-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Biophysics
p-ISSN: 2168-4979 e-ISSN: 2168-4987
2013; 3(1): 26-32
doi:10.5923/j.biophysics.20130301.03
The Effect of Exposure of Dry and Soaked Grains of Durum Wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) to Static Magnetic Field
Amal Harb1, Ibrahim Abu-Al Jarayesh2
1Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, Yarmouk University, Irbid, Jordan
2Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Yarmouk University, Irbid, Jordan
Correspondence to: Amal Harb, Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, Yarmouk University, Irbid, Jordan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
To test the effect of a static magnetic field on the water uptake of wheat grains, dry and soaked wheat grains were exposed to a constant static magnetic field of 480 mT for different exposure times: 10, 30, 60, 120 min. After magnetic treatment, the grains were kept in water to imbibe and germinate. The results showed a significant decrease in water uptake and electrical conductivity of the leachate of soaked grains exposed to the magnetic field for 10 and 30 min. Seed germination and seedling growth were not affected by the magnetic treatment for 10, 30 and 60 min. The results suggest a positive effect of the magnetic treatment in reducing the amount of the imbibed water required for normal germination. Hence, this might help in the alleviation of the negative effect of drought on seed germination of crops in areas with limited water resources.
Keywords: Static Magnetic Field, Water Uptake, Electrical Conductivity, Durum Wheat
Cite this paper: Amal Harb, Ibrahim Abu-Al Jarayesh, The Effect of Exposure of Dry and Soaked Grains of Durum Wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) to Static Magnetic Field, International Journal of Biophysics , Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 26-32. doi: 10.5923/j.biophysics.20130301.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The effect of magnetic field on seed germination and plant growth has been studied since 1930[1]. Previous studies showed different results on plant response to magnetic treatment. Large body of literature showed a positive effect of the magnetic treatment on seed germination, seedling growth and plant growth[1-9]. The exposure of flax, rye, barley and oats to weak magnetic field stimulated germination and seedling growth[2]. Stimulatory effect on seed germination and seedling growth was also shown in barley[3]. In a study on tobacco seeds, seed germination was accelerated in the magnetically treated seeds compared to the untreated seeds[5]. The rate of germination and seedling growth of maize seeds exposed to strong magnetic field was enhanced[1]. The same effect was also shown in chickpea, sunflower and soybean in response to strong magnetic field of 50 – 250 mT[8, 9].A few studies showed a negative effect of the magnetic treatment on seed germination and other plant growth parameters[10, 11]. Pregermination exposure of dry durum wheat grains to 400 mT magnetic field resulted in the reduction of radicle emergence rate[10]. A delay in seed germination was resulted after exposure of wheat grains to 125 mT and 250 mT magnetic field for different time periods[11]. In general, the interaction of the static magnetic field with materials depends on external and internal factors. This interaction can be classified into two types: the first one, the static magnetic field (B) interacts with the magnetic moments (μ) of the different components of the material. In this regard, the energy of magnetic moments (potential energy) (U)) decreases by an amount given by the product of the value of the magnetic field multiplied by that of the magnetic moment (U= - μB). For a plant sample, trace elements have a magnetic moment, but the majority of its components are diamagnetic. The second type of interaction, which presumably plays a major role, is the interaction between the external magnetic field and the ionic currents in the biological sample (Lorentze force). This type of interaction results in the redistribution of ions, which changes the osmotic pressure and affects water movements in the biological samples as was shown in lettuce seeds[12, 13]. Both types of interactions affect the osmotic pressure of the biological samples, which is the main driving force of water movements in these samples. Seed germination is the first developmental stage in seed plant. It started by water uptake (imbibition), degradation of stored material and radicle emergence[14]. Water uptake is crucial for successful seed germination. The dry seeds absorb water to stimulate the biochemical reactions needed for the degradation of the stored macromolecules to generate enough energy for the growing embryo. One study showed the effect of magnetic treatment on seed - water relations. In lettuce seeds, a significant increase in water uptake starting at 8 hrs of imbibition was shown when seeds were exposed to 2, 6 and 10 mT for 10 min[13]. The main objective of this study is to test the effect of a static magnetic field on the water uptake of dry and soaked wheat grains. Because of the importance of mineral composition of wheat grains especially on ionic currents, which affect electrical conductivity and ultimately grain – water relations, the mineral composition of wheat grains and the electrical conductivity of grains' leachates of the control and the magnetically treated grains were determined.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
- Grains of durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) cv. Hourani 27 were provided by the National Center for Agriculture Research and Extension (NCARE)/Jordan.
2.2. Determination of Water Content of Wheat Grains
- Three samples of 10 grains/ sample were prepared and weighed. Then they were oven dried for 48 h at 80 ºC. After that, the dry weight was measured and water content of the grains was calculated as follows: Water content % = (Wi – Wd)/ Wi X 100Wi: initial weight before dryingWd: Weight after oven drying
2.3. Determination of Mineral Composition of Wheat Grains by Atomic Absorption
- The mineral composition of wheat grains was analyzed by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Dry wheat grains were ground to a fine powder. Two milligrams of the powder were digested with perchloric acid and nitric acid (1:4) solution in boiling water bath for 2 h. Then, the samples were left to cool. After that they were filtered, and the filtrate volume was made up to 100 ml with distilled water. Samples from the 100 ml solutions were analyzed by atomic absorption spectrophotometer (NOVA A300, Analytik Jena, Leybold, Germany).
2.4. Exposure of Wheat Grains to Static Magnetic Field
2.4.1. Description of the Permanent Magnet and Magnetic Field Measurements
- A permanent magnet of horseshoe shape was used in this study (Fig. 1A). The distance between the two poles is 1.6 cm (Fig. 1A and B). The diameter of each pole is 7.4 cm (Fig. 1C). The magnetic field was measured by Teslameter (UCNW and Yarmouk University, Leybold, Germany) at different heights of the area between the two poles. A constant and homogenous magnetic field of 480 mT between the two poles was found to cover 6.0 cm of the poles’ diameter (Fig. 1D).
2.4.2. Preparation of Wheat Grains for Magnetic Treatment
- A transparent glass tubes were filled with wheat grains for a height of 5.5 cm to be exposed to the homogenous magnetic field of 480 mT (Fig. 2A and B). Wheat grains were divided into two groups: dry and soaked. A total of 60 visibly healthy and uniform grains of each group were kept in transparent glass tube to be exposed to the magnetic field. Four tubes each containing 60 grains were prepared for the dry group and the same number of tubes were prepared for the soaked group. Control tubes of the dry and the soaked groups were prepared as mentioned above , but were not exposed to the magnetic field.
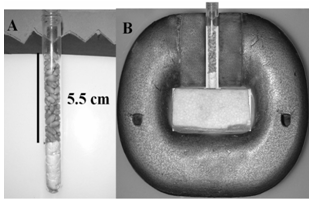 | Figure 2. Magnetic treatment of wheat grains. (A) A glass tube filled with wheat grains for a height of 5.5 cm, (B) Wheat grains during magnetic treatment |
2.4.3. Magnetic Treatment of Wheat Grains
- Magnetic treatment of wheat grains was carried out under laboratory conditions between 8- 11 AM under natural light and room temperature of 25 ± 2ºC. Grains in the transparent glass tubes were placed between the two poles of the permanent magnet to fit the region that generates a homogenous magnetic field of 480 mT (Fig. 2B). Four sets of grains in four tubes for the dry group were exposed to the magnetic field for different time intervals: 10, 30, 60 and 120 min. Another four sets of grains for the soaked grains were soaked in water during the magnetic treatment for different exposure times as mentioned above. The control sets of grains of the dry and the soaked groups were not exposed to the magnetic field. For the soaked groups, control grains were soaked in water for the same time interval as their corresponding treated grains.
2.5. Water Uptake of Magnetically Treated Grains
- After magnetic treatment, grains were distributed into 6 plates, about 10 grains/ plate. The initial weight (Wi) of grains in each plate was taken before they were soaked in water. After that, grains were kept on moistened filter paper in a plate, and then they were weighed every hour during the first 4 h of imbibition. A group of grains was kept soaked and they were weighed after 24 h. Water uptake (WU) was calculated as shown below:WU% = (Wt –Wi) /Wi X 100Wt: weight after specific time period. Wi: initial weight before soaking in water.
2.6. Electrical Conductivity of Grain Leachate
- In a separate experiment, dry and soaked wheat grains were magnetically treated as shown above. Then, the treated and untreated dry and soaked wheat grains (6 replicates of 10 grains per each replicate) were kept in distilled water for 1 h. After that, grains were discarded and the electrical conductivity of the leachates was measured by conductivity meter (CyberScan 500, Metex, New York, USA).
2.7. Germination of the Magnetically Treated Grains
- Germination of the treated and the untreated dry and soaked wheat grains was monitored after 48, 72, 96 and 120 h of imbibition and germination percentage was calculated:Germination Percentage = (No. of germinated seeds/ Total seed number) X 100Grains were considered germinated when the radicle length reached 1.0 mm.
2.8. Seedling Growth of the Magnetically Treated Grains
- The treated and the untreated dry and soaked wheat grains were left to grow in dark for 6 days at 25ºC. At day 7, seedlings were harvested and their length, fresh weight and dry weight were measured.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
- All data were analyzed by Student’s - T test. Differences with p-value less than 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Mineral Composition of Wheat Grains
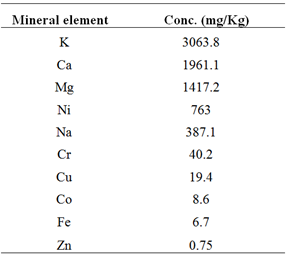
- To determine the elemental composition of wheat grains, 10 mineral elements were analyzed by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Table 1 shows the concentration of the different elements in wheat grain. The highest concentration of 3063.82 mg/kg was shown for potassium (K). Calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), nickel (Ni) and sodium (Na) also showed high concentration in wheat grain with values of: 1961.115, 1417.2, 762.95, 387.08 mg/kg, respectively. The concentration of iron (Fe) was 6.725 mg/ kg. Cr, Cu and Co showed intermediate concentration and Zn was the least abundant element in wheat grains.
|
3.2. The Effect of Magnetic Field of Wheat Grains on
3.2.1. Water Uptake by Wheat Grains
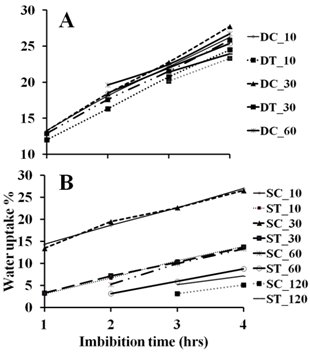
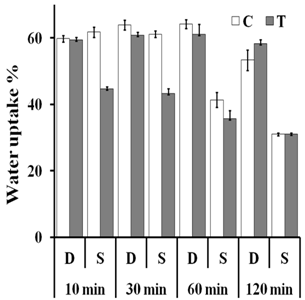
- Water uptake of the treated and the untreated dry and soaked grains during the first 4 h of imbibition was monitored. The treated dry grains for 10, 30, 60 and 120 min showed no significant change in water uptake compared to the untreated control (Fig. 3A). A highly significant reduction in water uptake was shown in the treated soaked grains for 10, 30 and 60 min (P-value < 0.01). Exposure of soaked grains to the magnetic field for 120 min had no effect on water uptake (Fig. 3B). Water uptake was also determined after 24 h of imbibition. For the all exposure times: 10, 30, 60 and 120 min, no significant change in water uptake of the treated dry grains was shown. Exposure of soaked grains to the magnetic field for 10 and 30 min resulted in a highly significant reduction in water uptake. Soaked grains exposed to the magnetic field for 60 and 120 min showed no significant change in water uptake (Fig. 4).
3.2.2. Electrical Conductivity of Grains Leachate
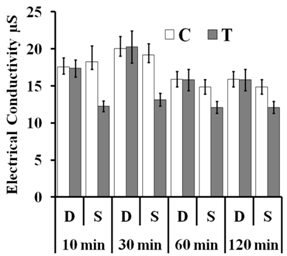
- The electrical conductivity of the treated dry grains was not different from that of the untreated control. Magnetic treatment of the soaked grains for 10 and 30 min resulted in a significant decrease in the electrical conductivity compared to the untreated control (P-values 0.03 and 0.007, respectively). The treated soaked grains for 60 and 120 min showed no significant change in their electrical conductivity compared to the untreated control (Fig. 5).
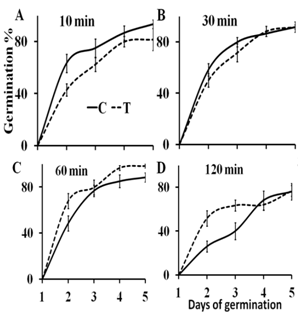
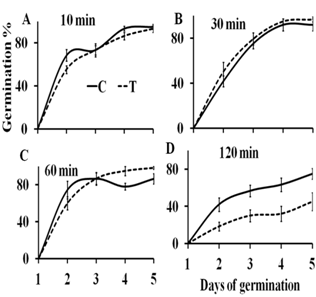
3.2.3. Seed Germination
3.2.4. Seedling Growth
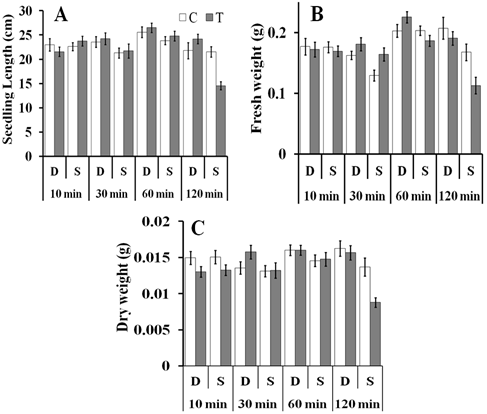
- To test if the effect of the magnetic treatment of grains persists until seedling stage, the treated dry and soaked grains were left to germinate and grow for 6 days. At day 7 seedlings were harvested and their length, fresh weight and dry weight were measured. Magnetic treatment of dry grains for 10, 30, 60 and 120 min had no effect on seedling growth in terms of seedling length, fresh weight and dry. Soaked grains that were magnetically treated for 10, 30 and 60 min showed no difference in seedlings length, fresh weight and dry weight compared to the untreated control. Treatment of the soaked grains for 120 min significantly reduced seedlings length, fresh weight and dry weight (P-values < 0.01) (Fig. 8A-C).
4. Discussion
- The elemental analysis of wheat grain revealed that for a grain of 1 mg contains approximately 1018 magnetic atoms (Fe, Ni and Co). Presuming that these magnetic atoms interact with magnetic field through their magnetic moments, thus their potential energy is changed and consequently water uptake is affected. Moreover, a substantial amount of elements such as: K, Ca and Mg may interact with the magnetic field through ionic currents (Lorentz force). This interaction results in a redistribution of ions and hence affects osmotic pressure, which in turn affects water uptake during imbibition phase.In this study, water uptake of wheat grains was significantly reduced in soaked grains that were magnetically treated with 480 mT magnetic field for 10 and 30 min. In a detailed study on the effect of magnetic treatment on seed-water relations, the main assumption was that static magnetic field affects the ionic currents and consequently the ionic distribution across the cell membrane[12, 13]. Hence, the osmotic pressure changes on both sides of the cell membrane, which affects water flux across the membrane[12, 13]. Water content of the seeds is also an important factor that influences plant’s response to the magnetic field. Water molecule has diamagnetic properties, which has a small negative response to the external magnetic field. The water content of dry wheat grains used in this study was 7%. A differential response to the magnetic field was revealed between dry and soaked grains. The soaked grains absorb water during the magnetic treatment, which increases their water content above 7% and explains the significant effect of the magnetic treatment on these grains compared to the dry grains.A significant reduction in the electrical conductivity of the leachate of wheat grains was resulted after exposure of soaked grains to 480 mT for 10 and 30 min. In chickpea, the reduced electrical conductivity as a result of enhanced integrity of seed coat membrane was suggested as an explanation for the significant improvement in seed germination[7]. But, the researchers showed no measurement of the electrical conductivity to support their explanation. The majority of the previous studies showed a significant increase in seed germination after the magnetic treatment of seeds. In this study, magnetic treatment of dry grains for 120 min enhanced seed germination at day 2 and 3 of germination. A significant reduction in seed germination was shown at day 2, 3 and 4 of germination after the exposure of soaked grains to the magnetic field for 120 min. The enhanced seed germination of dry grains after 120 min of magnetic treatment is consistent with the stimulatory effect of the magnetic treatment on seed germination and seedling growth of flax, rye, barley and oats[2]. The exposure of sunflower and chickpea seeds to magnetic field of 50 to 250 mT for 1 to 4 h resulted in the enhancement of germination and seedling growth[7, 8]. The same positive effect on seed germination was shown in tomato seeds exposed to 125 and 250 mT for 1, 10, 20 min and 24 h and continuous exposure during the whole germination process[15]. In disagreement, one study on two wheat cultivars revealed a negative effect of pregermination magnetic treatment on seed germination. Magnetic treatment of wheat grains with 125 and 250 mT for 10, 20, 30 and 60 min resulted in a reduced rate of germination[16]. This shows that at least three main factors play crucial role in seed response to magnetic treatment: the plant species, the strength of the magnetic field and the duration of exposure to the magnetic field. Our results on the effect of the magnetic treatment on seedling growth are consistent with the results of durum wheat, which showed that seedling biomass was not affected by exposure to 400 mT magnetic field[10].
5. Conclusions
- Magnetic treatment resulted in a significant decrease in the water uptake of germinating wheat grains. A detailed study of the effect of magnetic treatment on water –seed relationships will be invaluable in findings ways to improve plant growth at earlier stages of growth - seed germination stage - under normal and harsh conditions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors thank Miss Asma Alhasan and Miss Ghada Abu Ali for their technical help in the experiments.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML