-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Bioinformatics Research
p-ISSN: 2167-6992 e-ISSN: 2167-6976
2013; 3(2): 25-29
doi:10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20130302.03
Function Inferences from a Molecular Structural Model of YoeBXn Toxin from Xenorhabdus nematophila
Jitendra Singh Rathore
School of Biotechnology, Gautam Buddha University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India
Correspondence to: Jitendra Singh Rathore, School of Biotechnology, Gautam Buddha University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Toxin–antitoxin (TA) complexes function in programmed cell death or stress response mechanisms in bacteria. The YefM–YoeB TA complex of Escherichia coli consists of YoeB toxin that is counteracted by YefM antitoxin. When liberated from the complex, YoeB acts as an endoribonuclease, preferentially cleaving 3’ of purine nucleotides. In this study YoeBXn toxin from Xenorhabdus nematophila is reported for first time. As no crystallographic structure is available so far, therefore a 3-D Model for Xenorhabdus nematophila YoeBXn toxin was built using SWISS-MODEL, a program for automated modeling. The Model was further validated using VERIFY-3D program as well as Ramachandran plot analysis program. Ramachandran plot analysis showed that 97.56% residues fall in the most favoured and allowed regions. Structural similarity search employing PHYRE server showed as the best matches YoeB and RelE families. The Model also showed similarities with other microbial ribonucleases. A possible homologous deep cleft of active site was identified by CASTp programme and Model was viewed by CHIMERA software. Additional studies to investigate the endoribonuclease activity in YoeBXn toxin protein are needed. The predicted Model allows initial inferences about the unexplored 3-D structure of the YoeBXn toxin and may be further used in rational design of molecules for structure-function studies.
Keywords: X. Nematophila, TA System, YoeBXn Toxin, Homology Modelling, Active Site
Cite this paper: Jitendra Singh Rathore, Function Inferences from a Molecular Structural Model of YoeBXn Toxin from Xenorhabdus nematophila, American Journal of Bioinformatics Research, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2013, pp. 25-29. doi: 10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20130302.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules were originally identified as plasmid maintenance or stability modules[1]. They are very abundant in the genome of different bacteria and archaea[2]. The role of these systems in the genome is not deciphered yet; however, they have been reported to serve as protection against invading DNA, act as guardians against DNA lost as well as involved in stress management either through programmed cell death of a wide part of the population[2]. Recently, there contribution to the origin of persister cells by inducing a dormant stage that permit to the cells to be highly tolerant to antibiotics withdraws great attention[3]. They are further classified into three types according to the nature and action of the antitoxin -class I, II, and III- have been described and class II is being found to be the most abundant[4]. In class II of TA systems comprises two small proteins, which act as a toxin-antitoxin complex (due to differences’ in their Isoelectric point) in which the toxicity of the toxin is inactivated by the antitoxin. There is difference in lifetime between the toxin and antitoxin which is key factor for toxicity of the toxin[5].The lifespan of antitoxin is shorter than the toxin due to its high susceptibility to protease activity where as toxins are highly resistant to proteases. When the toxins are released from the complex they produce their toxic effect in the host via different modes of action including, poisoning DNA gyrase, acting as endoribonucleases, inhibiting protein synthesis or elongation or inducing defects in cell wall synthesis[5,6].Generally, antitoxin neutralizes the toxicity of the toxin by direct protein-protein interaction as well as by repressing transcription of the TA system through interaction with palindromic sequences within the promoters. In this regulation of their own promoter, toxins act as co-repressors, cooperatively improving the DNA interaction. However, in the case of three component systems, antitoxin and DNA-binding activities are encoded by two separated genes[7,8,9].Escherichia coli, gram-negative bacteria is studied in greatest depth in which at least 33 TA systems have been identified so far[10] and in case of Mycobacterium tuberculosis more than 41 TA system have identified[11,12]. The availability of a large number of genomes and the use of bioinformatics tools have permitted the identification of a huge number of putative TA systems in different microorganisms[11]. In regards to the structure of these proteins and their activities, up to 12 toxin super-families and 20 antitoxin super-families have been described and validated[9].Xenorhabdus nematophila is a motile gram-negative bacteria belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae[13]. It forms symbiotic association in the gut of a soil nematode of family Steinernematidae[14]. All the Xenorhabdus isolates, studied so far have been obtained from nematodes harvested from soil samples. Free-living forms of the bacterium have not yet been isolated from soil or water sources, which suggest that the symbiotic association may be essential for the survival of the bacteria in the environment[14]. The bacteria, in turn, are essential for effective killing of the insect host and are required by the nematode to complete its life cycle[15, 16]. X. nematophila can be grown under standard laboratory conditions. Growth in vitro is probably supported by the rich nutrient supply of the laboratory growth media and lack of competition that normally exists in the soil environment. As the bacteria enter the stationary phase of their growth cycle, they secrete several extracellular products, which include lipase(s), phospholipase(s), protease(s), and several broad spectrum antibiotics[17, 18] that can be assayed in the culture media. In our earlier studies we predicted of the existence of three putative TA systems in the chromosome of Xenorhabdus nematophila including RelB, RelE and MazF homologs[19]. Further, in this study we have predicted novel putative TA system which shows considerable similarity to the YefM/YoeB system from E. coli, composed of the putative toxin protein YoeBXn, and its putative antitoxin protein YefMXn. In E. coli YefM/YoeB form a heterotrimer (toxin:antitoxin 1:2) that inactivates the effect of the toxin[20] and free toxin acts by inhibiting protein synthesis by associating directly with the 50S ribosome subunit. In particular, it interacts with the A site, originating mRNA cleavage and releasing the 3’-end portion of the mRNA from the ribosome[21].Here we have identified and reported the location of yoeBXn gene in the genome of X. nematophila for first time. Physiochemical properties have been identified with bioinformatics’ tool. The 3-D structure of YoeBXn has been deciphered with homology modelling. The 3-D structure has been verified with VERIFY-3D software and its qualitative analysis was performed by Ramachandran plot. Structure and active of the YoeBXn have been analysed by CHIMERA software and CASTp programme.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Identification and Genetic Organization of Putative TA Module
- Genome sequence of X. nematophila ATCC 19061 was available in NCBI server (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) in two different databases; INSDC database with accession number FN667742.1 and RefSeq database with accession number NC_014228.1. The entire genome sequence of X. nematophila was downloaded from the Refseq database due to its nonredundant nature and was analyzed bioinformatically. Indentified operon coding putative toxin-antitoxin module was downloaded and analyzed with ORF (Open Reading Frame finder) finder software from NCBI server. (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html)
2.2. Sequence Alignment
- The protein data banks were searched against YoeBXn protein, using BLASTP (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) program. All protein sequences were obtained from NCBI sequence database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
2.3. Molecular Homology Modeling
- The primary sequence of X. nematophila YoeBXn toxin was used to find template proteins through PHYRE2 sever[22] (http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre), which is an online tool for searching similar sequences, based on sequence and structure-wise similarity. From the homology searching, templates from YoeB and RelE families were selected. By having greater identity, the protein sequence of E. coli YoeB toxin was used as template for homology modeling. A 3-D model of YoeB was built by using SWISS-MODEL[23, 24, 25] (http://swissmodel.expasy.org) in automated mode.
2.4. Analysis of the Model
- Predicted structure was verified by VERFIFY-3D[26, 27] (http://nihserver.mbi.ucla.edu/Verify_3D) and further analysed by Ramachandran plot 2.0 software[28] (http://dicsoft1.physics.iisc.ernet.in/rp/select.html)
2.5. Active site Analysis
- After the final Model was built, the possible active site of YoeBXn was explored applying CASTp program[29] (http://sts.bioengr.uic.edu/castp) and model viewed with CHIMERA software (http://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Template Identification, Homology Modeling and Model Quality
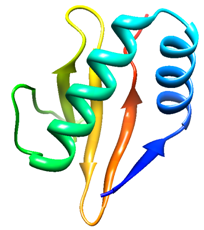
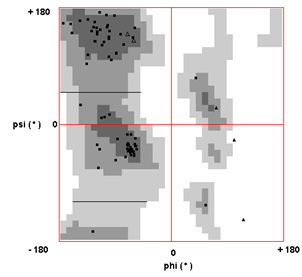
- The primary sequence of the YoeBXn toxin was obtained from the genome of the X. nematophila by genome mining using bioinformatics tools. It is 84 amino-acid residues (~ 9.5kDa) protein encoded by 254 bp located in the operon designated as “XNC1_operon0711”. To find homologous sequences with resolved three-dimensional structure, the X. nematophila YoeBXn protein sequence was selected and submitted to PHYRE server. This server allows searching similar sequences based on sequence and structure-wise similarity[22]. As expected, no 3-D structure of YoeB toxin from X. nematophila was observed. The search identified YoeB and RelE families as the best matches for templates structures. These families belong to RelE superfamily in which YoeB family is also included. Two templates were selected, one of the YoeB family (PDB id d2a6Sa1) and other of the Relk family (PDB id c3oeiH). Each of the sequences templates selected was aligned with the X. nematophila YoeBXn protein sequence. In sequence alignment the E. coli YoeB toxin (PDB id d2a6Sa1) showed 64% identity whereas Mycobacterium tuberculosis Relk toxin showed 51 % identity. Therefore, E. coli YoeB toxin (PDB id d2a6Sa1) was selected as template. Structural model was built using SWISS-MODEL program[23, 24, 25] as shown in figure 1. Z-Score of the C_β interaction energy is 0.74, all-atom pair wise energy is 0.41 and solvation energy is 0.11 for the Model. The quality of the model was assessed by the VERIFY-3D program and Ramachnadran plot programme. Analysis using VERIFY-3D program showed 100% of the positive score values and 100% higher than 0.2. Ramachandran plot calculations showed 97.56% of the residues in favoured and allowed regions as shown in figure 2. As most of the residues are in the favoured region[28] therefore, the analysis indicates that the model has a good quality .
3.2. Structure and Active Sites Analysis
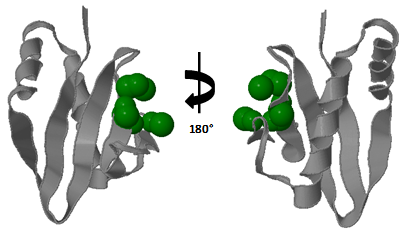 | Figure 3. Identified active site of the X. nematophila YoeBXn toxin. A possible deep cleft active site was identified using CASTp program |
- Toxins of the RelE superfamily are characterized by a core of the five-stranded β-sheet, with four of the strands antiparallel each other, while the first and last strands are positioned parallel. The core of β-sheets is flanked on one side by two N-terminal α-helixes and on the other side by one C-terminal α-helix which together with the loop connecting β2 and β3, forms a deep cleft that encompasses the RNase active site[4]. As the E. coli YoeB toxin[20] was employed as template in molecular modeling, the proposed Model for X. nematophila YoeBXn protein showed a similar molecular structure including five-stranded β sheet and two α helix at N-terminal as shown in figure 1. Model predicted for X. nematophila YoeBXn toxin was also submitted to CASTp program to identify accessible surface pockets and/or cavities. The analysis identified several cavities including one formed exactly in region delimited by C terminal β3 as well as β4 sheet and the loop connecting α2 helix and β2 sheet which is indicate as a possible deep cleft that encompasses the endoribonuclease active site in the Model protein as shown in figure 3. Cleft is composed of 44D, 46E, 57S, 58R, 59R, and 65R. Presence of acidic and basic amino acid residues in the cleft might be act as acid-base pair for RNA hydrolysis and positively charged Arginine might also be responsible for the neutralization of the negatively charged RNA substrate.
4. Conclusions
- A satisfactory Model for YoeBXn toxin from X. nematophila was obtained by automated modeling with satisfaction of spatial restraints using SWISS-MODEL. This model shows a similar architecture for the general structure of the RelE superfamily. Structural similarity search, using atomic coordinates of the obtained Model as query, showed best matches with YoeB and RelE families, as well as with others microbial ribonucleases. A surface topography analysis identified a cavity formed by the region delimited by the C-terminal β3 as well as β4 and the loop connecting α2 and β2 sheets, which is indicate as a possible endoribonuclease active site for YoeBXn toxin. However, new studies with recombinant YoeBXn protein from X. nematophila are necessary to confirm its endoribonuclease activity as well as to establish a mechanism for its action. The Model presented here allows initial inferences about the structure of the YoeBXn toxin and will allow the rational design of peptide derivatives for structure-function studies.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML