-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2014; 4(1): 47-50
doi:10.5923/j.chemistry.20140401.08
Synthesis and Structural Analysis of a Cu (II) Complex Incorporating Pyridoxal-S-Methylisothiosemicarbazone (PLITSC) Ligand
Violeta Jevtovic
Department of Chemistry, College of Sciences, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates
Correspondence to: Violeta Jevtovic, Department of Chemistry, College of Sciences, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Reaction between pyridoxal hydrochloride (PL.HCl) and S-methyilisothiosemicarbazidehydroiodide (SMeTSC.HI) in the presence of Na2CO3, resulted in the formation of the pyridoxal S-methylisothiosemicarbazone (PLITSC; H2L) ligand. Reaction of the ligand with CuBr2 yielded a dark-brown, pentacoordinated Cu(II) complex, [Cu(PLITSC) Br(CH3OH)] Br, having a square-pyramidal structure.
Keywords: Pyridoxal-S-methylisothiosemicarbazone, Cu(II) complex, Synthesis, Crystal structure
Cite this paper: Violeta Jevtovic, Synthesis and Structural Analysis of a Cu (II) Complex Incorporating Pyridoxal-S-Methylisothiosemicarbazone (PLITSC) Ligand, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 47-50. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20140401.08.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- A large number of complexes incorporating PLTSC (pyridoxal-thiosemicarbazone)[1] and PLSC (pyridoxal- semicarbazone)[2,3,4] ligands has been reported, including a recent review[5], while only a couple of complexes incorporating PLITSC (pyridoxal-S-methylisothiosemicarbazone) have been synthesized thus far[6]. Isothiosemicarbazide and his derivatives carbazons, including their complexes with metals, have been subjected to intensive research for a very long period resulting in a large number of scientific publications[7], including a monograph[8]. Arguably, the main reason for this affirmation is that this class of compounds is quite interesting due to their structural features as well as potential biological activity[9]. Coordination chemistry of isothiosemicarbazones is interesting, in general, due to a wide variety of possible ligand systems, their denticity and the nature of the donor atoms. Systematical investigations of the coordination properties of these ligands, with different denticity, unexpectedly showed, based on numerous complexes[10,11], that the isothiosemicarbazon fragments used the thioamide nitrogen atom for coordination instead of the sulfur atom. There are many complexes with tridentate ligands which were obtained based on this class of ligands especially employing pyridoxalS-methylisothiosemicarbazone (PLITSC) using the ONN set as donor atoms. The synthesis and physical properties of several iron-based complexes incorporating this ligand have already been reported, including [Fe(PLITSC)(PLITSC-H)](NO3)3, [Fe(PLITSC)Cl3]. H2O and [Fe(PLITSC)2] OAc.2H2O [12,13,14]. Lastly, synthetic and structural investigations involving these ligand systems were a topic of a doctoral dissertation[15].
2. Experimental
- All commercially obtained reagent-grade chemicals were used without further purification, except for the ligands.
2.1. Synthesis of Ligand PLITSC
- 2.0g (10mmol) of PL•HCl and 2.30g (10mmol) of SMeTSCPL were added to 20 cm3 of H2O and the mixture was warmed to completely dissolve the reactants. To this warm mixture 3.0 g (10 mmol) of Na2CO3.10H2O in 20 cm3 of H2O was added. Immediate sedimentation of pale-yellow fibrous crystals was observed and after a couple hours they the crystalline material was collected by filtration and washed with water and ethanol. Yield: 2.40g.
2.2. Syntheses of Complex[Cu(PLITSC)Br(CH3OH)]Br
- To a warm methanol solution (10 cm3) containing 0.14g (0.5mmol) of PLITSC was added 0.15g (0.07 mmol) CuBr2 in 5 cm3 methanol. Resulting green mixture is left at room temperature for about 50 hours, after which green monocrystals were separated. Yield: 0.13g.
2.3. Crystal Structure Determination
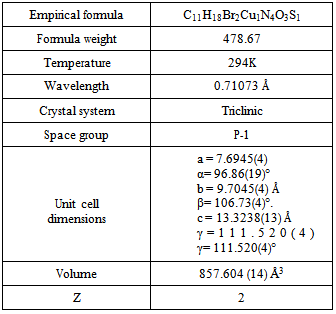
- Data for complex were collected on a Philips PW1100 diffractometer with MoKα radiation[λ= 0.7107Å]. The structure was solved using direct methods SIR92[16] and refined using SHELXL97[17] on F2 by full matrix least squares with anisotropic displacement parameters for all non-hydrogen atoms.Details concerning crystal data and refinement are given in Table 1. Crystallographic data have been deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Base as CCDC reference number 735806 for the complex.
|
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Synthesis and Structure of Complexes
- Pyridoxal-Smethylisothiosemicarbazone(PLITSC, H2L), is synthesized according to formerly described procedure[15], by reaction of a warm water mixture of PL-hydrocloride(PL.HCl), [3-hydroxi-5-(hydroxymethyl) -2-methylpyridine-4-carbaldehydehydrochloride] and S- metilisothiosemicarbazidehydroiodide (SMeTSC.H2O) in the presence Na2CO3.10H2O (Scheme 1.)
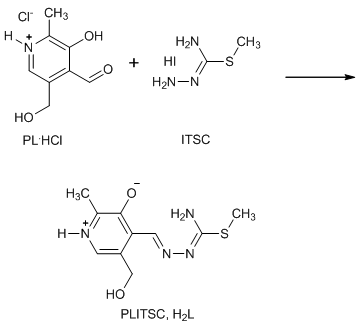 | Scheme 1. Synthesis of Pyridoxal-S-methylisothiosemicarbazone (PLITSC) |
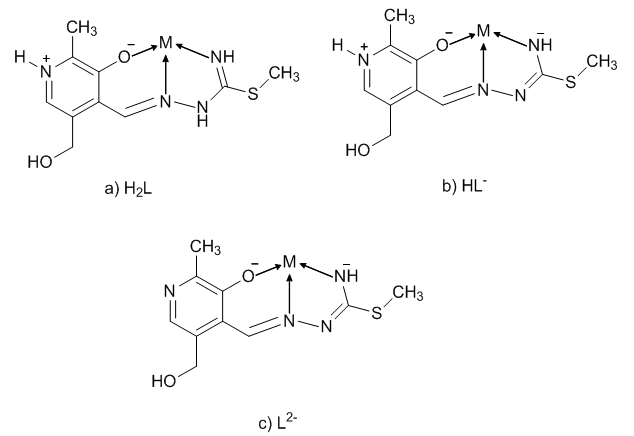 | Scheme 2. Coordination models and ligand forms: a) neutral, b) mono- and c) dianionic |
|
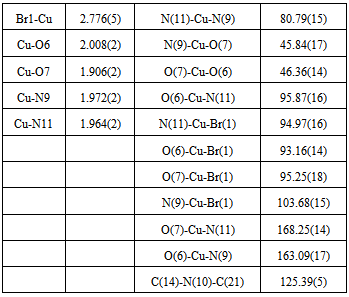
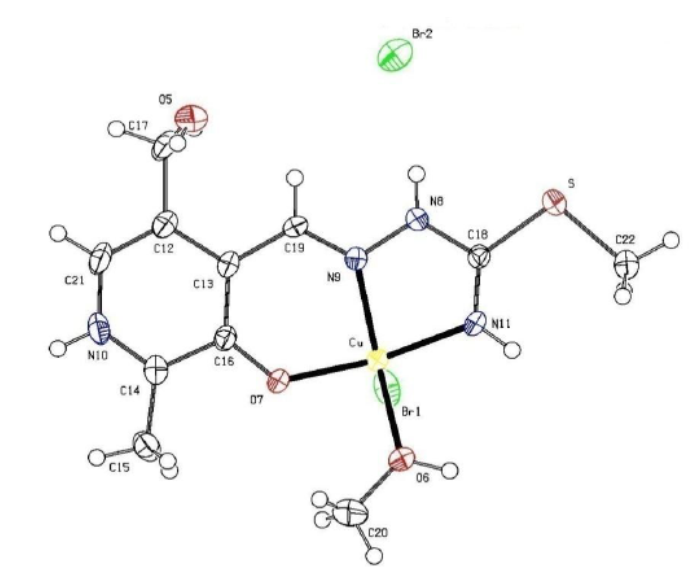 | Figure 1. The molecular structure of the complex, with the atom and ring-labeling scheme |
4. Conclusions
- The structure of the title compound C11H18Br2Cu1N4O3S1, is an interesting metal complex with a Schiff base ligand derived from isothiosemicarbazide and pyridoxal (pyridoxal is a 3-hydroxy-5hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyridine-4- carboxaldehyde).Ligand pyridoxal-S-methylisothiosemicarbazone(PLITSC; H2L) is a tridentate ONN ligand. The Cu(II) environment is best described as a square pyramid. The equatorial plane is formed by the tridentate ligand and a molecule of methanol, while the Br atom is in the apical position. This compound crystallizes in triclinic symmetry, in space group P-1, with lattice constants: a=7.6945(4)Ǻ, b=9.7045(4)Ǻ, c=13.3238(13) Ǻ, α=96.86(19), β=106.73(4), γ=111.520(4), V=857.604(14) Å3.
5. Supplementary Information
- CCDC 735806 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for the complex. Copies of this information may be obtained free of charge from The Director, CCDC, 12 Union Road, Chambridge, CB2 1EZ, UK (fax:+44-1223-336033;e-mail:deposit@ccdc.cam.ac.uk
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- The author acknowledge the Oxford Chemical Crystallography Service for the use of the instrumentation and many thanks D.J. Watkin research group for help.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML