-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Bioinformatics Research
p-ISSN: 2167-6992 e-ISSN: 2167-6976
2017; 7(2): 49-58
doi:10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20170702.01

3D Structure Modeling of Major Subunit and Chaperone of CS3 Pili: Prediction of Residues Conferring Assembly of Fimbriae
Vajiheh Eskandari1, Bagher Yakhchali2, Seyed Shahriar Arab3
1Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Zanjan University, Zanjan, Iran
2National Institute of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (NIGEB), Tehran, Iran
3Department of Biophysics, Faculty of Biological Science, Tarbiat Modarres University, Tehran, Iran
Correspondence to: Vajiheh Eskandari, Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Zanjan University, Zanjan, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The objective of the current study is to model the three dimensional (3D) structures of major subunit (CstH) and chaperone (CS3-1) of CS3 pili using computational methods, particularly comparative protein modeling. The generated models of CstH and CS3-1 have been deposited into the PMDB database under the ID numbers PM0079873 and PM0078481, respectively. The 3D structures were utilized in the molecular dimerization in order to identify the potential interaction sites in the CstH molecule. The interacting surface areas of the dimer molecules were determined using the PDBePISA server. The interaction affinities and electrostatic potential of the CstH subunit surfaces and its complexes were calculated by PPEPred server and APBS software, respectively. The results indicated that analysis of the 3D models presents an important insight into the permissive sites, binding mode and contact sites of the CstH protein and our method can be a useful tool for other experimental studies in the biology of the pili and their applications.
Keywords: CstH, Homology modelling, Permissive site and Molecular dimerization
Cite this paper: Vajiheh Eskandari, Bagher Yakhchali, Seyed Shahriar Arab, 3D Structure Modeling of Major Subunit and Chaperone of CS3 Pili: Prediction of Residues Conferring Assembly of Fimbriae, American Journal of Bioinformatics Research, Vol. 7 No. 2, 2017, pp. 49-58. doi: 10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20170702.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Gram negative bacteria can produce surface hair-like structures referred to as pili or fimbriae. They comprise subunits called pilin which are assembled into pili with the aid of a periplasmic chaperone and an outer membrane transporter protein [1-3]. In the pilus assembly pathway, after translation and signal peptide cleavage of the precursor proteins, Pilin subunits interact with their cognate chaperones to ensure proper folding [2, 3]. Some fimbriae of the chaperone/usher assembly class, curl into non-fimbrial, capsule-like structures on the cell surface [4], while most such chaperone/usher pilin transport systems assemble into pili on the cell surface [3].Despite low-sequence homology among Gram-negative bacterial fimbriae, all pilin subunits share an incomplete immunoglobulin (Ig)-like fold, which lacks the seventh, C-terminal, final antiparallel β-strand (strand G), creating a deep hydrophobic cleft that makes the subunits unstable outside the pili or chaperone–subunit complex. The periplasmic chaperone contains two Ig-like domains that meet at a right angle, giving the molecule an overall `boomerang' shape with a cleft between the two domains. Chaperones bind fimbrial subunits by insertion of their N-terminal strand G (β-strands G1) into the hydrophobic cleft of the pilin in a parallel orientation, so creating a non-classical Ig-like fold [5, 6]. Pilus assembly entails a similar principle of complementing the incomplete Ig-fold of the pilins. The assembly of subunits into pili carries out through a donor strand exchange reaction in which the inserted G1 β-strand of the chaperone, with a parallel directionality; into the subunit hydrophobic cleft is replaced by the N-terminal domain of a second subunit in the more energetically suitable anti-parallel orientation to complete the Ig-like fold and joining subunits into a fiber [3]. The N-terminal structural characterization of several fimbriae such as F1 capsule antigen from Yersinia pestis indicates that the N-terminal of capsule subunit contains a large unstructured region which is important in interacting with β-strand of the next subunit, presumably by adopting ‘new-structural’ state [4]. The fimbrial proteins also indicate a fair amount of sequence variability making them amenable for the acceptance of foreign sequences and displaying on the bacterial surface [7]. The CS3 fimbriae/pili expressed by most strains of enterotoxigenic E. coli afford several potential advantages which make it a suitable system for high-valence display of heterologous peptides on the bacterial cell surface [8-10].The present study was conducted to model the three dimensional structure of the major subunit (CstH) and chaperone (CS3-1) of the CS3 pili and identify the CstH self-dimerization as well as CstH and CS3-1 hetero dimerization regions and potential CstH interface residues. Knowledge on 3D structure of a protein provides important information for understanding its biochemical function and interaction properties in molecular detail which may have important applications. Therefore, it is plausible to expect that our molecular modeling efforts along with previous experimental [10] and literatures data can facilitate the identification of permissive foreign peptides insertion sites, ligand-binding sites along with rational designing of mutations in the protein subunit for the purpose of tightening and loosening of the pili structure.
2. Methods
2.1. Template Identification, Sequence Alignment, Model Generation and Assessment
- The amino acid sequence of target proteins: CS3 fimbrial subunit A (CstH) and CS3 chaperone (CS3-1) were retrieved from the UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot database with accession numbers P15488 and P15483 respectively [11]. Modeling of CstH and CS3-1 were carried out sequentially: the target proteins were searched for their homologues through the Protein Data Bank (PDB) [12] using BLAST [13] and PSI-BLAST [14]. Generation of the 3D model for the CS3-1 chaperone was performed by Modeller 9v10 [15] based on the crystallographic structure of its homologue. The quality of the generated model was assessed using Modeller objective function, DOPE score [16] and stereochemical assessment using the Procheck program [17] and ProSA II-web server [18].For CstH modeling, the query protein sequence was subjected to fold-recognition using GenTHREADER meta-servers [19] including: FUGUE [20], FFAS03 [21], mGenTHREADER [22] and Phyre-2 [23] servers. The structure- based sequence alignment was carried out to build homology model for CstH using Swiss-Model Alignment-Mode [24, 25]. Finally, the best model was selected based on the QMEAN Z-score [26], stereo-chemical assessment using the Procheck program, ProSA II-web server and the Verify-3D server [27] and also structural comparison with respect to the template.The CstH and CS3-1 generated models were energetically optimized by applying the all atom OPLS-AA force Field available in GROMACS package-5.0. Molecular modeling (MD) simulations were carried out at a constant temperature (300 K) and pressure (1 bar) for 25 ns. The consensus secondary structural elements of the proteins were obtained through the SOPM [28], GOR IV [29], PHD [30] and SIMPA96 [31] servers.The information about solvent accessibility of CstH and CS3-1 models were obtained using the Accelrys Discovery Studio Visualizer 2.5. Pro-origami [32] was used to generate the topology diagram from an uploaded PDB file. Protein topology diagrams are 2D representations of protein structure which are particularly useful in understanding and comparing protein folds.
2.2. Protein-protein Dimerization and Prediction of Protein-Protein Interaction Sites
- The ternary Caf1M:Caf1:Caf1 (chaperone: subunit: subunit) complex (PDB ID: 1P5U) from Yersinia pestis were used as template for dimerization of CstH/CstH and CstH /CS3-1complexes. The 1p5u; pdb file was broken into two file; one file had two Caf1 subunits (Caf1:Caf1) and the other had the caf1 chaperone with caf1 subunit (Caf1:Caf1M). Models of protein complexes and interaction sites between CstH and CstH and also CstH- and Cs3-1 were retrieved by applying symmetry against Caf1:Caf1 and Caf1:Caf1M, respectively, using Swiss-Pdb Viewer. Molecular dynamics simulation of the complexes was carried out with the GROMACS as described above. The surface interaction area of dimer models were calculated using the PDBePISA server [33]. The electrostatic potential surfaces for CstH/CstH and CstH/CS3-1 complexes were calculated by APBS [34] and displayed using PyMOL [35]. The binding affinities of dimer complexes were measured using a web server PPEPred [36].
2.3. Construction of Phylogenetic Tree
- For generation of phylogenetic tree, amino acid sequences of various fimbriaes [37] were retrieved from Swiss-Prot database. Multiple sequence alignment was done using ClustalW [38]. Putative phylogenetic tree for multiple sequence alignment was performed by TreeTop [39] Phylogenetic tree prediction online server. In the bootstrap, multiple alignments were reassembled 100 times.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification of the Best Templates for CstH and CS3-1
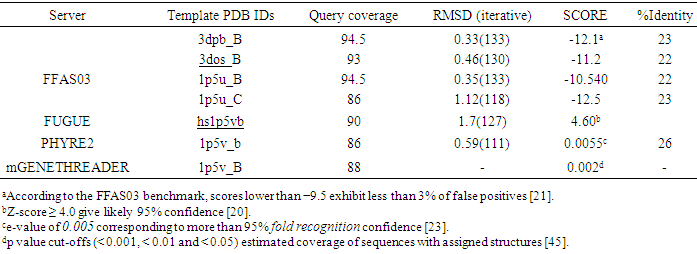
- Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure, so BLAST searching was performed for identifying significant similarity to one or more proteins with known 3D structure using CstH and CS3-1 sequences (Swiss-Prot: P15488 and P15483, respectively). Significant similarities were found with several Chaperone families for CS3-1. A Prosite analysis of query sequences also indicated the presence of Gram-negative pili assembly chaperone signature for CS3-1, but no hits were obtained for CstH. In addition, a PSI-BLAST search for CS3-1 against the structures in Protein Data Bank (PDB) also found chaperone protein Caf1M (PDB ID: 1P5U_A) from Yersinia pestis, with lower E-values; 3e-49 and ~39% sequence identity as the most appropriate template for the CS3 chaperone, but no significant hits were obtained for the CstH. The CstH sequence was therefore submitted to the GenTHREADER meta-server for template identification. Fold-recognition servers; FFAS03 using jackal method, FUGUE, 3DPSSM, PHYRE2 and mGENETHREADER reported the crystal structures of F1 capsule antigen (Caf1) from Yersinia pestis (PDB entries: 3dbp_B, 1p5v_B, 1p5u_C, 1p5u_B and 3dos_B) as the best potential templates. Moreover the Fold-recognition servers also predicted the 3D models for the query sequence. As indicated in the Table 1, query coverage of the resulted models was not complete. Further investigation of all models showed that the N-terminal of the target protein was not modeled (data not shown). Due to the importance of pilin N-terminal in assembly of the pili, the results of the fold recognition methods were only used for template selection and the F1 capsule antigen (PDB entry; 3dbp_B) with higher scores in compare to other templates (Table 1), was selected as the appropriate template for CstH modeling.
|
3.2. Modeling of CstH and CS3-1
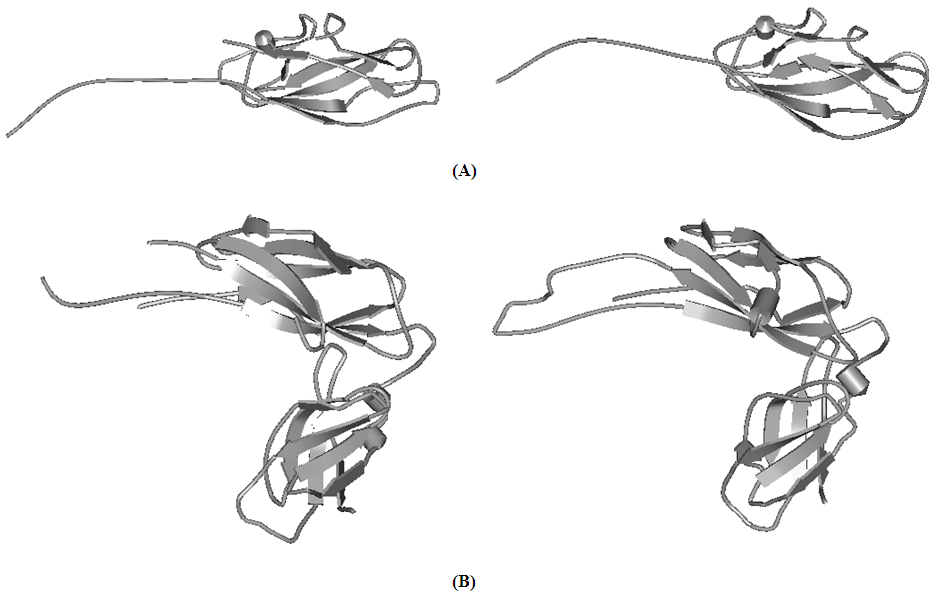
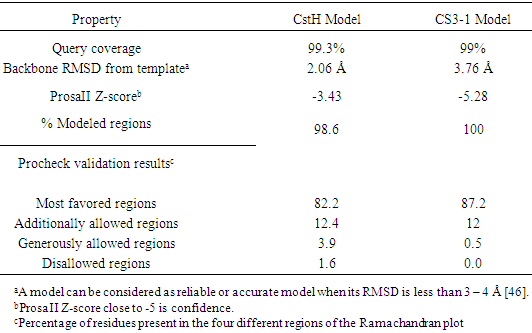
- The 3D models of CstH and CS3-1 (Fig. 1) were produced using available crystal structures of Caf1 and Caf1M as structural templates by employing the computational methods. Since the CstH and CS3-1 target proteins and related templates belonged to the same family in which the structures and functions were well conserved, it seems that the functional information and overall structure similarities can overcome the problem of low-sequence identity (below 30%) between CstH and related template.
|
 | Figure 2. The sequence alignment between CstH and Caf1 (PDB ID: 3dpb_B) which retrieved from FFAS03 server and used to build the CstH model |
 | Figure 4. CLUSTALW multiple sequence alignment between CS3-1 and Caf1M |
3.3. Comparison of CS3 Fimbrial Subunit A with F1 Capsule Antigen Caf1
- As shown in Figure 6, each monomer of CS3 pili has a fold consisting of one α- helix and ten β-strands (β1-β2-α1-β3-β4-β5-β6-β7-β8-β9-β10), which is compatible with 3dpb_b template. We also investigated the structural relation between the target and template through phylogenetic analysis (Fig. 7). The major subunit of several pilus were used for phylogenetic analysis. Inspection of the phylogenetic tree indicated a close relation between the CS3 major subunit (CstH) and F1 capsule antigen (Caf1) that explains conserved amino acids across protein families sharing the same fold, resulting in an identification of the Caf1 protein as the appropriate candidate for accurate modeling of the CstH. In the model building, accurate alignment of the model structure with the selected template is a crucial step and poor alignments are commonly responsible for inaccurate models. As expected, the model is quietly super-imposable with the template (Table 2) and the root-mean-square deviations (RMSD) using Cα atoms being 2.11 Å. These results show a strong structural resemblance of template and model and confirm the accuracy of the generated model for CS3.
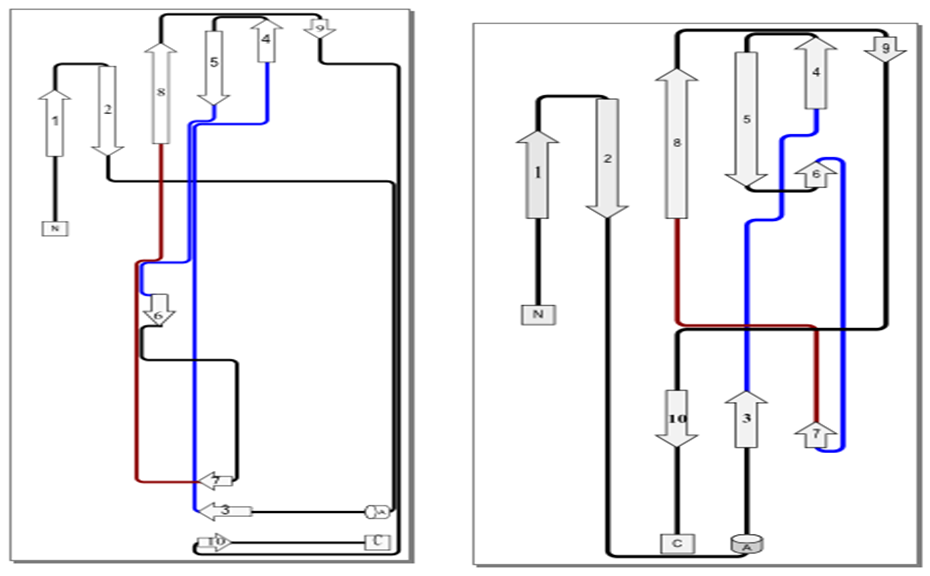 | Figure 6. Topology diagrams of the CstH model (left image), and Caf1 (3dpb_b) template (right image) |
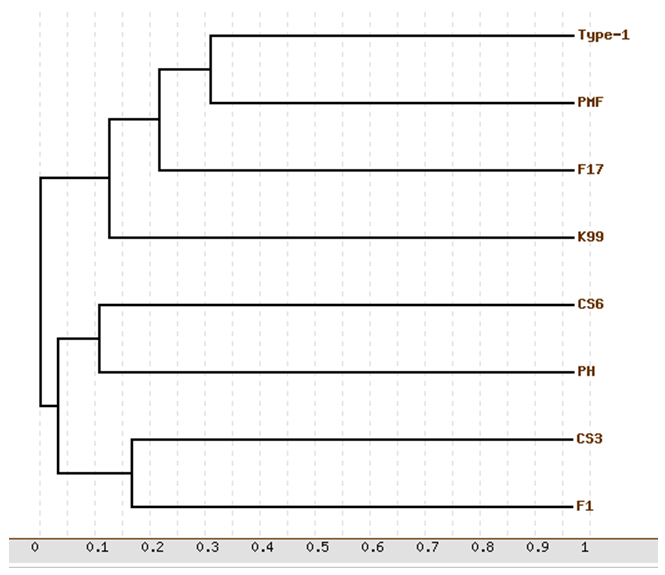 | Figure 7. Phylogenetic relationship between some pilus family members. F1 is referred to F1 capsule antigen. The phylogenetic show the CS3 pili to be closest to the F1 capsule antigen |
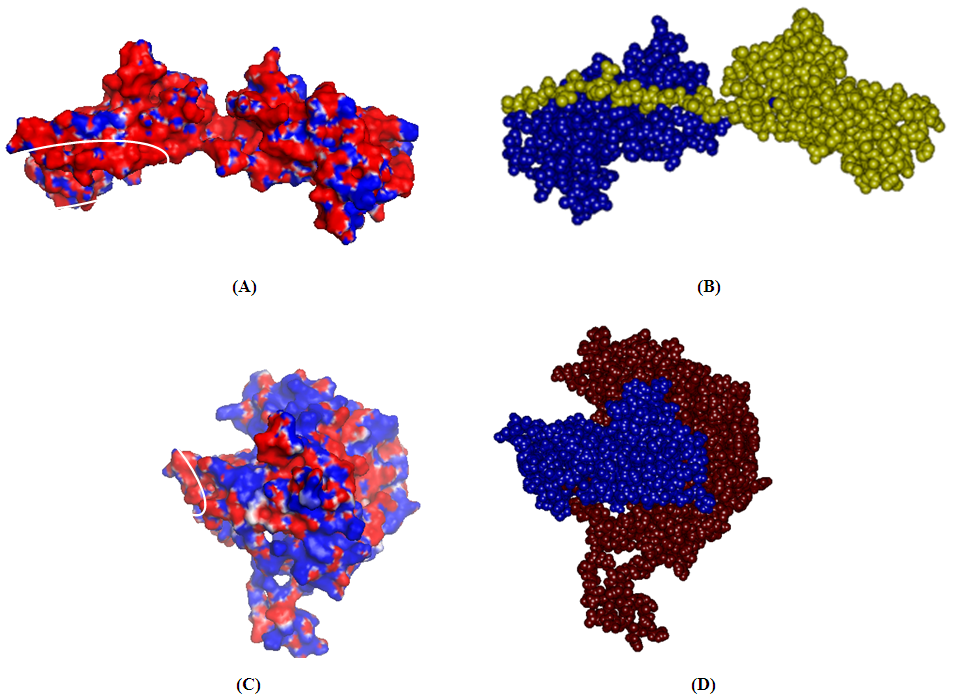
3.4. Dimerization Interface of Subunit-Subunit Homodimer and Subunit-Chaperone Heterodimer
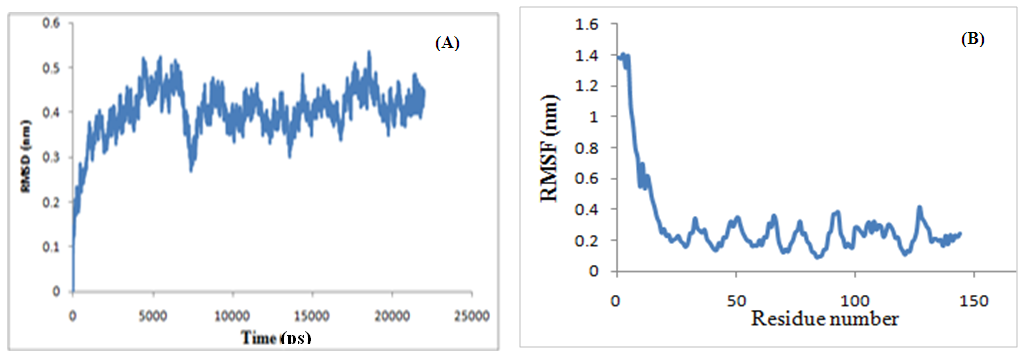
- A pilus is a polymer of protein subunits that, before assembly, form transient complexes with a chaperone in the periplasm. Then, during pilus assembly, the chaperone is replaced by another subunit [1, 3].In this study, dynamically stability of dimer interface in CstH/CstH and CstH-/CS3-1 dimer complexes were measured by estimating the root mean square deviation (RMSD) during MD simulation. Plots of RMSD versus simulation time (Fig. 8) shows that the 15 ns simulation time is sufficient for equilibration of all systems, thereby providing best evidence for introduction of the intact mere of CstH homodimer as model.
 | Figure 8. Root mean square deviation (RMSD) plot for complexes of CstH-CstH (A) and CstH-Cs3-1 (B) during molecular dynamic simulation |
|
4. Conclusions
- The understanding of protein structures provides useful information about the biochemical function and interaction properties of the protein and it is very important in medicine (such as, drug design), biotechnology (such as, novel enzymes design). The fact that experimentally methods such as Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) or X-ray crystallography which are used to determining protein structures are very expensive and time consuming. Therefore for minimizing the time and costs, bioinformatics methods are used for the prediction of the 3D structure of proteins. In this paper, we predicted the 3D structure and interface areas of CstH with a computational methods.The CstH protein (major subunit of CS3 pili is a (relatively) small protein (146 amino acids) with no cysteine residues. These properties make CS3 fimbriae a good candidate for use as a carrier in the bacterial cell surface display. Dimer complexes (CstH-CstH and CstH-CS3-1) revealed that homo and hetero-dimerization of CstH with CstH and CS3-1 mostly occupy its N-terminal and also C-terminal interacting sites, which are in agreement with fimbriae assembly mechanism [3, 4]. Additionally, PDBePISA and Swiss-Pdb Viewer EPS analysis of dimer complexes revealed details interaction sites of CstH model.Our other finding in this study is that when there are low sequence identities between the targets and templates sequences, the best template can be identified with the fold recognition methods using multiple sequence alignment algorithms. The target and best template sequence alignment can be used for building of the model using Swiss - Model homology mode.In summary, our study provides structural insights into the architecture of CstH protein, which can facilitate the identification of permissive foreign peptide insertion sites, ligand-binding site prediction and also rational engineering of the subunit for hybrid pili construction, in order to engineer tightening and loosening of the pili structure which is a great importance for many biotechnological applications.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML