-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Bioinformatics Research
p-ISSN: 2167-6992 e-ISSN: 2167-6976
2013; 3(1): 1-9
doi:10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20130301.01
Review of Genome Sequence Short Read Error Correction Algorithms
M. Tahir1, M. Sardaraz1, Ataul Aziz Ikram1, Hassan Bajwa2
1Department of Computing and Technology, Iqra University, Islamabad, Pakistan
2Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Bridgeport
Correspondence to: M. Tahir, Department of Computing and Technology, Iqra University, Islamabad, Pakistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Next-generation high throughput sequencing technologies have opened up a wide range of new genome research opportunities. High throughput sequencing technologies produces a massive amount of short reads data in a single run. The large dataset produced by short read sequencing technologies are highly error-prone as compared to traditional Sanger sequencing approaches. These errors are critical and removing them is challenging. Therefore, there are peremptory demands for statistical tools for bioinformatics to analyze such large amounts of data. In this paper, we present review of and measuring parameters associated with genome sequence short read errors correction tools and algorithms. We further present comprehensive detail of datasets and results obtained with defined parameters. The reviews present the current state of the art and future directions in the area as well.
Keywords: Algorithms, Genome Sequence, Hadoop MapReduce, High Throughput, Next-Generation Sequencing, Short Reads Error Correction
Cite this paper: M. Tahir, M. Sardaraz, Ataul Aziz Ikram, Hassan Bajwa, Review of Genome Sequence Short Read Error Correction Algorithms, American Journal of Bioinformatics Research, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20130301.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Biological sequences contain very important and useful information. The sequences are composed of A, T, G and C in a DNA structure. The compositions determine various traits such as personality, habits, and inheritance characteristics of species[1]. Next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies produce high throughput short read (HTSR) data at a lower cost[2]. High throughput platforms have open up a myriad of new and existing applications such as transcript-tome analysis, meta-genomics, single cell assembly and variation detection[3]. NGS technologies have become prominent tools in biological research[4, 5]. HTSR is changing the way genetic data are collected, stored and produced[4], and each aspect has its own challenges that need to be overcome.As compared to traditional Sanger sequencing methods, next generation sequences have the advantages of deep and cheap coverage at the shorter read and high error rate[6, 7]. Shotgun fragment assembler is optimized for HTSR data such as, Altas, ARACHNE, Celera, and PCAP[8-11]. In de novo genome assembly, the goal is to build contiguous and unambiguous sequences known as contigs[12]. Due to different erroneous characteristics in assembling repeat regions, various contig extensions have been developed[2]. Greedy short read algorithms and graph theory have been adopted and used in assembly programs such as SSAKE, SHARCGS, VCAKE and Taipan[13-16]. De Bruijin graphs approach has also actuated new quest in short read assembly[2, 17]. Various short read assemblers based on de Bruijin graphs have also been developed. Other visceral approaches for Sanger read such MisED[18-23] use alignment approach. Such alignments technologies are not feasible for millions of short reads alignment and does not adopt well at short reads[24, 25]. Short read error correction of different platforms is complex hence making error correction is difficult task[26]. A common approach for error correction of sequence reads is to determine a threshold and correct k-mers[3,17,18, 27]. Selection of correct thresholds is decisive task as low thresholds can result in too many uncorrected errors, while high thresholds will result in loss of correct k-mers[3]. Some researchers have developed and implemented SAP based read correction algorithms in assembly tools[19,28], other consider quality value of per-base and optimize the k-mer counting, but k-mer counting limits the performance of SAP-based error correction tools[6, 12, 29,30].The NGS technologies generate short sequences that are prone to high error rates[31-32]. So, assemblies of long repeats and duplication suffer from short read length[33]. A Critical analysis on whole genome assembly algorithms, various types of errors and requirements for short read assemblies has been discussed in[34-40]. Sequencing technologies are bringing new possibilities for genome sequencing by generating read data with massive throughputs. These reads are shorter and more prone to errors. This poses challenges for de novo fragment assembly algorithms such as accuracy and scalability[41-45].
2. Short Read Error Correction Tools and Algorithms
- This section provides a review of short read error correction tools and algorithms. Due to unknown nature of the source genome, the reads from the same genomic location are inferred by relying on the assumption that they typically share sub-reads of fixed length, such as k-mers. Other techniques use multiple sequence alignments and some use suffix tree method. Therefore different researchers use different parameters for evaluation. This may lead to improper interpretation and cross comparison of all available methods. We classified them on the basis of methods and parameters that can be correctly understood.
2.1. K-Spectrum Based
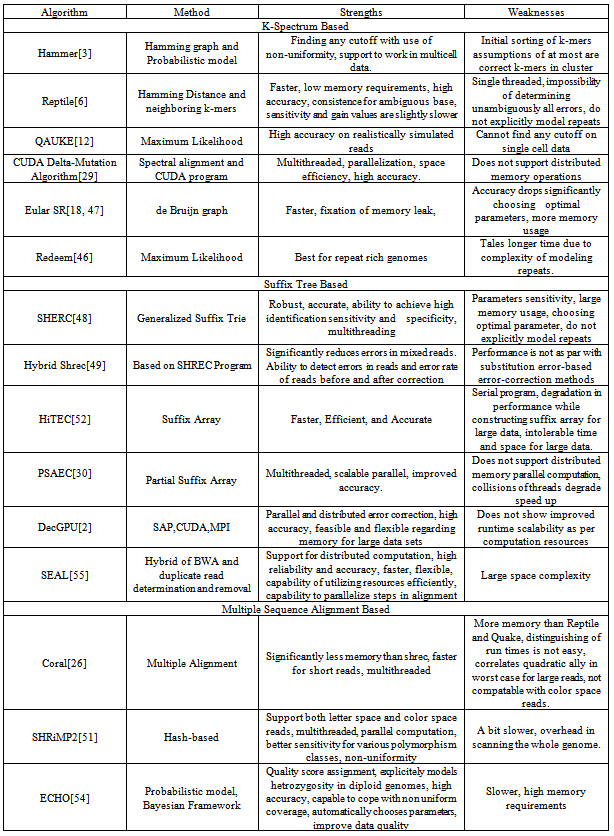
- In[3] authors present an algorithm “Hammer” developed for error correction in illumina/Solexa reads without uniformity assumptions. Hammer is based on hamming graph and a simple probabilistic model to correct sequencing errors. Hammer makes use of a sort technique to identify the set k of distinct k-mers in the reads as well as a table for sorting the multiplicity k-mers. It finds the connected components of hamming graph. Given s1,...s
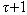 be a disjoint partition of {1,…,k}. These partitions represent spaced seeds into k-mers and also denote the restriction of k-mer x to the seed sj as x(sj). Then k-mers are denoted as d(x,y)
be a disjoint partition of {1,…,k}. These partitions represent spaced seeds into k-mers and also denote the restriction of k-mer x to the seed sj as x(sj). Then k-mers are denoted as d(x,y) 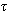 for x and y, there exists j such as x(sj)=y(sj). Based on observations it creates spaced seeds “
for x and y, there exists j such as x(sj)=y(sj). Based on observations it creates spaced seeds “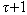 ” denoted as sj= {j, j+
” denoted as sj= {j, j+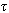 +1,j+2(
+1,j+2(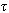 +1),…}. It also makes “
+1),…}. It also makes “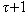 ” copies of set “k” k-mers with the jth copy that have the restriction of k to the indices sj, and sorts each copy lexicographically. In the next step it linearly scans each copy and identifies equivalence blocks. This is then used to compute hamming distance for each block corresponding to a full length k-mer. In case of k-mer pair that is within the hamming distance
” copies of set “k” k-mers with the jth copy that have the restriction of k to the indices sj, and sorts each copy lexicographically. In the next step it linearly scans each copy and identifies equivalence blocks. This is then used to compute hamming distance for each block corresponding to a full length k-mer. In case of k-mer pair that is within the hamming distance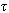 shows that their components are joined[50]. The algorithm finds connected components “cluster” that does not have size one and the consensus string is unique. It corrects every k-mer in the cluster to the consensus string. Singleton k-mer is trivially the consensus. It must be either the only element in the generating set of k-mer or simply contain more than
shows that their components are joined[50]. The algorithm finds connected components “cluster” that does not have size one and the consensus string is unique. It corrects every k-mer in the cluster to the consensus string. Singleton k-mer is trivially the consensus. It must be either the only element in the generating set of k-mer or simply contain more than 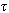 errors. Multiple consensus string exists in small clusters of size two or three, which creates ambiguity. In each case hamming graph does not provide good information regarding the correctness of the k-mers. Therefore, it makes decision solely based on the multiplicity of each k-mer x. If it is greater than the threshold value it keeps x in the dataset, otherwise it removes x from the dataset. Computation of the consensus of the cluster performs in
errors. Multiple consensus string exists in small clusters of size two or three, which creates ambiguity. In each case hamming graph does not provide good information regarding the correctness of the k-mers. Therefore, it makes decision solely based on the multiplicity of each k-mer x. If it is greater than the threshold value it keeps x in the dataset, otherwise it removes x from the dataset. Computation of the consensus of the cluster performs in 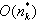 time.In[6] authors present a novel approach “Reptile” to cope with error correction problem of short read sequence in illumine/Solexa reads. Reptile performs the operation with k-mers spectrum and corrects errors using hamming distance. It also makes use of neighboring k-mers for correction possibilities for both potential as well as contextual information. This algorithm has two phases (a) Information extraction: in which k-spectrum Rk of R is extracted for given threshold d-extract hamming graph GH= (VH,EH) where
time.In[6] authors present a novel approach “Reptile” to cope with error correction problem of short read sequence in illumine/Solexa reads. Reptile performs the operation with k-mers spectrum and corrects errors using hamming distance. It also makes use of neighboring k-mers for correction possibilities for both potential as well as contextual information. This algorithm has two phases (a) Information extraction: in which k-spectrum Rk of R is extracted for given threshold d-extract hamming graph GH= (VH,EH) where 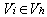 represents αi Rk and
represents αi Rk and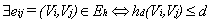 . This is used to compute tile occurrences. (b) Individual read correction: It points to a tile t at the beginning of read, identifying d-mutant tiles of t. The next step is to correct errors in t, wherever applicable. This is done by adjusting tile t and identifying d-mutant step repeatedly until tile placement choices are exhausted. This amounts to a total run time of O (nLlog(nL)) and space usage of O(|Rk|+|R|t||). Reptile is faster, has low memory requirements, and provides high accuracy. However it is single threaded, and lacks the possibility to determine unambiguously all errors. It also does not show explicitly model repeats. In[12] authors present an algorithm “Quake” for detection and correction of errors in Illumine/Solexa short read sequences. Quake is based on maximum likelihood paradigm which incorporates quality values and nucleotide specific miscall rates. Quake makes use of k-mers coverage for differentiation of trusted k-mers in genome sequence, and searches error correction. Let observed nucleotide be denoted by O=O1,O2,…,On, and actual nucleotide of sequence fragment be denoted by A=A1,A2,…,An. Conditional probability is applied using bayes’ rule to the observed nucleotides as given in equation 112.
. This is used to compute tile occurrences. (b) Individual read correction: It points to a tile t at the beginning of read, identifying d-mutant tiles of t. The next step is to correct errors in t, wherever applicable. This is done by adjusting tile t and identifying d-mutant step repeatedly until tile placement choices are exhausted. This amounts to a total run time of O (nLlog(nL)) and space usage of O(|Rk|+|R|t||). Reptile is faster, has low memory requirements, and provides high accuracy. However it is single threaded, and lacks the possibility to determine unambiguously all errors. It also does not show explicitly model repeats. In[12] authors present an algorithm “Quake” for detection and correction of errors in Illumine/Solexa short read sequences. Quake is based on maximum likelihood paradigm which incorporates quality values and nucleotide specific miscall rates. Quake makes use of k-mers coverage for differentiation of trusted k-mers in genome sequence, and searches error correction. Let observed nucleotide be denoted by O=O1,O2,…,On, and actual nucleotide of sequence fragment be denoted by A=A1,A2,…,An. Conditional probability is applied using bayes’ rule to the observed nucleotides as given in equation 112.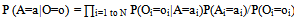 | (1) |
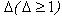 for the correction within a weak l-tuple. CUDA delta mutation consists of two phases, i.e delta (Δ) mutation voting and identifying all l-tuples. On successful completion of the first phase corresponding counters in voting matrix are incremented to point positions of mutation and errors are fixed, based on the highest scores in matrix. CUDA provides multithreading, parallelism, space efficiency and accuracy, but it does not support distributed memory operations.Research in[18, 47] presents a short read error correction algorithm “Eular SR” for applied Biosciences and Illimina/Solexa reads based on spectral alignment method. This method first establishes a spectrum of trusted k-mers from input data set and then correct each read in the sequence that it contains based on spectrum only. However this algorithm is faster and provides fixation of memory leak, but its accuracy drops significantly while choosing optimal parameters, it also require large memory. Another related research presented in[46] depicts a computation method to detect and correct errors in the genomic sequence repeats for the Pacific Biosciences platform. Computation method is available in the form of software package REDEEM (Read error detection and correction via expectation maximization). To correct errors in read r, it considers each of the nucleotide to have appeared at least once upto k-mers. Let’s suppose that the nucleotide at position 1≤i≤L of the read appear at position 1≤t≤k of k-mer xl. The probability that the true nucleotide at position t was b prior to possible misread as given in equation 2[46].
for the correction within a weak l-tuple. CUDA delta mutation consists of two phases, i.e delta (Δ) mutation voting and identifying all l-tuples. On successful completion of the first phase corresponding counters in voting matrix are incremented to point positions of mutation and errors are fixed, based on the highest scores in matrix. CUDA provides multithreading, parallelism, space efficiency and accuracy, but it does not support distributed memory operations.Research in[18, 47] presents a short read error correction algorithm “Eular SR” for applied Biosciences and Illimina/Solexa reads based on spectral alignment method. This method first establishes a spectrum of trusted k-mers from input data set and then correct each read in the sequence that it contains based on spectrum only. However this algorithm is faster and provides fixation of memory leak, but its accuracy drops significantly while choosing optimal parameters, it also require large memory. Another related research presented in[46] depicts a computation method to detect and correct errors in the genomic sequence repeats for the Pacific Biosciences platform. Computation method is available in the form of software package REDEEM (Read error detection and correction via expectation maximization). To correct errors in read r, it considers each of the nucleotide to have appeared at least once upto k-mers. Let’s suppose that the nucleotide at position 1≤i≤L of the read appear at position 1≤t≤k of k-mer xl. The probability that the true nucleotide at position t was b prior to possible misread as given in equation 2[46]. 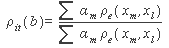 | (2) |
2.2. Suffix Tree Based
- Authors of[48] presented short read error correction (SHREC) algorithm for short read error correction in Illuminia/Solexa based on generalized suffix trie method. It constructs trie from all reads and their complements. Trie is then traversed to point out and analyze the potential errors in associated reads. Depth first traversal of ST (
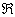 ) is performed for inspection of nodes from level s to level t+q. The algorithm identifies all nodes with at least two children in which one of the children w has smaller weight than the threshold weight. Subsequently it finds a set of reads R (w). So correction is performed to a sibling of w that fits the suffix and examines each read Ri that belongs to R (w). SHREC points error position in Ri and performs the correction of the associated sibling’s nucleotide edge. It is robust, accurate and has the ability to achieve sensitivity and specificity. It has the drawbacks of large memory usage, does not explicitly model repeats, and difficult choice of optimal parameters. Research in[49] depicts a modified version of SHREC algorithm aiming to correct SOLEXA/Illumina reads. The SHREC’s statistical model is modified to put up reads of variable lengths. Given a set of s reads contains r reads of various lengths and are denoted by l1,l2,…,lr. It is assumed that the number of reads of length li is ki and let m be large enough that each sequence having length m appears once. Weight Wm of a node at level m is the number of suffixes whose path in the trie passes through that node. Level m’s node weight is denoted by Wm=∑i=1 to r W(m,i), where W(m,i) represent the contribution of reads length li to the weight of node. If li<m,W(m,i)=0, otherwise each read is a Bernoulli trail to get the path label. There are n substrings of length m in the genome and a read of length li samples Ai=li-m+1, of them. Thus the success probability of Bernoulli trail is ai/n. Ki is the number of trails and W(m,i) is distributed according to the binomial distribution Bin(Ki,ai/n). Therefore, expected value of W(m,i) is E(W(m,i)=kiai/n for li>=m, and 0 otherwise. Variance is as given in equation 3[49].
) is performed for inspection of nodes from level s to level t+q. The algorithm identifies all nodes with at least two children in which one of the children w has smaller weight than the threshold weight. Subsequently it finds a set of reads R (w). So correction is performed to a sibling of w that fits the suffix and examines each read Ri that belongs to R (w). SHREC points error position in Ri and performs the correction of the associated sibling’s nucleotide edge. It is robust, accurate and has the ability to achieve sensitivity and specificity. It has the drawbacks of large memory usage, does not explicitly model repeats, and difficult choice of optimal parameters. Research in[49] depicts a modified version of SHREC algorithm aiming to correct SOLEXA/Illumina reads. The SHREC’s statistical model is modified to put up reads of variable lengths. Given a set of s reads contains r reads of various lengths and are denoted by l1,l2,…,lr. It is assumed that the number of reads of length li is ki and let m be large enough that each sequence having length m appears once. Weight Wm of a node at level m is the number of suffixes whose path in the trie passes through that node. Level m’s node weight is denoted by Wm=∑i=1 to r W(m,i), where W(m,i) represent the contribution of reads length li to the weight of node. If li<m,W(m,i)=0, otherwise each read is a Bernoulli trail to get the path label. There are n substrings of length m in the genome and a read of length li samples Ai=li-m+1, of them. Thus the success probability of Bernoulli trail is ai/n. Ki is the number of trails and W(m,i) is distributed according to the binomial distribution Bin(Ki,ai/n). Therefore, expected value of W(m,i) is E(W(m,i)=kiai/n for li>=m, and 0 otherwise. Variance is as given in equation 3[49].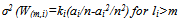 | (3) |
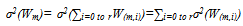 | (4) |
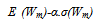 | (5) |
2.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment Based
- A similar work based on multiple sequence alignment is given in[26], called “Coral”. Coral is adjustable to reads of Illumina/Solexa Genome Analyzer and Roche/454. Coral takes reads that share common k-mers and forms multiple alignment correction based on alignment and corresponding consensus sequences. The operation begins with indexing that occurs in the reads or in its components. Coral extracts all reads that form k-mers index sharing at least one k-mer with base read. Reads in k-mer neighbourhood are aligned and corrected several times. Indexing k-mer causes the reads to be aligned and also locates the probable position for sequence alignment. It tries to align the read without error in consensus. Therefore total computation is skipped to save time. Gap positions are ignored in fraction computation with quality value that is higher than 1-e. For each alignment read the algorithm checks and compares it with the consensus sequence in each aligned position. If not agreed upon comparison, correction of reads at each position is done to agree with consensus sequence. The consensus value is ts, where (
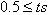 < 1.0). It performs the correction of base only if the quality threshold tQ (0.5tQ<1.0) exceeds from value Lmmax to eLmmax. Time complexity of quality threshold tQ is O (L) and worst case time complexity is O (Lmmax) to detect potential errors. O (eL2mmax) time is taken to correct them. Coral has less memory requirements compared to SHREC, is faster for short reads and is multithreaded. Coral also has some disadvantages i.e. large memory requirement than Reptile and Quake, and is not compatible with color space reads. In[51] authors present a mapping algorithm”SHRiMP2” based on original short read mapping techniques. SHRiMP2 points to the mapping sensitivity. It also has the ability to achieve high rate of accuracy at significant speed with the use of caching heuristic over previous versions. SHRiMP2 supports input format of fasta and fastq, output format of SAM and mapping of Illumina/solexa, Roche/454, AB /Solid reads. Additionally it has paired mapping mode and parallel computation capability. It supports both letter space and color space reads, provides multithreaded and parallel computation and has better sensitivity. It is however slower and has overhead in scanning the whole genome.In[54] authors present a novel algorithm “ECHO” for correcting base-call errors in the short reads without genome reference for Illumina/Solexa platform. ECHO is based on a probabilistic model and has the ability to assign quality score to each corrected base. There is no need to specify parameters or unknown values for optimization. ECHO sets the parameters automatically and estimates error characteristics specific in each sequence run. ECHO has the ability to improve the accuracy of previous error correction methods modified for specific sequence coverage depth and position in the read. ECHO performs error correction as a pre-processing step and considerably facilitates de novo assembly. ECHO presents improvement towards the end of the reads where previous methods are less effective. But it is slower and has high memory requirements.
< 1.0). It performs the correction of base only if the quality threshold tQ (0.5tQ<1.0) exceeds from value Lmmax to eLmmax. Time complexity of quality threshold tQ is O (L) and worst case time complexity is O (Lmmax) to detect potential errors. O (eL2mmax) time is taken to correct them. Coral has less memory requirements compared to SHREC, is faster for short reads and is multithreaded. Coral also has some disadvantages i.e. large memory requirement than Reptile and Quake, and is not compatible with color space reads. In[51] authors present a mapping algorithm”SHRiMP2” based on original short read mapping techniques. SHRiMP2 points to the mapping sensitivity. It also has the ability to achieve high rate of accuracy at significant speed with the use of caching heuristic over previous versions. SHRiMP2 supports input format of fasta and fastq, output format of SAM and mapping of Illumina/solexa, Roche/454, AB /Solid reads. Additionally it has paired mapping mode and parallel computation capability. It supports both letter space and color space reads, provides multithreaded and parallel computation and has better sensitivity. It is however slower and has overhead in scanning the whole genome.In[54] authors present a novel algorithm “ECHO” for correcting base-call errors in the short reads without genome reference for Illumina/Solexa platform. ECHO is based on a probabilistic model and has the ability to assign quality score to each corrected base. There is no need to specify parameters or unknown values for optimization. ECHO sets the parameters automatically and estimates error characteristics specific in each sequence run. ECHO has the ability to improve the accuracy of previous error correction methods modified for specific sequence coverage depth and position in the read. ECHO performs error correction as a pre-processing step and considerably facilitates de novo assembly. ECHO presents improvement towards the end of the reads where previous methods are less effective. But it is slower and has high memory requirements.3. Results and Discussion
|
|
|
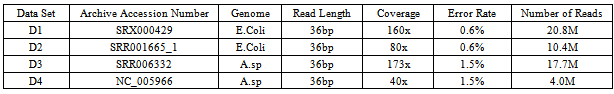
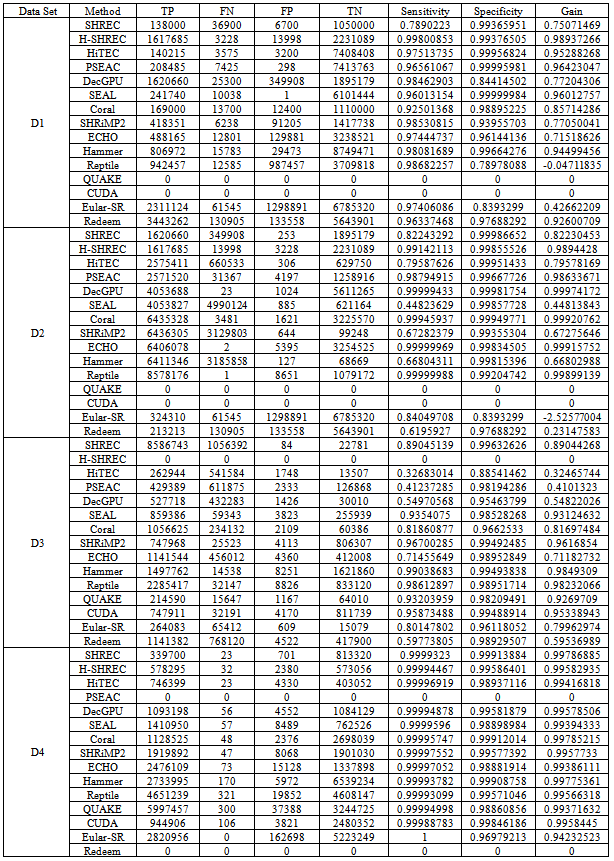
- Algorithms discussed in above section have been simulated and evaluated by sole authors in individual papers. We have selected benchmark datasets as shown in (Table 1) from all the experiments to comparatively evaluate and analyze the algorithms. The results of the corresponding dataset D1 (Accession Number: SRX000429), D2 (Accession Number: SRR001665_1), D3 (Accession Number: SRR006332) and D4 (Accession Number: NC_005966) are shown in (Table 2). The two algorithms Quake and CUDA were generated errors while simulating on datasets D1 and D2 due to cutoff value and not supporting proper distribution respectively. Simulation of Hybrid-SHREC on dataset D3 produced garbage values due to large space complexity. Also PSEAC and Redeem cannot be properly run on D4 due to collision of threads and modeling repeats. That is why these were excluded in comparative analysis. The remaining algorithms are analyzed as follows.Analysis parameters are based on Time and space complexity and are, True Positive (TP): is any erroneous base that is changed to the true base, a False Positive (FP): is any true base changed wrongly, a True Negative (TN): is any true base left unchanged, and a False Negative (FN): is any erroneous base left unchanged. Sensitivity =TP/ (TP+FN) and Specificity =TN/ (TN+FP). Gain= (TP-FP)/ (TP+ FN) represents the total percentage of erroneous bases removed from the dataset post-correction. Clearly, best methods generate gain that approach to 1 but in some cases its value may be negative that actually introduces more errors than they correct[2, 6, 44, 46, 48]. Results analysis of SHREC[48] shows that its accuracy with low coverage is at least 80% and the accuracy rate of Eular-SR[18, 47] reduces significantly with low coverage. The analysis of Coral[26] shows that it has relatively high error rate. That provides whole read alignment with slight edge over k-mers based method. On the other hand due to significant lower TP rates Reptile[6] fall short perceptible of the performance of Coral. Analysis of SEAL[55] describes the capability of throughput levels comparable to single node operation, which minimizes the distribution overhead due to implementation on Hadoop framework. Despite increase in size of the cluster throughput consistency of each node remains the same. SEAL also has the ability of utilizing the available resources efficiently in presence of massive data thus achieves scalability. HiTEC[52] and ECHO[54] yield higher gain value comparable to other methods and also have automated parameter selection for performance optimization. For dataset D1 the SHRiMP2[51] produces negative gain values, which increase errors instead of correcting them. The results of Hammer[3] are also comparable but it neither detects nor corrects errors in clusters without uniformity. The DecGPU[2] analysis shows that it is a superior method in terms of error correction and execution speed. In summary HiTEC, ECHO and DecGPU are comparatively more accurate and efficient. A theoretical comparison in terms of strengths and weaknesses of reviewed algorithms are also presented in (Table 3). Further investigation is necessary to develop specific tools and algorithms to achieve high throughput.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
- The aim of the reviewed algorithms is to compare error rate in next generation sequencing technologies. The growth of NGS technologies present significant bioinformatics challenges, specifically design of bioinformatics tools that handle the operation of massive amounts of data efficiently. In this paper, we have described genome sequence short read error correction algorithms in detail. We concluded that most of the illumine/ Solexa sequencer algorithms focused on substitution errors, while the algorithms build for Roche/454 sequencers have slightly focused on error correction due to longer reads and low error rates. The improvement in sequence platforms and introduction of high throughput sequencing technologies such as Ion Torrent has changed the traditional way of reads and of insertion and deletion errors. Therefore the current methods are unable to achieve good results and hence need improvement.To achieve the potential of NGS, it is important to maximally construe and utilize these short reads. For successful NGS technology application it is essential to develop large amounts of data storage, management and build informatics tools that can efficiently analyze data. It is also required to develop high performance computing and intensive bioinformatics applications to achieve the benefits of NGS technologies. The most significant footprint of NGS is successful aligning and assembling short reads to the reference genome. Efficiently aligning short reads to reference genome is a challenging task, particularly in development of new algorithms to manage ambiguity and alignment errors. It is important to develop such algorithms that support distributed-memory parallel computation to speed up the processes. It is also essential to develop algorithms that simultaneously estimate error parameters from data in regard to fast computation and handle large datasets via better memory management. It is also essential for error correction algorithms to distinguish errors from polymorphism.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML