-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Biophysics
p-ISSN: 2168-4979 e-ISSN: 2168-4987
2016; 6(2): 21-25
doi:10.5923/j.biophysics.20160602.03

An Analytical Approach to Anti-Parkinsonian Effect of Bacopa Monnieri in the Context of Protein Vibration
Brajagopal Majumder
Former Chairman, S.R.C - Tripura, India
Correspondence to: Brajagopal Majumder, Former Chairman, S.R.C - Tripura, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Parkinson's Disease (PD) belonging to neurodegeneration class is associated mainly with aggregation of alpha synuclein protein and degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. These result in memory loss, cognitive decline and motor impairment in patients. The disease has no complete cure till the date. Scholars are exploring the effects of Bacopa monnieri (BR) - Commonly known as Brahmi in Indian Aurvedic system on parkinson's disease from the view point of its neuroprotective and cognition enhancing effects. A good number of scholars are conducting study on the therapeutic aspects of B.M. Particularly on P.D. Here we have attempted to establish an analytical approach on the mechanism of chaperoning activity of HSP - 70 available in B.M on P.D particularly from the view point of protein vibration due to electrostatic force generated within proteins.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease, Alpha-Synuclein Protein, HSP-70, Caenorhabditis elegans, Neurodegeneration, Protein vibration, EEG rhythms
Cite this paper: Brajagopal Majumder, An Analytical Approach to Anti-Parkinsonian Effect of Bacopa Monnieri in the Context of Protein Vibration, International Journal of Biophysics , Vol. 6 No. 2, 2016, pp. 21-25. doi: 10.5923/j.biophysics.20160602.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, Huntington's and other multiple neurodegenerative diseases are associated commonly with the process of memory loss and decline of cognition. These as the scholars held, are particularly due to accretion of aggregated protein and selective death of particular neural cells [1]. Movement disorder and nonfunctioning of motor are found to be involved in parkinson's disease (P.D). Basically affected dopamine-producing neurons in the brain are the major causes of P.D. Dopamine are associated with motor activity. Hence, progressive loss of dopeminergic neurons results in muscle rigidity. Moreover, tremors and bradykinesia, memory loss and cognition disorders, mental disorders and personality failure (loss) are the common symptoms in P.D. patients. It is an age related disorder and the symptoms are found in population of above 60 years of age [2]. At present etiology of P.D. is not clear. However, alpha synuclein has been identified as the major protein in affected bodies. This protein plays key role in pathogenesis of both familial and sporadic P.D [4].No permanent cure for P.D. is still available. So far the drugs used are basically dopamine agonists and monoamines oxidize - B (MAO - B) inhibitors. However, these provide only symptomatic relief.Considering the challenges that several natural products are being used for treating various ailments, Bacopa Monnieri (BM) commonly known as Brahmi - an ayurvedic medicinal herb is, as the scholars held, found to act as anti-oxidant, anti-depressant, anti-inflammatory and anti microbial. [5-8] It is now also regarded as the most neurotonic and memory boaster [9]. Over all, it is tested for its beneficial effects on neurodegenarative diseases like P.D. etc. Ayurvedic use of B.M also extends now-a-days to the treatment of anxiety, epilepsy, bronchitis, asthma and gastric ulcers etc.The name brahmi is derived from Brahma- the mythical creator in Hindu mythology. The word brahmi is related to the brain which is responsible for creative activity. Bringing knowledge of the "Supreme Reality" also stands for literary meaning of brahmi. In India brahmi is used as a revitalizing herb by the Ayurvedic medical practitioners for almost 3000 years. [10]. It is small creeping herb. It belongs to scrophulariaceae family. It has got number of branches, small oblong leaves and light purple. It grows in damp and marshy lands or sandy areas near streams in tropical regions. Apart from India, it grows in Nepal, Srilanka, China, Taiwan and Vietnam, it is also found in Florida and other Southern parts of USA. A team led by Aamir Zakir (II) conducted an experiment with caenorhabditis Elegans to examine the effect of B.M on parkinson’s disease with the assumption that C. elegans many help in establishing an insights into therapeutic aspects of P.D. since their (60-80)% genes are homologous to human and it is also orthologs of P.D associated genes. The reason lies in the fact that dopaminergic neurodegeneration is induced by neurotoxins like 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) which in turn provides a pharmacological model for P.D. Basing on these facts, the team members conducted study on C. Elegans for examining the anti-parkinson's effect of neuron protective botanical species like B.M. However, other groups also conducted studies on anti-parkinson's effect of B.M. In a number of papers [12-14] the authors attempted to examine analytically the working mechanism of proteins responsible for learning and memory traces along with emotion, attention and super activity of the children from the view point of protein vibration characteristic due to external stimuli in the form of EEG rhythms. The authors [15] also conducted studies on the physical characteristics of aggregated prions (molecular weight 300 to 600 KD) and found responsible for Alzeimer's disease from the same approach of protein vibration.In all the papers it was established the fact that the number of vibration frequencies are less in protein of large molecular weights but these are responsible for stable memory while number of vibration frequencies are high in proteins of comparatively small and lower molecular weights. But these proteins are responsible for middle term and short term memories. For example, the author [16] explained the fact that insulin of small molecular weight (5KD) is responsible for diabetic type – 2.
2. Objectives
- Objective of the present study focuses the analytical approaches on the mechanism of disaggregation of alpha synuclein protein and its effects on P.D. from the view point of protein vibration due to electrodtatic potential.
3. Methodology
- Recently, Aamir Nazir (II) and others observed under confocal Microscope nearly 3.5 fold reduction (P < 0.05) in alpha synuclein protein aggregation with B.M exposed worms (NL5901). It was reported by D.K Choudhury [17] and others that B.M is able to induce chaperoning protein called HSP-70 when it comes in contact with brain cells. Aamir Nazir also observed that chaperoning protein namely HSP-70 has got an effect in leading to disaggregation of alpha synuclein deposits or it is capable to unfold the proteins that otherwise are the constituents of toxic aggregates. Thus HSP 70 found in B.M may act as a therapeutic agent of Parkinson's disease which reduces alpha synuclein protein aggregation responsible for the disease P.D.An attempt has been taken here to examine the dynamics of therapeutic activity of HSP-70 on alpha synuclein protein from the view point of protein vibration approaches taking into account of their respective electrostatic contribution. It is established fact that with respect to exposure to stressful conditions, some proteins are produced by the cells. These are presently known as Heat shock proteins (HSP). Formerly, they were related to heat shock [18]. But at present these are found to be exposed to cold, UV light and also in wound healing or tissue remodeling etc [19, 20]. These proteins are now used as (i) up regulator in stress and (ii) as chaperones. In this paper the author tried to examine the chaperoning effect of HSP-70 on aggregated alpha synuclein protein responsible for partkinson's disease by way of segment wise disaggregation of the same. In a paper [21] one of the authors developed an approach of association or dissociation of the constituent of protein molecules either by external stimuli or by internal electrostatic potential along with their vibration characteristics. A protein in its native state executes regular vibrations and these are due to electrostatic potential/force. Let us consider a protein molecule as shown in Fig. 1 where there classes of bonds are present. Covalent bonds in the chain itself, hydrogen bonds separating between the members of the chain and vanderwaal's bonds between residues of different chains. Each bond means that the atoms so attached have a position of equilibrium with respect to each other.
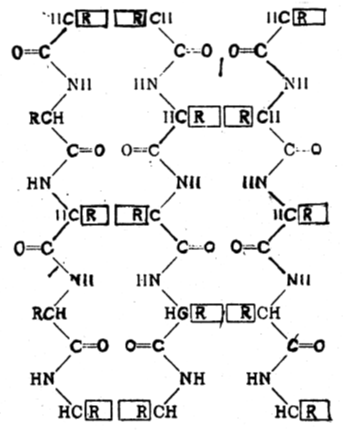 | Figure 1. Representation of the part of a protein molecule. R represents amino acids |
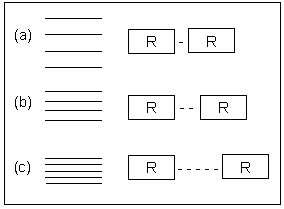 | Figure 2. Vibrations of protein shown in Figure (a) high molecular weight protein, (b) medium range molecular weight protein, (c) low molecular weight protein |
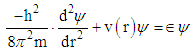 | (1) |
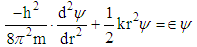 | (2) |
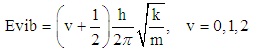 | (3) |
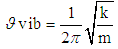 | (4) |
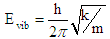 | (5) |
4. Results and Discussion
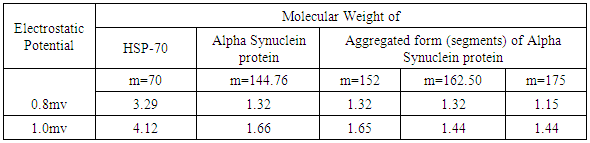
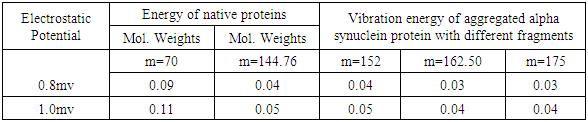
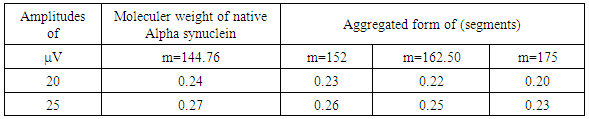
- It is an established fact that alpha synuclein protein in aggregated form that gets stiffened with reduction in energy is responsible for parkinson's disease. The molecular weight of this protein is 144.76 KD. This may be increased due to aggregation. The aggregation may follow self proteolytic activity of the protein within its full length of amino acids like(i) Protein of molecular weight 12.16KD with (14-133) amino acids.(ii) Protein of molecular weight 10.44 KD with (40-140) amino acids formed through C-and N-terminal truncation.(iii) Protein of molecular weights 7.27 KD with (72-140) amino acids formed through C-terminal.It was observed by the scholars that 7.27 KD fragment gets aggregated even faster than a full length alpha-synuclein protein. Practically speaking, autoproteolytic products play a role as intermediates or co-factors in aggregation of alpha synuclein protein, This kind of aggregation of alpha synuclein protein is basically responsible for parkinson's disease.Cure or symptomatic relief of the patient depends on the disaggregation of this alpha synuclein protein. It is expected that HSP-70 available (over expressed in presence of B.M) is able to undertake disaggregation of alpha synuclein protein. Now it is expected that fragment wise disaggregation in alpha synuclein protein may follow the process of self proteolytic activity as discussed. This means HSP-70 may disaggregate the aggregated alpha synuclein protein segment wise as in the case of aggregation. Under these conditions, an attempt has been taken here to evaluate frequency of vibrations and vibration energy thereof with the applications of equations (4) and (5). These vibrations are expected to be generated due to electrostatic potential. An accurate amount of electrostatic potential at the surface of protein may be measured by considering the average potential over the surface of a protein which follows the contour of the dielectric discontinuity between protein interior and the solvent. The magnitudes of this type of electrostatic potential is <30mV with respect to pH value [22]. However, for the interest of the paper, the magnitude of electrostatic potential has been considered in between (0.8 to 1) mv with respect to variable pH value.Vibration frequencies and energies of HSP 70, and alpha synuclein proteins have been calculated by considering electrostatic potential in two phases like 0.8 and 1 mv. The magnitudes of vibration frequencies and vibration energies so derived are tabled in Table 1 and Table 2.
|
|
|
5. Conclusions
- From the above analysis, it reveals that HSP-70 by its characteristics functions as intra-cellular champerones for aggregated alpha synuclein protein responsible for parkinson's disease. It is shown that HSP-70 helps in disaggregating the segment wise aggregation of alpha synuclein protein and thus helps to stabilize the protein conformation. The present analysis supports the findings of Aamir Nazir and others [11] that mother tincture (raw extract) of Bacopa monnieri (B.M) may decrease the aggregation of alpha synuclein protein and thereby may reduce its toxic out comes in the cells of C. elegans. Hence, identification and Isolation of proteins like HSP in Indian medicinal plants may take the lead in therapeutic treatment of a number of neurodegenerative diseases. Thus the studies conducted by the scholars [11] with respect to anti-parkinsonian effect of B.M along with our analytic approach may open a new dimension regarding the utility of Indian system of Ayurvedic medicine.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The author is thankful to Dr. U. C. De, Associate Professor, Dept. of Chemistry, Tripura University, Agartala, India for helpful discussion. The author is also thankful to Mr. Sanjay Kr. Pal for undertaking the computer work of the paper.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML