-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2011; 1(2): 52-55
doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20110102.11
Antimycobacterial Friedelane-terpenoid from the Root Bark of Terminalia Avicennioides
Abdullahi Mann 1, 2, Kolo Ibrahim 3, Adebayo O. Oyewale 2, Joseph O. Amupitan 2, Majekodumi O Fatope 4, Joseph I. Okogun 5
1Department of Chemistry, Federal University Technology, Minna, , Niger State, P. M. B. 65, Nigeria
2Department of Chemistry, Ahmadu Bello University Zaria, Kaduna State, Nigeria
3Department of Microbiology and Biotechnology, National Institute for Pharmaceutical Research and Development (NIPRD), Garki ,Abuja, P.M.B.21, Nigeria
4Department of Chemistry, College of Science, Sultan Qaboos University, Al-Khod, Muscat, P. O. Box 36, Postal Code 123,Oman
5Department of Medicinal Plant Research and Traditional Medicine, National Institute for Pharmaceutical Research and Development (NIPRD), Garki , Abuja, P.M.B. 21, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Abdullahi Mann , Department of Chemistry, Federal University Technology, Minna, , Niger State, P. M. B. 65, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
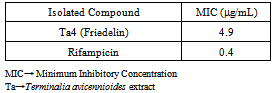
Terminalia avicennioides is used to treat tuberculosis in the folk medicine of the Nupes of North Central Nigeria. Activity guided fractionation of the extract resulted in the isolation of triterpenoid friedelin. The structure of the isolated compound was elucidated with the aid of spectral comparison of IR, UV, one and two dimensional NMR experiments values. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time friedelin is reported from this plant. The in vitro antimycobacterial activity of the isolated compound (friedelin) was performed against Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG) with MIC value at 4.9 μg/mL.
Keywords: Antimycobacterial Activity, Friedelin, Terminalia Avicennioides, Tuberculosis
Cite this paper: Abdullahi Mann , Kolo Ibrahim , Adebayo O. Oyewale , Joseph O. Amupitan , Majekodumi O Fatope , Joseph I. Okogun , "Antimycobacterial Friedelane-terpenoid from the Root Bark of Terminalia Avicennioides", American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 1 No. 2, 2011, pp. 52-55. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20110102.11.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Terminalia avicennioides Guill & Perr (Combretaceae) is found in the savanna region in West Africa[1]. It is a tree known as ‘kpace’ in Nupe, ‘kpayi’ in Gwari, and ‘baushe’ in Hausa[2]. Several medicinal uses have been attributed to this plant[3-7], but the treatment of bloody sputum and cough in humans by the Nupes of North Central Nigeria[8] using the roots, attracted us to investigate T. avicennioides for antimycobacterial activity. Previously, several bioactive hydrolysable tannin compounds including ellagic acid, punicalagin, flavogallonic acid and terchebulin[9] have been isolated from this plant, and none of them have been shown to have antimycobacterial activity at low concentrations. Compounds with antimycobacterial activities have been isolated from plants, marine organisms, and fungi[10]. An extensive array of triterpenes has been reported to exhibit antimycobacterial activity[11]. The oleane series of triterpenoids exhibit significant antimycobacterial activity. Therefore, the present objective is to isolate the antimyco bacterial active compounds from root bark of T. avicennioides.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
- The root bark of Terminalia avicennioides (Nupe: Kpace) were obtained from their natural habitats in a forest near Emitete, Lavun Local Government, Niger State, Nigeria in August, 2008. This plant was identified and authenticated by Mallam Ibrahim Muazzami of the Department of Medicinal Plant Research and Traditional Medicine of National Institute for Pharmaceutical Research and Development (NIPRD) where a voucher specimen (NIPRDH 5735) was deposited at the herbarium unit of this same institution.
2.2. Extraction
- Air-dried ground root bark of Terminalia avicennioides (710 g) was macerated twice each successively with petroleum ether (PE), ethyl acetate (EtOAc), chloroform (CHCl3) and methanol (MeOH) (2 x 2.5 L each) at room temperature for 72 h and concentrated under reduced pressure at 35 oC using rotavapor. The extracts were stored in vials or wrapped with aluminum foil and kept in the fridge.
2.3. Fractionation and Isolation
- Petroleum ether (PE) soluble extract was purified by chromatography on silica gel column (Φ2.0 x 40 cm) eluted successively with gradient mixtures of PE-EtOAc) (9:1), (4:1), (3:2), (1:1), (2:3), (1:4), (1:9); (EtOAc). The eluents were analyzed by tlc, and similar fractions were combined after TLC analysis. The petroleum ether (PE) extract subjected to successively elution with gradient mixtures gave nine fractions namingly: TaF1 (F1-9), TaF10 (F10-16), TaF17 (F17-19), TaF20 (F20-30), TaF31 (F31-46), TaF47 (F47-77), TaF79 (F79-96), TaF97 (F97-110) and TaF111 (F111-126). These fractions were combined based on their TLC behaviour. Further purification of the fraction TaF10 (F10-16) by repeated PTLC (0.25 mm) eluted with EtOAc/MeOH/AcOH (9: 1: one drop) afforded subfractions: Ta1 (3.8 mg, Rf: 0.95), Ta3 (3.8 mg, Rf: 0.85), Ta4 (20.1 mg, Rf: 0.41), Ta5 (3.2 mg, Rf: 0.33), Ta6 (3.2 mg, Rf: 0.21), Ta12 (3.8 mg, Rf: 0.14). Subfraction Ta4 (PE-EtOAc 4: 1 eluate) gave fine white needles upon recrystallization from MeOH, (20 mg) with MP 262-263 oC;[α]D25 +2.0o (c.1.0, MeOH) and TLC Rf value of 0.36 (EtOAc–MeOH–AcOH, 9:1: one drop).
2.4. Determination of Antimycobacterial Activity
- The susceptibility test was conducted using modified Broth Microdilution Method (BMM) in 96 well microtitre plates[12]. To Wells No 2-12 of the 96-well microtitre plate was added fifty microlitres (50 µL) of media solution which was added in triplicate to the top of the microtitre plate. Extracts were first dissolved in DMSO and then diluted in Middlebrook 7H9 broth, to give a starting concentration of 5000 μg/mL which was diluted across the 96-well microlitre plate in a two-fold serial dilution to give final testing concentrations of 2500, 1250, 625, 312,156, 78, 39, 19.5, 9.8 and 4.9 μg/mL. 50 μL of extract was then pipetted into Wells No 1 & 2. The content of Well 2 was then mixed thoroughly and 50 μL was transferred to Well 3, the dilution process was repeated through out the plate and the final 50 μL from Well 12 was then discarded. The same procedure was repeated for the control (Rifampicin) with the initial concentration of 32 μg/mL with the subsequent dilution to the final testing concentrations of 1, 0.5, 0.25, 0.125, 0.06, 0.03 μg/mL. Appropriate DMSO, growth and sterile controls were carried out with rifampicin as positive control. Rifampicin control and negative control sets were triplicated for all the sets on each plate. The inoculated culture medium was incubated at 37 oC for 30 mins shaking it at 130 rpm and using the multichannel pipette and multistepper pipetter the adding, transferring and mixing of the inoculum were performed on the wells of the plates. All plates were incubated initially at 37 oC for 14 days in an environment with 90% relative humidity. The plates were re-incubated at 37 oC for further 2 weeks. After this incubation, any well before those that turned cloudy were recorded as the highest dilution of test compound that prevented bacterial growth (MIC). The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was defined as the lowest extract concentration at which no mycobacterial growth was observed. The MIC was also determined for DMSO as a control measure.
3. Results and Discussion
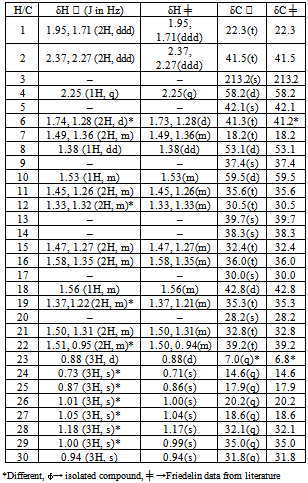
- Previous investigations of the crude extract of the T. avicennioides root bark exhibited broad growth inhibition against microbes causing infectious diseases[13-15] and in particularly it was found to significantly inhibit activity of M. tuberculosis and BCG at 78 and 200 μg/ml respectively[16, 17]. Consequent upon further extraction and fractionation, the root bark of T. avicennioides on concentration in vacuo yields petroleum ether (0.30, oily); ethyl acetate (8.56, yellowish solid); chloroform (7.56, whitish yellow solid); and methanol (15.36, brownish solid) % (w/w) respectively. The antimicrobial activities results[13-17] were considered as basis for the selection of the PE extract for silica gel column chromatographic purification in order to exploit the individual bioactive constituents responsible for the exhibited activities. The constituents of petroleum ether fraction of the plant may be responsible for the associated activity. Pentacyclic triterpenes have been isolated from related species of Terminalia[18-21]. The comparison of the NMR spectral features of the existing literature[22, 23] suggests that the isolated compound is a pentacyclic triterpene (Table 1). Therefore, the structure of the isolated compound (Figure 1) was assigned based on the chemical shifts obtained from 1D (1H and 13C NMR) and 2D (HMQC, HMBC, COSY and NOESY) NMR spectral data (Table 1) which revealed the presence of 30 carbons and suggestive of a triterpenoid typical of friedelane skeleton[18, 22, 23] and were consistent with reported values of friedelin[18, 23-26] as shown in Table 1. Therefore, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of the presence of friedelin in T. avicennioides.The isolated compound (Ta4) was investigated for antimycobacterial activity against BCG as summarized in Table 2. The isolated compound (Ta4) exhibited most significant activity (MIC 4.9 μg/mL), when compared to the positive control, rifampicin (MIC 0.4 μg/mL). From the phytochemical analysis, Ta4 is a terpenoidal derivative, suggesting that this group of terpenoidal moiety might be important for the observed activity. Triterpenoids such as imberbic acid had earlier been shown to possess potent bactericidal activity against Mycobacterium fortuitum and S. aureus[20]. The isolated compound (friedelin) had earlier been reported to exhibit antifeedant and anti-inflammatory activities[27] without cytotoxicity. Friedelin had also been found to show significant hepatoprotective activity[28]. The related compounds such as lupeol, betulin, ursolic acid and oleanolic acid have been found to be antimycobacterial[29]. Some extracts containing friedelin inhibit bacterial growth including antimycobacterial activity[30]. The isolated compound (friedelin) investigated for antimycobacterial activity against BCG revealed significant activity against BCG at 4.9 μg/mL. From the results obtained so far, there appears to be a rationale for the use of T. avicennioides to treat bloody sputum and cough in humans, as certain extracts of T. avicennioides had an inhibitory effect on some selected pathogenic bacteria causing tuberculosis and other respiratory diseases. The present study demonstrates that Nigerian medicinal plants could be good sources of compounds with antimycobacterial activities. Further investigation involving mice model and in vivo anti-TB studies and detailed toxicity studies are required.
|
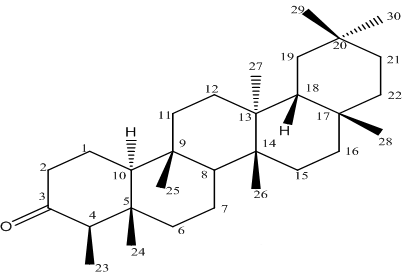 | Figure 1. Structure of friedelin isolated from the root bark of Terminalia avicennioides |
|
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- AM thanks Federal Polytechnic, Bida which enabled 3 months’ study leave at the SQU, Department of Chemistry. We will also like to thank Drs Hiroko Murata and Yuka Inatomi, both of Setsunsu University, Faculty of Pharmacetical Sciences, Osaka-Japan for the performance of some NMR experiments as well as Mr Mahmud Al-azwani, Department of Chemistry; and Drs Tabisam Khan and Ahlam Al-Azkawi of Central Analytical & Applied Research Faculty (CAARF), all of College of Science, Sultan Qaboos University, Muscat for the NMR and MS spectral analyses respectively. The assistance of the Department of Chemistry, of , , , Sultanate of Oman for providing bench space for this work is highly appreciated.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML