| [1] | Abdolali, A., Hasanzade, H., & Salary, M. M. (2014). The antenna analysis of insect antennae. World Journal of Modeling and Simulation, 9(3), 235-240. |
| [2] | Abdulrahman, H. M., Amoo, A. L., & Muhammad, B. U. (2019). Design and Construction of Electronic Pest Repellent for use in Homes and Farmland. Iconic Research and Engineering Journals, 3(1), 400-407. |
| [3] | Albert, J. T., & Kozlov, A. S. (2016). Comparative Aspects of Hearing in Vertebrates and Insects with Antennal Ears. Current Biology, 26(20), R1050-R1061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2016.09.017. |
| [4] | Andrade, C. F., & Bueno, V. S. (2001). Evaluation of electronic mosquito-repelling devices using Aedes albopictus (Skuse) (Diptera: Culicidae). Neotropical Entomology, 30(3), 497-499. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1519-566x2001000300030. |
| [5] | Arthur, B. J., Emr, K. S., Wyttenbach, R. A., & Hoy, R. R. (2014). Mosquito (Aedes aegypti) flight tones: Frequency, harmonicity, spherical spreading, and phase relationships. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 135(2), 933-941. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.4861233. |
| [6] | Au, W. W., Carder, D. A., Penner, R. H., & Scronce, B. L. (1985). Demonstration of adaptation in beluga whale echolocation signals. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 77(2), 726-730. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.392341. |
| [7] | Barnard, D. R. (2005). Biological assay methods for mosquito repellents. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association, 21(sp1), 12-16. https://doi.org/10.2987/8756-971x(2005)21[12:bamfmr]2.0.co;2. |
| [8] | Barnard, D., Bernier, U., Xue, R., & Debboun, M. (2006). Standard methods for testing mosquito repellents. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association, 21(14), 12-6. https://doi.org/10.2987/8756-971X (2005)21(12: BAMFMR) 2.0.CO; 2. |
| [9] | Barredo, E., & DeGennaro, M. (2020). Not just from blood: Mosquito nutrient acquisition from nectar sources. Trends in Parasitology, 36(5), 473-484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2020.02.003. |
| [10] | Baughman, T., Peterson, C., Ortega, C., Preston, S. R., Paton, C., Williams, J., Guy, A., Omodei, G., Johnson, B., Williams, H., O’Neill, S. L., Ritchie, S. A., Dobson, S. L., & Madan, D. (2017). A highly stable blood meal alternative for rearing aedes and anopheles mosquitoes. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 11(12), e0006142. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0006142. |
| [11] | Bee, M., Reichert, M., & Tumulty, J. (2016). Assessment and recognition of rivals in Anuran contests. Advances in the Study of Behavior, 48, 161-249. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.asb.2016.01.001. |
| [12] | Bhatt, S., & Gething, P. (2014). Insecticide-treated nets (ITNs) in Africa 2000-2016: Coverage, system efficiency and future needs for achieving international targets. Malaria Journal, 13(S1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-13-s1-o29. |
| [13] | Bimbilé, S. N.S., Poda, B. S., Sawadogo, P. S., Gnankiné, O., Maiga, H., Fournet, F., Lees, R. S., Bouyer, J., Gilles, J., Sanon, A., 27, A., & Dabiré, K. R. (2018). Ecology of reproduction of Anopheles arabiensis in an urban area of Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso (West Africa): Monthly swarming and mating frequency and their relation to environmental factors. PLoS ONE, 13(11), 1-11. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0205966. |
| [14] | Bousema, T., & Drakeley, C. (2011). Epidemiology and infectivity of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax gametocytes in relation to malaria control and elimination. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 24(2), 377-410. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.00051-10. |
| [15] | Branstetter, B. K., DeLong, C. M., Dziedzic, B., Black, A., & Bakhtiari, K. (2016). Recognition of frequency modulated whistle-like sounds by a bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) and humans with transformations in amplitude, duration and frequency. PLOS ONE, 11(2), e0147512. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0147512. |
| [16] | Buescher, M. D., Rutledge, L. C., Wirtz, R. A., & Nelson, J. H. (1983). The dose-persistence relationship of DEET against Aedes aegypti. Mosquito News, 43, 364-366. https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201302195337. |
| [17] | Cator, L. J., Ng'Habi, K. R., Hoy, R. R., & Harrington, L. C. (2010). Sizing up a mate: Variation in production and response to acoustic signals in Anopheles gambiae. Behavioral Ecology, 21(5), 1033-1039. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/arq087. |
| [18] | Center for the Advancement of Health (CAH). (2007). Electronic mosquito repellents don't work, say researchers. Science Daily. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2007/04/070417194230.htm. |
| [19] | Childs, L. M., Cai, F. Y., Kakani, E. G., Mitchell, S. N., Paton, D., Gabrieli, P., Buckee, C. O., & Catteruccia, F. (2016). Disrupting mosquito reproduction and parasite development for malaria control. PLOS Pathogens, 12(12), e1006060. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006060. |
| [20] | Choumet, V., Attout, T., Chartier, L., Khun, H., Sautereau, J., Robbe-Vincent, A., Brey, P., Huerre, M., & Bain, O. (2012). Visualizing non infectious and infectious Anopheles gambiae blood feedings in naive and saliva-immunized mice. PLoS ONE, 7(12), e50464. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050464. |
| [21] | Clements, A. N. (1992). The biology of mosquitoes: Development, nutrition and reproduction. Chapman & Hall, London, UK. |
| [22] | Combemale, P., Deruaz, D., Villanova, D., & Guilaumont, P. (1992). Les insectifuges ou les répellents. Annals of Dermatology, 119, 411-434. |
| [23] | Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada (COSEWIC). (2014, April 8). Beluga whale (Delphinapterus leucas) COSEWIC assessment and status report (CW69-14/ISBN 798-1-100-23284-3). St. Lawrence Estuary population in Canada. http://985.so/btpnu. |
| [24] | Cranford, T. W., Elsberry, W. R., Van Bonn, W. G., Jeffress, J. A., Chaplin, M. S., Blackwood, D. J., Carder, D. A., Kamolnick, T., Todd, M. A., & Ridgway, S. H. (2011). Observation and analysis of sonar signal generation in the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus): Evidence for two sonar sources. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 407(1), 81-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2011.07.010. |
| [25] | Dahalan, F. A., Churcher, T. S., Windbichler, N., & Lawniczak, M. K. (2019). The male mosquito contribution towards malaria transmission: Mating influences the Anopheles female midgut transcriptome and increases female susceptibility to human malaria parasites. PLOS Pathogens, 15(11), e1008063. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1008063. |
| [26] | Day, J. (2016). Mosquito oviposition behavior and vector control. Insects, 7(4), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects7040065. |
| [27] | Diabaté, A., Yaro, A. S., Dao, A., Diallo, M., Huestis, D. L., & Lehmann, T. (2011). Spatial distribution and male mating success of Anopheles gambiae swarms. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-11-184. |
| [28] | Dippel, S., Kollmann, M., Oberhofer, G., Montino, A., Knoll, C., Krala, M., Rexer, K., Frank, S., Kumpf, R., Schachtner, J., & Wimmer, E. A. (2016). Morphological and Transcriptomic analysis of a beetle Chemosensory system reveals a gnathal olfactory center. BMC Biology, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-016-0304-z. |
| [29] | EarthSky in Earth. (2015, July 22). How mosquitoes find you to bite you. EarthSky. https://earthsky.org/earth/how-mosquitoes-find-you-to-bite-you. |
| [30] | Ellis, S., Franks, D. W., Nattrass, S., Currie, T. E., Cant, M. A., Giles, D., Balcomb, K. C., & Croft, D. P. (2018). Analyses of ovarian activity reveal repeated evolution of post-reproductive lifespans in toothed whales. Scientific Reports, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31047-8. |
| [31] | Enayati, A., & Hemingway, J. (2010). Malaria management: Past, present, and future. Annual Review of Entomology, 55(1), 569-591. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-112408-085423. |
| [32] | Enayati, A., Hemingway, J., & Garner, P. (2007). Electronic mosquito repellents for preventing mosquito bites and malaria infection. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 3, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd005434.pub2. |
| [33] | Foster, W. A., B., & Walker, E. D. (2009). Medical and veterinary entomology. In Mosquitoes (Culicidae) (2nd ed., pp. 207-259). Academic Press. |
| [34] | Fullman, N., Burstein, R., Lim, S. S., Medlin, C., & Gakidou, E. (2013). Nets, spray or both? The effectiveness of insecticide-treated nets and indoor residual spraying in reducing malaria morbidity and child mortality in sub-Saharan Africa. Malaria Journal, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-12-62. |
| [35] | Gething, P. W., Casey, D. C., Weiss, D. J., Bisanzio, D., Battle, K., Coates, M. M., & Hay, S. I. (2016). Mapping Plasmodium falciparum mortality in Africa between 1990 and 2015. The New England Journal of Medicine, 1, 33. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1606701. |
| [36] | Glotin, H. (2015). Beluga high velocity recordings. SABIOD project. |
| [37] | Glotin, H, & Dolle, A. (2016). High Velocity bioacoustic an Anthropophony monitoring in Indian Ocean. SABIOD, NortekMed project. |
| [38] | Godfray, H. C. (2012). Mosquito ecology and control of malaria. Journal of Animal Ecology, 82(1), 15-25. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.12003. |
| [39] | Gonzales, K., & Hansen, I. (2016). Artificial diets for mosquitoes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(12), 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13121267. |
| [40] | Guyatt, H. L., & Snow, R. W. (2004). Impact of malaria during pregnancy on low birth weight in sub-Saharan Africa. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 17(4), 760-769. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.17.4.760-769.2004. |
| [41] | Hanboonkunupakarn, B., & White, N. J. (2016). The threat of antimalarial drug resistance. Tropical Diseases, Travel Medicine and Vaccines, 2(1), 2-5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40794-016-0027-8. |
| [42] | Harwood, L. A., Norton, P., Day, B., & Hall, P. A. (2002). The harvest of beluga whales in Canada's western Arctic: Hunter-based monitoring of the size and composition of the catch. ARCTIC, 55(1). https://doi.org/10.14430/arctic687. |
| [43] | Hoy, R. (2006). A boost for hearing in mosquitoes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103(45), 16619-16620. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0608105103. |
| [44] | Ikeri, H. I., Onyia, A. I., Chima A. I., & Nwobodo A.N. (2017). Construction and Empirical Study of Electronic Piezzo Buzzer Mosquito Repellent. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, 8(11), 1605-1610. ISSN 2229-5518. |
| [45] | Jackson, J. C., & Robert, D. (2006). Nonlinear auditory mechanism enhances female sounds for male mosquitoes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103(45), 16734-16739. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606319103. |
| [46] | Kaindoa, E. W., Ngowo, H. S., Limwagu, A., Mkandawile, G., Kihonda, J., Masalu, J. P., Bwanary, H., Diabate, A., & Okumu, F. O. (2017). New evidence of mating swarms of the malaria vector, Anopheles arabiensis in Tanzania. Wellcome Open Research, 2, 88. https://doi.org/10.12688/wellcomeopenres.12458.1. |
| [47] | Kröber, T., Kessler, S., Frei, J., Bourquin, M., & Guerin, P. M. (2010). An in vitro assay for testing mosquito repellents employing a warm body and carbon dioxide as a behavioral activator. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association, 26(4), 381-386. https://doi.org/10.2987/10-6044.1. |
| [48] | Kweka, E. J., Zhou, G., Munga, S., Lee, M., Atieli, H. E., Nyindo, M., Githeko, A. K., & Yan, G. (2012). Anopheline larval habitats seasonality and species distribution: A prerequisite for effective targeted larval habitats control programmes. PLoS ONE, 7(12), e52084. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052084. |
| [49] | Ladich, F., & Winkler, H. (2017). Acoustic communication in terrestrial and aquatic vertebrates. Journal of Experimental Biology, 220(13), 2306-2317. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.132944. |
| [50] | Lammers, M. O., & Castellote, M. (2009). The beluga whale produces two pulses to form its sonar signal. Biology Letters, 5(3), 297-301. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2008.0782. |
| [51] | League, G. P., Onuh, O. C., & Hillyer, J. F. (2014). Comparative structural and functional analysis of the larval and adult dorsal vessel and its role in hemolymph circulation in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Journal of Experimental Biology. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.114942. |
| [52] | Lindsay, S. W., Parson, L., & Thomas, C. J. (1998). Mapping the range and relative abundance of the two principal African malaria vectors, Anopheles gambiae sensu stricto and A. arabiensis, using climate data. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 265(1399), 847-854. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.1998.0369. |
| [53] | Lockyer, C., Hohn, A. A., Doidge, W. D., Heide-Jørgensen, M. P., & Suydam, R. (2007). Age determination in belugas (Delphinapterus leucas): A quest for validation of Dentinal layering. Aquatic Mammals, 33(3), 293-304. https://doi.org/10.1578/am.33.3.2007.293. |
| [54] | Lubis, Z. M., Pujiyati, S., Hestirianoto, T., & Wulandari, P. D. (2016). Bioacoustic Characteristics of Whistle Sounds and behaviour of male Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops aduncus) in Indonesia. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 6(2), 163-169. http://985.so/btpnh. |
| [55] | Madsen, P. T., Lammers, M., Wisniewska, D., & Beedholm, K. (2013). Nasal sound production in echolocating delphinids (Tursiops truncatus and Pseudorca crassidens) is dynamic, but unilateral: Clicking on the right side and whistling on the left side. Journal of Experimental Biology, 216(21), 4091-4102. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.091306. |
| [56] | Mang’are, P. A., Maweu, O. M., Ndiritu, F. G., & Vulule, J. M. (2012). The Startling Effect of the Sound of C. afra and A. tormotus on the Female A. gambiae. International Journal of Biophysics, 2(3), 40-52. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.biophysics.20120203.02. |
| [57] | Marques, J., Cardoso, J. C., Felix, R. C., Santana, R. A., Guerra, M. D., Power, D., & Silveira, H. (2018). Fresh-blood-free diet for rearing malaria mosquito vectors. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 17807. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35886-3. |
| [58] | Marques, J., Cardoso, J. C. R., Félix, R. C., Power, D. M., & Silveira, H. A. (2020). Blood-Free Diet to Rear Anopheline Mosquitoes. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 155, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3791/60144. |
| [59] | Maweu, O. M., Deng, A. L., & Muia, L. M. (2009). A Comparative study of A. gambiae male mosquito’s response to frequency modulated (FM) and pulse modulated (PM) waves at different acoustic frequencies and distances. Indonesian Journal of Physics, 20, 81-84. http://repository.seku.ac.ke/handle/123456789/1069. |
| [60] | McMeniman, C., Corfas, R., Matthews, B., Ritchie, S., & Vosshall, L. (2014). Multimodal integration of carbon dioxide and other sensory cues drives mosquito attraction to humans. Cell, 156(5), 1060-1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.044. |
| [61] | Mohankumar, D. (2010, April 8). Ultrasound and insects. Mohan's electronics blog. https://dmohankumar.wordpress.com/2010/04/08/ultrasound-and-insects/. |
| [62] | Okal, M. N., Lindh, J. M., Torr, S. J., Masinde, E., Orindi, B., Lindsay, S. W., & Fillinger, U. (2015). Analysing the oviposition behaviour of malaria mosquitoes: Design considerations for improving two-choice egg count experiments. Malaria Journal, 14(1), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-015-0768-2. |
| [63] | Okorie, P. N., Okareh, O. T., Adeleke, O., Falade, C. O., & Ademowo, O. G. (2015). Effects of an in-built ultrasonic device on Anopheles gambiae s.l mosquitoes in an indoor environment. International Research Journal of Engineering Science, Technology and Innovation (IRJESTI), 4(1), 5-11. https://doi.org/10.14303/irjesti.2015.074. |
| [64] | Oliva, C. F., Benedict, M. Q., Lempérière, G., & Gilles, J. (2011). Laboratory selection for an accelerated mosquito sexual development rate. Malaria Journal, 10(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-10-135. |
| [65] | Pennetier, C., Warren, B., Dabiré, K. R., Russell, I. J., & Gibson, G. (2010). “Singing on the wing” as a mechanism for species recognition in the malarial mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Current Biology, 20(2), 131-136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.11.040. |
| [66] | Rodriguez, S. D., Drake, L. L., Price, D. P., Hammond, J. I., & Hansen, I. A. (2015). The efficacy of some commercially available insect repellents forAedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae). Journal of Insect Science, 15(1), 140. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/iev125. |
| [67] | Rutledge, L. C., Wirtz, R.A., 16, M. D., & Mehr, Z. A. (1985). Mathematical models of the effectiveness and persistence of mosquito repellents. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association, 1(1), 56-62. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/21596336.pdf. |
| [68] | Shen, J., Xu, Z., Yu, Z., Wang, S., Zheng, D., & Fan, S. (2011). Ultrasonic frogs show extraordinary sex differences in auditory frequency sensitivity. Nature Communications, 2(1), 1-26. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1339. |
| [69] | Shen, J., & Xu, Z. (2016). The Lombard effect in male ultrasonic frogs: Regulating antiphonal signal frequency and amplitude in noise. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27103. |
| [70] | Sinka, M. E., Bangs, M. J., Manguin, S., Coetzee, M., Mbogo, C. M., Hemingway, J., Patil, A. P., Temperley, W. H., Gething, P. W., Kabaria, C. W., Okara, R. M., Van Boeckel, T., Godfray, H. C., Harbach, R. E., & Hay, S. I. (2010). The dominant anopheles vectors of human malaria in Africa, Europe and the Middle East: Occurrence data, distribution maps and bionomic precis. Parasites & Vectors, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-3-117. |
| [71] | Sinka, M. E., Bangs, M. J., Manguin, S., Rubio-Palis, Y., Chareonviriyaphap, T., Coetzee, M., Mbogo, C. M., Hemingway, J., Patil, A. P., Temperley, W. H., Gething, P. W., Kabaria, C. W., Burkot, T. R., Harbach, R. E., & Hay, S. I. (2012). A global map of dominant malaria vectors. Parasites & Vectors, 5(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-5-69. |
| [72] | Stromsky, V. E., Hajkazemian, M., Vaisbourd, E., Mozūraitis, R., & Noushin Emami, S. (2021). Plasmodium metabolite HMBPP stimulates feeding of main mosquito vectors on blood and artificial toxic sources. Communications Biology, 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02689-8. |
| [73] | Sumarnrote, A., Overgaard, H. J., Marasri, N., Fustec, B., Thanispong, K., Chareonviriyaphap, T., & Corbel, V. (2017). Status of insecticide resistance in Anopheles mosquitoes in Ubon Ratchathani province, northeastern Thailand. Malaria Journal, 16(1), 299. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-017-1948-z. |
| [74] | Thiévent, K., Hauser, G., Elaian, O., & Koella, J. C. (2019). The interaction between permethrin exposure and malaria infection affects the host-seeking behaviour of mosquitoes. Malaria Journal, 18(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-019-2718-x. |
| [75] | Tizifa, T. A., Kabaghe, A. N., McCann, R. S., Van den Berg, H., Van Vugt, M., & Phiri, K. S. (2018). Prevention efforts for malaria. Current Tropical Medicine Reports, 5(1), 41-50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40475-018-0133-y. |
| [76] | Tripet, F., Dolo, G., Traoré, S., & Lanzaro, G. C. (2004). The "Wingbeat hypothesis" of reproductive isolation between members of theAnopheles gambiaeComplex (Diptera: Culicidae) does not fly. Journal of Medical Entomology, 41(3), 375-384. https://doi.org/10.1603/0022-2585-41.3.375. |
| [77] | United Nations (UN). (2015). Millennium development goals report 2015. United Nations. http://985.so/btpn5. |
| [78] | United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). (2014). Malaria major cause of child death and poverty in Africa. UNICEF. https://factsforlife.org/pdf/malaria_rev_5296_Eng.pdf. |
| [79] | Walther, B., Miles, D. J., Crozier, S., Waight, P., Palmero, M. S., Ojuola, O., Touray, E., Sande, M. V., Whittle, H., Rowland-Jones, S., & Flanagan, K. L. (2010). Placental malaria is associated with reduced early life weight development of affected children independent of low birth weight. Malaria Journal, 9(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-9-16. |
| [80] | Warren, B., Lukashkin, A. N., & Russell, I. J. (2011). The dynein–tubulin motor powers active oscillations and amplification in the hearing organ of the mosquito. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 278(1712), 1760-1760. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2011.0319. |
| [81] | Wheelwright, M., Whittle, C. R., & Riabinina, O. (2021). Olfactory systems across mosquito species. Cell and Tissue Research, 383(1), 75-90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03407-2. |
| [82] | White, S. A., & Kaufman, P. E. (2014, August 19). EENY601/IN1048: African malaria mosquito anopheles gambiae Giles (Insecta: Diptera: Culicidae). Ask IFAS - Powered by EDIS. Retrieved November 7, 2021, from https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/IN1048. |
| [83] | World Health Organisation, WHO. (2011). World malaria report 2011. World Health Organisation. https://www.who.int/malaria/world_malaria_report_2011/WMR2011_factsheet.pdf. |
| [84] | World Health Organization, WHO. (2013). Guidelines for efficacy testing of spatial repellents. In WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data. World Health Organization. http://985.so/btpnn. |
| [85] | World Health Organisation, WHO. (2014). Severe Malaria. Tropical Medicine & International Health, 19(1), 7–13. https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/world_malaria_report_2013/wmr13_summary_key_points.pdf?ua=1. |
| [86] | World Health Organisation, WHO. (2015). World malaria report 2014. World Health Organisation. https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/world_malaria_report_2014/wmr-2014-no-profiles.pdf. |
| [87] | World Health Organisation, WHO. (2016). World malaria report 2015. World Health Organisation. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/252038/9789241511711-eng.pdf. |
| [88] | World Health Organisation, WHO. (2018). World malaria report 2018. World Health Organisation. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/275867/9789241565653-eng.pdf. |
| [89] | World Health Organisation, WHO. (2019). World malaria report 2019. World Health Organisation. https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789241565721. |
| [90] | World Health Organisation, WHO. (2020). World malaria report 2020. World Health Organisation. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240015791. |
| [91] | World Health Organization & Global Partnership to Roll Back Malaria. (2006). Malaria vector control and personal protection: Report of a WHO study group. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43425. |
| [92] | Wulandari, P. D., Pujiyati, S., Hestirianoto, T., & Lubis, M. Z. (2016). Bioacoustic characteristic click sound and behaviour of male dolphins bottle nose (Tursiops aduncus). Journal of Fisheries & Livestock Production, 04(01), 1-5. https://doi.org/10.4172/2332-2608.1000160. |
| [93] | Zohdi, V., Sutherland, M. R., Lim, K., Gubhaju, L., Zimanyi, M. A., & Black, M. J. (2012). Low birth weight due to intrauterine growth restriction and/or preterm birth: Effects on nephron number and long-term renal health. International Journal of Nephrology, 2012, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/136942. |




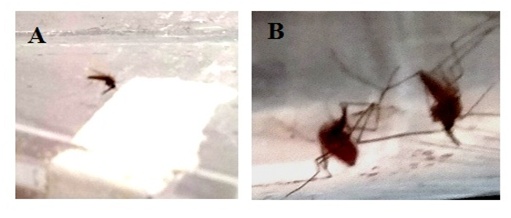

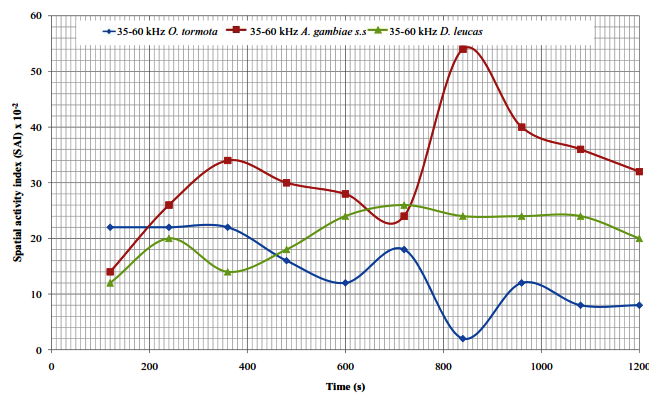
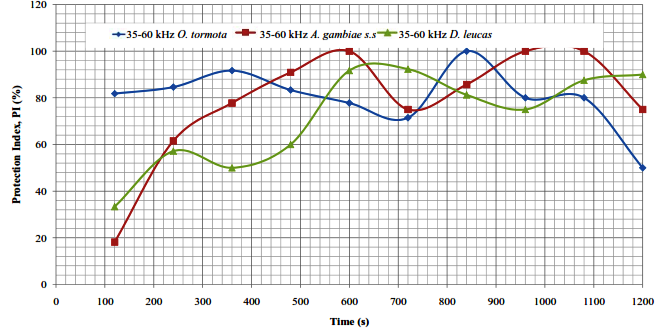
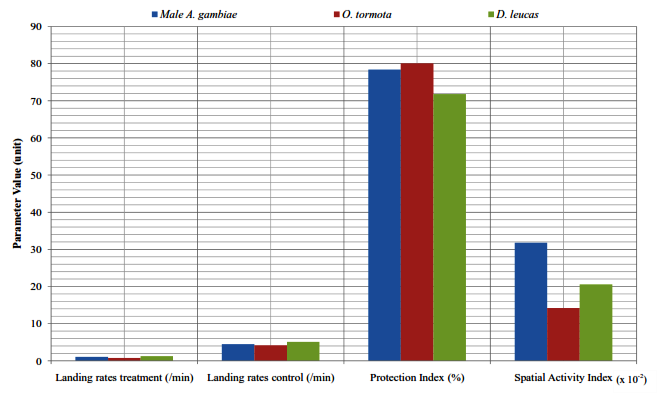
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML