-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2015; 5(4): 91-95
doi:10.5923/j.chemistry.20150504.01

A Study of the Substituent Effects on the O−H Bond Dissociation Enthalpies of Phenol Derivatives Using the ONIOM Method
Nguyen Minh Thong1, Thi Chinh Ngo2, Truc Xuyen Nguyen Phan3, Duy Quang Dao2, Truong Van Nam1, Phan Thi Tuyet Trinh1, Pham Cam Nam4
1The University of Danang - Campus in Kon Tum, 704 Phan Dinh Phung, Kon Tum, Viet Nam
2Institute of Research and Development, Duy Tan University, 03 Quang Trung, Danang, Viet Nam
3Department of Environment, Duy Tan University, K7/25 Quang Trung, Danang, Viet Nam
4Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology - The University of Danang, 54 Nguyen Luong Bang, Lien Chieu, Danang, Viet Nam
Correspondence to: Nguyen Minh Thong, The University of Danang - Campus in Kon Tum, 704 Phan Dinh Phung, Kon Tum, Viet Nam.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The O–H bond dissociation enthalpies (BDE) of various substituted phenol derivatives were determined using the ONIOM(ROB3LYP/6-311++G(2df,2p):PM6) approach. Computed BDE(O–H)s of all phenol derivatives were in good agreement with available experimental values, and also well correlated with the Hammett constants, σp. It is found that the strong electron-donating NH2 and N(CH3)2 substituents induce a significant decrease in the BDE(O–H)s. On the contrary, the strong electron withdrawing NO2 and CF3 groups result in an increase in BDE(O–H)s.
Keywords: Bond dissociation enthalpies, Antioxidant, Phenol derivatives, ONIOM method
Cite this paper: Nguyen Minh Thong, Thi Chinh Ngo, Truc Xuyen Nguyen Phan, Duy Quang Dao, Truong Van Nam, Phan Thi Tuyet Trinh, Pham Cam Nam, A Study of the Substituent Effects on the O−H Bond Dissociation Enthalpies of Phenol Derivatives Using the ONIOM Method, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 5 No. 4, 2015, pp. 91-95. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20150504.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Phenolic antioxidants (ArOH) play an important role in the prevention of several chemical and biological processes including the biological ageing, foodstuff deterioration, synthetic polymer degradation [1-3], etc. The function of phenolic antioxidants is a scavenger active against reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as superoxide anion radical, singlet molecular oxygen and hydroxyl radical. There are several mechanisms of phenolic antioxidant action, and the net result of all mechanisms is similar to each other: transferring hydrogen atom radical to the free radicals [4-8]. A high rate of hydrogen atom transfer is expected to be related to a low O–H bond dissociation enthalpy (BDE). Therefore, the BDE parameter (capacity to donate an H atom) is a key feature for evaluating the antioxidant activity of a natural compound. Sterically hindered phenols (Figure 1b) represent a large group of synthetic antioxidants widely used in synthetic polymers stabilization [9]. It is well-known that phenolic compounds act as chain-breaking antioxidants.Numerous attempts have already been investigated to measure or predict the accurate BDEs of organic compounds in both experimental [10-14] and quantum chemical [15-19] techniques. Although quantum chemical study is already well established for accurately predicting BDEs, there are still many challenges in treatment of large compounds. The ONIOM approach, which is an integrated method proposed by Morokuma and co-workers [20-22], is an efficient computational tool for the study of large molecular systems. In our previous studies, we performed an integration of the ROB3LYP/6-311++G(2df,2p) level with the semi-empirical PM6 method into a two-layer ONIOM to reasonably produce accurate BDE(O–H)’s of phenolic compounds. Deviation of calculated values from experiment is ± (1–2) kcal/mol [23, 24]. In the present paper, we thus apply the ONIOM(ROB3LYP/6-311++G(2df,2p):PM6) approach to determine the BDEs of the O–H bonds of various substituents of sterically hindered phenols and mono-substituted phenols (as shown in Figure 1) in the gas-phase, and to assess the effect of various electron-donating or electron-withdrawing groups at the para-position on the change of the BDE. The obtained results for mono-substituted phenols will then be compared with identical group of substituents in para-position, in order to describe the effect of the two tert-butyl (t-Bu) groups on studied enthalpies. In addition, our observation will also be compared to the available experimental data. The relationship between the calculated BDEs and Hammett constants will be also correlated.
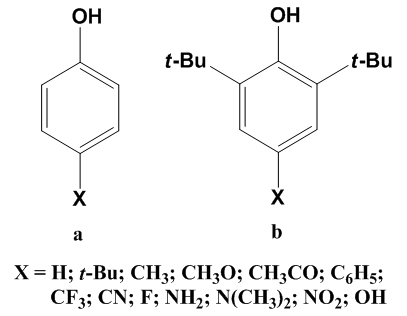 | Figure 1. Structure of mono-substituted phenols (a) and sterically hindered phenols (b) |
2. Theoretical and Computational Methods
- All computations were performed using the Gaussian 09 suite of program [25]. Geometry optimizations and vibrational frequency calculations were conducted using the semi-empirical PM6 method. Vibrational frequencies obtained at the PM6 level were subsequently scaled by a factor of 1.078 [26] for estimating the zero-point vibrational energies (ZPE). The BDE value was determined from total enthalpies of the individual species in the gas-phase, as follows:BDE(ArO−H) = H(ArO•) + H(H•) − H(ArOH)Where H’s are the enthalpies of different species at 298.15 K and 1.00 atm. The enthalpies were estimated from the given expression: H(T) = E0 + ZPE + Htrans + Hrot + Hvib + RT. The Htrans, Hrot, and Hvib are the translational, rotational, and vibrational contributions to the enthalpy, respectively. E0 is the total energy at 0 K and ZPE is the zero-point vibrational energy. The enthalpy value for the hydrogen atom in the gas phase was taken at its exact energy of −0.5 hartree at 0 K and thermal correction at the given temperature is added the value of 2.5RT.By improving the results of the previous paper [24], we choose a partitioning scheme for the two-layer ONIOM (as described in Figure. 2) that generates an accurate estimation of BDE(O−H) within 1–2 kcal/mol deviation. According to this, each molecule is divided into two layers, the atoms at the breaking bond is treated as a high layer while the leftover atoms of the molecule belong to the second layer, which is treated as a lower layer. The ROB3LYP/6-311++G(2df,2p) method is thus applied for the atoms in the high layer, whereas the PM6 procedure is applied for the low one. In this model (Figure. 2), the core layer which has only one oxygen atom and one hydrogen atom, relates to the target bond for estimating BDE at the high level. The rest are defined as the low layer.
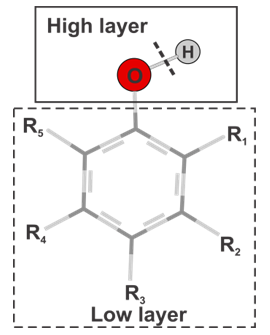 | Figure 2. Schematic description of two-layer proposed ONIOM model |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Agreement between Calculated and Experimental BDE(O–H)s
- In this part, the ONIOM(ROB3LYP/6-311++G(2df,2p):PM6) approach were used to determine the BDEs of the O–H bonds of 26 para-substituted sterically hindered phenols and phenols. The calculated BDE(O–H) values are summarized in Table 1. In order to evaluate the reliability of employed computational approach for substituent effect description, it is necessary to compare the calculated and the experimental values. From the calculated results for a series of substituted phenols (as shown in Table 1), the largest deviation (ΔBDE) between the calculated and the experimental BDE(O–H) values is 2.5 kcal/mol which is found in the case of p-CH3CO-C6H2(t-Bu)2OH. For the other substituted compounds, the deviation are smaller and in the range from –1.8 to 0.7 kcal/mol. The results also show that the BDE(O–H) values obtained from the ONIOM method are reasonably accurate and in agreement with the best experimental data with the deviation of only ±1.0 kcal/mol.
|
3.2. Effect of Substituents on BDE(O–H)s
- The substitution of a functional group in the molecule generally causes considerable changes in physico-chemical properties. Therefore, the understanding of substituent effect on O–H bond cleavage as well as on various molecular properties is important. The substituent effects were described in terms of ∆’BDEs, where ∆’BDE is the difference between the bond dissociation enthalpies of the substituted and the parent phenol, ∆’BDE = BDE(substituted phenols) – BDE(phenol). Relationship between ∆’BDE values and substituents was shown in Table 1 and Figure 3.
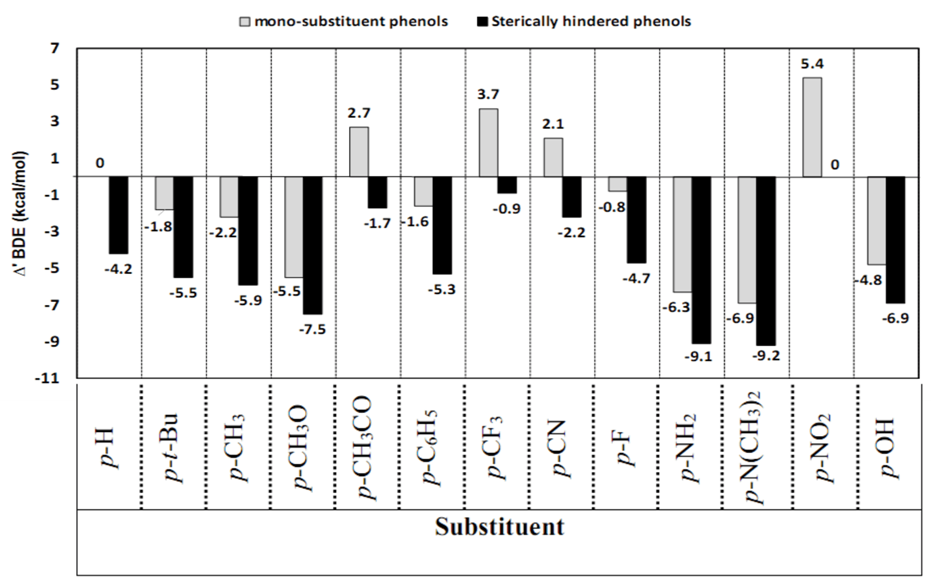 | Figure 3. Effect of substituents on BDE(O–H)s of mono-substituent phenols and sterically hindered phenols |
3.3. Relationship between the Calculated BDEs and Hammett Constants
- The Hammett equation (and its extended forms) has been one of the most widely used means for the study and interpretation of organic reactions and their mechanisms. Hammett constants σm (for substituent in meta position) and σp (for substituent in para position) obtained from the ionization of organic acids in solutions can successfully predict equilibrium and rate constants for a variety of families of reactions [28]. Hammett constants correlate very well with the changes in BDE(O−H) in the case of phenols [15]. The correlation between calculated BDE values and Hammett constants, σp, for mono-substituent phenols and sterically hindered phenols is presented in Figure 4. The equations obtained from the linear regression are as follows:BDE (kcal/mol) = 7.63σp + 86.01 (R2 = 0.9329) (mono-substituent phenol)BDE (kcal/mol) = 5.83σp + 82.43 (R2 = 0.9561) (sterically hindered phenol)
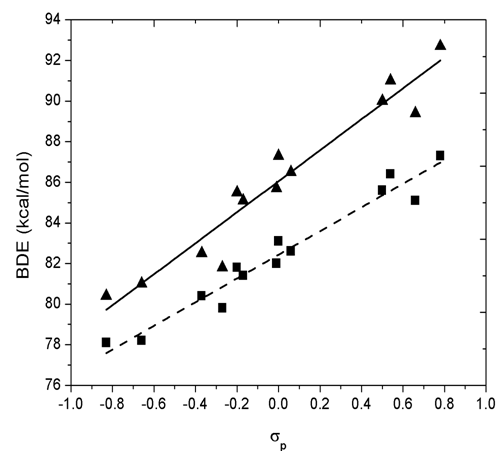 | Figure 4. Dependence of BDE on σp for mono-substituted phenols (solid triangles, solid line) and sterically hindered phenol (solid squares, dashed line) in gas phase |
4. Conclusions
- In this paper, the bond dissociation enthalpies of para-substituted phenols and sterically hindered phenols in the gas-phase were investigated usingONIOM(ROB3LYP/6-311++G(2df,2p):PM6) approach. The calculated results are in very good accordance with available experimental data. In addition to the character of substituents, the influence of number of substituents was also evaluated. The largest decrease in BDE(O–H)s results from the strong electron-donating NH2 and N(CH3)2 groups. On the contrary, the strong electron withdrawing NO2 and CF3 groups result in an increase in BDE(O–H)s. Therefore, the improvement of the phenolic antioxidant effectiveness, i.e. the decrease of the BDE(O–H), can be accomplished by the substitution of electron-donating groups at the para position.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 104.06-2013.21.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML