations while Benzene/Toluene ratio indicated a traffic related emission. m/p - xylene and propene were the major contributors to O3 formation at SL1, SL2 and SL3 respectively. Ozone determined was VOC sensitive at all locations. Factor analysis using principal component analysis suggested traffic, industrial related emission sources solvent evaporation as sources for toxic pollutants and VOCs.
Keywords: Toxic pollutants, Ozone formation, Principal component analysis, Diurnal pattern, VOCs
Cite this paper: Azeez L., Oyedeji O. A., Adewuyi S. O., Tijani K. O., Adebisi S. A., Olaogun M. A., Precursors Influencing Tropospheric Ozone Formation and Apportionment in Three Districts of Ilupeju Industrial Estate, Lagos, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 6 No. 3, 2016, pp. 65-73. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20160603.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
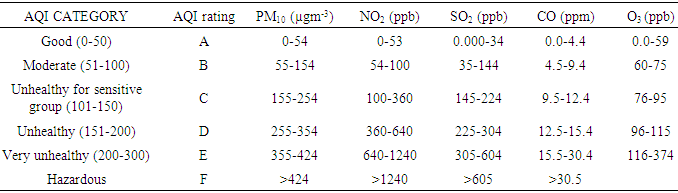
- Air pollution is a well-documented problem in urban centres especially where residential houses are in the neighborhood of industries. Anthropogenic emissions such as vehicular activities, industrial emissions and solvent evaporation are the largest sources of air pollution in most urban cities [1-3]. Air emissions from these sources are usually critical and have been associated with numerous diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, fatigue, headache, immune impairment and cancer [4, 5]. Most of these primary pollutants are acid anhydrides reacting with moisture to form acidic compounds that are dangerous to human health, plants and materials [6, 7]. Aside high toxicity these pollutants induce, they also combine to form secondary pollutants which are sometimes more toxic than them [8, 9].Tropospheric Ozone (O3) also known as bad ozone is a secondary air pollutant formed in the atmosphere through a complex photochemical reaction sequence requiring reactive hydrocarbons, sunlight and nitrogen oxide (NOx) [10, 11]. It is one of the criteria air pollutants, a major constituent of photochemical smog and a powerful oxidant which plays important role in the oxidative capacity of atmosphere [12]. It is a highly corrosive and toxic air pollutant whose pollution is still a serious problem that needs our collective attention [13].O3 is an irritant to lung tissues and has been reported to cause respiratory inflammation, impair photosynthesis and damage human health by oxidizing biological tissues [14, 15]. O3 concentration is usually high at noon basically due to photo-oxidation of the precursor gases such as CO, CH4 and non-methane hydrocarbons in the presence of sufficient amount of nitrogen oxide (NOx) [16]. O3 production during the day could also be driven by the photochemical reaction between hydroxyl radicals, organic peroxy radicals and NO while it is removed at night by deposition and destruction by alkenes and NO [17].Non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHCs) are major volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the ambient atmosphere. They are ozone-producing precursors and also play key role in the formation of secondary organic aerosol. They are usually emitted from vehicular activities and solvent evaporation [15, 18, 19, 20]. They have been reported to induce a wide range of acute and chronic health effects, such as sensory irritation, nervous system impairment, asthma and cancer. Many VOCs are known to be toxic, carcinogenic and mutagenic [21]. Benzene, formaldehyde and carbon tetrachloride have been shown to damage liver, kidney, lung and intestine and DNA [22].Understanding and identifying ozone precursors’ emission sources are important for policy-makers and for the improvement of air quality. Moreover, these precursors have been well documented and discussed as part of criteria air pollutants in most countries especially Nigeria but same attention has not been given to tropospheric ozone formation and its distribution. Therefore, this study was focused on providing baseline concentration data on toxic air pollutants, and their contribution to ozone formation and apportionment in one of the largest industrial estates with a lot of commercial activities.
2. Sampling Location
- Ilupeju Industrial Estate is one of the industrial estates established in Lagos in Oshodi-Isolo, Local Government Area. The Estate has a number of industries such as PZ Cussons Nigeria Plc; Poly Products Nigeria Plc (manufacturer of polyethylene products); Bhojsons Industries Plc; Nestles Nigeria Plc, Patplast and Allied Rubber Products Nigeria Limited, Nigeria Foundries limited, Atlantic Textile Manufacturing Company Limited; Enpee Industries; Absco Industries; Pharmchem Industries; Kiwi Industries. Vehicular activities are usually high on the roads within the industrial estate because many houses and other towns are connected together by these roads.Measurements of pollutants were conducted in three (3) different sampling locations (SL) selected randomly within the Estate for three consecutive months (February – April, 2014). Measurements were carried out between 0700hr and 1800hr daily. Geographical locations of sampling locations 1, 2 and 3 are 06°33’16.8’’N and 003°21’15.4’’E, 06°33’03.1”N and 003°21’33.4’’E, and 06°33’22.9”N and 003°21’27.0’’E respectively. Sampling locations and industries cited within are shown in figure 1.
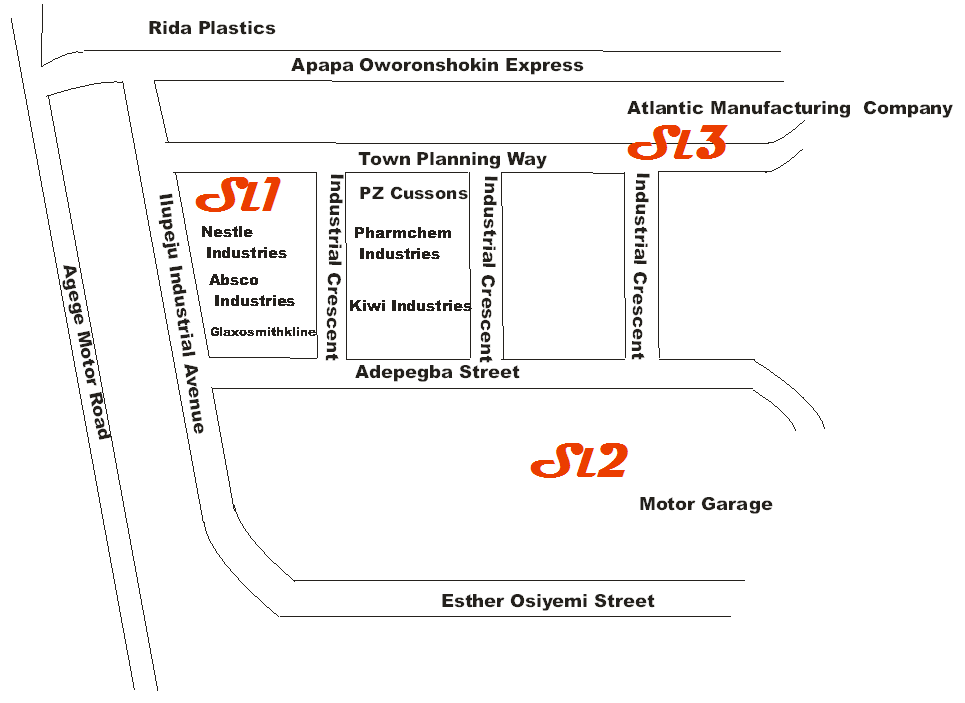 | Figure 1. Map of Ilupeju Industrial estate showing sampling locations |
2.1. Sampling Methodology
2.1.1. Measurement of Toxic Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters
- The concentrations of air pollutants of concerns were determined in-situ with the use of digital hand-held MultiRAE IR monitoring instruments. The MultiRAE IR is a programmable multi-gas monitor designed to provide continuous exposure monitoring of toxic gases (CO, NO, NO2, SO2) in potentially hazardous environments. It uses the following sensors; Organic vapours with the supplied Photo-Ionization Detector (PID) using 9.8eV, 10.6eV gas discharge lamp and toxic gases with several interchangeable electrochemical sensors. All instruments underwent background checks and were purged with high purity zero air to correct instrument drifts.Meteorological parameters were measured using Kestrel 4500 NV Weather Meter (USA).
2.1.2. Determination of Ozone
- Method of Olajire et al. [23] was used to determine ozone concentration. Air samples were drawn with P4LC air sampler into the impinger containing 10 ml oxidant absorbing solution (1% KI in 0.1 M phosphate buffer at pH 6.8) at a flow rate of 2 l min_1 for 1 hr. The absorbance of exposed absorbing solution was read at 352 nm using unexposed solution as reference. Concentrations of ozone in each solution was extrapolated from the calibration curve prepared from standard iodine solution against ozone concentration. Oxidant concentration in the air was calculated using this equation
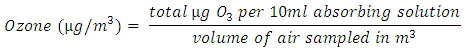
2.1.3. Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
- Concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) were determined using method described by Olajire and Azeez [34] with slight modification. Tubes for sampling were conditioned at 90°C and checked for target VOCs before sampling. Air was drawn into tube containing 100 mg activated charcoal with P4LC sampler at rate of 0.5 l/min for 30 min. After each sampling, the tubes were tightly sealed and wrapped in aluminum foil. Duplicate samples were collected at each sampling point. The content in each tube was transferred into 10 ml vial borosilicate glass. The vial and its content were stoppered by silicone material and were transferred to the cell of headspace sampler coupled with gas chromatography equipped with flame ionization detector (GC-FID) for analysis of VOCs. An HP-VOC capillary column (25 m x 0.32 μm i.d x 0.12 μm film thickness) was used and carrier gas was ultra-pure hydrogen. The GC oven temperature was set initially to 35°C for 2 min., increasing at a rate of 5°C /min to 80°C and then holding for 10 min. Detector and injector temperatures were maintained at 300°C. The target VOC species were identified by their individual retention time.Laboratory and field blanks were prepared and analyzed as sample.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
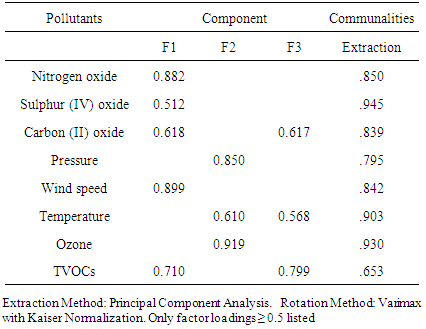
- Data obtained are expressed as mean ± standard deviation and were subjected to multivariate statistics using correlation and factor analyses. Correlation analysis was done using Pearson correlation to establish the relationship among different toxic pollutants. R was obtained at 99% confidence levels. Factor analysis was done using principal component analysis (PCA) technique. It was employed to reveal the likely sources and the contributions of different pollutants. Time series was used to provide diurnal pattern of pollutants. SPSS 17 was used for all analyses.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Toxic Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters
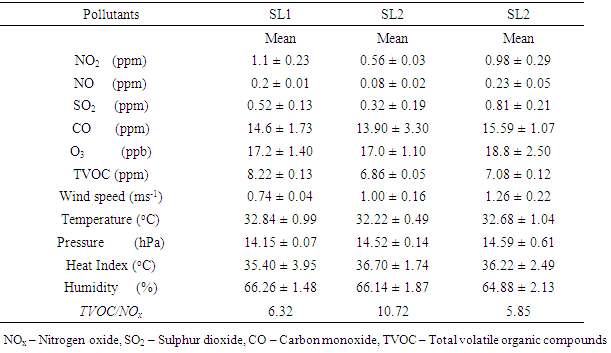
- Concentrations of toxic pollutants and meteorological data are presented in table 1.
|
|
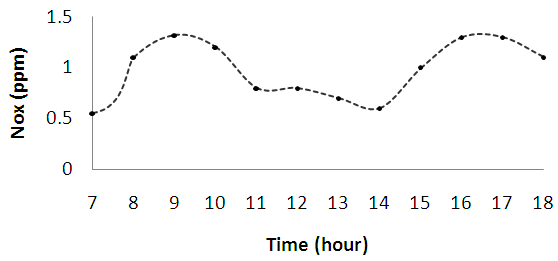 | Figure 2a. Diurnal variations of nitrogen (IV) oxide (NO2) |
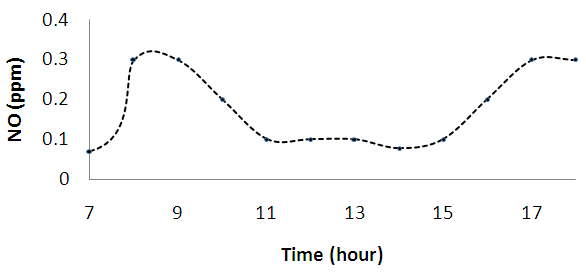 | Figure 2b. Diurnal variations of nitrogen (II) oxide (NO) |
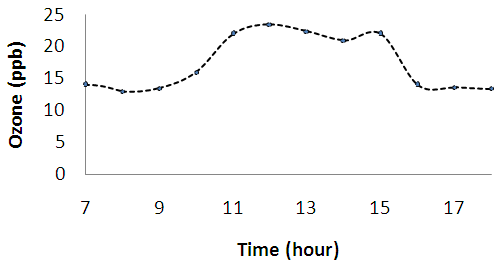 | Figure 2c. Diurnal variations of ozone (O3) |
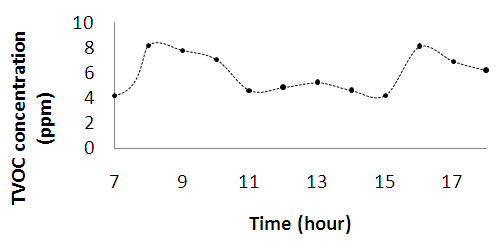 | Figure 2d. Diurnal variations of total volatile organic compounds (TVOC) |
|
3.2. Volatile Organic Compounds Concentrations
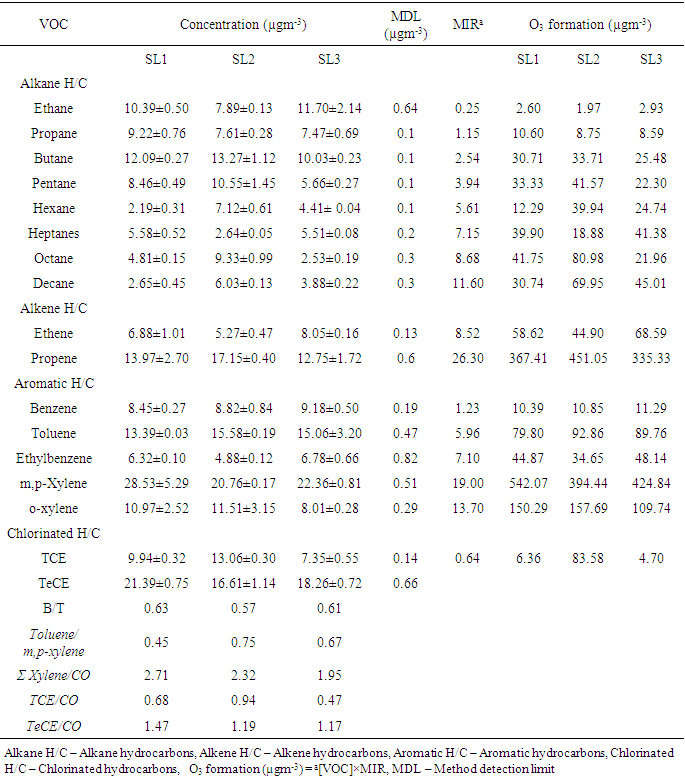
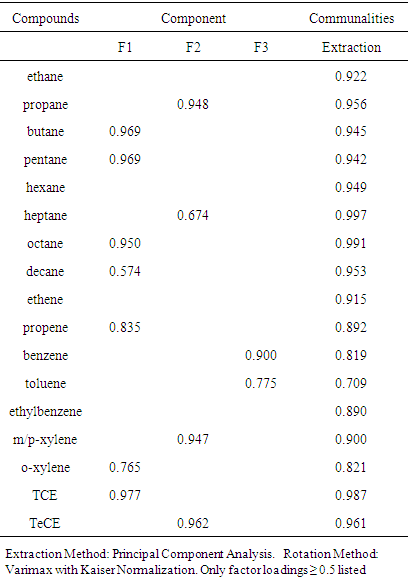
- Average concentrations of seventeen VOCs measured belonging to alkane, alkene, aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons are presented in table 4. Abundance of VOCs species measured follows SL2 (34.70%) > SL1 (34.20%) > SL3 (31.10%). n - ethane, propene, m,p – xylene and tetrachloroethene dominated alkane, alkene, aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons groups respectively. Aromatic hydrocarbons were found to be most abundant at SL1 and SL3 while alkane hydrocarbons accounted for highest abundance at SL2. Alkene hydrocarbons had the lowest abundance at all locations. m/p – xylene was the most abundant at all locations accounting for 16.28%, 11.66% and 14.06% at SL1, SL2 and SL3 respectively.
|
|
3.3. Ozone Formation and Apportionment
- The ratio of VOCs/NOx can be used to evaluate whether the production of O3 is VOC-sensitive or NOx-sensitive [34]. Morning VOCs/NOx ratios lower than 10 were equated with VOC-sensitive peak ozone and Morning VOCs/NOx ratios greater than 20 correspond to NOx-sensitive peak ozone [11, 35]. In this study, TVOC to NOx ratios (table 1) are lower than 10 in SL1 and SL3 while it is higher than 10 at SL2. This indicates that at all locations, O3 formation is VOCs sensitive.VOCs are ozone-forming species, thus, photochemical reactivity of measured VOCs were estimated using maximum incremental reactivity (MIR). The results are presented in table 4. m/p – xylene was the highest contributor to O3 formation at SL1 and SL3 while propene had highest contribution at SL2. Ethane contributed the least to O3 formation. Since O3 formation at all locations was VOC sensitive and m,p- xylene which is solvent related played the most important role in O3 formation at all locations, it could therefore be deduced that solvent use and unburned fuel were the major contributors to O3 formation at all locations.
4. Conclusions
- In this study, we have reported the concentrations of toxic pollutants, volatile organic compounds and meteorological parameters measured in three locations of Ilupeju indusrial Estate. Concentrations of toxic pollutants such as CO, NO2 and SO2 were higher than acceptable limits and were dependent on meteorological parameters such as temperature, pressure, humidity and wind speed. Majority of VOCs ratios revealed solvent related and unburned fuel emissions from these locations except B/T ratio which indicated a traffic related emission. m,p - xylene and propene were the major contributors to O3 formation at SL1, SL2 and SL3 respectively. Ozone determined was VOC sensitive at all locations. PCA of the results showed traffic related emission sources for toxic pollutants and solvent use as sources for VOCs.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML