-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Biophysics
p-ISSN: 2168-4979 e-ISSN: 2168-4987
2019; 9(1): 12-21
doi:10.5923/j.biophysics.20190901.02

Comparative Characterization of the Natural Sounds of the Bottlenose Dolphin Tursiops truncatus and Odorrana tormota Fundamental in the Startle of the Female Anopheles gambiae
Mang’are P. A.1, 2, Ndiritu F. G.1, Rotich S. K.3, Makatiani J. K.4, Rapando B. W.2
1Physics Department, Egerton University, Egerton, Njoro, Kenya
2Physics Department, Masinde Muliro University of Science and Technology, Kakamega, Kenya
3Department of Physics and Mathematics, Moi University, Eldoret, Kenya
4Department of Biological Sciences, Moi University, Eldoret, Kenya
Correspondence to: Mang’are P. A., Physics Department, Egerton University, Egerton, Njoro, Kenya.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Malaria prevention, control and treatment has over the years relied on chemicals. However, the malaria vectors and pathogens have developed considerable resistance lowering the decline rate of malaria related mortality and morbidity. Studies on mosquito vectors involving sounds generated naturally and electronically have yielded altercative findings in regard to the repellence of the mated female Anopheles gambiae s.s. However, other findings on the startle response of the African female A. gambiae to animal sounds showed a 46% evasive response educed by 35-60 kHz recorded sound of Odorrana tormota. These findings showed practicability of using animal sound in the startle of mosquitoes. Therefore, there was need to research further on other natural sounds, in comparison with the sound of O. tormota with a view of determining superior acoustic propagation parameters for the startle of the mated A. gambiae. This study therefore comparatively analysed the acoustic propagation parameters of the natural sounds of the bottlenose dolphin Tursiops truncatus and O. tormota fundamental in the startle of the female A. gambiae. Spectral analysis of the sound of T. trancatus revealed predominance of frequency modulation (FM), signal breaks and chaos stretching to ultrasonic levels similar to the sound of O. tormota. The sounds of T. truncatus and O. tormota differed in modulation due to the absence of constant frequency modulation in the sound of T. truncatus. The acoustic propagation parameters of the sound of T. truncatus and O. tormota compared using T-test at a confidence interval of 95% differed significantly (p < 0.05) with a low Pearson’s correlation. The mean fundamental frequency (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus was 0.9095 kHz which was 4.9387 kHz less than the mean fundamental frequency (mean entire) of the sound of O. tormota. The greatest measurement in frequency recorded in the sound of T. truncatus was 52.70 kHz under the maximum frequency (maximum entire). The sound of T. truncatus recorded the least mean, minimum and maximum parameter values in bandwidth (maximum entire), bandwidth (mean), peak amplitude (end), peak amplitude (maximum), peak amplitude (maximum entire), peak amplitude (mean), peak amplitude (mean entire) and peak amplitude (start) compared to values for the sound of O. tormota. A narrow bandwidth was observed in the means of all bandwidth measurements of the sound of T. truncatus compared to the values of the sound of O. tormota. The maximum measurements of the bandwidth (start) of the sound of T. truncatus exceeded the respective measurements of the sound of O. tormota by 7.80 kHz.The acoustic power and energy for the sound of T. truncatus were less than the that of the sound of O. tormota, though both sounds were pulsate and declined with increase in frequency. The maximum and mean acoustic energy of the sound of T. truncatus was 1.93937 Pa2s and 0.14392 Pa2s respectively which were 2.86936 Pa2s and 0.42714 Pa2s less than the sound of O. tormota. The delta power (ΔP) of the sound of T. truncatus was 47.3 dB higher than the respective measurements in the sound of O. tormota. The aggregate entropy, average entropy, average power, maximum entropy, maximum frequency, maximum power, minimum entropy and peak power of the pulsate sound of T. truncatus were 2.40 Bits, 2.40 Bits, 24.00 dB, 2.40 Bits, 6.84 kHz, 18.3 dB, 2.40 Bits and 18.3 dB less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota. The delta power (ΔP) of the sound of T. truncatus was 47.30 dB greater than the corresponding delta power recorded by the sound of O. tormota. The acoustic propagation parameters of the sound of T. truncatus were comparatively inferior to the corresponding parameters of the sound of O. tormota hence not feasible for mosquito startle.
Keywords: Fourier transform, Sub-harmonics, Frequency jumps, Pneumatic actuation, Formants
Cite this paper: Mang’are P. A., Ndiritu F. G., Rotich S. K., Makatiani J. K., Rapando B. W., Comparative Characterization of the Natural Sounds of the Bottlenose Dolphin Tursiops truncatus and Odorrana tormota Fundamental in the Startle of the Female Anopheles gambiae, International Journal of Biophysics , Vol. 9 No. 1, 2019, pp. 12-21. doi: 10.5923/j.biophysics.20190901.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
1.1. Tursiops truncatus and Odorrana tormota
- There are two species of the bottlenose dolphin: Tursiops truncatus and Tursiops aduncus which are similar but distinguished primarily habitat, morphology and the ventral spotting, present in adult T. aduncus and absent in T. truncatus [13,14,16,22,24]. The bottlenose dolphin, Tursiops aduncus has a relatively robust body, moderately long beak, and a falcate dorsal fin. It has a proportionately longer rostrum and, most distinctively, develops ventral spotting at about the time of sexual maturity [15]. The Bottlenose Dolphins inhabit areas with rocky and coral reefs, or sea grass preferring water temperatures of 10-30°C, with a minimum of 12°C [28,30]. Off the coast of Zanzibar, Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphins forage on a relatively large number of prey species. The maximum age recorded for the T. truncatus and T. aduncus was 58 and 43 years respectively [28,29]. Other studies revealed that the oldest ages for the female and male T. truncatus were 41 years and 33 years respectively; with the male and female growing to a length of 268.0 cm and 246.7 cm respectively [11]. Other research findings showed that females of T. truncatus gave birth from 6 to 13 years of age with a mean age of 8 years [25]. The concave-eared torrent frog, Odorrana tormota breeds along streams in Central China [3]. O. tormota species is a frog restricted to Huangshan in Anhui Province, and Jiande and Anji counties in Zhejiang Province, China [27].
1.2. The Sounds of the T. truncatus and O. tormota
- Sound in animals play a crucial role in communication and whose whistles intensity depends on environmental ambient noise for efficient transmission [21]. Notably, T. truncatus generate communicative sounds important for social behavior, maintaining group cohesion and coordinating foraging with whistle production increases during disturbances [6]. Recent research findings have reported that T. truncatus use the frequency contour of whistles produced by conspecifics for individual recognition by recognizing the frequency modulated whistle-like sounds [4]. The sounds of T. truncatus are most commonly classified as whistles (tonal, frequency modulated, typical frequencies 5-10 kHz) or clicks (impulsed and mostly ultrasonic) [26].The Odorrana tormota species is notable for its exceptionally complex vocal repertoire with large fluctuations in spectral properties within calls and prominent ultrasonic harmonics, which aid communication in noisy stream environments [3,9,10]. During the reproductive season, O. tormota males emit a variety of high-pitched calls at night with energy spectrums extending into the ultrasonic range [9,10]. Recent research with the O. tormota calls showed some degree of downward frequency modulation with a subset of calls having a carrier of constant frequency.As observed in recent studies, sound from animals had shown feasibility of its use in malaria vector control by evoking startle responses. Sounds generated naturally or artificially and whose frequencies stretch into the 38 - 44 kHz range and beyond causes startle effect in mosquitoes [20]. The 35-60 kHz recorded sound of O. tormota having exhibited 46.0% evasive startle responses in mosquitoes provided grounding for further investigation of other animals that generate sound naturally. However, sound from electronic mosquito repellents (EMRs) had evoked low repellency (20.0 - 30.3%) in mosquitoes hence the need for investigation natural animal sounds [2,7]. This study focuses on the sound of T. trancatus and compares its acoustic transmission parameters with that of the sound of O. tormota in order to determine superior acoustic transmission parameters critical in malaria vector control. Emphasis on insect control forms an essential part of reducing malaria transmission [8]. The acoustic propagation parameters determined in this study include and not limited to call duration, acoustic energy, peak frequency (mean), peak amplitude (mean), minimum frequency, maximum frequency (mean), bandwidth (mean), peak frequency (minimum entire), minimum frequency (minimum entire), maximum frequency (minimum entire), bandwidth (minimum entire), peak frequency (maximum entire), peak amplitude (maximum entire), minimum frequency (maximum entire), maximum frequency (maximum entire), peak frequency (mean entire), peak amplitude (mean entire), minimum frequency (mean entire), and maximum frequency (mean entire). The acoustic energy E, amplitude
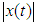 power P, frequency f and intensity I are related as:
power P, frequency f and intensity I are related as: 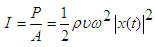 | (1) |
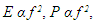 and
and 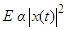 . Where, I is intensity of the sound wave, ρ is the density of the medium, v is the speed of sound being transmitted, ω is the angular frequency,
. Where, I is intensity of the sound wave, ρ is the density of the medium, v is the speed of sound being transmitted, ω is the angular frequency, 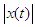 is the amplitude of sound and A is cross section area. For an acoustic signal of amplitude
is the amplitude of sound and A is cross section area. For an acoustic signal of amplitude 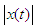 , the acoustic energy of the signal is defined as:
, the acoustic energy of the signal is defined as: 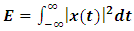 | (2) |
1.3. Statement of the Problem
- The use of ultrasound in mosquito repellency has been litigious, at times casting doubts on its application in malaria vector control. However, the mosquitoes and malaria pathogens have developed resistance to chemicals currently in use. This in turn slowed down the rate at which the mortality and morbidity is declining worldwide. The morbidity and mortality trend reversed in Kenya beginning in 2010, and recording an age standardised deaths per 10,000 due to malaria of 10.72 deaths in 2016 [19]. The Electronic Mosquito Repellents (EMRs) devices mimicking animal sounds and currently in use have been found to give a low repellency of 20.0 - 30.3% repellency [7]. However, studies involving the 35-60 kHz recorded natural sound of O. tormota and mated female A. gambiae elicited 46% repellence, an improvement from the reported 20.0 - 30.3% repellency in EMRs. However, the sound of the T. truncatus had not been investigated. This research comparatively analysed the acoustic propagation parameters of the natural sounds of the bottlenose dolphin Tursiops truncatus and Odorrana tormota fundamental in the startle of the female Anopheles gambiae. The acoustic propagation parameters determined would be useful in the bioassay study involving the of female A. gambiae and design of a mosquito repellent device. The experimental results from this study provide additional knowledge about the sounds of T. truncatus.
1.4. Objectives
1.4.1. General Objective
- Analysis of the acoustic propagation parameters of the natural sounds of the bottlenose Dolphin Tursiops truncatus and Odorrana tormota fundamental in the startle of the female Anopheles gambiae.
1.4.2. Specific Objectives
- i. To determine the acoustic propagation parameters of the sounds of Tursiops truncatus.ii. To analyse and compare the acoustic propagation parameters of the sounds of Tursiops truncatus and O. tormota fundamental in the startle of the female A. gambiae.
2. Methodology
2.1. Sound of T. truncatus and O. tormota
- The sound of the Bottlenose Dolphin Tursiops truncatus recorded by Nortek SA system at a sampling frequency of 8 kHz when moving for fishing and socialising in the wild were supplied by Prof. Herve Glotin of Institut Universitaire de France [12]. The recorded sound of O. tormota was recorded by 702 digital recorder from the Huangshan Hot Springs, Anhui Province in China at a sampling frequency of 192 kHz and were acquired through Prof. Albert Feng, Illinois University. The Avisoft-SAS LAB Pro version 5.2 programme was also used in the conversion of sampling frequencies to 500 kHz and append various sound clips to a duration of 1,200 s.
2.2. The Acoustic Propagation Parameters of Sounds of T. truncatus
- The sounds of T. truncatus and O. tormota were subjected to Fourier transforms using Avisoft SASLab Pro version 5.2 in order to determine the acoustic propagation parameters through automatic parameter measurements. The calibration was set to SPL with reference to sound at a SPL reference of 20µPa. The parameters were determined using Avisoft SASLab Pro version 5.2 and Raven Pro. 1.5 and included call duration, acoustic energy, peak frequency (mean), peak amplitude (mean), minimum frequency, maximum frequency (mean), bandwidth (mean), peak frequency (minimum entire), minimum frequency (minimum entire), maximum frequency (minimum entire), bandwidth (minimum entire), peak frequency (maximum entire), peak amplitude (maximum entire), minimum frequency (maximum entire), maximum frequency (maximum entire), peak frequency (mean entire), peak amplitude (mean entire), minimum frequency (mean entire), and maximum frequency (mean entire). Also, Fast Fourier transform (FFT), an option under the spectrogram parameters was set to 512 and hamming window selected for display. The temporal resolution overlap was set to 50% with the colour palette set to graypal. The frame size was set to 100% for real time spectrogram parameters and the black and white box (B/W) checked for display. The acoustic energy whose SI unit is Pa2s is a product of the square of amplitudes and sample time. The energy produced is the sum of the squared amplitudes multiplied by time. Also, 1 Pascal pressure is equal to SPL of 94 dB. The data obtained was transferred into an excel worksheet for editing and further analysis through the direct data exchange (DDE)/ Logfile settings. The acoustic propagation parameters of the natural sounds of T. truncatus and O. tormota were analysed statistically using Avisoft SASLab Pro version 5.2, Raven Pro 1.5 and SPSS software.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of Transmission Parameters of Sounds of T. aduncus
3.1.1. Generation and Modulation of the Sounds of T. truncatus and O. tormota
- The sound sample of T. truncatus investigated was composed of 6,639 calls generated naturally through pneumatic actuation of phonic lip pairs within the blowhole [18]. The calls of T. truncatus were compared to the 2,061 calls of O. tormota which were naturally generated through vocal apparati [1]. The sounds of bottlenose dolphin T. truncatus are used for social purposes, foraging and navigating; with whistles intensity depending on environmental ambient noise for efficient transmission [17,21,26]. The calls studied lasted for a minimum, maximum and average duration of 0.0005s, 0.6067s and 0.07476 s respectively. The spectrogram in Figure 1 and 2 represent the signal spectral composition of the sound of T. truncatus which was predominantly linear accompanied with frequency jumps, subharmonics, breaks and a chaotic background. The chaotic background was attributed to the habitat of the of T. truncatus. The 6,639 calls studied consisted of frequency modulated (FM), constant frequency modulated (CF) extending to ultrasonic levels similar to those of the sound of O. tormota as given in Figure 3 and 5. Also, the sounds of T. truncatus and O. tormota were useful for communication and conspecifics for individual recognition due to the conditions of their habitat [1,6,9,10,21]. The spikes or sharp signals (whistle production) visible in Figure 31 and 32 increase during disturbances. The pulsate sound of T. truncatus similar to O. tormota was characterised by harmonics that extended to ultrasonic levels beyond 150 kHz as shown in Figure 1 and 2. Recent studies involving T. truncatus showed presence of ultrasound through the plots of peak frequency versus estimates of radiated acoustic power for all three of the bottlenose dolphins demonstrated a tendency to produce peaks in two frequency bands, one above and one below 70 kHz which is in agreement with the findings of this study [5]. The nature of the sound of T. truncatus compared favourably with the sound of the Chinese frog O. tormota which had proven effective in the startle of the female A. gambiae. The oscillogram in Figure 4 showed immense amplitude variation with time, evidence of pulsate sound in T. truncatus similar to the sound of O. tormota given in Figure 6. The short duration clicks and whistles were observed in the sound of T. truncatus compared to bursts in O. tormota in their pulsate nature.
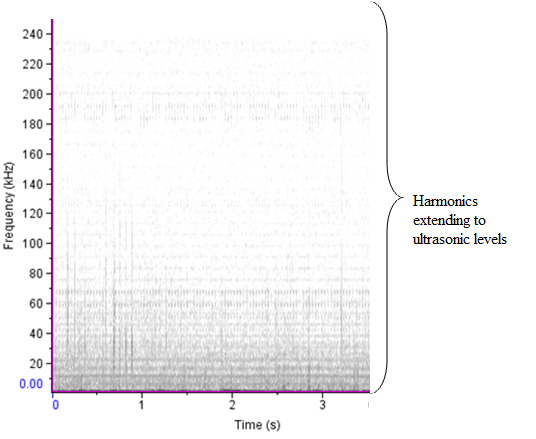 | Figure 1. The sound spectrum of T. truncatus showing harmonics |
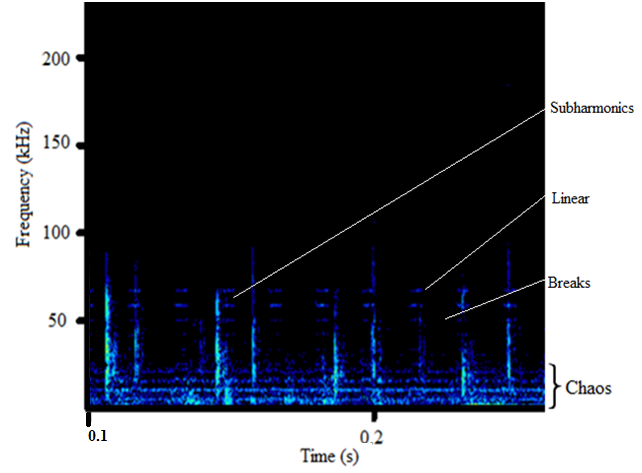 | Figure 2. Spectral features in the sound of T. truncatus |
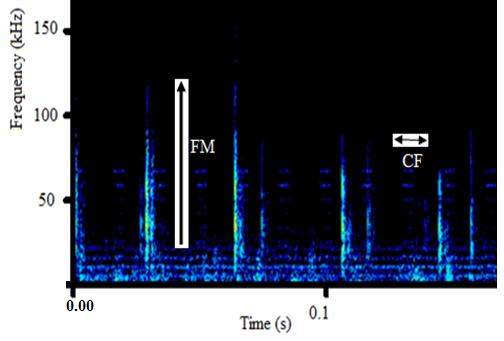 | Figure 3. Frequency modulation in the sound of T. truncatus |
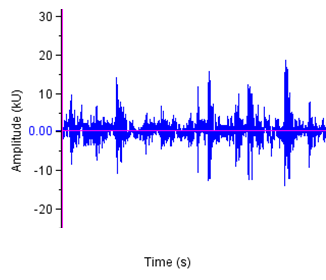 | Figure 4. Amplified oscillogram for the sound of T. truncatus |
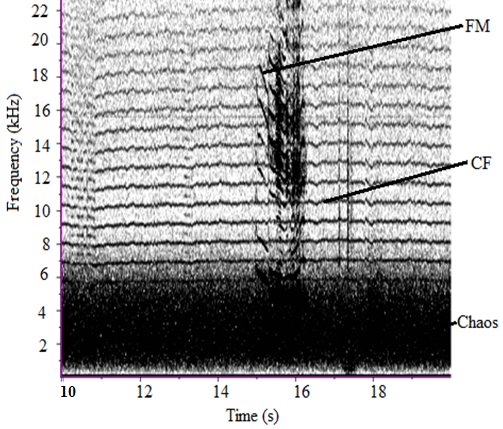 | Figure 5. Spectral features in the sound of O. tormota |
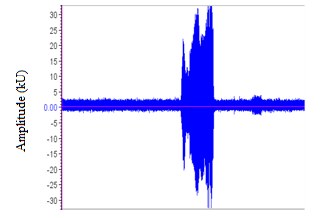 | Figure 6. A portion of the oscillogram for the sound of O. tormota |
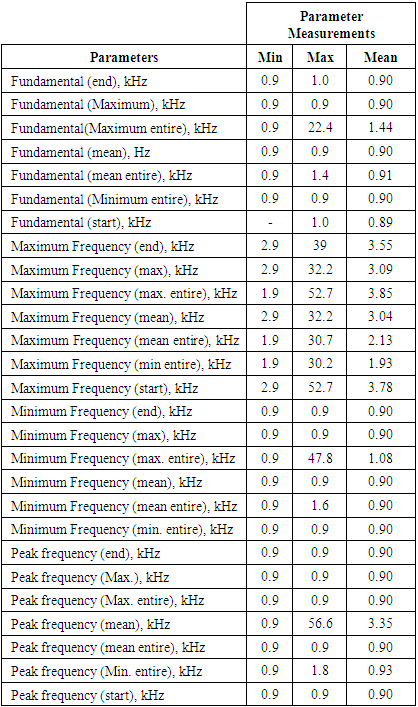
3.1.2. Acoustic Propagation Parameters of the Sounds of T. truncatus
- The acoustic propagation parameters of T. truncatus determined and analysed in the study included call duration, acoustic energy, acoustic power, entropy, peak frequency (mean), peak amplitude (mean), minimum frequency, maximum frequency (mean), bandwidth (mean), peak frequency (minimum entire), minimum frequency (minimum entire), maximum frequency (minimum entire), bandwidth (minimum entire), peak frequency (maximum entire), peak amplitude (maximum entire), minimum frequency (maximum entire), maximum frequency (maximum entire), peak frequency (mean entire), peak amplitude (mean entire), minimum frequency (mean entire), and maximum frequency (mean entire) whose measurements are given in Table 1.
|
3.1.2.1. Fundamental Frequency and Harmonics
- The formants shown in the spectrogram given in Figure 1 and 2 and whose data was given in Table 1 elucidated the complexity of the sound of T. truncatus by revealing presence of the fundamental frequencies and their harmonics. The mean fundamental frequency (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus was 0.9095 kHz which was 4.9388 kHz less than the mean fundamental frequency (mean entire) of the new sound samples of O. tormota as given in Table 1. A paired samples T-test comparison of the fundamental frequency (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus by that of the sound of O. tormota at a confidence interval of 95% yielded the significance value, p = 0.000 < 0.05, implying that there exist a highly significant difference between the fundamental frequency (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus and the sound of O. tormota. The difference in the fundamental frequency (mean entire) of the two sounds correlated weakly with a negative Pearson’s correlation r = -0.0036. The minimum fundamental frequency (minimum entire and maximum entire) of the sound of T. truncatus was 900 Hz. At the start of the calls, the mean measurements of peak frequency, minimum frequency and maximum frequency of the sound of T. truncatus were 900 Hz, 900 Hz, and 3.78 kHz, which were 6.46 kHz, 3.50 kHz, and 14.78 kHz less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota. The maximum and mean measurement of the maximum frequency (mean) of the sound of T. truncatus were 32.20 kHz and 3.04 kHz being 12.70 kHz and 16.69 kHz less than that of the sound of O. tormota. A paired samples T-test comparison of the maximum frequency (mean) of the sound of T. truncatus by that of the sound of O. tormota at a confidence interval of 95% yielded the significance value, p = 0.000 < 0.05, which indicated a highly significant difference between maximum frequency (mean) of the sound of T. truncatus and the sound of O. tormota. The difference in the maximum frequency (mean) for the two sounds correlated weakly with a negative Pearson’s correlation r = -0.0276. The mean measurements of the maximum frequency (mean entire), peak frequency (mean entire), minimum frequency (mean entire) of all the 6,639 calls of T. truncatus whose values are shown in Table 1 were 13.60 kHz, 6.55 kHz and 4.64 kHz respectively less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota. The maximum frequency (mean entire), peak frequency (mean entire) and minimum frequency (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus differed significantly (p = 0.000 < 0.05) from the that of the sound of O. tormota with a low Pearson’s correlation (r = -0.0022, 0.0212, -0.0293 respectively). The maximum values of the maximum frequency (start), minimum frequency (maximum entire) and peak frequency (maximum entire) for the sound of T. truncatus were exceedingly higher than corresponding parameter values for O. tormota by 7.80 kHz, 34.20 kHz and 16.60 kHz. However, the minimum, maximum and mean value of the maximum frequency (end) for the sound of T. truncatus was 3.345, 1.3, and 5.507 times greater than the corresponding parameters value of the sound of O. tormota respectively. The maximum frequency (end) of the sound of T. truncatus differed significantly (p = 0.000 < 0.05) from the that of the sound of O. tormota with a low negative Pearson’s correlation (r = -0.026). The maximum and mean measurements of the minimum frequency (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus was 5.200 kHz and 4.636 kHz less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota. The formants in Figure 2 for the sound of T. truncatus represented spectral features which were similar to those of the sound of O. tormota. The maximum frequency for the all calls of T. truncatus studied was 52.70 kHz, showing that the harmonics stretched from the audible to ultrasonic range. Also, the maximum and mean measurements values of the minimum frequency (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus was 4.25 and 6.14 times less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota. The difference in the minimum frequency (mean entire) between the sound of T. truncatus and O. tormota was highly significant (p = 0.000 < 0.05) with a low negative Pearson’s correlation (r = -0.0293). However, the minimum, maximum and mean values of the minimum frequency (minimum entire) of the sound of T. truncatus was equal to the minimum value of the minimum frequency (minimum entire) for the sound of O. tormota. Acoustic frequency is related to the acoustic energy E as E α f2 and Power as P α f2 [23,31]. The acoustic propagation frequencies determined in this study were low for the sound of T. truncatus compared to the sound of O. tormota hence yielded lower acoustic energy and power. The large variations in frequencies for the entire signal of T. truncatus accounted for the pulsate signal resulting in fluctuations in energy trends. The significant variation in minimum, maximum and mean frequencies of the sounds of T. truncatus explained the presence of clicks which were basically impulsed and mostly ultrasonic which were exhibited whenever disturbed or in noisy habitation [17,21,26]. The complexity in the formants for the sound of T. truncatus was attributed to bisonality and collective calling of the dolphins. At the start of the calls, the maximum peak frequency, minimum frequency and maximum frequency were 900 Hz, 900 Hz, and 3.7832 kHz respectively. Notably, the sound of T. truncatus was significantly different from that of O. tormotus whose sound had been reported to startle to the female A. gambiae. The parameters of the sound of T. truncatus and O. tormota correlated extremely low as given in Figure 7. This in effect inferred low acoustic power and energy.
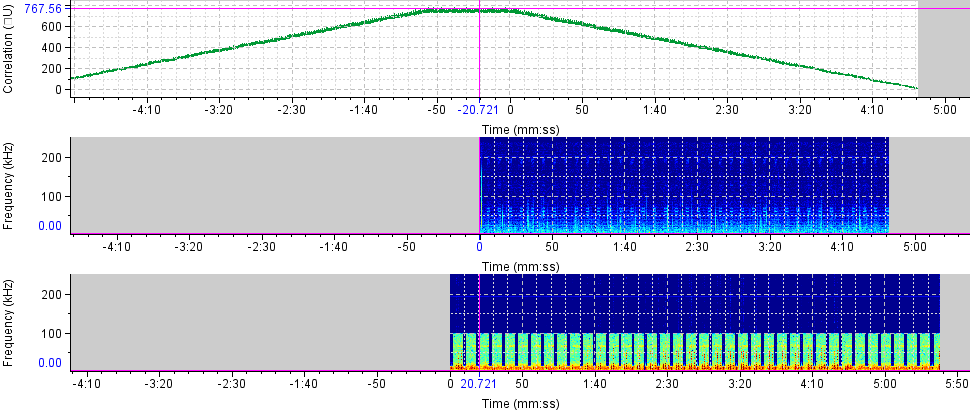 | Figure 7. Raven Pro 1.5 Spectrogram correlator for the sound of T. truncatus and O. tormota |
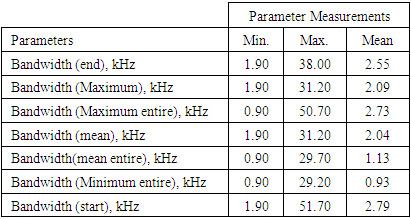
3.1.2.2. Bandwidth
- The bandwidth parameters for the sound of T. truncatus studied were bandwidth (end), bandwidth (maximum entire), bandwidth (maximum), bandwidth (minimum entire), bandwidth (start), bandwidth (mean entire) and bandwidth (mean) whose measurements are given in Table 2. The minimum, maximum and mean values of bandwidth (maximum entire) for the sound of T. truncatus were 0.90 kHz, 50.70 kHz and 2.73 kHz respectively being 5.33 kHz, 2.00 kHz and 7.13 kHz times narrower than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota. The minimum value for the bandwidth (minimum entire) for the sounds of T. truncatus and O. tormota was equal to 900.00 Hz. The maximum and mean values of the bandwidth (end), bandwidth (maximum), bandwidth (maximum entire), bandwidth(mean), bandwidth(mean entire) and bandwidth (minimum entire) for the sound of T. truncatus were less than the corresponding measurements of sound of O. tormota. The maximum and mean bandwidth (mean entire) for the sound of T. truncatus was 2.73 kHz, which was 22.49 kHz narrower than that of the sound of O. tormota pointing to less energy and power. Significantly, the maximum and mean values bandwidth (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus was 10.80 kHz and 8.99 kHz less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota respectively as shown in Table 2. A highly significant difference was established from a paired samples T-test comparison of the bandwidth (end), bandwidth (maximum), bandwidth (maximum entire), bandwidth(mean), bandwidth (mean entire), bandwidth (minimum entire) and bandwidth (start) of the sound of T. truncatus by that of the sound of O. tormota at a confidence interval of 95% yielded the significance value, p = 0.00, 1.0105 x 10-252, 1.0668 x 10-232, 0.00, 1.8967 x 10-234, 3.7306 x 10-102 and 3.3829 x 10-241 <<< 0.05. A Paired Samples Correlations of the sound of T. truncatus and O. tormota in bandwidth (end), bandwidth (maximum), bandwidth (maximum entire), bandwidth (mean), bandwidth(mean entire), bandwidth (minimum entire) and bandwidth (start) yielded a very low negative Pearson’s correlation (r = -.026, -0.0034, -0.0062, -0.0326, -0.0043, -0.0158 and -0.0210 respectively). The significantly narrowed bandwidths of the sound of T. truncatus compared to the sound of O. tormota, was a precursor to low acoustic power and energy compared to that of the sound of O. tormota.
|
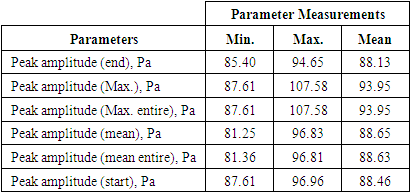
3.1.2.3. Amplitude
- The acoustic propagation parameters for the sound of T. truncatus investigated included Peak amplitude (start), Peak amplitude (end), Peak amplitude (Maximum), Peak amplitude (mean), Peak amplitude (Maximum entire) and the Peak amplitude (mean entire) whose values are given in Table 3. By considering the acoustic signal of amplitude
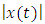 and acoustic energy
and acoustic energy 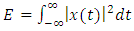 , then
, then 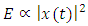 . The minimum, maximum and mean measurements were equal to 87.61 Pa, 107.58 Pa and 93.95 Pa respectively for the peak amplitude (maximum) and peak amplitude (maximum entire) in the sound of T. truncatus as given in Table 3. The minimum, maximum and mean measurements of the peak amplitude (maximum) for the sound of T. truncatus were less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota by 1.21 Pa, 1.24 Pa and 3.33 Pa respectively. Also, the minimum, maximum and mean measurements of the peak amplitude (maximum entire) for the sound of T. truncatus were less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota by an equal margin as in the peak amplitude (maximum). The paired samples T-test comparisons of peak amplitude (maximum) and peak amplitude (maximum entire) of the sound of T. truncatus by that of the sound of O. tormota at a confidence interval of 95% yielded the significance value, p = 3.6310 x 10-60 and 4.4364 x 10-60 respectively showing existence of a highly significant difference with the corresponding parameters for O. tormota. The measurements in peak amplitude (maximum) and peak amplitude (maximum entire) of the sound of T. truncatus and the sound of O. tormota correlated negatively low with a Pearson’s correlation of r = -0.0234 and -0.0236 respectively. The minimum, maximum and mean measurements for the peak amplitude (mean) and peak amplitude (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus were also less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota. The minimum, maximum and mean measurements for the peak amplitude (mean) of the sound of T. truncatus were less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota by 5.01 Pa, 2.49 Pa and 3.93 Pa respectively. Additionally, the minimum, maximum and mean measurements for the peak amplitude (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus were less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota by 6.03 Pa, 5.31 Pa and 4.82 Pa respectively. The peak amplitude (mean) and peak amplitude (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus differed significantly high from the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota with significant values, p = 2.1432 x 10-253 and 1.7449 x 10-274 < 0.05 respectively. The correlation of peak amplitude (mean) and peak amplitude (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus with the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota yielded a low correlation with Pearson's correlation values r = 0.5598 and -0.0228 respectively. The mean measurements of the peak amplitude (end) and the peak amplitude (start) of the sound of T. truncatus was 1.25 Pa and 1.16 Pa less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota. The signal amplitude forms an important parameter in acoustic energy which is critical in the study the investigation of the effect of sound on mosquitoes. The low values of amplitudes for the sound of T. truncatus compared to those of O. tormota yielded a reduced acoustic energy and power in conformity to the relation
. The minimum, maximum and mean measurements were equal to 87.61 Pa, 107.58 Pa and 93.95 Pa respectively for the peak amplitude (maximum) and peak amplitude (maximum entire) in the sound of T. truncatus as given in Table 3. The minimum, maximum and mean measurements of the peak amplitude (maximum) for the sound of T. truncatus were less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota by 1.21 Pa, 1.24 Pa and 3.33 Pa respectively. Also, the minimum, maximum and mean measurements of the peak amplitude (maximum entire) for the sound of T. truncatus were less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota by an equal margin as in the peak amplitude (maximum). The paired samples T-test comparisons of peak amplitude (maximum) and peak amplitude (maximum entire) of the sound of T. truncatus by that of the sound of O. tormota at a confidence interval of 95% yielded the significance value, p = 3.6310 x 10-60 and 4.4364 x 10-60 respectively showing existence of a highly significant difference with the corresponding parameters for O. tormota. The measurements in peak amplitude (maximum) and peak amplitude (maximum entire) of the sound of T. truncatus and the sound of O. tormota correlated negatively low with a Pearson’s correlation of r = -0.0234 and -0.0236 respectively. The minimum, maximum and mean measurements for the peak amplitude (mean) and peak amplitude (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus were also less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota. The minimum, maximum and mean measurements for the peak amplitude (mean) of the sound of T. truncatus were less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota by 5.01 Pa, 2.49 Pa and 3.93 Pa respectively. Additionally, the minimum, maximum and mean measurements for the peak amplitude (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus were less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota by 6.03 Pa, 5.31 Pa and 4.82 Pa respectively. The peak amplitude (mean) and peak amplitude (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus differed significantly high from the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota with significant values, p = 2.1432 x 10-253 and 1.7449 x 10-274 < 0.05 respectively. The correlation of peak amplitude (mean) and peak amplitude (mean entire) of the sound of T. truncatus with the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota yielded a low correlation with Pearson's correlation values r = 0.5598 and -0.0228 respectively. The mean measurements of the peak amplitude (end) and the peak amplitude (start) of the sound of T. truncatus was 1.25 Pa and 1.16 Pa less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota. The signal amplitude forms an important parameter in acoustic energy which is critical in the study the investigation of the effect of sound on mosquitoes. The low values of amplitudes for the sound of T. truncatus compared to those of O. tormota yielded a reduced acoustic energy and power in conformity to the relation 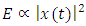 and
and 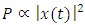 . The sound of T. truncatus was not feasible in the startle of the mated female A. gambiae s.s in spite being pulsate and possessing ultrasonic components.
. The sound of T. truncatus was not feasible in the startle of the mated female A. gambiae s.s in spite being pulsate and possessing ultrasonic components.
|
3.1.2.4. Acoustic Energy and Power
- The minimum, maximum and mean acoustic energy of the sound of T. truncatus was 0.00023 Pa2s, 1.93937 Pa2s and 0.14392 Pa2s with the maximum and mean measurements less than the corresponding energy possessed in the sound of O. tormota by 2.86936 Pa2s and 0.42714 Pa2s respectively. However, the minimum acoustic energy of sound of T. truncatus exceeded the energy prossessed by the sound of O. tormota by 0.00013 Pa2s. This low acoustic energy of the sound of T. truncatus compared to the acoustic energy of the sound of O. tormota was attributed to low amplitude, low frequency and narrow bandwidth. There existed a significant difference in acoustic energy of the sound of T. truncatus compared to that of the sound of O. tormota at a confidence interval of 95% (p = 7.5976 x-53 < 0.05) correlating negatively low (r = -0.03058). The acoustic power spectra of the sound of T. truncatus and O. tormota are given in 23 and 36 repectively with the vertical green line, horizontal green (or purple) line and the Orange line showing the peak frequency (coinciding with maximum power frequency), peak power and average power respectively. The aggregate entropy, average entropy, average power, delta power (ΔP), maximum entropy, maximum power frequency, maximum power, minimum entropy and peak power of the pulsate sound of T. truncatus were 0.92 bits, 0.92 bits, 50.20 dB, 79.10 dB, 0.92 bits, 0.00 kHz, 72.90 dB, 0.92 bits and 72.90 dB respectively as given in Table F1 at the appendix. The average acoustic power and maximum acoustic power (equal to peak power) of the sound of T. truncatus was 24.00 dB and 18.30 dB less than the corresponding power recorded by the sound of O. tormota. The the sound of D. leucas recorded the least disorder attributed to fewer frequency bins with the aggregate entropy, average entropy, maximum entropy and minimum entropy less than the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota equally by 2.40 bits. The change in the coustic power for the sound of T. truncatus exceeded the corresponding measurements of the sound of O. tormota by 5.90 dB. The maximum power and peak power of the sound of T. truncatus coincided at the maximum power frequency of 0.00 kHz, which was 6.84 kHz less than the respective measurements of the sound of O. tormota.
4. Conclusions
- The sound of T. truncatus was generated through pneumatic actuation of phonic lip pairs within the blowhole, predominantly being frequency modulated (FM) and constant frequency modulated (CF) extending to ultrasonic levels similar to the sound of O. tormota. The sound of T. truncatus was composed of frequencies which stretched from audible to ultrasonic levels similar to the sound of O. tormota. Low frequencies, narrow bandwidths and low peak amplitudes contributed to low acoustic energy and power. The sound of T. truncatus exhibited inferior acoustic propagation parameters compared to the sound of O. tormota and other sounds under study hence not feasible in the startle of the mated female A. gambiae.
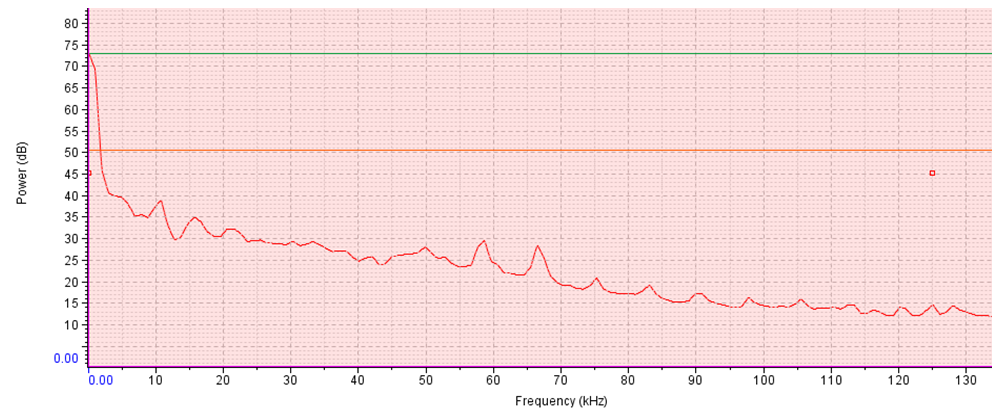 | Figure 8. Signal power spectrum of the sound of T. truncatus |
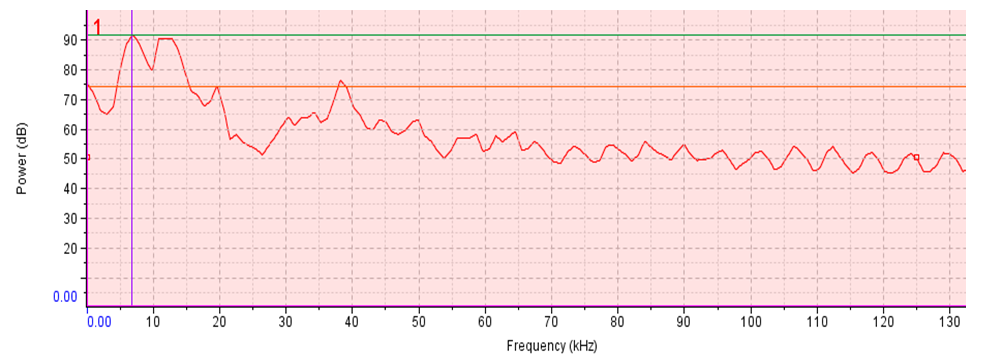 | Figure 9. Signal power spectrum of the sound of O. tormota |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- I am greatly indebted to my Universities Egerton University and Masinde Muliro University of Science and Technology for allowing me to conduct this study. Also, my sincere thanks are extended to Prof. Feng, Raimund Specht of Avisoft Bioacoustics, Pettersson Elektronik AB, Cornell Lab of Ornithology and Prof. Herve Glotin of Institut Universitaire de France for their kind donations and support. Many thanks go to Soccliff Ludeshi Isiaho and Felix Andambi, both of Masinde Muliro University of Science and Technology, Emmanuel Mbuka of Murang'a University and Bernard Agwanda of the National Museums (Kenya) for their support during the study. I also thank the Staff of Masinde Muliro University of Science and Technology (Department of Physics), KEMRI (Kisumu), Egerton University and Moi University for their encouragement and valuable input.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML