-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Biophysics
2012; 2(3): 40-52
doi: 10.5923/j.biophysics.20120203.02
The Startling Effect of the Sound of C. Afra and A. Tormotus on the Female A. Gambiae
Mang’are P. A. 1, Maweu O. M. 2, Ndiritu F. G. 1, Vulule J. M. 3
1Physics Department, Egerton University. P. O Box 536, Egerton, Njoro. Kenya
2Physics Department, SEUCO , University of Nairobi. P. O Box 170-90200, Kitui. Kenya
3Entomology Department, Kenya Medical Research Institute Centre for Global Health Research. P. O Box 1578, Kisumu. Kenya
Correspondence to: Mang’are P. A. , Physics Department, Egerton University. P. O Box 536, Egerton, Njoro. Kenya.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The female Anopheles gambiae, a malaria vector, detects ultrasound by its antenna, initiating an attractive or repulsive response. Modern electronic mosquito repellents exploit this concept in attempt to control malaria, but have shown only 20 % effectiveness. This work determines the startle response of the female A. gambiae to recorded sound of C. afra and A. tormotus and optimum acoustic transmission parameters needed for the design of an effective electronic mosquito repellent. A bioassay involving 3-4 day old female A. gambiae bred and reared under standard conditions was conducted in a standard glass cage yielding evasive behavioural responses on exposure to varied frequencies. The 35-60 kHz sound of A. tormotus and C. afra, the optimum frequency range, evoked evasive responses in an average of 46 % and 23 % of the mosquitoes, higher than the reported 20 % effective repulsion of EMR sound. The evasive response was characterized by 58.5o antenna erection, physical injury, unusual rest and movement, fatigue and falls; attributed to neural stress and fear for predation. The steady increase in signal intensity, maximum and mean acoustic energy in the sound of A. tormotus over all frequency ranges yielded greatest startle response in the female A. gambiae.
Keywords: Startle Response, Optimum Frequency Range, Bioassay, Hardlock Key, Electronic Mosquito Repellent, Insecticide Treated Nets, Indoor Residual Spray
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Malaria, caused by a protozoan parasite of genius Plasmodium and transmitted by the female Anopheles gambiae, has led to high mortality and morbidity in Africa[6, 11]. The plasmodium parasites kill over a million people per year, and another 500 million people suffer from the clinical disease[12]. The female A. gambiae requires blood either from human or animal, for egg development and lays 30-150 eggs in 2-3 days. Control measures such as chemotherapy, chemoprophylaxis, vector control strategies and development of malaria vaccine had been employed with minimal success. Currently malaria vector control-methods preferred include the use of insecticide treated nets, indoor residual spray, destruction of mosquito breeding sites and use of mosquito repellents. However, the use of insecticides to control malaria vectors and drugs to control malaria parasites had failed due to build up of resistance in mosquitoes and the disease agent[10, 22]. The female A. gambiae detects ultrasound by its antenna, which can initiate an attractive or repulsive response[14, 16]. Electronic mosquito repellent devices exploit this concept in attempt to control malaria. The African sheath tailed bat; C. afra and the Chinese torrent frog; A. tormotus which are predators of mosquitoes, generate ultrasound naturally through vocalisation[3, 4, 7]. This work determines the startling effects of the sound of A. tormotus and C. afra on the female A. gambiae and optimum startle frequency range.Electronic mosquito repellents (EMR) that mimic ultrasonic calls from bats and male mosquitoes, A. gambiae have been designed and used in startling the female mosquitoes, A. gambiae. Earlier studies with electronic mosquito repellents yielded 20% significant repulsion on the female A. gambiae, due to a wide bandwidth of the sound rendering it less intense and ineffective[6]. Hence, there was need to investigate the sounds of C. afra and A. tormotus; determine their startle effect on the female A. gambiae and optimum startle frequency range.
1.1. Statement of the Problem
- Electronic mosquito repellents (EMR) that mimic ultrasonic calls from bats and male mosquitoes, A. gambiae have been designed and used in startling the female mosquitoes, A. gambiae. Earlier studies showed that the electronic mosquito repellents yielded only 20% significant repulsion on the female A. gambiae, due to a wide bandwidth of the sound rendering it less intense and ineffective. Hence, there was need to investigate the natural ultrasounds from the African sheath tailed bat, C. afra and the Chinese torrent frog, A. tormotus; determine their startle effect on the female A. gambiae and the frequency range of optimum startle.
1.2. Objectives
1.2.1. General Objective
- To determine the startling effect of the sounds of C. afra and A. tormotus on the female A. gambiae, a malaria vector and the frequency range of optimum startle.
1.2.2. Specific objectives
- i. To determine the startling effect of the sound of A. tormotus on the female A. gambiae.ii. To determine the startling effect of the sound of C. afra on the female A. gambiae.iii. To determine the sound frequency range of optimum startle on the female A. gambiae.
1.3. Justification
- Electronic mosquito repellents which mimic ultrasound from animal species are currently in use. However, these electronic mosquito repellents which generated wide bandwidth sound, yielded only 20% startle response in the female A. gambiae rendering them less effective. The African bat C. afra and the Chinese frog A. tormotus generated ultrasound naturally through vocalisation. Investigation into these sounds on their startle effect on the female A. gambiae had not been conducted and reported. It was therefore important to investigate the effect of these naturally generated ultrasounds on the behaviour of the Anopheles mosquito. This research was also conducted in order to establish whether there was an improvement on the 20% startle effect on mosquitoes by using ultrasound from C. afra and A. tormotus. Given that C. afra and A. tormotus were natural predators of mosquitoes, their sounds ware expected to effectively startle the female A. gambiae due to natural fear of predation. The behavioural startle response of the female A. gambiae elicited by the sound of C. afra and A. tormotus was also observed and the significant startle effect noted. The parameters determined from the current research are critical to electronic mosquito repellents designers since effective devices could be realized. Thus, the results provide an additional tool in mosquito control which is environment friendly.
1.4. Hypotheses
- 1. The sound of C. afara and A. tormotus do not have any significant startling effect to the female A. gambiae.2. The 10-34 kHz, 35-60 kHz and 61-90 kHz frequency ranges of the sound of C. afara and A. tormotus do not significantly startle the female A. gambiae.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- a) The A. gambiae mosquitoesThe A. gambiae mosquitoes were bred and reared at the Kenya Medical Research Institute Centre for Global Health Research laboratories, Entomology department at 60-80 % humidity, 25±2℃ temperature and light-day cycle of 12 hours light and 12 hours darkness. Three sets of 10 female A. gambiae, 3-5 day old were used in the study. Morphologically, the female mosquitoes have a sharp proboscis. They were fed on 10% glucose solution soaked in cotton wool.b) Sound of A. tormotus and Sounds of C. afraSix samples of the sound of A. tormotus were recorded individually for varied duration ranging from 1.60 s to 2.90 s using the 702 digital recorders from the Huangshan Hot springs, Anhui Province; China at a sampling frequency of 192 kHz which was converted to 500 kHz. Nine sound samples from C. afra were recorded from a colony in Kit-Mikayi caves, Kisumu; Kenya using the Avisoft recorder which consisted of the AUSG (Model 112) individually for a duration which varied from 45.00 s to 300.00 s at a sampling frequency of 500 kHz. c) EquipmentA computer running on Windows XP and office 2007 mounted with a sound card, hardlock key and sound output ports was used together with the Avisoft recorder during the first stage of the study. The Avisoft recorder, compatible with Windows XP, consisting of the AUSG (model 112) running on specific software RECORDER USG (rec_usg.exe), ultrasound microphone with high pass filter with cut-off frequency of 10 kHz was used in the recording of ultrasounds from the African bat, C. afra. During the second stage of the study, two Panasonic 8.0 Ω ordinary external speakers were used to play sound from a single source directed to the bioassay cage housing the female A. gambiae. The sound was amplified externally using an amplifier with an output power of 18 W, impedance of 4.0 Ω and separation ≥ 45.0 dB. The stopwatch option in the Samsung cell phone was used to capture activity duration. Softwares which included the Avisoft-SAS LAB Pro Version 5.1 and Batsound were installed in the laptop to facilitate automatic analysis of sound signals. An aspirator was used to transfer the female A. gambiae from the rearing cage to the bioassay cage and also remove them from it.d) The bioassay arena (Cage)A standard bioassay glass cage of dimensions 0.50 m by 0.25 m by 0.25 m was fitted with untreated mosquito net on the 0.25 m by 0.25 m faces and used in the bioassay. A small hole was perforated on both nets to allow the mosquito samples in and out the cage. The cage was divided into three equal sections; A, B and C. Section C was the central region of the bioassay cage. Section A was to the right whereas section B was to the left of the cage. Both the 25 cm by 25 cm faces of the cage were covered with untreated mosquito which had a 1.0 cm diameter hole perforated in the middle of the net. The two holes were covered with cotton wool. Either holes on side A or B could be used as mosquito release points. However, the hole on side B of the net was used as the mosquito release point for consistence whereas the hole on side A was closed permanently using a piece of cotton wool. Two speakers were attached to side A of the cage.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Recording and Filtering of Sounds
- (a). Recording of the Sound of Coleura afra and A. TormotusThe Avisoft recorder which consists of the AUSG (model 112) was used in recording the sound from C. afra. The condenser microphone capsule (CM16) which consisted of a thin metalized polyester film and a metal black plate was used in the study. It was connected to the AUSG (model 112) which was then connected to the laptop through one of the universal serial bus (USB) ports. The omnidirectional microphone was selected as a default microphone from the voice recording settings in the laptop. The time domain filter, Finite Impulse Response (FIR) was set to zero for both upper cut-off frequency (fuco= 0 kHz) and lower cut-off frequencies (flco= 0 kHz). The Fast Fourier transform (FFT) was also set to 512 and the Hamming window selected for the display. The temporal resolution overlap was also set to 50% with the graypal selected for the colour palette. The frame size was set to 100% for real time spectrogram parameters. The black and white box (B/W) was checked for the display option. The Avisoft-SAS LAB Pro, Version 5.1 software was started and the microphone directed to the source of sound. The gain on the AUSG (model 112) was adjusted to an appropriated level to avoid over modulation and the recording level from the computer set to 20 dB. Recording of the sound was started by pressing the record button on the AUSG. Nine sound samples from C. afra were recorded separately from a colony in Kit-Mikayi caves, Kisumu at a sampling frequency of 500 kHz for a duration varying from 45.00 s to 300.00 s. The sound samples were saved in the hard disc. The sound sample for the study was obtained by appending four quality sound samples and gave a 1754.07 s playback duration which was saved as “Coleura Sample 2.wav” hard disc. Six samples of sounds of A. tormotus were recorded individually for a total duration of 12.4 s using the 702 digital recorder from the Huangshan Hot springs, Anhui Province; China at a sampling frequency of 192 kHz. The sound samples were appended with a view of increasing playback duration using the AvisoftSASLab Pro Version 5.1 installed in the laptop computer hard disc. The appended sound was further appended to ensure a uniform duration of 1754.07 s and saved as “A. tormotus.wav” in the hard disc and the sampling frequency converted from 192 kHz to 500 kHz using AvisoftSASLab Pro Version 5.1 for compatibility. The samples were donated by Feng of Illinois University (USA) to facilitate the study.(b). Filtering of sounds samplesThe high pass filter, band pass filter and low pass filter, inbuilt in the AvisoftSASLab analysis software, were used to segment the appended sounds into appropriate frequency ranges essential for the study. All the sounds were subjected to a high pass filter with a cut-off frequency fco= 10 kHz in order to attenuate noises and a low pass filter with a cut-off frequency fco= 90 kHz. Three sound segments, namely, 10-34 kHz, 35-60 kHz and 61-90 kHz from every sound sample were required for the investigation. In order to obtain the 10-34 kHz the frequency range segment, the sounds saved as “Coleura Sample 2.wav” and “A. tormotus.wav” were subjected to a band pass filter with an upper cut-off frequency, fuco= 34 kHz and a lower cut-off frequency, flco=10 kHz. Frequencies below 10 kHz and above 34 kHz were gradually attenuated (amplitude = 0 i.e. off), allowing those in the range of 10-34 kHz (amplitude = 1, or on). Similarly, the band pass filter settings that yielded the 35-60 kHz and 61-90 kHz frequency ranges were flco= 35 kHz, fuco= 60 kHz and flco= 61 kHz, fuco= 90 kHz respectively. The settings were made from the time domain filter (FIR). These sound segments were also saved in the hard disc. The predator sounds could not be played by ordinary moving coil speakers hence the need to amplify them. The predator signal was internally amplified and then externally amplified before getting into the external speakers, placed 5 cm from the cage from side A. The speaker was set to face the cage. The amplitude modulation constant of the appended sound of A. tormotus was set to n = 0.8 i.e. Normalize at 80% for the entire duration for the A. tormotus signal. Similarly, the sound of C. afra was internally amplified by setting the 10-34 kHz to volume = 150 %, 35-60 kHz to volume = 130 % and the 61-90 kHz was set to 600 %. The sound was also 50 % amplified using an external amplifier in order to enhance diaphragm vibrations.
2.2.2. Bioassay
- The bioassay study involved determination of the effect of sound on the female A. gambiae by varying frequency in order to establish the frequency range where startling effect was optimum. Three to five day old female A. gambiae were used in the bioassay experiment. The female A. gambiae are characterized by large body size and affinity to blood meal. The criteria for the choice of the female A. gambiae included the size, status (fed or unfed), activity, mouth parts, resting position and age. The sound of the African bat C. afra and the Chinese frog A. tormotus were played separately through two external speakers attached to the cage at the end labelled A. The sound frequency ranges included 10-34 kHz, 35-60 kHz and 61-90 kHz, obtained by use of filters incooperated in the AvisoftSASLab software. The background noise, which was below 10 kHz, in the sound signals was attenuated using high pass filters. A set of ten, 3-5 day old female A. gambiae were released into the cage using an aspirator, one at a time, through the release hole in the net. The bioassay study involved investigation into the behaviour of one mosquito at a time when exposed to 10-34 kHz, 35-60 kHz and 61-90 kHz sound frequency ranges in prose. Investigation into the behavioural startle response in mosquitoes was conducted and the number of mosquitoes exhibiting the traits expressed as a percentage. The behavoural traits considered included directional body movement, jumps, hiding, raising of limbs, raising and lowering of body, body shaking associated with bending of abdomen, wing and limb rubbing, nature of body rest, mosquito movement, spreading of limbs, antennae erection, fatigue, rolling and loss of body parts. Antennae erection from the proboscis was measured from unmodified photo printout of the mosquito and the angle measured using a protractor. The antennae and proboscis were extrapolated for convenience in angle measurement by protractor. The second part of the bioassay involved playing of predator sound for various frequency ranges and the number of activities and duration, in this case flight (F) and rest (R) recorded correspondingly. The predator sound was played and simultaneously starting the stopwatch, observing and recording duration for activities. The observation of each mosquito took a total duration of 7016.28 s with each exposure taking 1754.07 s. The saved sound files of A. tormotus and C. afra were played from a laptop. The bioassay study involved the use of ten mosquitoes, one mosquito studied at a time. An initial observation was made on the mosquito without playing any of the predator sounds. That was the control experiment whose results were compared to those obtained when sounds were played. Each mosquito was exposed to sounds of frequency ranges 10-34 kHz, 35-60 kHz and 61-90 kHz, obtained by subjecting them to appropriate filters inbuilt in the AvisoftSASLab filters.
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
- The data collected from the bioassay study was analysed using the SPSS programme.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of the Initial Behavioural Response of the Female A. Gambiae Elicited by the Sound of A. Tormotus and C. Afra
- In the control experiments the female A. gambiae exhibited normal flight and moved freely within the cage and occasionally rested behind barriers. The mosquito samples maintained body rest at 45o from surface with wings laid along the abdomen as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 respectively. Normal body movement within the cage and at times none was exhibited. Rubbing of limbs and wings; and raising of limbs was also occasionally observed under the control experiment. Mosquitoes rested their limbs and proboscis on the net surface; the proboscis almost collinear with the antennae. The total number of mosquitoes exhibiting specific behavioural traits at the control was determined and expressed as a percentage. Table 1 shows the percentage of mosquito samples under the control experiment for sounds of A. tormotus and C. afra different behavioural traits. These behavioural responses of the mosquito samples at the control were an evidence of the use of active mosquito samples in the bioassay study.
 | Figure 1. The female A. gambiae at normal rest |
 | Figure 2. The female A. gambiae resting at angle β = 45o |
 | Figure 3. The female A. gambiae squeezing through barrier |
 | Figure 4. Mosquito antennae erection at 18.5o due to the 10-34 kHz sound of A. tormotus |
 | Figure 5. The female A. gambiae resting by side with antennae erection at 58.5o |
 | Figure 6. The female A. gambiae rests by side with erected antennae |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Figure 7. Mosquito resting on spread limbs with abdomen curved towards thorax |
3.2. Determination of the Mosquito Activity and Optimal Startle Frequency Range under the Influence of the sound of A. tormotus and C. Afra
- Recent findings based on mosquito landing rates on bare human body parts with ultrasound from functioning EMR yielded 20 % effective repellency[1, 6]. The mosquito activities in this section of the research was limited to flight and rest besides the behavioural response. All the mosquitoes exposed to predator sounds separately, had their flight time above the control. However, 6.7 % and 33.3 % of these mosquito samples displayed their flight time below the control when exposed to the sounds of A. tormotus and C. afra respectively. Fig. 8, Fig. 9, Table 3 and Table 4 show the relationship between flight duration with frequency for ten mosquitoes exposed to the sounds of A. tormotus and C. afra. When the mosquitoes were exposed to 10-34 kHz, 35-60 kHz and 61-90 kHz sound frequencies of A. tormotus, the flight duration increased by an average duration of 433.52 s, 352.52 s and 654.88 s respectively, above the control experiment as shown in Table 3. The mosquito samples exhibited a decline in the average flight duration by 18.249 s from the control in the 10-34 kHz of the sound of C. afra as shown in Table 4. This response was because of acoustic energy for the sound of C. afra declining by 2.534 Pa2s and the signal power also declining uniformly from -55 dB to -59 dB in the 35-60 kHz frequency range. The mosquitoes, under the influence of the sound of C. afra and A. tormotus spent most time in air in the 35-60 kHz and 61-90 kHz range as shown in Table 5 and Table 6 respectively. The mosquitoes exposed to sound of A. tormotus also yielded remarkable suspension time in the 10-34 kHz sound range. Ultrasound in the 35-60 kHz range, yielded significant acoustic energy as earlier reported with the sound from bats[19]. The sound of A. tormotus recorded progressive increased in energy from 10-34 kHz to 35-60 kHz. However, the energy declined as the frequency changed from 35-60 kHz to 61-90 kHz by 3.1445 Pa2s, recording an energy of 7.699 Pa2s, which was still higher than that of C. afra. The signal power maintained the maximum value at -100 dB with the minimum value less by -10 dB from the minimum power in the 35-60 kHz frequency range. Energy and power variation in predator sounds enhanced both flight and rest activities above the control for sample mosquitoes investigated. The mosquitoes’ behaviour in the 10-34 kHz and 35-60 kHz under the sound from C. afra and A. tormotus respectively was attributed to search for safe conditions within the cage. The mosquitoes were characterized by immobilization though they struggled to escape; occasionally taking long flights. The mosquitoes’ evasive behaviour was attributed to the stress caused on the nervous system and fear of predation[8, 16, 21].
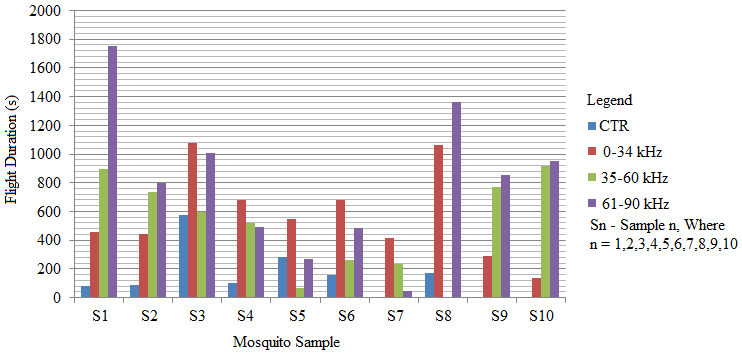 | Figure 8. The relationship between mosquito flight duration with frequencies of A. tormotus |
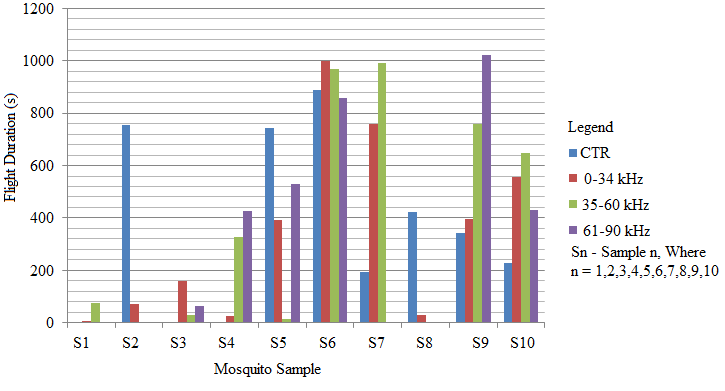 | Figure 9. The relationship between mosquito flight duration with frequencies of C. afra |
|
|
|
|
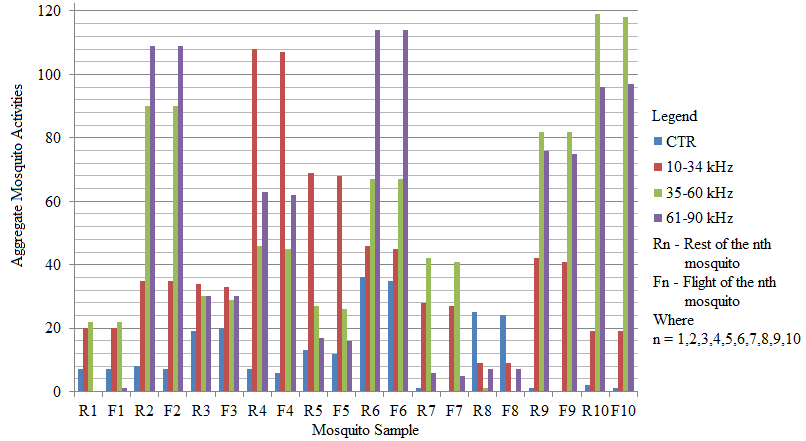 | Figure 10. The number of mosquito activities under varied sound frequencies of A. tormotus |
 | Figure 11. The total mosquito activity under varied sound frequencies of A. tormotus |
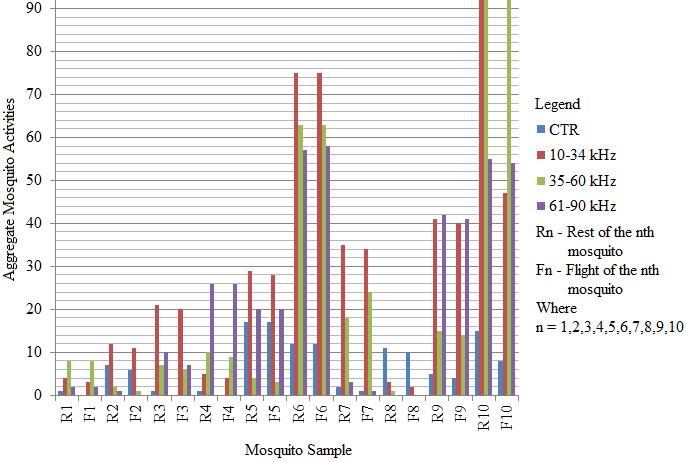 | Figure 12. The number of mosquito activities under varied sound frequencies of C. afra |
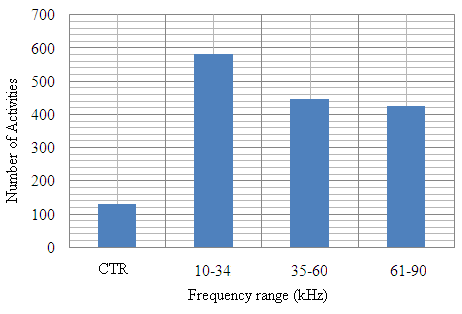 | Figure 13. The total mosquito activity under varied sound frequencies of C. afra |
|
|
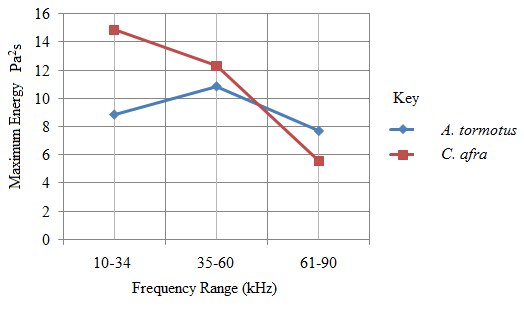 | Figure 14. The variation of predator maximum energy with frequency |
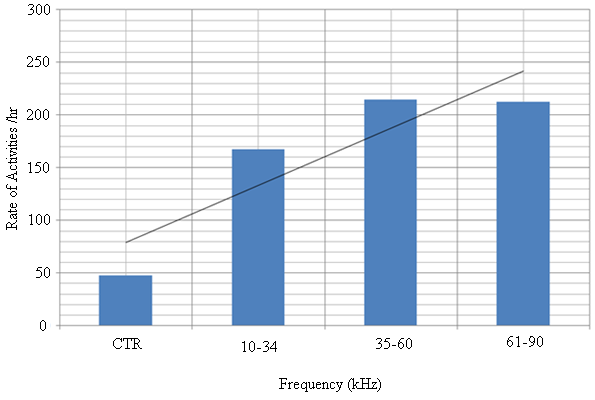 | Figure 15. The trend of rate of activity per hour with sound frequency ranges of A. tormotus |
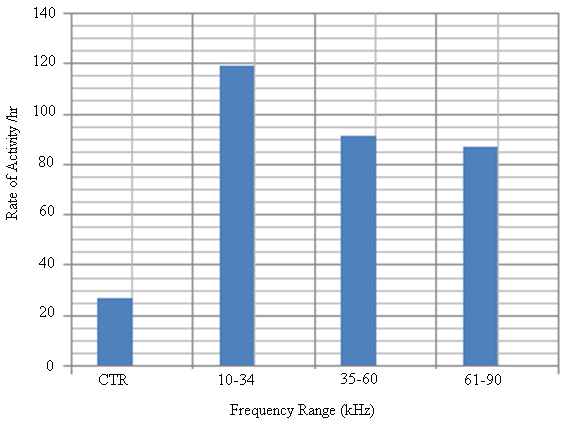 | Figure 16. The trend of rate of activity per hour with sound frequency ranges of C. afra |
|
4. Conclusions
- The average percentage of the mosquitoes affected by sound of A. tormotus and C. afra in the 35-60 kHz frequency range was 45.88 % and 22.94 % higher than the reported 20.0 % effective repulsion by EMR sound. The high response in the sound of A. tormotus was due to progressive increase in maximum and mean acoustic energy from the 10-34 kHz frequency range. Similarly, the signal intensity for A. tormotus in 35-60 kHz was greater than that of the 10-34 kHz frequency range. However, the energy and signal power for C. afra declined from their value in 10-34 kHz rendering it weak compared to the constant power of A. tormotus. The decline in the energy and power in C. afra yielded a reduced number of the mosquitoes affected by the ultrasound in this range. The sound of A. tormotus significantly startled the female A. gambiae compared to the sound of C. afra. The startle response in the female A. gambiae due to the sound of A. tormotus and C. afra was predominantly evasive, characterized by 58.5o antenna erection, unusual rest and movement, attributed to stress on nervous system and fear of predation. Secondary effects of the ultrasound on the mosquitoes included physical injury, fatigue and falls. The optimum startle frequency for the individual sound of A. tormotus and C. afra on the female A. gambiae was 35-60 kHz.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Special thanks go to Prof. Feng, who donated sound samples for the Amolops tormotus from Illinois University, free of charge and continued to offer technical help on interpretation. May I specially extend my sincere appreciation to Raimund Specht of Avisoft Bioacoustics; Germany, for donating the ultrasound recording system, sound recording and analysis software which were the backbone of this research work. Raimund offered continued support throughout the research period. His wide experience in acoustics helped me come up with logical deductions. This work would not have been possible without their material and technical support besides availing their honest critique of the work. Many thanks go to Pettersson Elektronik AB and Acoustics; Australia, for donating the Batsound software and microphone essential in generating acoustic parameters. I also thank the Kit-Mikayi staff for allowing me record sound samples of Coleura afra. I feel greatly indebted to the KEMRI/CDC fraternity for providing samples of the female A. gambiae and facilities for the bioassay study. Special appreciations are extended to Dr. Atieli for his tireless effort in offering essential critique of this document. I appreciate Mr. Amito of KEMRI/CDC for his valuable advice and tireless support. I also thank Mr. Agwanda of National Museums (Nairobi), head of Mammalogy department for classifying the Microbats in Kit-Mikayi caves.
References
| [1] | Ahmad, A., Subramanyam B. and Zurek, L. Responses of mosquitoes and Germancockroaches to ultrasound emitted from a random ultrasonic generating device. Entomologia Experimentaliset Applicata. 123: Pp 25–33. (2007). |
| [2] | Balanis, A.C. Antenna Theory Analysis and Design. John Wiley and Sons, USA. Pp 1-120. (1982). |
| [3] | Barlow, J. Rare Chinese frogs communicate by means of ultrasonic sound. Inside Illinois. 25. P1. (2006). |
| [4] | Berry, P. Y. The food and feeding habits of the torrent frog, Amolops larutensis. Journal of Zoology. 149: Pp 204–214. (1966). |
| [5] | Craig, B.G. and Nijhout, F.H. Reproductive isolation in Stegomya mosquitoes. Entomologia. Experimentalis Et Applicata. 14: Pp 399-412. (1971). |
| [6] | Enayati, A., Hemingway, J. and Garner, P. Electronic mosquito repellents for preventing mosquito bites and malaria infection. The Cochrane Library Journal. 3: Pp 1-16. (2010). |
| [7] | Feng, A.S., Narins, P.M., Xu, C.H., Lin, W.Y., Yu, Z.L., Qiu, Q., Xu, Z.M. and Shen, J.X. Ultrasonic communication in frogs. Nature, International Weekly Journal of Science. 440: Pp 333-336. (2006). |
| [8] | Forrest, T.G., Farris, H.E. and Hoy, R.R. Ultrasound acoustic startle response in scarab beetles. The Journal of Experimental Biology. 198: Pp 2593 – 2598. (1995). |
| [9] | Gerlach, J. Social vocalisations in the Seychelles sheath-tailed bat Coleura seychellensis. Le Rhinolophe. 18: Pp1-6. (2007). |
| [10] | Ghaninia, M. Olfaction in mosquitoes: Neuroanatomy and electrophysiology of the olfactory system. Doctoral dissertation. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences. (2007). |
| [11] | Hay, S. I., Guerra, C. A., Gething, P. W., Patil, A. P., Tatem, A. J., Noor, A. M., Kabaria, C. W., Manh, B. H., Elyazar, I. R. F., Brooker, S., Smith, D. L., Moyeed, R. A. and Snow, R. W. (2009). A world malaria map: Plasmodium falciparum endemicity in 2007. PLoS Medicine Journal. 6: Pp 281 - 291. |
| [12] | Hillyer J. F. Transcription in mosquito hemocytes in response to pathogen exposure. Journal of Biology. 8: Pp 1- 4. (2009). |
| [13] | Martin, C. G. and Daniel, R. Nanometre-range acoustic sensitivity in male and female mosquitoes. The Royal Society Journal. 267: Pp 453-457. (2000). |
| [14] | Martin, C.G. and Daniel, R. Active auditory mechanics in mosquitoes. The Royal Society Journal. 268: Pp 333-339. (2001). |
| [15] | Maweu, O. M., Deng, A. L. and Muia, L. M. A Comparative study of A. gambiae male mosquito’s response to frequency modulated[FM] and pulse modulated[PM] waves at different acoustic frequencies and distances. Indonesian Journal of Physics. 20: Pp 81-84. (2009). |
| [16] | Mohankumar, D. Ultrasound and insects. Electronics and Animal Science. http://electroschematics.com/. Accessed on 14-June-10 10:00 AM. (2010). |
| [17] | Monto, G. Bats. Current Science Journal. 99: Pp 13-14. (2010). |
| [18] | Morton, C. K. and Offenhauser, W. The first field tests of recorded mosquito sounds used for mosquito destruction. American Journal of Tropical Medicine. 29: Pp 811-825. (1949). |
| [19] | Narins, P. M., Feng, A. S., Lin, W., Schnitzler, H., Denzinger, A., Suthers, A. R. and Xu, C. Old World frog and bird vocalizations contain prominent ultrasonic harmonics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115: Pp 910–913. (2004). |
| [20] | Robert, D. and Jackson, J.C. Nonlinear auditory mechanism enhances female sounds for male mosquitoes. 103. Pp 16619-16620. (2006). |
| [21] | Roxanne, R.C. Mosquito control devices and services for Florida homeowners. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in171. Accessed on 03-July-10 4:22 PM. (2008). |
| [22] | WHO. World malaria report 2009: Impact of malaria control. P39. http://wholibdoc.who.int. Accessed on 26-May-10 3:18 PM. (2009). |
| [23] | Yager, D. D., Cook, A. P., Pearson, D. L. and Spangler, H. G. A comparative study of ultrasound-triggered behaviour in tiger beetles (Cicindelidae). J. Zool. 251: Pp 1-14. (2000). |
| [24] | Zwiebel, J. L. and Pitts, R. J. Antennal sensilla of two female Anopheline sibling species with differing host ranges. Malaria Journal. 5: Pp 1-12. (2006). |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML