-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2013; 3(2): 30-35
doi:10.5923/j.chemistry.20130302.02
Kinetics and Mechanism of L-Tryptophan Oxidation by Chloramine-T in Basic Medium: A Spectrofluorometric Study
K. B. Sudha Rani1, S. Ananda1, N. M. Made Gowda2
1Department of Studies in Chemistry, University of Mysore, Manasagangothri, Mysore–570 006, India
2Department of Chemistry, Western Illinois University One University Circle, Macomb, IL 61455, USA
Correspondence to: N. M. Made Gowda, Department of Chemistry, Western Illinois University One University Circle, Macomb, IL 61455, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
One of the greatest challenges in oxidation research today is the determination ofin vivo oxidative stresses. In this investigation, the spectrofluorometry is used to monitor the kinetics of chloramine-T (CAT) oxidation of L-tryptophan (Trp) in basic solutions. The Trp-CAT reaction progress has been monitored at λmax = 485 nm (after using the excitation wavelength of 360 nm) over the temperature range, 293-313 K. The redox reaction follows a first-order dependence of the rate each on [CAT] and [Trp], and an inverse fractional-order on [OH-]. Variations of the ionic strength and the solvent dielectric constant have no effect on the rate. An addition of the reduction product of CAT, p-toluenesulfonamide, to the reaction mixture also has no influence on the rate. Based on the temperature effect, activation parameters are evaluated. A mechanism consistent with the observed kinetic and activation data has been proposed and the rate-law derived.
Keywords: Oxidation, Reduction,L-Tryptophan, Chloramine-T, Spectrofluorometry, Mechanism, Rate Law
Cite this paper: K. B. Sudha Rani, S. Ananda, N. M. Made Gowda, Kinetics and Mechanism of L-Tryptophan Oxidation by Chloramine-T in Basic Medium: A Spectrofluorometric Study, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2013, pp. 30-35. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20130302.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- One of the greatest challenges in oxidation research today is the determination of oxidative stresses in vivo. Under normal circumstances there is a well-managed balance between the formation and neutralization of free radicals, so that there is minimal modification of biomolecules. Free radicals are reactive oxygen species, which have the ability, either directly or indirectly to damage all biomolecules, including proteins, lipids, DNA and carbohydrates. They are formed in the course of normal metabolism through leakage of electrons from the electron transport chain and by the oxido-reductase enzymes. Under normal physiological conditions, cellular homeostasis is incessantlyChallenged by stressors arising from both internal and external sources[1-3]. To guard against these stressors, the cell has evolved its own defense mechanisms[4]. These involve mobilization of various cellular constituents and the functional integration of specific defense components[5], including membrane associated and cytosolic soluble free radical neutralizing and scavenging enzymes[6].All biological oxidants such as superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radicals, hypochlorous acid, and chlora mines are products of PMS leukocytes and other phagocytic cells used to damage invading organisms in defense reactions of the host. In addition, they may be produced inadvertently, when stimulated in the course of inflammatory processes or other tissue damage, as PMN leukocytes react via an oxidative burst. Myeloperoxidase, which is activated and released from PMN leukocytes during stimulation, facilitates the reaction of H2O2 with Cl- to form H2O and OCl-[7].Hypochlorite can react with amines to form chloramines. Biological molecules such as aromatic amino acids, Trp and Tyr, can act as intrinsic fluorescent probes of protein conformation, dynamics and of intermolecular interactions.N-haloaromaticsulfonamides containing a polar N- halogen bond act as mild oxidants. The diverse chemical behavior of N-haloamines has been attributed in general to their ability to act as halonium cations, hypohalites and N-anions, which behave both as electrophiles and bases[8]. As a result, these compounds react with a wide range of functional groups and effect an array of molecular transformations[8]. The prominent member of this class of compounds is sodium N-chloro-p-tolunesulfonamide or chloramine-T (CAT), which has diverse chemical properties and physiological importance. Chloramine-T has been used as a model agent for endogenously produced chloramines (N-Cl derivatives), which are formed as a result of the inflammatory process from myeloperoxidase secreted by stimulated monocytes and neutrophillic polymorphonuclear leukocytes[9]. The N-Cl derivatives are a class of long-lived oxidants produced by simulated phagocytes. Other phagocytes-generated oxidants have been shown to cause genetic damage in cultured mammalian cells. CAT has been used as a surrogate for the endogenously produced chloramines[9]. Chloramine-T oxidation studies involving many substrates have been reported[10-14]. However, the literature survey reveals that only a few studies are made from the kinetics and mechanistic view point on the oxidation of chosen aromatic amino acids by CAT. When the free radicals are the source of oxidative stress, it might be more useful to assay the products of tryptophan, tyrosine, methionine, and histidine as these amino acids are more susceptible to the attack by free radicals. In this investigation, fluorescence spectroscopic technique has been used to monitor the kinetics of L-Trp oxidation by CAT in phosphate buffered basic solutions.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
- L-Tryptophan (99.9% purity) was obtained from Aldrich Chemical Co. and used as supplied. Phosphate buffer, 50 mM, pH 8, prepared from sodium phosphate monobasic and sodium phosphate dibasic salts, was used as the standard buffer system. Stock solutions of Trp were prepared in 50 mM phosphate buffer of pH 8. Concentrated aqueous solutions of CAT (Fluka Chemical Company) were prepared in amber colored bottles, iodometrically standardized, and stored as stock solutions. All other chemicals used were of analytical grade. Double distilled water was used in all preparations. A spectrofluorimeter (Systronics, S.R. No. 128) was used to measure the fluorescence.
2.2. Kinetic Procedure
- Kinetic runs were performed under pseudo first order conditions of [CAT]0 >> [L-Trp]0, Requisite amounts of solutions of L-Trp, NaOH, and the phosphate buffer were mixed in a stoppered Pyrex glass tube. The tube was thermostated in a water bath at 300 K. The reaction was initiated by adding a measured amount of pre-equilibrated, standard CAT solution. The reaction progress was monitored following changes in the fluorescence intensity at regular time intervals at the emission wavelength maximum of 485 nm after using the excitation wavelength of 360 nm using 50 mM phosphate buffer of pH 8 as a blank solution. The rate constant (k') of the reaction is calculated by plotting a graph of log of fluorescence reading vs. time.
2.3. Stiochiometry and Product Analysis
- Reaction mixtures containing different compositions of L-Trp and CAT in the presence of 0.130 M OH- were equilibrated at 300 K for 24 h. The iodometric determination of unreacted CAT in the reaction mixtures showed that one mole of L-Trp reacted with two moles of CAT. The reaction stoichiometry is represented by the equation,
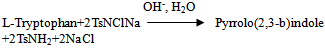 where chloramine-T is TsNClNa with Ts=p-MeC6H4SO2. The products in the reaction mixture were extracted several times with diethyl ether. The combined ether extract was evaporated and subjected to the column chromatography on silica gel (60-200 mesh) using gradient elusions. p-toluenesulfonamide (PTS or TsNH2), in the reaction mixture, was identified by its mass spectrum obtained on a 70eV Shimadzu GCMS-QP5050 spectrometer which showed a parent molecular ion (M+) peak at 171 amu. The formation of the oxidation product of L-Trp, pyrrolo(2,3-b) indole, was analyzed by its IR spectral data. The IR data showing the absence of carbonyl group band at 1700-1725 cm-1 indicated the product.
where chloramine-T is TsNClNa with Ts=p-MeC6H4SO2. The products in the reaction mixture were extracted several times with diethyl ether. The combined ether extract was evaporated and subjected to the column chromatography on silica gel (60-200 mesh) using gradient elusions. p-toluenesulfonamide (PTS or TsNH2), in the reaction mixture, was identified by its mass spectrum obtained on a 70eV Shimadzu GCMS-QP5050 spectrometer which showed a parent molecular ion (M+) peak at 171 amu. The formation of the oxidation product of L-Trp, pyrrolo(2,3-b) indole, was analyzed by its IR spectral data. The IR data showing the absence of carbonyl group band at 1700-1725 cm-1 indicated the product.3. Results
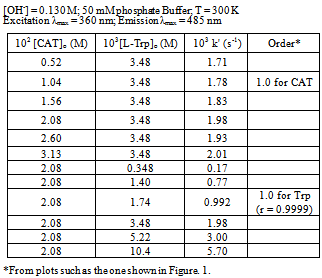
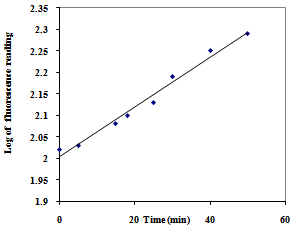
- The kinetics of oxidation of L-Trp by CAT was investigated under pseudo first-order conditions of [CAT]0 >> [L-Trp]0 at various concentrations of the reactants in basic solutions at 300 K.Effect of CAT concentration on the rate:When [CAT]0 was varied keeping all other reaction conditions constant, linear plots of log (fluorescence) vs. time with nearly the same slope suggesting constant k' values were obtained (Figure. 1). This behavior indicated a first-order dependence of the rate on [CAT]. The values of k' are presented in Table 1.
|
 | Figure 1. Representative first-order plot for the oxidation of L-Trp by CAT.[L-Trp]0 = 3.48×10-3 M, [CAT]0 = 2.08×10-2 M, [OH-] = 0.130 M, T = 300K, Excitation λmax = 360 nm, Emission λmax = 485 nm |
 | Figure 2. Effect of varying concentrations of L-Trp on the reaction rate. [CAT]0 = 2.08×10-2 M, [OH-] = 0.130 M, T = 300K |
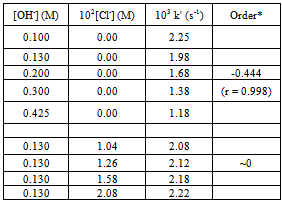
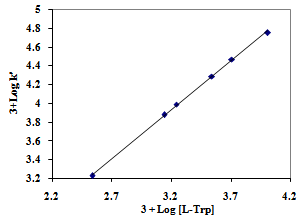
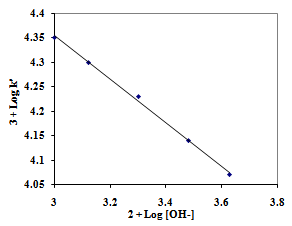 | Figure 3. Effect of OH- ion concentration on the oxidation of L-Trp.Reaction conditions are as in Table 2 |
|
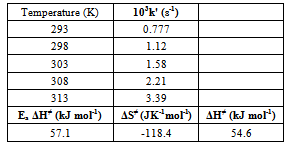
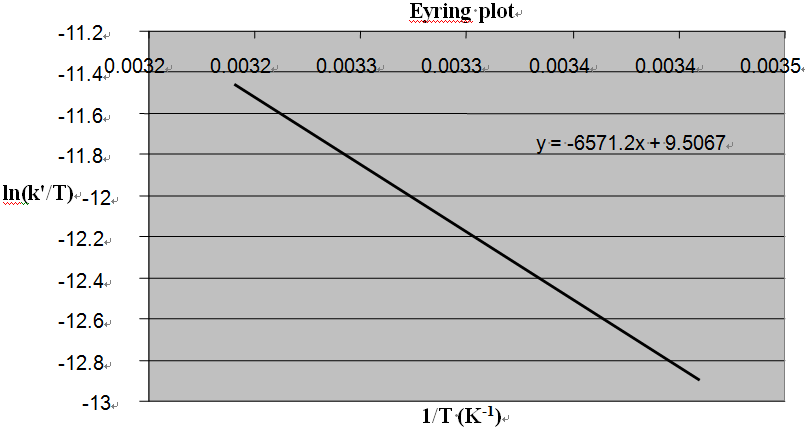 | Figure 4. Eyring plot for the oxidation of L-Trp by CAT. Reaction conditions are as in Table 3 |
4. Discussion and Mechanism
- In this study, CAT is used to mimic an oxidative stress produced in pathophysiological conditions. The oxidant enables monitoring of the oxidation of L-Trp by spectrofluorimetry. The kinetic data presented indicate that L-Trp yields visible fluorescence when treated with CAT. The data show that the reaction leads to the visible fluorescence in two steps. The step 2 is influenced by phosphate or OH- ions.
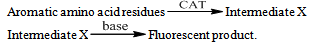 The slight increase in pH indicates low fluorescence intensity which may be caused by the reaction with OH- ions forming a non-fluoroscent compound. Furthermore, the slow increased reaction rate with increased concentration of chloride ions indicates the increased fluorescent intensity. Pryde and Soper[15], Morries et al.[16], and Bishop and Jennings[17] have shown the existence of similar equilibria in acid and alkaline solutions of N- metallo- N- hallo- arylsulphonamides. Chloramine-T behaves as a strong electrolyte in aqueous solutions, forming different species as shown in equations (1) to (6) [8].
The slight increase in pH indicates low fluorescence intensity which may be caused by the reaction with OH- ions forming a non-fluoroscent compound. Furthermore, the slow increased reaction rate with increased concentration of chloride ions indicates the increased fluorescent intensity. Pryde and Soper[15], Morries et al.[16], and Bishop and Jennings[17] have shown the existence of similar equilibria in acid and alkaline solutions of N- metallo- N- hallo- arylsulphonamides. Chloramine-T behaves as a strong electrolyte in aqueous solutions, forming different species as shown in equations (1) to (6) [8]. | (1) |
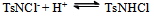 | (2) |
 | (3) |
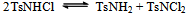 | (4) |
 | (5) |
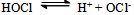 | (6) |
 | (7) |
 | (8) |
 | (9) |
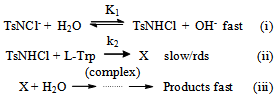 | Scheme 1. Oxidation of L-Trp by CAT |
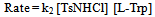 | (10) |
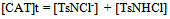 | (11) |
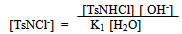 | (12) |
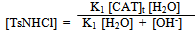 | (13) |
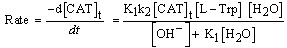 | (14) |
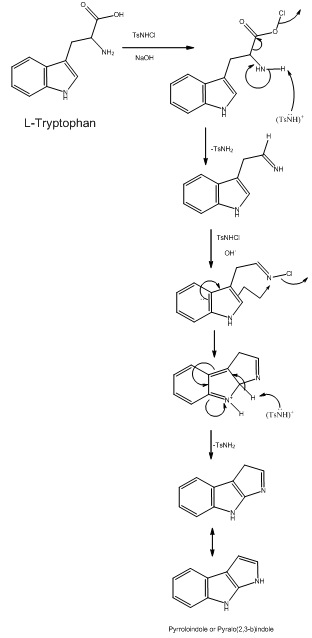 | Scheme 2. Electronic scheme for the Trp oxidation by chloramines-T in basic medium |
References
| [1] | Crapo. J. D., D. F. Tiernry, Am. J. Physiol., 226, 1401-1407, 1974 |
| [2] | Fridovich. I., Science., Washington D. C. 201, 875-880, 1978 |
| [3] | Griffiths. H. R., J. Unsworth., D. R. Blake., J. Lune Pathology and Medicine., London: Richelieu 439-454, 1988 |
| [4] | Gregory E. M., I. Fridovich., J. Bacteriol., 114, 1193-1197, 1973 |
| [5] | Davies K. J. A., A. L. Goldberg., J. B. C., 262, 8220-8226, 1987 |
| [6] | Diplock A. T., J. Am. Clin. Nutr., 53, 189-193, 1991 |
| [7] | Clark R. A., Kleoanoff. S. J., J. Clin. Invest., 64, 913-920, 1979 |
| [8] | M.M. Campbell, G. Johnson, Chem. Rev. 78 (1978) 65 |
| [9] | Weitnerg. A. B., Mutat. Res., 190, 277-280, 1987 |
| [10] | K.K. Banerji, B. Jayaram, D.S. Mahadevappa, J Sci. Ind. Res. 46 (1987) 65 |
| [11] | D.H. Bremner, Synthetic Reagents 6 (1986) 9 |
| [12] | K.S. Rangappa, M.P.Ragavendra, D.S. Mahadevappa, D.C. Gowda, J. Org. Chem. 63 (1998) 531 |
| [13] | A.C. Hegde, B.T. Gowda, Oxid. Commun. 23 (2000) 546 |
| [14] | Puttaswamy, R.V. Jagadeesh, Nirmala Vaz, A. Radhakrishna, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chemical, 229 (2005) 211 |
| [15] | Pryde. B. G., Soper. F. G., J. Chem. Soc., 1514, 1931 |
| [16] | Morris. J. C., Salazar. J. A., Wineman M. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 70, 2036, 1948 |
| [17] | Bishop. E., Jennings. V. J., Talanta., 9. 581, 1962 |
| [18] | T. Demappa., S. Ananda., Asian J. Chem., 11, 376-383, 1999 |
| [19] | Stadtman. E. R., Ann. Rev. Biochem., 62, 797-821, 1993 |
| [20] | Weck. D.de; Nielsen. H. K., Finot. P. A., J. Sci. Food. Agric., 41,179-185, 1987 |
| [21] | Nielsen. H. K., Finot. R. A., Hurrell. R. F., Br. J. Nutri., 53, 75-86, 1985b |
| [22] | Elderfield. A. J., Truscott. R. J. W., In Recent Advances in Tryptophan Research- Tryptophan and Serotonine Pathways, Allegiri Filippini-G., Costa.C. V. L., Bertazzo. A., Eds;Plenum Press; New York 1996 |
| [23] | Chidan Kumar, C. S., Chandraju, S., and Made Gowda, N. M., Manganese(III) Oxidation of Alanine in Aqueous Ethanoic Acid Medium: A Kinetic and Mechanistic Study, Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic, Metal-Organic, and Nano-Metal Chemistry, In Press |
| [24] | Cholkar, K., Kouassi, G., Ananda, S., Veeraiah, M.K., and Made Gowda, N. M., Osmium(VIII) Catalyzed Kinetics and Mechanism of Indigo Carmine Oxidation by Chloramine-B in Basic Medium, Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic, Metal-Organic, and Nano-Metal Chemistry, In Press |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML