M. Serajian Ardestani1, A. Badrian2
1Shahid Beheshti Teacher training University, Tehran, Iran
2Studies Institute of the Ministry of Education, Tehran, Iran
Correspondence to: M. Serajian Ardestani, Shahid Beheshti Teacher training University, Tehran, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Abstract
One of the most important imperfections of traditional teaching methods is the instability of teaching contents in students’ mind and the weakly interest of students to these contents. So teaching on an experimental base could be an effective method of education. One can study the influence of experimental teaching methods by sharing the students in the teaching process and also benefiting the research principles and statistical methods, as used in this study, in order to deduce which one of virtual, electronic or manipulation experimental methods could be more effective on the chemistry education. In this study, in order to study the effect of different experimental teaching methods on the comprehension of theoretical concepts of chemistry, we have applied an experimental and practical study on the high school students. The statistical society is all second and third grades students of high school. We have chosen randomly 131 persons among them. Data processing is performed by applying the pretest and posttest, as teacher made writing test, which are analyzed by descriptive statistics (abundance table, percentage and diagram) and inductive statistics (agent variance analysis, chasing test and computing the most significant difference). Among the various teaching method stages, the electronic and manipulation methods show a significant relation with the chemistry learning rate. Also we have shown that the integrating of the expository, discovery, problem solving and excavator type experiments have a maximum effect on the learning rate.
Keywords:
Virtual experiments, Electronic experiments, Manipulation experiments, Experimental activities
Cite this paper: M. Serajian Ardestani, A. Badrian, The Comparison of Experimental Education of Chemistry by Manipulation, Virtual and Electronic Methods, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 51-58. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20140401.09.
1. Introduction
One of the educational problems in our cuntry, Iran, is teachers’ weak information of the variety teaching methods, whereas it is possible to define a teaching and learning method for each student separately, because the viewpoint, the subjective frame work and the learning concepts of each student are different from the others. The most misunderstanding in chemistry teaching comes from these reasons. Because many of chemistry concepts are abstract, they are not easy to understand so the different teaching methods would help the teacher to make them clear. Applied science is one of the human knowledge whose a big part of finding is researchable by observing and experience. Its main objective is teaching the concepts, theories and skills which help students to have a good understanding from their surrounded world, and to find good answers for their questions. In the modern applied science education methods, in addition to student’s activeness; discovering process, research and problem solving have very important roles. These activities are done in the laboratories, scientific and industrial centers[1]. Practical activities said to a set of activities by which, the student have opportunity to engage with things by a scientific observation and gathering information via models and instruments which take place in laboratory[2]. The practical activities are considered as an inseparable part of teaching and learning of applied science. Experimental activities not only include the meditative and skillful development fields, but also cause the growth of social skills. Since the most of experimental activities take place in small groups, the students have this possibility to get out some skills to cooperating, co-understanding and having opinion tolerance in addition to obtain experiences and skills during a group activity[3].The school education program should prepare an opportunity to do the experiment and observe via seeing, touching, listening and smelling. The student should habituate to collecting pure and exact scientific observation and also he/she should learn how to save and present an exact report. One of the other educational aims in this field is to learn the safety precautions about working with chemical materials and experimental instruments.
1.1. Virtual Type Experiments
These types of experiments as computerized experiments are known as an essential learning source. The computer could be used for simulating the experimental situation in order to do the sample experiments, preparing the fundamental data and information and solving the problems or exercises[4]. Also this type could be used for molecular and computational modeling to predict the special molecules’ behavior in a chemical system, especially for cases which are not easy accessible or they are expensive to experiment[5]. This method is mainly dependent to computerized possibilities. It is possible to use it as a real laboratory by using for example, the quantum mechanical methods or molecular characteristics driven from solving the Schrodinger equation or using the Gaussian software. By using these methods, students will learn the teaching subjects better. Also by having a profound knowledge in the related media, they could see virtually experiments and repeat them as they want[6].
2. Different Virtual Type of Experiments
2.1. Simultaneous Experiments (Real)
This type of experiment performed in distance and via internet. One could inter the required parameters in the laboratory webpage as the internal data and the results will be returned as a real performed experiment. E. Fereyduni in collaboration with M.Kamali have discussed about the importance of practical education and its influence on the student’s learning rate by organizing an educational workshop in the 6th conference of chemistry education. The related article presents a favorable solution for the problems of an appropriate use of laboratories by Vlab software (virtual chemistry lab)[7]. Dr. Z. Ahmadabadi in collaboration with Dr. M. Keikhaie, in the same conference, present a research article subjected to the experiment and chemistry education which suggests that it should expand the definition of laboratory from its today definition and the merely physical concept to the profiting the educational software and electronic devices and instruments[7].
3. The Simulated Experiments
This is an artificial situation. The students begin to experience without scaring of not be succeeded[4]. T. Dastyar and M. Salehi Veisi from Khuzestan[8], in a research article as “virtual chemistry lab” considered the virtual experiment idea as a favorable response in the educational systems of some developed countries which could replace the traditional methods of experiments. In an in distance and a virtual education, the accessibility and using of different experimental parts is possible by computational simulating. J.E. Jones in his article “simulated experiments of physics and chemistry” speaks about a set of experiments done by computer and by an experimental group whereas the control group has done the same experiments by experimental instruments. The results show that at first, the experimental group opinion about using computer as a lab was not different from control group’s one while at the end, their opinion was changed more greatly than the control group’s one[9].
4. The Importance of Chemistry Education and Attending to Experiment and Its Real Role in Development
There are always great changes in all fields of human life, and his permanent need to keep the equilibrium and having a good adaptability to the very changeable conditions of society, make it necessary to perform fundamental and comprehensive changes in objectives of educational concepts and activities and also in the evaluation methods [7]. It is clear that to achieve this purpose; it is not privilege to repeat the pervious and common models. Whether the old educational models remain stable or possible to be used by making a few reforms in different time periods, they contain fundamental criticism. In order to coordinate and manage the educational politics and programming, especially teaching methods, versus the personal needs and the fast economical and social development, it is necessary to attend to some rules and structures. The great increasing growth of scientific knowledge, make it necessary to have a profound and general appeal in teaching methods, quality of contents of textbooks and the mode of students learning evaluations. Today, in course programming and scientific process of chemistry education, one gives more importance to the students’ operational skills which is improved intentionally in laboratories. Also, it is shown that the most adequate method to take scientific process is doing the research by an excavator and problem solving way. The specialists of chemistry education emphasis these methods for applying in education and learning because in such activities, students are strongly motivated to learn and also in addition to learn a knowledge, they achieve to understand many of principles concepts, models, scientific thorium and their applications in their life and surrounded world[10].
5. Experiments Types
5.1. Expository Type Experiment
This type of experiments is based on an agenda prepared already. The skill used in this type is further comparative from whole to component type. In according to the six steps of science education, this style contains just the first three steps means: knowledge, perception and application. It could not reach the next three steps which is its main disadvantage.
5.2. Discovery Type Experiment
It means specializing information taken by students which help them to have a better understanding. The skills used in this type of experiments are as same as an inductive style (from component to whole). In such activities, all work steps are done by student and the teacher has just a guide role. In this type, in spite of the first one, student has an essential role.
5.3. Problem Solving Type Experiment
Skills used in this type are as the same as an comparative style (from whole to component). Firstly, the teacher should explain the problem and then learners will analyze it and in according to their knowledge, they will re-describe it. There exist some backgrounds to solve a problem that for proving them, it should describe an experiment. So in this type of experiments, the agenda is the experiment definition. Firstly one defines the experiment while the result is clear from the beginning.
5.4. Excavator Type Experiments
Learners could organize the facts and realities significantly to achieve a general and fundamental rule. The deductive skills in obtaining a research mentality, having knowledge about the essence of science and logical thought of learners have an essential role. In this type of experiments, learners should present all steps of process such as problem drafting, suggesting the solution, results and their analysis. Darestani[11] has mentioned in his article titled as “research in order to verifying the influence of experimental activities on the students’ academic progress in Chemistry” that using the experimental teaching methods causes an academic progress and make student well motivated. In this way the student will have a more stable learning rate in his mind. N.M. Arshad[12] from the Iowa University has shown that in a study of evaluating the influence of computer simulated experimental teaching of Chemistry against the traditional experimental teaching of solid state electrical circuits, comparing the average pretest and posttest scores has shown that the simulating group score is greater than the control group’s one.In another study by M.Inces et al[13], he has compared the teaching of the acid and base concepts by computer and also by a traditional method. The students’ 3D space visualization, computational point of view and learning methods were studied in the two groups. At first, there was not a significant difference between their scores and their ability of 3D space visualization or their learning methods but the posttest results shown that the experimental group had a 52% growth against the growth of 31% of the control group.
6. Problem Explanation and Necessity of Research
The reports from the studies on the effect of experiment have shown that one should define a relation between the high school experiments level and society[6]. Many of educational studies in the chemistry teaching fields show that the scientific facts would not be memorized unless by doing experiments[14]. It is recommended always to use the experimental methods for teaching science which had a main role during some periods of science teaching history. This modification of science teaching methods has been begun from the 60 decay so that some of science teachers felt that the majority of science teaching should be guided via experiment. The designers of educational courses emphasized greatly on the probing of scientific process from the 60s. They believed that working on a problem in a lab is more important than taking the results in a classroom and in this way, because of uncertainties in the practical works; they suggested that it is better to have a more emphasis on the data processing instead of special results[15]. Planning of the intentional courses should lead to training skills and favorable habits as scientific skills, capability of dealing with a problem and finding a logical solution for it. The main reason of an experimental work is studying the authenticity of the concepts of textbooks. It has been seen that the teacher has to spend a long time to give to understand a subject in the classroom whether it is more satisfying to define and use a simple experiment about the same subject to make it clear to understand. Educating of many of chemistry concepts is possible via an experimental way. The group characteristics and the periodical properties of chemical elements, the conductivity of aqueous solution of ionic compounds, cations’ identification, calorimetry, verifying the colligative properties and … could be taught by doing the simple experiments. So the main importance of this study is the understanding of the improvement of learning of the concepts of chemistry. Learning means an organized and logical procedure in order to increase a more favorable operation by the experimental activities and also improving the student’s learning motivation about the chemical concepts. The objectives of this study are as below:− Study of the influence of experimental teaching methods by manipulation, virtual and electronic skills on the student’s learning rate of the theoretical concepts of chemistry.− Comparing of the different experimental teaching methods and study the effect of experimental teaching method in expository, discovery, problem solving and excavator type levels.
7. Method
This is an applied study and its data processing is based on experiment which is done as a posttest by control group. Here the test and regression factors have no meaning. The maturity and choice factors are the well controlled parameters. The concurrency, measurement instruments, the experiment fluctuations might cause the uncertainty on the plan validity. In this study we selected the operational plans and since the subjects are selected randomly, the operational plan is a complete random one.
7.1. Society, Sample and Sampling Method
The statistical society of this study is all mathematics and applied science students of second and third grades of high school in Tehran city. Since this is an experimental study and the rate of samples could be between 30 – 60 persons, in according to have more precision and validity, we have considered 131 persons as sample. The sampling procedure is as a random one.
7.2. Instruments
We have used the opinion of the executer teachers of this plan to determine the conceptual validity of teacher made test which contained 12 questions. The studied experimental samples were divided in three groups for a two weeks experimental education period. The groups are considered as follow: a group of virtual education, another group of electronic education and the last group of practical and manipulation education. We have affected these groups by writing tests as pretest and the obtained results of posttest were studied in comparison with the pretest ones. In according to determine the stability of test questions, we have used the stability editor method. The correlation coefficient of the two sets of final scores was determined by Pierrson method with help of SPSS program because of having the qualitative data. The ‘’r’’ value is determined as 0.983 with α=1% and assurance factor of P=99%. We have used the Bayse program for planning the educational model.
8. The Study Hypothesis
8.1. The Essential Hypothesis
The experimental teaching methods like virtual, electronic and manipulation types have a great influence on the profound understanding of the theoretical concepts of chemistry.
8.2. The Secondary Hypothesis
The experimental teaching methods are effective on the learning rate of theoretical concepts of chemistry by integrating the four levels of expository, discovery, problem solving and excavator type experiments.
9. Descriptive Statistics
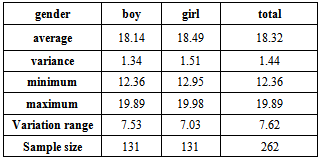
We have presented the educational progress scores of girls, boys and all of students verified by the descriptive statistics on the experiment groups and their final scores of final test separately in table 1.Table 1. description of students’ educational progress score
 |
| |
|
9.1. Description of the Pure Scores of Experimental Teaching of Sample Group
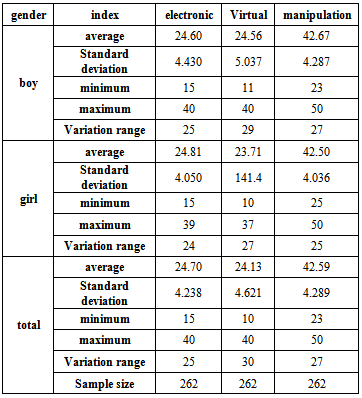
As it is shown in the table 2 the average scores of electronic experimental method for the total of the sample group is 24.7 and the variance (standard deviation) is 4.238. These values are different for boys and girls but they are very close together. The variation range of electronic method is 25 with a maximum of 40 and a minimum of 15. Also the average score of virtual experimental method for the total sample group is 24.13 and its standard deviation is 4.621. These values are different but close together for boys and girls. The variation range of the virtual method is obtained 30 with a maximum value of 40 and a minimum of 10. And finally for the manipulation teaching method the average score of the total sample group is 42.59 and its standard deviation is 4.289. These values are different but close together for boys and girls. The variation rate for this method is obtained 27 with a maximum and minimum value as 50 and 23 respectively. To have more precise data follow table 2.Table 2. Description of pure scores of different experimental teaching methods
 |
| |
|
9.2. Description of Pure Scores of Integrated Experimental Levels and Their Components in the Sample Group
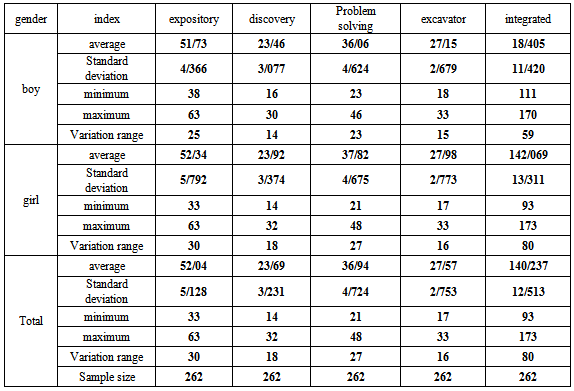
The pure score of integration of experimental methods in four different learning levels, means expository, discovery, problem solving and excavator types and their components are presented in table3. As you can see in this table the average score of expository experimental teaching component for the total sample group is 52.04 and the standard deviation is 5.128. The variation range of this distribution is 30 with a minimum of 43 and a maximum of 63.Also it is shown that the total average score of problem solving component is obtained 23.69 with a standard deviation of 3.231. The variation range of this distribution is 18 with a minimum and maximum rate of 14 and 32 respectively. We can see also that the total average score of excavator component is 36.94 with a standard deviation of 4.724. The variation rate of this distribution is 27. The minimum score for this component is obtained as 21 and the maximum score is 48. In the other column of this table we have shown that the total average score of discovery component is 27.57 and its standard deviation is 2.753. The variation range of this distribution is 16 with a minimum and maximum as 17 and 33 respectively. Finally the average score of the total sample group by integrating the four experimental teaching levels is obtained 140.231 with the standard deviation of 12.513. The variation range is 80 with a minimum score of 93 and a maximum of 173.The first hypothesisThe experimental teaching methods as virtual, electronic and manipulation types are more effective for well understanding and teaching the theoretical concepts of chemistry. As mentioned before in order to verify the main research hypothesis, we have used the multi parameter regression statistical analysis simultaneously, whose abstract of results is presented in table 4. In this table, it is presented the value of regression coefficient (b), standard betta (β), ‘’t’’ value and its significant levels (sig), determination coefficient (R²), the adjacent determination coefficient (R² adj), ‘’F’’ value and its significant rate.We can see in this table that for the three experimental education methods, one concludes a significant relation with the students’ learning rate by integrating the three methods. We will discuss more precisely the results as below: as shown in table 4, the driven regression value (-0.708) and standard betta (-0.240) with the ‘’t’’ value (-0.024) are significant at (P<0.0001) level which means that there is a significant inverse relation between the electronic method with the students’ learning rate by integration of the three teaching methods.Also it is shown that for the virtual teaching test, the significant regression coefficient value is -0.354 and the standard betta is -0.131 with t= -2.058 in (P< 0.041) level. That means there is a significant and inverse relation between the virtual teaching method with the integration of educational methods and the students’ learning rate. Table 3. Description of pure notes of experimental teaching and its components
 |
| |
|
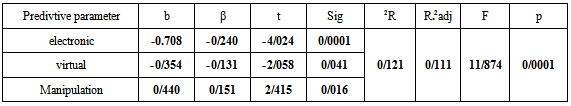
Table 4. the regression analysis results of three experimental teaching methods
 |
| |
|
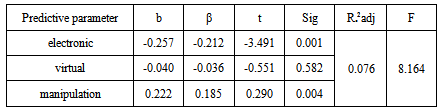
And finally from table 4, for the manipulation teaching method, the significant regression factor and standard betta are 0.440 and 0.151 respectively with t=2.415 in (P<0.0001) range which shows a significant and direct relation between the manipulation teaching method and the students’ learning rate by integrating the teaching methods. The determination factor is obtained 0.121. So we can conclude that the predictive parameters of this hypothesis defined as the experimental teaching methods components could predict a 12.1% of the total variance of creativity. This achieved determination factor with F=11.87 in the (P<0.0001) level is significant and confirms this hypothesis. Second hypothesisThe experimental teaching methods are effective on the learning rate of theoretical concepts of chemistry, by integrating the four levels of expository, discovery, problem solving and excavator types. In according to verify the second hypothesis we have used the simultaneous multi parameter regression statistical analysis which is summarized in table 5. In this table we have reported the values of regression coefficient (b), standard betta (β), ‘’t’’ value and its significant level (sig), determination factor (R²), adjacent determination factor (R² adj), ‘’F’’ value and its significant level. In table 5 we can see that from the three experimental education methods of students’ learning subtests by integrating the four stages, the two electronic and manipulation methods show a significant relation on the students’ learning rate. More precisely we can say that for the experimental education methods subtest, the regression coefficient value of electronic method obtained significantly -0.257 and the standard betta is -0.212 with t=-3.491 in (P<0.001) range. This means that there is a significant inverse relation between students’ learning rate and the subtest of electronic learning method with considering the four integrated stages. For the subtest of manipulation experimental education method the regression coefficient value reached at 0.222 with β=0.185 and t=2.910 in the (P<0.004) range which shows a significant direct relation between this subtest and students’ learning rate.Also as mentioned in table 5, for the experimental virtual method subtest the obtained significant rate is greater than the test error bar (P> 0.582) so the results of this subtest with four integrated levels are not significant for the students’ learning rate.Table 5. the results of regression analysis for four integrated evels: expository, discovery, problem solving and excavator types
 |
| |
|
The weakly determination coefficient value is (-0.087) which means that the predictive parameters in this hypothesis as the experimental teaching methods components, predict 8.7% of the total variance of four integrated stages components. This coefficient has a significant value with F=8.164 in the (P<0.001) range which confirms the second hypothesis.
9.3. Comparison with the Same Researches in Other Countries
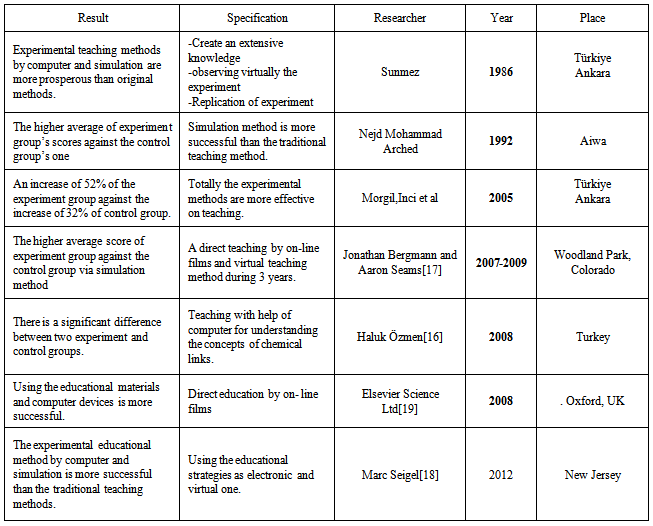
In order to compare the results of this study with the same researches performed in other countries, we have realized a study to verify these kinds of experiences. This study shows that the obtained results are to some extent as the same. It is shown that the experimental method has the better results in the experiment group than the control group. The abstract of this study and its comparison is presented in table 6.Table 6. Abstract of the same researches performed in other countries and their results
 |
| |
|
By comparing these studies one can conclude that today, whether the chemists prefer the quantitative information in order to understand a chemical phenomenon, for teaching the chemical concepts and manipulation skills in the lower stages like schools, it could be used the descriptive and qualitative methods. So it is useful to understand the role of qualitative ideas in the laboratory then modify them for using as a teaching method. Performing an experiment by a computer is essentially a learning source. Computer can be used for simulating the experimental situation of the sample experiment, modeling, and basic data, taking information and taking exercises and solving them. So it is recommended to use the virtual experiment and simulation since it is less expensive, more safety and we have replication possibility. Our results are in the same direction presented before [9,12,13,16-18 .20].
10. Conclusions
The main goal of this study is to verify the influence of experimental teaching methods on the students’ learning rate of chemical concepts and also comparing the effect of each of three methods on the students’ learning rate. The results show that the factor of teaching method is a significant parameter which means that this factor has a great influence on the learning rate of theoretical concepts of chemistry. But the factors such as gender, school type, field of study have not important effect on the students’ learning rate of theoretical concepts of chemistry. We have shown that there is a significant difference between the teaching methods by comparing pretest and posttest and the average scores of four experimental groups. This confirms the effect of the factor of experimental teaching method in this study. So we can suggest that in the case of a significant modification in education methods and their skills and preparing the possibilities for the teachers to get familiar with experimental methods in order to use them, one can provide a good situation for teachers to profit the favorable methods which are more effective on the students’ learning rate. The most important results of this study are summarized as below: 1. As shown before, the experimental methods are effective on the learning rate. 2. Among all types of experimental methods, the excavator type has the main influence on the learning rate. 3. The integration of different expository, discovery, problem solving and excavator methods is the most important effective factor on the learning rate. 4. Among the experimental education methods, the electronic and manipulation skills have the more favorable results than the virtual method. So doing the experiments helps students to have a practical understanding of scientific concepts and theories and also due to have more activities, they can reach the new subjective models. These types of activities have caused that the students, in according to realize the science nature, understand the scientific models, can improve the ability of solving problem, analyzing data and having a scientific argument.
References
| [1] | A. Tohidi Far, “verification of lab situation of biology and science teaching of high school courses all over the country”; Tehran, Research Plan, P.250, 1995,. |
| [2] | Hofstein, A and Lunette, V. N.. The laboratory in science education: Foundations for the twenty-first century, Science Education, 88, 28; 2004. |
| [3] | A. Asfa; “verification of the influence of experimental activities in practical science education in high school in point of view of learning models”. Tehran, summer the research group of mathematics science and technology course programming. 2009. |
| [4] | M. Ahadian, O. Ramezani, D. Mohammadi; the fundamental educational technology. Tehran, Aiish Publication; 2002.. |
| [5] | N. Mohajeri, “The computational methods instead of experimental methods in chemistry”; Research Plan, Khuzestan, 2010. |
| [6] | Hillocky, Schuman Schumacher. As the basis for teaching science labs, science labs in college? It took the efforts and costs in this area is valuable enough? Journal of Chemical Education, version 75, pages 100 to 104. 1998. |
| [7] | Group of Chemistry, The Scientific Association of Chemistry, The article abstracts of the 6th conference of Chemistry Education, Iran, Ahvaz, Mellat Publication, P.191, 2006. |
| [8] | T. Dastyar, M. Salehi Veisi, “Virtual experiment of Chemistry” ; Research Plan, Khuzestan, 2010. |
| [9] | Jones, James Edvard, ‘Computer simulated Expriments in high school Physics and chemistry ‘: Dissertation thesis absract. 1992. Availble in: http://www.eric.ed.gov/eric web portal / homportal |
| [10] | A. Badrian, Chemistry Education, Tehran, Mabnaye kherad Publication, First Edition, P.242, 2009. |
| [11] | A. Darestani, “A Research study of the effectiveness of experimental activities on the students’ educational progress in chemistry course”; Reserch Plan, Tehran, 1995. |
| [12] | Nejad , Mahmod Arshad: ‘A Compurison and Evaluation of Effecctiveness of computer similated labratory instruction versus braditonal labratory instruction in solid state electronics circuity’ Dissertation Abstracts international , Vd , 53, No, 12, PP: 41-80 1992. |
| [13] | Morgil, Inci, Sone, Yarus, ozge ozyalcin and etal, ‘Traditional and computer assisted learning in teaching acid and bases’ Chemical education Research and Practice Ankara (cERP), Vol.6 , No , 2, PP52-60. 2005. |
| [14] | Peterman yak ;fieldtrips and put chemistry in context roar non-science major journal of chemical Education 12 (2) 648to 754; 2008. |
| [15] | Hurd, P.P, theory in to attion. Washington, DC: ERIC / SMEAC clearing house;1964. |
| [16] | H.Ozmen; Karadeniz Technical University, Faith Faculty of education, Department of Science Education, 61335 Sogutlu, Trabzon, Turkey; Published in Journal of Computers & Education archive Volume 51 Issue1, August 2008. |
| [17] | Jonathan Bergmann and Aaron Sams, both high school science teachers at Woodland Park High School in Woodland Park, Colorado 2007. |
| [18] | Marc Seigel, a chemistry teacher at a public school in New Jersey presented at Flipped Learning Conference in Chicago 2012. |
| [19] | Elsevier Science Ltd. Oxford, UK, UK table of contents doi>10.1016/j.compedu.2008.06.002- |
| [20] | Sunmez, V, ‘Teachers handbook in program develpoment’ yargle publications Ankara 1986. |

 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML




