-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Cell Biology
2012; 1(1): 1-7
doi: 10.5923/j.cellbiology.20120101.01
Chronicles of a Silent Death: Apoptosis
1Istituto di Genetica Molecolare, CNR, Pavia, 207, I-27100, Italy
2Centro de Biología Celular y Molecular, UTPL, Loja, 11–01–608, Ecuador
Correspondence to: Luis Miguel Guamán Ortiz , Istituto di Genetica Molecolare, CNR, Pavia, 207, I-27100, Italy.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In whole human body thousands and thousands of cells are produced by mitosis every second and a similar number dies at the same time through a genetically controlled pathway of cellular self-destruction: apoptosis. The homeostatic balance between proliferation and cell death occur in a finely regulated manner during embryonic development and throughout life. However, this balance is often altered by both internal and/or external agents such as inherited mutations or chemotherapy, respectively; acting like mutagens and providing an unlimited proliferation level where affected cells evade apoptosis and lead cancer. Currently, chemotherapy is the most used strategy for preventing and fight against cancer; nevertheless, it is not specific and it could produce serious side effects including the generation of a second tumor. Activation or reactivation of apoptosis in cancer cells using specific and natural drugs discovered is one of the key alternatives to combat this disease, which occurs in a silent manner and without adverse effects. This review presents the main dramatic features that occur during apoptosis activation and the main proteins, which trigger and inhibits this death pathway.
Keywords: Apoptosis, Cancer, Caspases, Cell Death, Chemotherapy
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In the mid XIX century it was discovered that cell death plays an important physiological function in multicellular organisms. Studies at this time revealed that during the embryonic development of insects, cells do not die accidentally, but through a set of genetically controlled biochemical reactions, thereby introducing the concept: "Programmed Cell Death" (PCD). Thereafter, investigations in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans allowed to determine that 12% of cells die during embryonic development. Subsequently, during an experiment with neoplastic liver cells, Kerr et al, in 1972 found that many cells of their cultures "disappeared". Then, cinematic images using an electron microscopy showed that cells die by dividing into small vesicles where several DNA fractions and degraded organelles were found. All this evidence allowed the discovery by Kerr and co-workers of a new model of cell death: Apoptosis[1-4].The apoptosis term is derived from the Greek words "apo" and "ptosis", which mean: "Falling of the leaves in autumn", and is closely related to the process where damaged cells are separated from healthy tissue to die discreetly and avoid side effects such as inflammation[5-8]. Moreover, apoptosis is defined as a beneficial "cell suicide" for whole body, which is activated in embryonic cell development, tissue homeostasis and to eliminate unwanted cells[7,9].Apoptosis pathway has been classified into four dramatic stages: The beginning, where the stimuli and death signals trigger their effects on damage cells. The decision, where both apoptosis and repair machinery are activated and depending on the severity of damage, cells can still decide whether to die or not. The execution, where all proteolytic mechanisms are activated. Therefore, cell death is unavoidable. Finally, The Clearance, where apoptotic bodies from dead cells are phagocytized by macrophages or adjacent cells[10]. During these four stages, cells undergo several morphological changes such as shrinkage of the nucleus, chromatin condensation and also changes in the surface of the cell membrane[11].
1.1. The Beginning of the End
- Several pro-apoptotic agents in both physiological and pathological conditions that stimulate cell death receptors or promote DNA damage can trigger apoptosis. Physiologically, during embryonic development, apoptosis is activated to remodel the different structures of the body, freeing up spaces or making roads for new tissue[10,12,13]. Thus, apoptosis eliminates membranes between the fingers of our hands, embryonic tails, useless neuronal connections, etc. [5]. Pathologically, apoptosis is activated to kill other cells, which proceed by overproliferation, typical of certain types of hyperplasia and wound healing processes[10,11,14]. Biological agents such as bacteria e.g. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus[15,16], virus e.g. HIV[17,18] or parasites e.g. Plasmodium[19-21] and physical agents such as radiation and chemicals[22], disturb the normal cell metabolism leading to death. Hereditary or internal agents like cellular stress e.g. ROS[23] also contribute to the pathology of the cell due to mutations at the genome level. The effect of both external and internal agents may cause different pathologies in which include: AIDS[17,18], ischemic heart, pulmonary and kidney diseases[24,25], proteinuric kidney diseases[26], neurodegenerative diseases[27,28] and even cancer. Therefore, affected cells activate the apoptosis pathway to "commit suicide" in order to protect healthy tissue[9,13].
1.2. A Decision between Life and Death
- After initiation, cells activate several repair machinery and pro-apoptotic proteins in order to decide whether to live or die. A well-known example is p53, the "angel" guardian of the human genome[29,30]. This transcription factor is the major tumor suppressor protein[31], and is named according to its molecular weight, i.e., 53 kDa[8]. It is involved mainly in the degeneration of cerebral cortical neurons in several cell types of animal models and in some human neurological disorders[27,28]. p53 is activated in response to DNA damage and several stress signals to initiates cell cycle arrest, senescence or apoptosis[31] through expression and overexpression of pro-apoptotic proteins such as CIP (CDK Inhibitor Proteins), a family of proteins that inhibit CDKs (Cyclin-Dependent Kinases) including p21, which arrest the cell cycle at G1 phase to inhibit the cell growth, to repair the damage or lead to death[9,30-35]. One of the proteins belonging to the repair machinery is PARP-1 or Poly (ADP- ribose) polymerase-1, a 113 kDa nuclear “multi-talented” protein, which detects single or double strand breaks in DNA and promotes their repair[36,37]. If the damage is irreparable or too late, cells inevitably enter apoptosis[38], while if the repair machinery does not work, then PCD can activate two pathways in which it triggers a series of biochemical reactions.
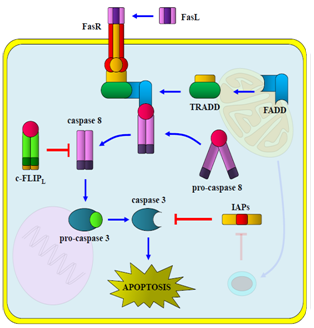 | Figure 1. The extrinsic pathway: apoptosis is triggered through death receptors, caspase 8, caspase 3 and other pro-apoptotic proteins |
1.2.1. The extrinsic pathway
- Cytotoxic T cells and Natural Killer (NK) are responsible for trigger apoptosis extrinsically in "sick" cells as a result of bacterial[15,16], viral[17,18] or parasite[20,21] infections. These immune system cells produce cytotoxic factors as pro-apoptotic ligands expressed on the cellular membrane surface or released into the extracellular space. These ligands: FasL (Fas ligand), TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α) and TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand), bind to death receptors expressed on the surface of damage cells[39,40]. FasL (CD95L), a homotrimeric integral membrane protein, binds to its receptor FasR (CD95, APO-1). FasR is an integral membrane protein and it is a monomer in its inactive form. Cytosolic death domains present in each FasR monomer become to trimerize by FasL action (Fig. 1), followed by the recruitment of TRADD (TNF-R1 death Associated domain), a cytosolic protein, which subsequently recruits FADD (Fas death domain activating), an adapter protein responsible of dimerization and activation of caspase 8[3].
1.2.2. The intrinsic pathway
- Also known as the mitochondrial pathway. It is mainly controlled by three groups of factors belonging to the Bcl-2 family proteins (B-cell lymphoma 2). Four domains homologous to Bcl-2 in their structure characterizes to the first subfamily: BH1, BH2, BH3 and BH4, and the main members are Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, Bcl-B, Bcl-W, Bfl-1 and Mcl-1, which possess an anti-apoptotic effect. The second subfamily has one of three domains, but lacks the BH4 domain. It is composed by Bax, Bak and Bok members, which possess a pro-apoptotic effect. The third subfamily have only the BH3 domain and it is composed by Bid, Bad, Bim, Bmf, Puma and Noxa members, also with a pro-apoptotic effect[12, 22, 39, 41].
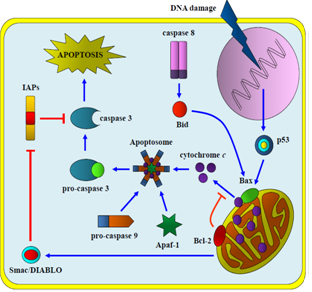 | Figure 2. The intrinsic pathway: apoptosis is triggered through DNA damage (radiation, chemotherapy, cellular stress), which activates apoptosome complex followed by caspase 3 activation |
1.3. The Execution: No Turning Back
- Both the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways result in the activation of caspase 3 (Fig. 1 and 2), which promotes several morphological changes in the apoptotic process (Fig. 3) where cells cannot escape from death. At this stage, caspase 3 and other proteolytic enzymes trigger a series of degradative events on the main proteins that maintain the integrity and functionality of the cells[3].
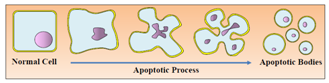 | Figure 3. Apoptotic process with several morphological changes |
1.3.1. Caspases
- Caspases, or cysteine-aspartic proteases, are a family of fourteen proteins that play an essential role in apoptosis. They are synthesized in the cytoplasm as pro-caspases or zymogens and they are activated only in response to apoptotic stimuli[4,11]. All caspases are characterized by a terminal cysteine residue that mediates the breakdown of other proteins at the level of aspartic acid[9,33].This family, analogous to the four main proteins: CED (Cell Death Abnormal)-3, CED-4, CED-9 and EGL-1 (egg-laying defective-1) in C. elegans[2], includes both effector and inducer caspases[44]. Inducer or initiator caspases: 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 and 13, after dimerization, process the inactive forms of effector caspases for their activation by cleavage or proteolysis, e.g. caspase 8 activates caspase 3 (Fig. 1). Effector caspases: 3, 6, 7 and 14, process and degrade all essential proteins inside cells such as: actin, tubulin, laminin, etc.; e.g. PARP-1 is inactivated through cleavage by caspase 3 or 7 into two fragments of 89 and 24 kDa[11,36].Approximately 400 substrates of caspases have been identified to date, but not all members of cysteine-aspartic proteases family are involved in apoptosis. It is known that caspases 1, 4, 5 and 12 also participate in inflammatory processes[45,46]. Furthermore, effector caspases are not the only proteins involved in dismantling cell; HtrA2/Omi (High Temperature Requirement protein A), Cathepsins and Calpaines are proteases, which also play an important role in the apoptotic process[11].
1.3.2. Dismantling Cell
- The cytoskeleton is composed of microtubules, actin microfilaments and others proteins, which together give shape and rigidity to the cell. During apoptosis, those proteins become substrates for caspases, mainly caspase 3, which destroy all the cytoskeleton through proteolysis. Caspases recognize as substrates the intermediate filaments that form the lamina and nuclear envelope, which becomes degraded. DNA is cleaved by several types of DNases including: Ca2+/Mg2+- dependent endonucleases, Mg2+/dependent DNAses, DFF (DNA fragmentation factor), CADs (Caspase-activated DNAses) and L-DNase II (acid, cation-independent DNase II) [47], which cut at the nucleosomes level, and it is fragmented in numerous fragments of approximately 200 bp. The DNA cleavage prevents unleashes antigenic responses of chromatin in the extracellular space and facilitates phagocytosis. Likewise, DNA transcription factors and protein translation factors are also cleaved by caspases to inhibit cell proliferation[45].Membrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) also are caspase substrates, being degraded and disabling their functions in protein synthesis. ER stress can trigger apoptosis due to dysfunction in Ca2+ channels induced by Bcl-2 family, increasing its permeability[48], realizing Ca2+ and promoting calpain proteins activation, which inducing caspases activation[11,24,49]. In addition, caspase 12 is activated during ER stress, which sequentially activates caspase 7 and/or 3 leading mitochondria-independent apoptosis[50]. During apoptosis, secretory protein traffic is blocked and the Golgi complex undergoes disassembly; therefore, individual cisternae are further disassembled into clusters of vesicles and tubules dispersed throughout the cell. A growing number of proteins implicated in Golgi structure and membrane trafficking are cleaved by caspases (2, 3 and 7) during apoptosis, including golgin-160, GRASP65, giantin, and GM130, as well as the vesicle transport protein p115, the t-SNARE, syntaxin-5, the intermediate chain of dynein, and the p150 Glued subunit of dynactin[51, 52]. Mitochondria, through the effect of Bax and Bid, as well as in ER and Golgi complex injury[50-52], increase their permeability to release pro-apoptotic components as cytochrome c, that help the activation of caspases. Accordingly, this permeability also allows the entry of water and other solutes that increase the volume of mitochondria making them more fragile and susceptible to degradation[45,53].
1.3.3. Apoptotic bodies
- The demolition phase of the cell is characterized by the formation of vesicles or blebs from apoptotic cells. Both the condensed chromatin and degraded organelles are coated into a ballooning, which is extirpated from plasmatic membrane and cytoplasmic vesicular structures known as apoptotic bodies are formed (Fig. 3). The membranes of these apoptotic bodies still remain intact, preventing intracellular components to be dispersed in the extracellular compartment[45].
1.4. The Clearance: without a Trace
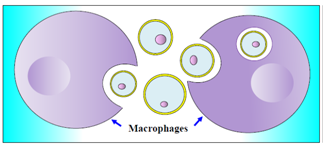 | Figure 4. Phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies |
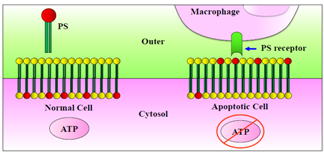 | Figure 5. Cytoplasmic membrane instability by ATP depletion and PS recognition by macrophages |
2. Apoptosis Deregulations: CANCER
- Apoptosis is often inactivated due to different agents that prevent cell death, promoting different types of diseases such as cancer[39,57,58]. According to the World Health Organization (2012), cancer is the leading cause of mortality worldwide. Cancer is characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal cells that end in the formation of a tumor. It is caused by external (tobacco, chemical, radiation, and microorganisms) and/or internal (inherited mutations, hormones, immunosuppressive conditions and metabolic disorders) agents, which can work together or individually to induce carcinogenesis. These agents produce mutations in the genome, altering several factors responsible for regulating the cell cycle in which p53 highlights. During tumor development, cancer cells can acquire many features such as: sustained proliferative signalling (active oncogenes), evasion of growth suppressors (inactive tumor suppressor proteins), invasion and metastasis in healthy tissues, replicative immortality, angiogenesis induction, and resistance to cell death by chemotherapeutic agents[59,60].
2.1. Alterations of the Extrinsic Pathway
- When mutations occur at death receptors level (e.g. FasR), cells lose susceptibility to the pro-apoptotic ligands created by T and NK cells. Therefore, affected cells cannot be recognized, thus the activation of apoptosis is blocked: hence, the cell can enter senescence or proliferate indefinitely[42]. Inactivation of this pathway may be also caused by Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP), an anti-apoptotic cytosolic protein. Two isoforms of c-FLIP are commonly detected in human cells: a long form c-FLIPL (55 kDa) and a short form c-FLIPS (26 kDa). Both isoforms can be recruited by FADD as the same way that pro-caspase 8. c-FLIPL is overexpressed in a number of different cancers and its overexpression is related to TRAIL resistance; thus, this protein competes with pro-caspase 8 for FADD affinity, inhibiting this death pathway by blocking the activation of caspase 8 and subsequent activation of caspase 3 (and BH3 subfamily) [61-63].On the other hand, IAPs (Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins), a group of anti-apoptotic proteins, can also directly inactivate both caspase 3 and caspase 7, and even inhibit the function of other caspases. IAP activity is regulated by Smac/DIABLO (Second mitochondria derived activator of caspase/direct IAP binding protein with low PI), a pro-apoptotic protein released from mitochondria together with cytochrome c (Fig. 2); when this protein is also mutated apoptosis can be inhibited[22,64,65]. Indeed, abnormal expression of the IAP family has been found in pancreatic cancer cells and is also demonstrated as responsible for resistance to chemotherapy[8].
2.2. Alterations of the Intrinsic Pathway
- In this pathway the main victim is p53, which is mutated in approximately 50% of the different types of cancers[8,32,33,39]. In response to DNA damage, overexpression of mutated form of p53 is useless, since it is not suitable to drive expression of genes that regulate both apoptosis and cell cycle. Therefore, these cells evade apoptosis and increase the rate of tumor development[9,66,67]. Mutations in the Bcl-2 family also highlight cancer. These proteins have been located in the mitochondria, ER and nuclear envelope[48] and their overexpression is associated with the loss of control of cell proliferation and even resistance to certain types of chemotherapy drugs[12,22]. A high level of these anti-apoptotic proteins blocks the pro-apoptotic activity of BH3 subfamily and Bax, inhibiting the release of cytochrome c[41,68].
3. Antineoplastic and Chemotherapy Alternatives
- Tobacco, diet and harmful alcohol consumption are the main factors promoting cancer worldwide according to WHO. The most common treatment is chemotherapy, based on intravenous administration of antineoplastic drugs that produce cytotoxic effects on cancer cells[69]. However, chemotherapy is not specific and can also affect normal cells or tissues, causing injuries and severe adverse effects on patients. In addition, chemotherapy and dosage are limited, as each patient reacts in a different manner, and after treatment it may cause resistance and generate secondary tumors[70,71]. Based on these considerations, it is necessary to find new compounds capable to activate the apoptotic death pathway.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- I want to thank Dr. A. Ivana Scovassi for reviewing the English version and and Dr. Natalia Bailon for reviewing the original first Spanish version. I acknowledge SENESCYT (Quito, Ecuador) and Centro de Biología Celular y Molecular, UTPL (Loja, Ecuador), for supporting my stage at the Instituto di Genetica Molecolare, CNR, Pavia, Italy, within the frame of the Scuola di Dottorato in Scienze della Vita: Genetica, Biologia Molecolare e Cellulare, Università degli studi di Pavia.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML