-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Bioinformatics Research
p-ISSN: 2167-6992 e-ISSN: 2167-6976
2015; 5(2): 21-25
doi:10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20150502.01

In Silico Analysis of Transcriptomes of Catharanthus roseus and Rauvolfia serpentina, Two Potent Medicinal Plants Using a Pipeline Developed from Publicly Available Tools
Lakshmi Priya P. M.1, K. K. Sabu2
1Department of Bioinformatics, Union Christian College, Alwaye, India
2Division of Biotechnology and Bioinformatics, Jawaharlal Nehru Tropical Botanical Garden and Research Institute, Palode, India
Correspondence to: K. K. Sabu, Division of Biotechnology and Bioinformatics, Jawaharlal Nehru Tropical Botanical Garden and Research Institute, Palode, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Until recently, there was no data available on the genome sequences of medicinal plants. But now, public databases for the transcriptomes of important medicinal plants are available. But an analysis pipeline effectively combining publicly available tools is lacking which would otherwise enable in-depth analysis of the transcriptomes. In this context, we have developed an effective in silico analysis pipeline using tools such as FastQC, FastQ Groomer, TopHat, Cufflinks, Cuffmerge and Cuffdiff available in Galaxy platform and other tools such as DAVID, ExPASy, MetaCyc and PlantCyc. We have tested the pipeline for comparative analysis of the transcriptome of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G.Don and Rauvolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. ex Kurz, two well-known medicinal plants. This study identified genes that are similarly expressing in the roots of these plants leading to the formation of the same secondary metabolite, “Strictosidine” and also identified differentially expressing genes in the leaves of C. roseus and R. serpentina lead to the formation of different metabolites, “Vinblastine” and “Ajmaline”. The findings of the study indicated that the pipeline developed is effective and helped to analyze the transcriptomes and expression data.
Keywords: Transcriptome, in silico, Pipeline, Catharanthus roseus, Rauvolfia serpentine, Medicinal plants, NGS, Next generation sequencing
Cite this paper: Lakshmi Priya P. M., K. K. Sabu, In Silico Analysis of Transcriptomes of Catharanthus roseus and Rauvolfia serpentina, Two Potent Medicinal Plants Using a Pipeline Developed from Publicly Available Tools, American Journal of Bioinformatics Research, Vol. 5 No. 2, 2015, pp. 21-25. doi: 10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20150502.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Recent advances in bioinformatics has transformed all areas of biological science. The central dogma of molecular biology describes how information in genes flows into proteins through two-step process, viz. transcription and translation. Gene expression can be regulated at several steps including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein [1].Out of various molecules produced through gene expression, secondary metabolites are unique in the sense that they offer diverse utilities such as drugs, flavor and fragrances, dye and pigments, pesticides, and food additives. Of the various types of these metabolites, alkaloids consist of an important group of low molecular weight nitrogen-containing organic compounds, usually with a heterocyclic structure. They are of particular interest because of their numerous biological activities including medicinal properties [2] and also proved as having important ecological functions [3]. Several studies on alkaloid-producing plants suggest that the biosynthesis and accumulation of these compounds are highly regulated process [4]. Among the alkaloid containing plants, those having monoterpenoid indole alkaloids are rich source of many pharmaceutical drugs. This class of compounds include alkaloids such as the antineoplastics vinblastine and vincristine, the antihypertensives ajmalicine and ajmaline, the antimalarial quinine. The first specific enzyme for monoterpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis identified was strictosidine synthase (STR) [2] in Rauvolfia serpentina, which condenses tryptamine and secologanin to form the first intermediate 3α (S)-strictosidine [5]. Before the characterization of the strictosidine synthase cDNA of STR, activity of the enzyme was known in different Catharanthus and Rauvolfia species, both from the Apocynaceae family [6].Powerful bioinformatics tools are required to extract knowledge from vital amounts of information generated by high throughput genomics technologies. Studies using transcriptomes and expression profiling provide opportunities for better understanding of the plant metabolic pathways and enables analyses of the formation of plant-derived pharmaceuticals in various plant species including R. serpentina and C. roseus [7-12].Aim of the study was to develop a suitable in silico analysis pipeline for transcriptome studies in medicinal plants and validate the same for analysis of gene expression in Rauvolfia serpentina and Catharanthus roseus using raw next generation sequence (NGS) data obtained from public databases.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. RNA-Seq Data
- RNA-Seq datasets used in this study were publicly available as single-end Illumina reads in FastQ format and retrieved from ENA Nucleotide database through Galaxy public server (usegalaxy.org). The Catharanthus roseus data SRR122254 (root) and SRR122251 (leaf) were 1.1Gbp and 886.4Mbp and the Rauvolfia serpentina data SRR125767 (root) and SRR125761 (leaf) were 989.3Mbp and 858.2Mbp respectively. Assembled transcripts of C. roseus and R. serpentina were downloaded from Medicinal Plant Genomics Resource (medicinalplantgenomics.msu.edu).
2.2. Preprocessing of RNA-Seq Dataset
- C. roseus and R. serpentina sequence data were preprocessed before used for mapping the reads. Integrity of the dataset was verified before starting the analysis. The quality of each dataset was analyzed using FastQC tool under the NGS:QC in Galaxy. Special attention was given for quality checks with respect to per base sequence quality and per base sequence content. Low quality sequence reads were discarded to ensure that more than 70% of the retained reads had quality greater than 30. Then FastQ Groomer was used to convert the FastQ files to standard format using Phred+33 (Sanger) quality score which were used by the Galaxy for downstream processing.
2.3. Read Mapping
- Reads were cleaned and mapped to the reference genome of C. roseus and R. serpentina (downloaded from plantbiology.msu.edu), which were recently sequenced, assembled and annotated [7]. The reads were mapped for each sample using the aligner TopHat under the NGS:RNA Analysis menu by selecting corresponding FastQGroomer FastQ file as RNA-Seq FastQ files. A genome was selected from the Galaxy History and the corresponding reference genome and other parameters were set as default. Using high-throughput short aligner Bowtie, Tophat aligned RNA-Seq reads to reference genome. Subsequently, the mapping results were analyzed for the identification of splice junctions between exons. RNA-Seq read alignments, among many other things, could reveal new alternative splicing events and isoforms.
2.4. Transcriptome Assembly and Expression Abundance
- Quantification of gene expression from the RNA-Seq requires precise identification of isoform of each read. Cufflinks was used to assemble individual transcripts from RNA-Seq reads that have been aligned to the genome. A predicted transcriptome for each sample was created using Cufflinks under the NGS:RNA Analysis menu. A text file of BAM alignments was given to Cufflinks as input which was produced by the RNA-Seq read mapper Tophat. Bias correction (from History) was turned ON and selected the Minimum Intron length and Pre mRNA fraction as 0.05. Then the Cufflinks constructed parsimonious set of transcripts that explained the reads observed in a RNA-Seq experiment. After Assembly phase, Cufflinks quantified the gene expression level of each transfrag in the sample and also estimated transcript abundances by using a reference annotation. Gene expression levels were normalized using fragments per kilobase of exon per million mapped reads.Cuffmerge is considered to be a ‘Meta-Assembler’- as it treats the assembled transfrags the way Cufflinks treats reads, merging them together parsimoniously. The predicted transcriptomes for all samples were merged using Cuffmerge under the NGS:RNA Analysis menu. During the merging, transcripts from all the assemblies were converted to representative reads in BAM format. Cuffmerge merged transcripts that were overlapping and shared a similar exon structure (or splicing structure) to generate a longer chain of connected exons. To merge reference transcripts with sample transfrags, Cuffmerge performed reference annotation-based transcript (RABT) assembly and produced a single annotation file for use in downstream differential analysis. Once, each reads were assembled and merged, the final assembly was screened for genes and transcripts that were differentially expressed.
2.5. Differential Expression
- In this study, genes were considered differentially expressed when their absolute value of log2 fold change was greater than 2 and their p value was less than 0.01. Cuffdiff calculates expression in two or more samples and examines the statistical significance of observed change in expression among them. The statistical model examined the changes that the number of reads produced by each transcript is proportional to its abundance. Cuffdiff compared BAM files generated by Tophat for each sample under the NGS:RNA Analysis menu. Gene and transcript expression level changes were reported as tabular output files containing statistics such as fold change (in log2 scale), p values (both raw and corrected for multiple testing) and gene- and transcript-related attributes such as common name and location in the genome. Cuffdiff reported additional differential analysis results which were used to identify differentially spliced or regulated genes via promoter switching.
2.6. Transcriptome Annotation
- Functional annotation of plant transcriptomes is a difficult task due to limited availability of reference genomes in public databases. Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID; david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov) is one of the most versatile tools for functional annotation of large gene sets. DAVID provides comprehensive set of functional annotation tools to understand biological meaning behind large list of genes. Besides DAVID, tools such as ENZYME databases in ExPASy (expasy.org) which is a repository of information relative to the nomenclature of enzymes, MetaCyc (metacyc.org) as a curated database of experimentally elucidated metabolic pathways from all domains of life containing 2260 pathways from 2600 different organisms and PlantCyc (plantcyc.org) which is part of the Plant Metabolic Network (PMN) providing a broad network of plant metabolic pathway databases that contains curated information from the literature and computational analyses about the genes, enzymes, compounds, reactions and pathways involved in primary and secondary metabolism in plants were also used for the functional analysis of the C. roseus and R. serpentina transcriptomes.
3. Result and Discussion
- The main objective of the study was to develop a pipeline for analysis of the transcriptome data of medicinal plants. Modern high throughput sequencers generate tens of millions of sequence reads in a single run. Before analyzing these sequences to draw biological conclusions one should always perform some simple quality control checks to ensure that the raw data quality problems which may otherwise affect the analysis during the later steps.The analysis was performed by a series of analysis modules (Figure 1). The output with respect to all critical parameters indicated that the data quality was good for further analysis. It was followed by conversion of FastQ files to Fasta format, read mapping through TopHat, transcriptome assembly using Cufflinks and Cuffmerge, differential expression using Cuffdiff through Galaxy platform. It was followed by grouping genes using gene ontology functional categories for better understanding the molecular processes, their functions and associated secondary metabolic pathways present in the two species.
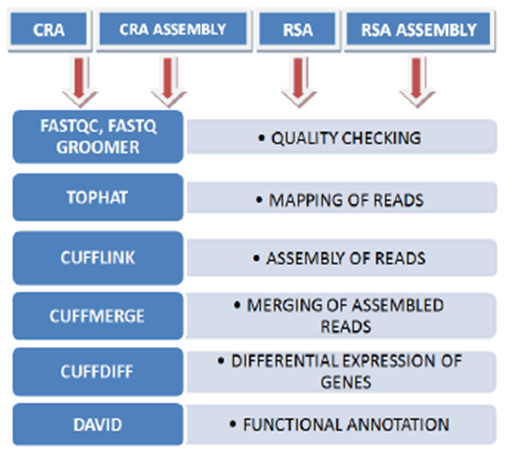 | Figure 1. Data analysis pipeline for transcriptome analysis in Catharanthus roseus and Rauvolfia serpentina |
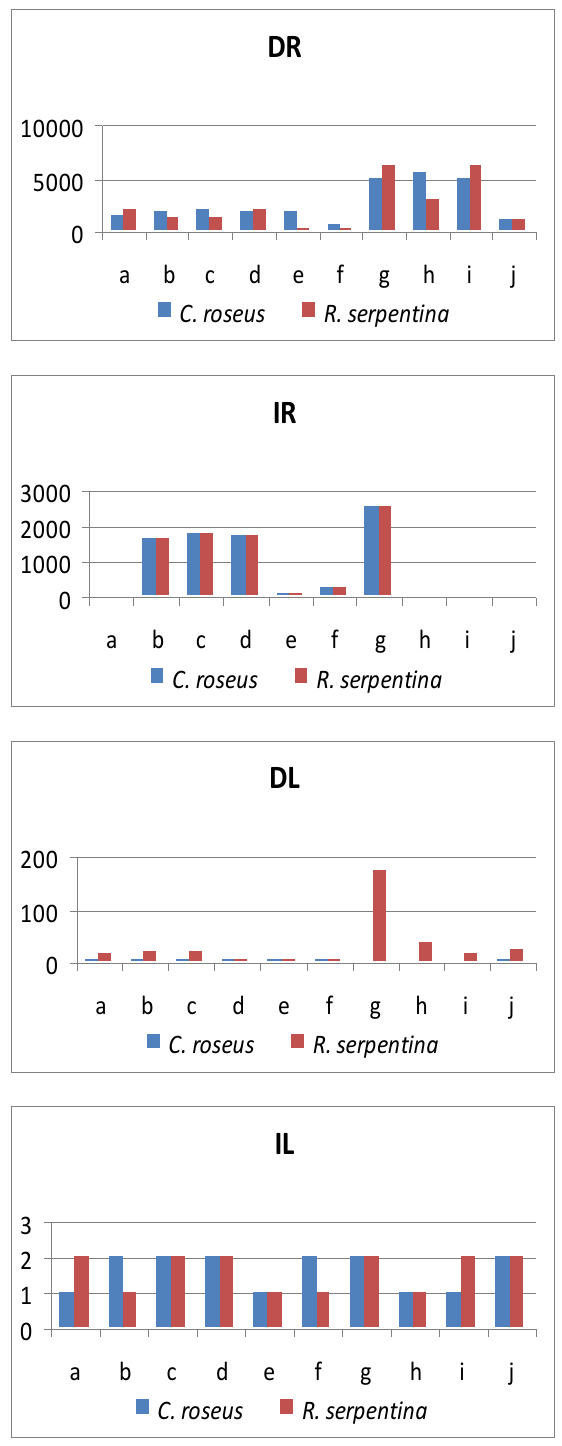 | Figure 2. Differentially (D) and identically (I) expressed genes in annotated categories (a-j) of Catharanthus roseus and Rauvolfia serpentina roots (R) and leaves (L) respectively |
4. Conclusions
- With appropriate controls for data quality, transcriptome analysis can be carried out to identify gene families [13]. By analyzing RNA-Seq data from C. roseus and R. serpentina roots and leaves using the newly developed pipeline, it was possible to identify transcripts expressing in these two important medicinal plants. It was clearly evident that there were many differentially and identically expressed genes and Strictosidine synthase, Vindoline and Ajmaline were only few examples cited to demonstrate the utility of the pipeline developed. It is expected that the in silico analysis pipeline developed would serve the purpose for locating genes present in different plant species.Transcriptomic datasets from the medicinal plants would enable discovery of new biosynthetic genes involved in the production of medicinally important secondary metabolites across these and other taxa. The capability of next-generation sequencing to generate a near-complete transcriptome now opens the door for elucidating some of the most chemically prolific, genetically intractable, species of plants.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Authors thank the Director of Jawaharlal Nehru Tropical Botanical Garden and Research Institute for permission granted to carry out this work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML