-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Bioinformatics Research
p-ISSN: 2167-6992 e-ISSN: 2167-6976
2018; 8(1): 12-18
doi:10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20180801.02

In Silico Analysis of Non Synonymous SNPs in DHCR7 Gene
Hind A. Elnasri, Afra M. Al Bkrye, Mona A. M. Khaier
University of Bahri, Khartoum North, Sudan
Correspondence to: Hind A. Elnasri, University of Bahri, Khartoum North, Sudan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

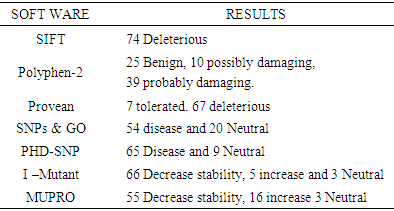
DHCR7 gene (7-dehydrocholesterol reductase) provides the necessary instruction for synthesis of the enzyme 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase which is needed for cholesterol synthesis. Cholesterol plays an important role as a precursor for synthesis of hormones, bile acids and acts as a structural component of cell membranes and myelin. One of the main health problems resulting from mutations in this gene is Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome. It is an autosomal recessive inheritance disease characterized by failure to thrive, intellectual disability and multiple anomaly. Aims: This study aimed to investigate the effect of non-synonymous SNPs (ns SNPs) of DHCR7 gene in protein function and structure using different computational software. Materials and Methods: Different nsSNPs and protein related sequences were obtained from NCBI and ExPASY database. Deleterious and damaging effect of SNPs were analyzed using SIFT, Polyphen 2, Provean and SNPs & GO software. Protein stability was investigated using I-Mutant and MUpro software. The interaction of DHCR7 with other genes was studied using GeneMANIA software. The structural and functional impact of point mutations was predicted using Project Hope software. Results: DHCR7 gene was found to have an association with 20 other genes such as TM7SF2 and LBR using GeneMANIA. After retrieval of SNPs from the NCBI database, 437 SNPs were classified as non synonymous SNPs (missense). Following analysis using SIFT software, a total of 74 SNP were predicted to have a deleterious effect. Using Polyphen– 2 (25 SNPs) were found to be benign, (11) were found to be possibly damaging, (39) SNPs were found to be probably damaging. Regarding the protein stability, using I-Mutant and MUpro software revealed that 55 SNPs showed decrease protein stability. To confirm the SNP effect two software were also used SNPs & GO and PHD-SNP. The results of these two software showed that 53 SNPs had a disease effect. After analysis using the different software, a total of 33 SNPs were found to be disease related. Some of these SNPs have previously been reported using DNA sequencing and were confirmed using the different software. Some new SNPs were identified to be disease related.
Keywords: DHCR7 gene, In silico analysis, Non synonymous SNP, SIFT, Polyphen-2, GeneMANIA
Cite this paper: Hind A. Elnasri, Afra M. Al Bkrye, Mona A. M. Khaier, In Silico Analysis of Non Synonymous SNPs in DHCR7 Gene, American Journal of Bioinformatics Research, Vol. 8 No. 1, 2018, pp. 12-18. doi: 10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20180801.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- DHCR7gene (7-dehydrocholesterol reductase) is also known as 7-DHC reductase, D7SR, delta-7-dehydrocholesterol reductase, DHCR7_HUMAN and sterol delta-7-reductase (Genetics Home Reference, 2017).The DHCR7 gene is located in chromosome 11 at position 13.4. It spans 14 kb and consists of two 5’ non-coding exons and seven coding exons (Fitzky et al., 1998). This gene is expressed mainly in the adrenal glands, liver and brain. The product of this gene is the DHCR7 protein, which is composed of 475 amino acid and weighs 54.5 kDa. This protein is localized in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, and contains nine putative transmembrane domains, a large intracellular loop (the fourth cytoplasmic loop) and a highly conserved C-terminal domain (Fitzky et al., 1998; Moebius et al., 1998).Among the main health problems resulting from mutations in this gene is Smith–Lemli–Opitz Syndrome (SLOS, OMIM #270400). It is an autosomal recessive inherited disease characterized by microcephaly, cleft palate, syndactyly of toes 2/3, polydactyl, visceral malformations, variable anomalies of the heart and kidneys, ambiguous genitalia in males failure to thrive, intellectual disability. Clinically some SLOS cases can be presented with mild dysmorphism (anatomical malformation) with moderate mental impairment or severe situations such as intrauterine death (Smith et al., 1964, Kelley and Hennekam, 2000; Witsch-Baumgartner et al., 2001). These abnormalities can be due to lack of cholesterol per se, or accumulation of toxic precursors or side products, deficiency of cholesterol hormones during embryogenesis or combination of these factors (Witsch-Baumgartner et al., 2001). A common anomaly in SLOS patients is the genital anomalies which is seen in more than 70% of patients. The mechanism of genital anomalies in SLOS patients has not been elucidated, it is suggested that it might be caused by the lack of substrate needed to produce adrenal and testicular steroids owing to low-cholesterol synthesis. This phenotype occurs usually before birth, and thus cholesterol treatment after birth is unlikely to be beneficial for treatment of such condition. However, early diagnosis and treatment of SLOS is important because cholesterol treatment appears to improve physical and neurological development (Mayuko et al., 2017).The incidence of SLOS varies between different populations studied due to several factors such as the heterogeneity of the population under study, the biochemical methods used for identification and the alleles assessed. Current estimates of SLOS indicates its more common among European Caucasian that are descent from Northern and Eastern Europe (1%-3%) and a lower incidence is described in individuals of Asian or African descent ( Kelley and Hennekam, 2000; Nowaczyk et al., 2012, Yunhui et al., 2018).The non-synonymous SNPs (nsSNPs), also called as missense variants are particularly important as they result in changes of the translated amino acid residue sequence and thus may affect the protein function by reducing protein solubility or by destabilizing protein structure (Chasman and Adams, 2001). More than 160 mutations have reported regarding DHCR7 (Witsch-Baumgartner et al., 2000, Wassif et al., 2005).The objective of this study is to investigate the nsSNPs in the DHCR7 gene and the effect they may impose on the protein structure and function using various computational software.
2. Material and Methods
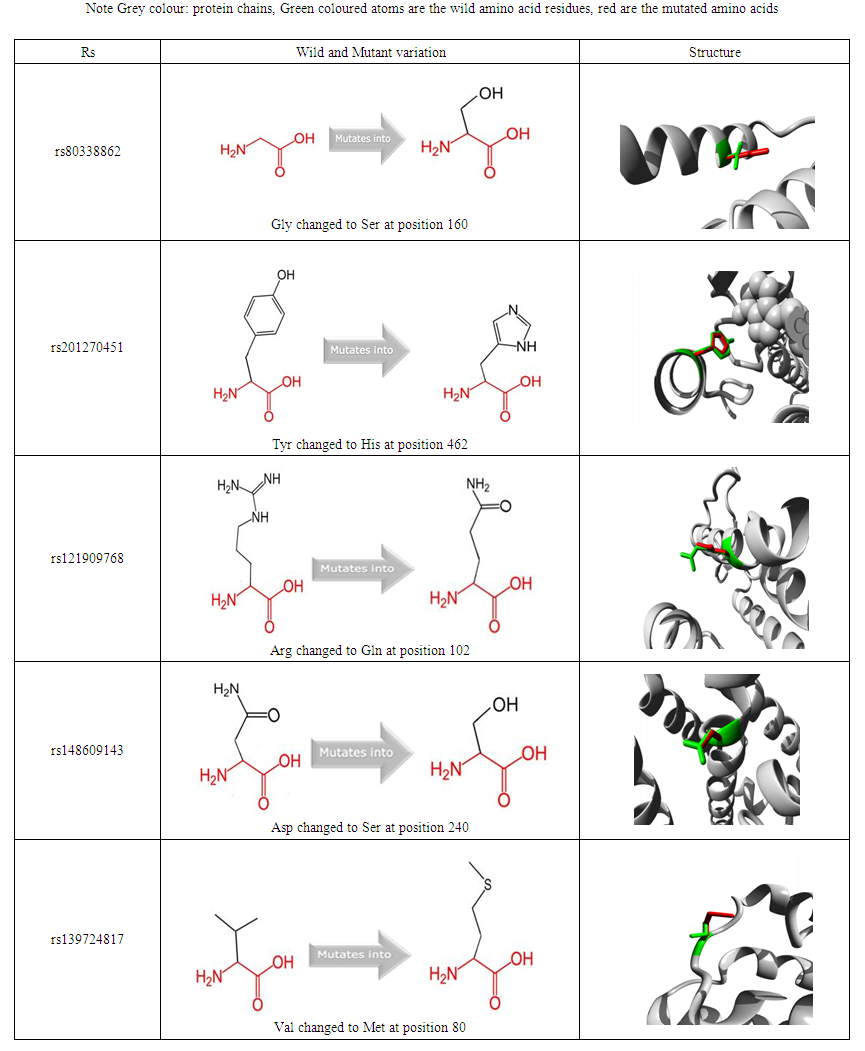
- 2.1. Data retrieval: Using the dbSNP (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/), information regarding SNPs of DHCR7 gene were obtained. Interaction of this gene with other genes was investigated using GeneMANIA. Further analysis was carried out using different software. Functional effect of the SNPs on the protein was investigated using SIFT, Polyphen-2, Provean, SNPs& GO and PHD-SNP. The stability of the protein as the result of the mutation was studied using I- Mutant and MUPro, and lastly the effect of the SNPs on the structure was predicted using Project hope.2.2. Gene MANIA (http://www.genemania.org) (Khalid et al, 2013) It is a web interface that finds other genes related to a set of input genes, using a very large set of functional association data. Association data include protein and genetic interactions, pathways, co-expression, co-localization and protein domain similarity.2.3. SIFT (Sorting Intolerant from Tolerant) http://blocks.fhcrc.org/sift/SIFT.html (Hu et al, 2012).It is an online tool that predicts if an amino acid substitution affects protein function or not by using sequence homology. It performs analysis based on different algorithms and it interprets the homologous sequences using the Swiss-Prot (version 51.3) and TrEMBL (version 34.3) (Kumar et al., 2009). It gives scores to each amino acid residue ranging from zero to one. The threshold intolerance score for SNPs is 0.05 or less.2.4. Polyphen-2 (Polymorphism Phenotyping v2) http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/It is used to predict the possible impact of an amino acid substitution on both structure and function of protein by analysis of multiple sequence alignment and protein 3D structure (Adzhubei et al. 2013). It estimates the position- specific independent count score (PSIC) for every variant and then determines the difference between them, the higher the PSI, the higher the functional impact of the amino acid on the protein function may be. Prediction outcomes could be classified as probably damaging, possibly damaging or benign according to the score ranging from (0–1). 2.5. Provean (Protein Variation Effect Analysis). (http://provean.jcvi.org/index.php). It is a software tool which predicts whether an amino acid substitution has an impact on the biological function of a protein. Prediction outcomes could be classified as tolerated or deleterious.2.6. SNPs &GO (Single nucleotide polymorphism & Gene Ontology), PHD-SNP (http://snps.biofold.org/snps-and-go) (Calabrese et al, 2009). SNPs& GO is an accurate method that, starting from a protein sequence, can predict whether a variation is disease related or not by exploiting the corresponding protein functional annotation. SNPs& GO collects in unique framework information derived from protein sequence, evolutionary information, and function as encoded in the Gene Ontology terms, and outperforms other available predictive methods. (Calabrese et al, 2009) The protein sequences is submitted in FASTA format that is obtained from UniproktB / ExPASY after submitting the sequence the mutations were submitted in the XPOSY format where X and Y are the wild-type and mutant residues respectively. The result is shown as Neutral or disease. PHD- SNP results are presented as part of SNPs& GO output.2.7. Protein stability prediction: For studying the effect of mutations on protein stability two software were used:a) I–Mutant 3.0 (http://gpcr2.biocomp.unibo.it/cgi/ predictors/I-Mutant3.0/I-Mutant3.0.cgi) It is a neural network based tool, predicts the change in the stability of the protein upon mutation (Capriotti et al., 2005). The output is obtained in the form of protein stability change upon mutation and Gibbs-free energy change (DDG) either increased or decreased stability.b) Mupro (http://mupro.proteomics.ics.uci.edu)It is a set of machine learning programs to predict how single-site amino acid mutation affects protein stability. It is developed based on two machine learning methods: Support Vector Machines and Neural Networks (Cheng et al, 2005). The output is either increased or decreased stability.2.8. Project Hope (http://www.cmbi.ru.nl/hope/) (Hanka et al, 2010) It is an automatic program that analyzes the structural and functional effects of point mutations. HOPE collects information from a wide range of information sources including calculations on the 3D coordinates of the protein by using WHAT IF Web services, sequence annotations from the UniProt database, and predictions by DAS services. HOPE builds a report with text, figures, and animations.
3. Results
- In this study DHCR7 gene was found to have an association with 20 other different genes. Among the most important ones is the TM7SF2 gene which is also a trans membrane protein (Figure 1. and Table 1). The physical interaction and co expression of this gene with other related gene is shown in Figure 1.
|
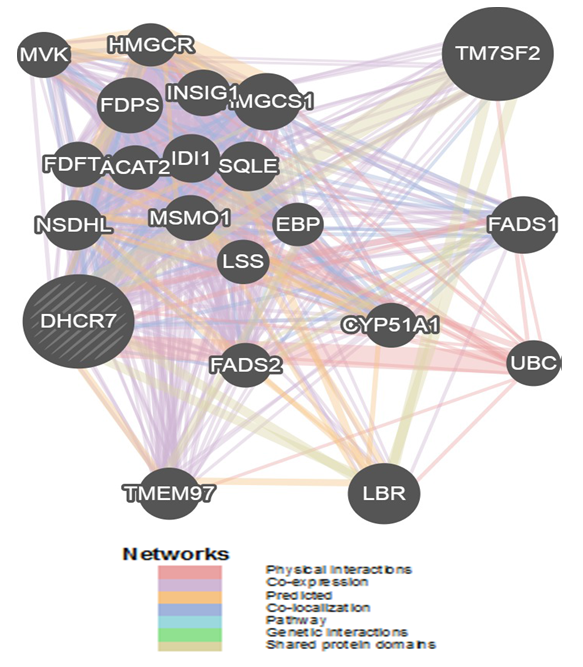 | Figure 1. GeneMANIA result for DHCR7 Gene |
|
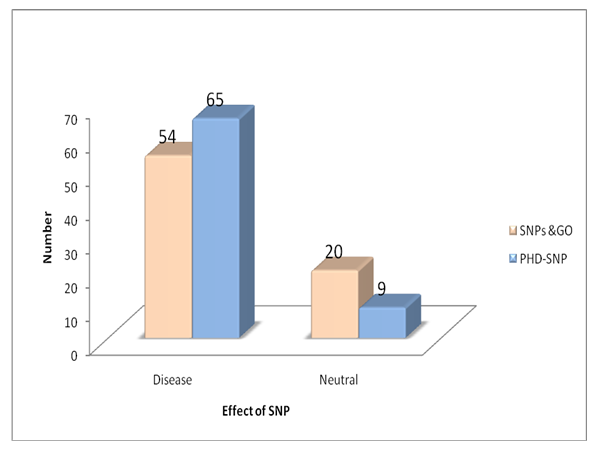 | Figure 2. The result of SNPs & GO compared to PHD-SNP |
4. Discussion
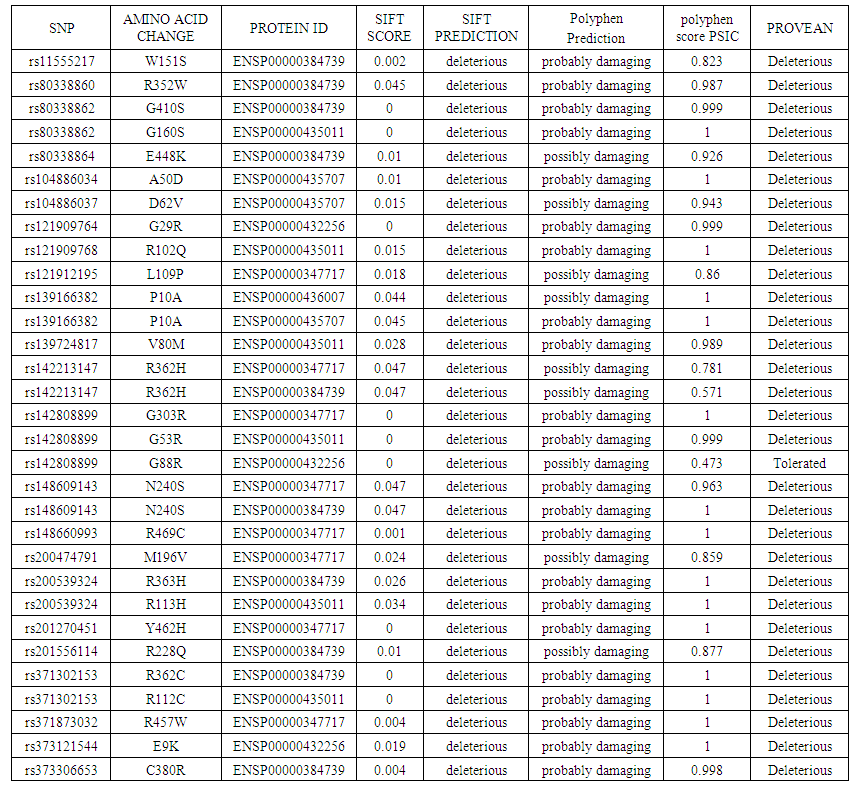
- Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome (SLOS) is an inherited diseases associated with mutations in DHCR7 gene. It is characterized by microcephaly, cleft palate, syndactyly of toes 2/3, anomalies of the heart and kidneys and s genitalia in males and failure to thrive (Kelley and Hennekam, 2000; Witsch-Baumgartner et al., 2001). To date, approximately 160 gene mutations have been identified across the DHCR7 gene (Waterham and Hennekam, 2012).In this study a total of 33 SNPs were shown to be disease related using 5 different software, 6 nsSNPs namely rs201270451 (Y462H), rs80338860 (R352W), rs371302153 (R362C), rs121912195 (L109P), rs80338862 (G410S), and rs373306653 (C380R) have already been previously reported as mutation in DHCR7 gene in patients with SLOS through direct DNA sequencing (Witsch-Baumgartner et al, 2001). Another 3 SNPs rs139724817 (V80M), rs11555217 (W151S), rs142808899 (G303R) were also reported but in this study the mutated amino acids were identified at different positions. While the mutation rs148660993 (R469C) showed a different substituted amino acid Cysteine instead of Proline. Another common mutations is T93M (Mayuko et al, 2017), but in this study it has been detected to be benign using Polyphen-2 software.In this study, the mutation R228Q (rs201556114) was found to pathogenic using the 5 different software used and this mutation has recently been reported as one of the important mutations in this DHCR & gene (Yunhui et al, 2018).Another mutation (Arg242Cys) has been reported in patients with mild condition of SLOS (Krakowiak et al 2000, Arianna et al, 2016) but in this study it was predicted to have a neutral effect using SNPs & Go software. It was found in this study that 55 SNPs had a decrease effect on the protein stability using both I Mutant and MUPro. It has been suggested that most missense mutations lead to loss of enzymatic activity as a result from protein instability or reduced protein expression (Arianna et al, 2016) Phe174Ser has only been reported in one Portuguese patient (Cardoso et al., 2005) but was not found to have a deleterious effect in this study.This study also showed the pathogenic effect of nsSNP (G303 R) which has been previously reported in Japanese SLOS case (Mayuko et al, 2017) which although reported the mutation H442R as a novel missense mutation located on exon 9 but it was not found in a single-nucleotide polymorphism database ( Mayuko et al, 2017) nor in this study.Another two mutations R242H and R352Q, mutations have been reported in non-Japanese populations (Krakowiak et al., 2000; Witsch-Baumgartner et al., 2000) but in this study they did not show to have pathogenic effect using SNPs & Go software for the former. While the latter SNP the substituted amino acid appeared at the same position but for a different amino acid and it was found to be pathogenic rs80338860 (R352 W).A recent study showed that that pathogenic mutations of DHCR7 are located either within the trans membrane region or are near the ligand-binding site and are highly conserved between species while the, non-pathogenic mutations are located outside the transmembrane region and have different effects on the conformational dynamics of DHCR7 (Yunhui et al., 2018) It has also been shown that 13 of the most frequent mutations account for approximately two-thirds of all mutant alleles found in DHCR7, indicating a large number of very rare or even private mutations (Waterham and Hennekam, 2012).Population genetic concerning studies on SLOS are presently sparse and very diverse. Most of the studies, including the two largest ones (Witsch-Baumgartner et al., 2000; Yu et al., 2000) were performed on SLOS patients from the US with European ancestors. Other ethnic groups have lower incidence or unknown cases of SLOS like Africans, Chinese, and Japanese (Yu et al., 2000; Tsukahara et al., 1998). For example a common frame shift mutation (IVS8-1G>C) is reported as the most common mutation in two studies (Witsch-Baumgartner et al., 2000; Yu et al., 2000) and was presented with a very high frequency on chromosomes of British SLOS patients(34%) but on only 3% of chromosomes from Polish SLOS patients. On the other hand, the common Trp151Ter mutation was very frequent among the Polish patients (33%) but had a low frequency (2%) on British SLOS chromosomes (Witsch- Baumgartner et al., 2000).
5. Conclusions
- Nowadays using in silico tools is becoming an important approach for screening of disease related SNPs. In this study an extensive analysis of DHCR7 gene was carried out using different computational tools aiming to investigate the effect of nsSNPs on structure and function of the protein.A total of 33 SNPs were found to be associated with mutations in DHCR7 gene. These mutations affected physicochemical properties of the protein, also affecting size, charge hydrophobicity of the amino acids which eventually affects protein stability, function and thus may be disease related. Some of these SNPs have been previously reported as disease related such as rs201556114 and rs142808899 while others were predicted to be diseases related using different computational software in this study. Although using computational tools to investigate the effects of the SNPs may help in determining disease related SNPs, but nevertheless population genetics and clinical studies are important to confirm the outcomes of such study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML