-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Biophysics
p-ISSN: 2168-4979 e-ISSN: 2168-4987
2017; 7(4): 60-68
doi:10.5923/j.biophysics.20170704.02

Microgravity and Nanomaterials
Melissa Palma-Jiménez1, Yendry Corrales Ureña2, Carlos Villalobos Bermúdez3, José Roberto Vega Baudrit4
1National Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Area of Nanobiotechnology, Costa Rica
2National Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Area of Nanotechnology, Costa Rica
3National Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Area of Mechatronics, Costa Rica
4National Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Area of Nanotechnology and Polymers, Costa Rica
Correspondence to: José Roberto Vega Baudrit, National Laboratory of Nanotechnology, Area of Nanotechnology and Polymers, Costa Rica.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Some experiments evidence that Microgravity (Micro-g) has influence in the morphology growth rate of materials and physiology of biological systems. Some Micro-g systems have been developed for experimentation under these conditions. The 2-D, 3-D clinostats and Random Positioning machines stimulate weightlessness. The aim of this review is to show the state of the art of the research related to Micro-g effect on inorganic and organic materials. Some noticeable examples related to changes in nanomaterial morphology; physiological effect, and cellular response in biological systems of plants cells as maize (Zea mays), rice (Oryza sativa) and bean (Phaseolus vulgaris); and osseous and muscular tissue will be shown. There has been identified the Micro-g as a new condition of significant structural and functional changes in the organization cellular.
Keywords: Organic and inorganic materials, Biological response, Morphology, Crystallization, 2-D clinostat
Cite this paper: Melissa Palma-Jiménez, Yendry Corrales Ureña, Carlos Villalobos Bermúdez, José Roberto Vega Baudrit, Microgravity and Nanomaterials, International Journal of Biophysics , Vol. 7 No. 4, 2017, pp. 60-68. doi: 10.5923/j.biophysics.20170704.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Recent advances in aerospace science have made it possible investigate the effect of Microgravity (Micro-g) within the confines of an earthbound laboratory [1-3]. Some experiments have evidenced that Micro-g alters the organization of inorganic materials as crystals [4] and mineralized structures [5]. Also, the morphology and physiology of biological systems; differentiation, proliferation, metabolism, and size are some of the cellular properties affected [6-8].The term Micro-g is frequently used as a synonym of weightlessness and zero-g, which indicates that the g-forces are not actually zero but just very small. Several experiments have been performed in Space or on Earth with simulators of Micro-g [9]. According to Eiermann et al. [10] experimental capacities in real Micro-g are limited due to high cost and due to the experimental time. Therefore, parabolic flights (with repetitive changes of Micro-g and hypergravity phases) or ground-based facilities (aiming to achieve conditions of simulated Micro-g) are often used to investigate samples under altered gravity conditions, which in turn provide a prerequisite for experiments intended to be flown in space.Experiments in Earth have made it possible to understand this phenomenon [4, 11]. Two and three-dimensional clinostat (2-D and 3-D respectively) and Random Positioning Machine (RPM) are tool used to simulate weightlessness [12]. Herranz et al. [9] explain that those tools are valuable for preparing spaceflight experiments, but they also facilitate stand-alone studies and thus provide additional and cost-efficient platforms for gravitational research. Fast-rotating 2-D clinostat is commonly used ground based facilities for exposition of inorganic and biological samples to simulated Micro-g conditions. This clinostat is able to generate high quality of reduced gravity conditions (≥0.001 g) and several studies have shown that results from various model systems using 2-D clinorotation are similar to results found in real Micro-g [10, 13-15].In the preparation for missions to Mars, basic knowledge of the mechanisms of growth and development of biological systems under Micro-g conditions is essential. Many studies have focused on the gravity effects on cell rigidity, including mechanisms of signal perception, transduction, and response in gravity resistance. These components of gravity resistance are related to the evolution and acquisition of responses to various mechanical stresses [16].The aim of the present review was to study the Micro-g effect on inorganic and organic materials; nanomaterials, physiological effect, and biological response on cell pants as maize (Zea mays), rice (Oryza sativa) and bean (Phaseolus vulgaris); also on osseous and muscular tissue.
2. Micro-g Systems: Clinostat Overview
- Gravity is the force of attraction between bodies. It is proportional to the mass of the objects, and inversely proportional to the square root of the distance separating those masses [17]. Just as any other planet, Earth has its own gravitational field, which applies a force described as an acceleration of 9.81 meters per second squared (expressed as 1 g as well) to every object on the surface of the planet. Micro-g is the equivalent of 1 µg (1x10-6 g), but the word is used to describe any other acceleration corresponding to gravity bellow 1 g on Earth’s surface [18].Micro-g occurs on any free falling object. Taking advantage of this phenomenon, some Micro-g systems have been developed for experimentation under these conditions, such as drop towers or parabolic flights of aircraft [9, 17]. There is one main problem for the general research of these effects: real Micro-g condition experiments are expensive and most of them have a limited effective time. Because of these limitations, special equipment was developed to generate simulated Micro-g conditions [10].Real Micro-g condition experiments are complex in execution, but easy to describe. A drop tower is not exactly an equipment, it is more like a complete facility composed of a long special tube or pit, and a laboratory for testing and analyzing results. Vacuum is applied to the tube, and the sample is dropped in free fall to examine the influence of Micro-g forces on it. Meanwhile, parabolic flights are composed of an aircraft performing an acrobatic maneuver, following a trajectory similar to the one a ball would describe when kicked strongly by a sportsman: a parabolic trajectory. This movement allows an environment of Micro-g for up to 25 seconds for any sample traveling inside the aircraft, which is later examined and evaluated by a group of experts [19].2-D, 3-D clinostats and RPM are some of the equipment utilized for Micro-g simulation. A 2-D clinostat has only one axis for rotation, and must be placed perpendicular to the gravity force direction in order to cancel the influence of the planet gravitational force [9, 20]. A 3-D clinostat has two axes for rotation, which must be perpendicular to each other. If the axes of the 3-D clinostat rotate at different speeds and directions, the device is considered a RPM [21, 22] which can be used to achieve completely different results compared to a 2-D or 3-D clinostat.A 2-D clinostat is a device able to achieve nullification of the gravity stimulus due to its rotational movement, which creates vector averaged gravity resulting on a net sum of all forces present equaling zero, but not an absence of gravity [13, 23, 24] (Figure 1). It is not a zero gravity system, but the gravitational forces are very small. In other words, the magnitude of the gravitational force of the planet cannot be changed or completely nullified, but its influence and effects can [25]. A great advantage of 2-D clinostat devices is the possibility to simulate not only a Micro-g environment, but also specific gravitational conditions (Figure 2). For example, an angle of positive 9 degrees off horizontal will produce a 0.18 g gravitational force, which is the gravity on the surface of the Moon. The same way, an angle of 17.5 degrees will generate a 0.33 g gravitational force, equivalent to Mars gravity [26]. However, it could generate centrifuge forces and particle oscillations that can be minimized using smaller reservoirs [1]. The clinostat model system (clinorotation) is an equipment that provides a vector-averaged reduction in the apparent gravity; the specimens are then forced to passively move along a circular path. In fact, it remains hitherto unknown if a specimen indeed receives functional weightlessness during clinorotation [27]. Gravity can produce effects related to displacement (motion) and/or deformation. The consequences of having weight are related to internal stress induced over an object manifested as tensile or compressive normal loads [28].
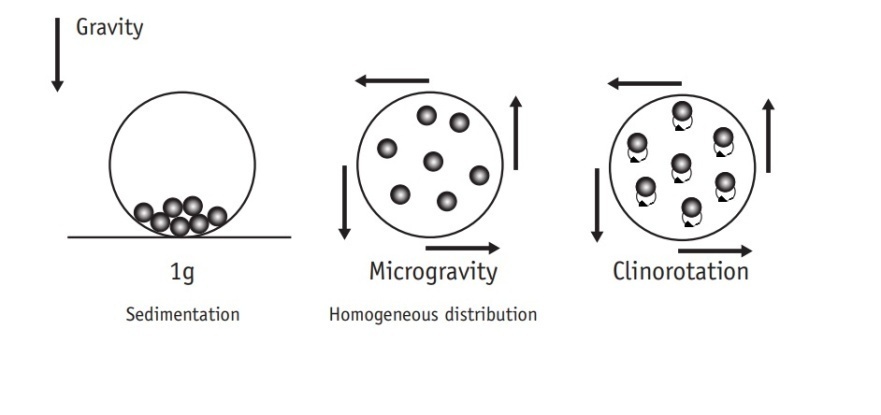 | Figure 1. Representation of the rotational movement of a 2-D Clinostat. Modified from UNOOSA [18] |
 | Figure 2. 2-D Clinostat equipment |
3. Influence of Micro-g in Nanomaterials and Thin Layers
- The research at nanoscale on Micro-g and space conditions has been focus on proteins and crystal growth [28]. Crystals of proteins as lysozyme, canavalin, serum albumin grew in space showed higher quality and generally of greater size. These results are associated with the movement and distribution of macromolecules in the contained fluid which is affected by the decrease in convection processes. Consequently, their mass transport and absorption [30-32].The Micro-g influence, using a clinostat, has been studied in fluids; mainly with suspensions of cell cultures. For this purpose, the clinostat was completely filled with liquid and let it to equilibrate. In the equilibrium process the rotational velocity of the is container wall is transferred radially inward until no relative fluid motion exists and the fluid rotates as a rigid body with the suspended particles being randomly distributed while following small circular paths [33]. Furthermore, recent studies suggest that cell surface charge density may also be modified in Micro-g. The complexities observed in Micro-g regarding electrostatic phenomena at the cell surface may also provide useful biomolecular engineering insight for improving separation technologies [34].The formation of ceria oxide have being reported by Ryu et al. [35] in solution and under Micro-g; showing that changes in gravitational forces and temperatures affected the properties of the solid [36]. To assess the effects of clinorotation on synthesis of nanoparticles Jagannath [33] used a 1-dimensional horizontal axis clinostat (1-D) and synthetized silver nanoparticles. The methodology used was simple. The container was placed in the center the horizontal axis of the clinonostat 1-D during certain time and the nanoparticles were synthetized. Metallic gold was prepared using ultrasound irradiationunder Micro-g and compared without Micro-g. A mean particle diameter of 10 nm and 80 nm was obtained in Micro-g and normal laboratory; respectively and an enhanced reduction rate in the reduction of gold chloride in Micro-g compared to the laboratory conditions [35, 37].Synthesis of biphasic Al/Al2O3 nanostructures by chemical vapor deposition under Micro-g showed that changes in the gravity produced differences in the bundle and cluster formation [38].Thin films have been grown in parabolic flight experiments. Hirai et al. [14] obtained multi-layered microporous honeycomb-patterned structures, which had never been obtained on earth ground conditions. They suggested the Micro-g as a new condition to be studied to modify processes and to obtain novel results. Li et al. [39] (1992) summarized the influence of Micro-g in thin films growth. They suggest of reduction of drainage of a liquid film and the possibility to obtain thinner, smoother liquid films.
4. Effect of Micro-g in Plants
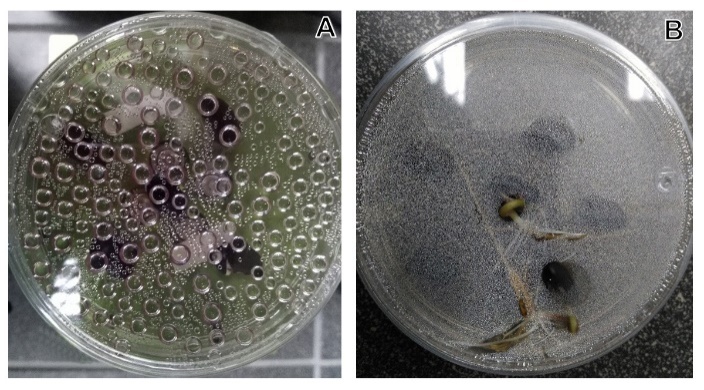
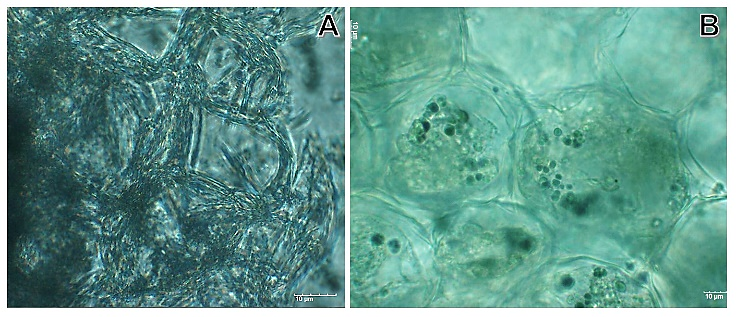
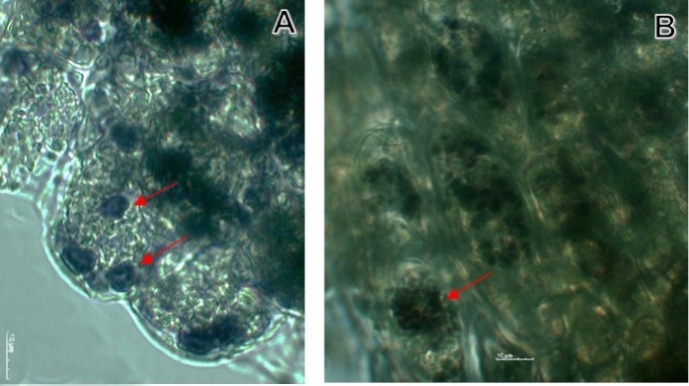
- Plant ancestors were directly exposed to gravitational acceleration of 1g on land, and only plants that successfully evolved a tough body with rigid cell walls were able to resist the force and survive [15]. The most typical gravitational response take place when a plant turned onto its side, the stem bends upwards and the root grows the opposite way [16]. Most studies on the effects of gravity alteration on plant growth and development have focused on the morphology and physiology [7]. The impact of Micro-g on cellular trafficking and energy state might alter plant cell construction and metabolism. The mechanisms of cell cycle regulation are altered due to growth in real and simulated weightlessness. This stress is set up from the very beginning of germination; and it shows that the intensity of the stress reduces the seedling grew [40]. It has seen in crops as maize (Z. mays) [41], beans (P. vulgaris) [42] and rice (O. sativa) [43].To understand this phenomenon under 2-D clinostat, we tested three last types of seeds, (Z. mays, O. sativa and P. vulgaris) in a 2-D clinostat. It presented a single rotational axis, which ran clockwise, perpendicular to the direction of the gravity vector. Next conditions were considered: temperature at 23°C, humidity at 80% and 15 rpm. Plants were grown up until the 8th day. After the incubation, seedlings were harvested and analyzed by Light Microscopy showing less development compared to control seeds (Figure 3).
5. Effect of Micro-g in Osseous and Muscular Tissue
- Simulating Micro-g on Earth is widely used in space life research. Understanding the impact of microgravity for the human body has taken great relevance on the last years [55]. How Micro-g affects the biology of human cells and the formation of cell cultures in real and simulated Micro-g is currently a hot topic in biomedicine [56].According to Kapitonova et al. [57] space flight experiments are very scarce, such conditions are delaying the advancement of research in areas such as cell biology and tissue engineering disciplines, which could profit tremendously from more frequent research options in a real Micro-g environment. Despite all limitations and contradictory reports, until the experiments are conducted under true Micro-g in space, validated earth-bound models will have to suffice [58].Studies from ground-based Micro-g simulators have revealed that many cell types, ranging from bacteria to mammalian cells, are sensitive to the Micro-g environment. The major affected cellular activities and parameters are cell proliferation, cell cycle, cell differentiation, apoptosis, genomic integrity and DNA damage repair. Ground-based Micro-g conditions can be achieved through the use of clinostats. Using such devices, detailed experiments have been performed towards the understanding of the effects of Micro-g on many cellular activities [59].The constant change in direction of the gravitational field may result in alteration of different signaling pathways, which may be different from those altered in response to a near-complete lack of any gravitational field [58]. Body movement is subject of interest for research on microgravity impact in humans. Unfortunately, there are no ground-based experiments for this matter, like clinostats or RPM. The most relevant system developed for these experiments is the opto-electronic system permanently installed on the International Space Station, dedicated exclusively for scientific observations on body movement under long-term microgravity conditions [60].Sayson [59] explain that Micro-g exposure may have adverse biological effects that ultimately weaken the structural components of the intervertebral disc and cause injury when re-introduced back to loading conditions in 1g. Paxton et al. [61] explain that effect of Micro-g lead to significant bone loss at the insertion point and a weakness in the join between tendon and bone. Exposure to the environment of space causes men and women of all ages to lose up to 1% of their bone mass per month due to disuse atrophy, a condition similar to osteoporosis.Back pain in Micro-g is known as one of the most common problems experienced by astronauts. This condition may be an indication of injury and may present as a possible detrimental factor to a crewmember’s ability to perform complex tasks. Micro-g exposure in itself is a unique condition variable to the astronaut population and therefore, a likely an important factor to be considered to cause group differences in Spinal stressors. In Micro-g, the body lengthens 4-6, 9-10 cm or about 2-3 times the normal diurnal increase (1-2 cm on Earth) [7].The mystery, for the moment, is what signals permit bone tissue to adapt to a weightless or an Earth (1 g) environment. Researchers do not yet know whether the biomechanical stimuli that are changed by directly affect osteoblast and osteoclast function or if other physiological factors such as hormone levels or poor nutrition contribute to bone loss. Discoveries made in the course of space biomedical research on bone are already contributing to a better understanding of osteoporosis and the treatment of bone mass loss on Earth as well as in space. The single most important contribution that NASA research has made to the understanding of bone deterioration in osteoporosis is heightened awareness of the importance of gravity, activity, and biomechanics that is, the mechanical basis of biological activity in bone remodeling [57].Zayzafoon et al. [58] explain that short-term modeled Micro-g (7 d) causes a decrease in bone growth and mineralization. Rodionova et al. [62] reported that, in addition to the decline in osteoid mineralization, there was a significant increase in the fibrotic zones in the bone, suggesting that osteoblasts were transformed to fibroblast-like cells. Skeletal abnormalities, including osteopenia, decreased bone formation, decreased mineralization, and reduced bone strength, have been identified in astronauts and animals after space flight, raising the concern that long-duration missions may have a negative impact on astronauts’ health [58]. Kapitonova et al. [57] point out that osteoblasts undergo a disintegration of their cytoskeleton, which may explain dramatic changes in size and shape of the cells and their surface specializations.Research on tissues under ground-based microgravity conditions provide valuable information that can’t be ethically derived from human subjects [63]. Experiments on tissues and individual cells to evaluate the impact of space exploration on the human body normally involve RPM for microgravity simulation and ionizing radiation machines to emulate the so called “galactic cosmic rays” and solar particle events. These experiments have the purpose of describing, in the most veracious way, the complete implications of space exploration for astronauts [55].Studies related to heart disease for example, have become a priority, due to the fact that this health issue claims more lives each year than any other diseases. It has been proven that cardiomyocytes derived from human pluripotent steam cells can provide cells to restore the lost cardiac muscle. According to recent studies, microgravity conditions can improve the production and survival of these cells, generating cardiomyocytes with 99% in purity and 90% viability [64].Micro-g has advanced the field of tissue engineering by facilitating diffusion of nutrients and oxygen. Under Micro-g conditions, aggregation of cells is also enhanced by induction of differentiative cellular signaling. These issues have led to achieving constructs larger than those engineered [11]. This indicates that simulated Micro-g can impair the early-stage repair of radiation-induced DNA lesions of embryonic stem cells [65].As first attempts of tissue engineering in Micro-g, rotating wall vessel bioreactors were used for formation of cartilaginous constructs composed of round cells, stem-cell-based therapies, collagen and glycosaminoglycan, and cardiac tissue constructs contracting spontaneously and synchronously. Constructs grown in Micro-g had the highest fractions of regenerated tissue and glycosaminoglycan content (the component required for cartilage to endure compressive forces) [11].Despite the progress in the field, it is still investigating which cellular and biochemical mechanisms are involved in the altered signal transduction and in the change of the cellular growth behavior [56]. In vitro system has been used as a model for investigation of molecular mechanisms of osteoblastogenesis and mesenchymal stem cell signaling. As such, it presents a unique opportunity to investigate molecular mechanisms for reversal of decreased osteoblastogenesis and tissues that may be translated to mechanisms highly relevant to human diseases [58].Since it has been given more attention to study this phenomenon on osseous and muscular tissue, the biomechanical properties and mechanical environment have been other focus of study. A 3-D growth, more resembling the tissue environment found in living organisms, is prevented by the presence of the gravitational field. For a scaffold-free 3-D tissue growth, it is therefore necessary to circumvent this problem by effectively eliminating the influence of the gravitational pull during cultivation cells will not settle like on Earth. This provides an increased opportunity for freely floating cells to interact with each other and develop 3-D structures. Various cell types were found to form 3-D structures. To understand the development of these structures, in vitro experiments using simulated Micro-g devices can provide valuable information about modulations in signal-transduction, cell adhesion, or extracellular matrix induced by altered gravity conditions. These systems also facilitate the analysis of the impact of growth factors, hormones, or drugs on these tissue [56]. Likewise, technologies as engineered bone constructs repair defects better than static counterparts after 24 weeks of in vivo implantation under dynamic culture [11], are alternatives to understand and improve alterations caused by Micro-g effects.
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
- Future space exploration research have being currently done for determining the differences and changes in biological and inorganic materials when in contact with Micro-g. New ideas for synthesis may include Micro-g as another parameter and to take advantage of the sedimentation deterioration to study the assembly and growing of metal oxides, metals and carbonate on surfaces from the nano, micro and macro scale size. Understanding the growth from the bottom to up is the base for creating new materials for space-based construction, repair and manufacturing. The study of the Micro-g from a nanoscale point of view is encourage because only few studies have been reported. The number of publications in the field have grown in the last years and there is a lot of work to be done to answer questions as: Which are the influence of mirogravity in the nucleation and growth of material in solution and/or in surfaces? How is the assembly at interfaces under Micro-g? How the processes lacking of convection will influence the interactions between molecules? Could the Micro-g favor the absorption of one type of material in a complex biopolymer mixture? Which are the differences in assembly between space and earth conditions and in Micro-g? Could nanotechnology understand the physiological phenomenon unexplored? Still need to be answered.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- We are grateful to Japan government and Ministry of Science, Technology and Telecommunications (Micitt, acronyms in spanish) because the 2-D clinostat donation.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML