-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Bioinformatics Research
p-ISSN: 2167-6992 e-ISSN: 2167-6976
2012; 2(6): 102-109
doi: 10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20120206.01
Statistical Approaches for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Biomarker Discovery
Mai S. Mabrouk 1, Esraa M. Hashem 1, Amr Sharawy 2
1Biomedical Engineering, MUST University, 6th of October, Egypt
2Biomedical Engineering, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt
Correspondence to: Mai S. Mabrouk , Biomedical Engineering, MUST University, 6th of October, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Bioinformatics provides an essential tool for the identification of diseases especially human cancer diseases. Also, the availability of the complete human genome has opened the door for the understanding of these diseases as recent technological advances in functional genomics and proteomics have fuelled interest in identifying the biomarkers of complex diseases such as liver cancer which mainly caused to death. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the common malignant tumours in the world; the liver cirrhosis is the most important leading cause of it. HCC relates to virus infection, carcinogenic compounds, pollution and genetic factors. This work provides a genomic study that focuses on using bioinformatics approaches to predict the molecular causes of HCC by the investigation of the chromosomal aberrations including gain, or loss of the genomic DNA copy number to provide accurate diagnoses of this disease using Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) arrays. Diagnosis and understanding of the disease processes will provide a potential treatment of the disease at an early stage. The aim is to apply two statistical approaches based on a circular binary segmentation (CBS) algorithm and a Bayesian Hidden Markov Model (HMM) to a number of human chromosomes for analysing array CGH data that accounts for the dependence between neighbouring clones in order to identify genome-wide alternations in copy number from the genomic data. Results provide a well identification of the aberration regions in human chromosomes that may lead to robust biomarkers for the early detection of human HCC.
Keywords: Liver Cirrhosis, Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (A-CGH), Copy Number Variation (CNV) ,Circular Binary Segmentation (CBS) , Hidden Markov Model (HMM)
Cite this paper: Mai S. Mabrouk , Esraa M. Hashem , Amr Sharawy , "Statistical Approaches for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Biomarker Discovery", American Journal of Bioinformatics Research, Vol. 2 No. 6, 2012, pp. 102-109. doi: 10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20120206.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Bioinformatics holds significant interest in the scientific community because of its potential to move scientific research forward more quickly and at less expense than traditional laboratory testing. A large amount of publicly available cancer genetic data becomes available now in a way that as the size of data on genetic and epigenetic abnormalities, gene expression profiles, microRNA expression profiles and proteomics increase, the role of bioinformatics in the prediction of new cancer biomarkers(Figure 1) will also increase and become more and more important.The availability of the complete human genome has paved the way for the systematic understanding of human cancer diseases.Liver tumours are divided into to two categories benign and malignant .Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common types of malignant tumours, Long-term survival of HCCpatients is poor partly due to HCC recurrence.It is the major type of liver cancerthat exhibits numerous molecular abnormalities which may be involved in the process of HCC development and progression[1]. For this reason, it is important to identify accurate predictors of prognosis and a reasonable selection criterion that can be applied to patients with HCC, particularly with early stage for early diagnosis and monitoring of recurrence of HCC[2]. According to the current studies, the majority of HCC patients contracted the disease from the accumulation of genetic abnormalities, probably induced by exterior etiological factors especially HBV and HCV infections[3]. These risk factors can induce mutations and damage in DNA sequences, such as p53 mutation induced by aflatoxin and DNA damage induced by the intrusion of the HBV genome[4].Genomic DNA copy number alterations (CNAs) are associated with many complex diseases[5], including cancer diseases as genetic alternations such as amplifications and deletions frequently contribute to tumorigenesis. These alternations change the level of gene expression which modify normal growth control and survival pathways. Characterization of these CNAs is important for both the basic understanding of Hepatocellular carcinoma and its diagnosis[6]. Array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) allows identification of copy number alterations across genomes[7].It is recently developed technology based on DNA microarrays that can be used to investigate DNA copy number differences between two samples[8-11]. In the CGH technique, a normal and a pathological DNA sample are differentially labelled and compared by competitive hybridization against a normal metaphase chromosome spread detecting gains and losses based on changes in signal ratios. The aCGH greatly improves the resolution (approximately 1 Mb) of the technique by substituting the hybridization target, the metaphase chromosome spread, with genomic segments spotted in an array format[12]. It provides many advantages including: easier standardization, higher resolution, and Array-CGH intensity ratios provide much useful information about genome-wide changes in copy number in DNA by calculating the intensity log ratio of chromosome[13].A genetic local search algorithm is applied to segment the clones into clusters[14]. Others used dynamic programming to define alternation points given known numbers of segments and a penalized maximum-likelihood[15-16]. Some recent approaches as in "Cluster along Chromosomes" (CLAC) method[17]. In this method, a hierarchical clustering-style trees bottom up along each chromosome arm (or chromosome) are built, and then "interesting" clusters can be selected by controlling the False Discovery Rate (FDR) at a certain level.
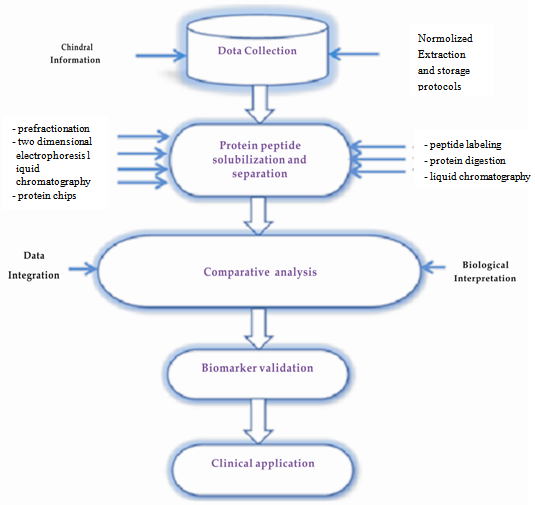 | Figure 1. Biomarker discovery in a cross-disciplinary domain |
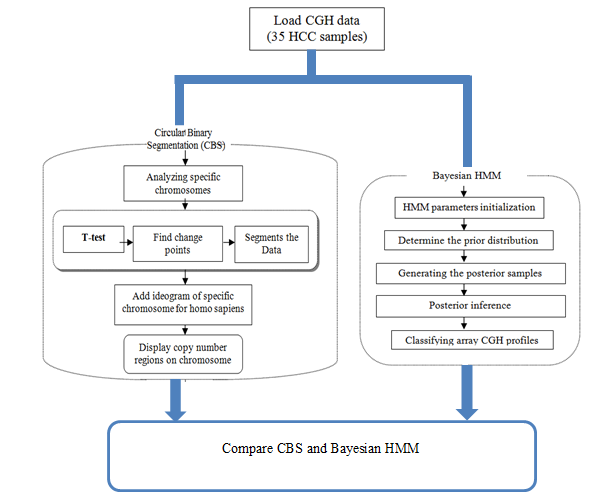 | Figure 2. The overall process of the proposed models |
2. Methods
- Array CGH techniques provide a powerful method for the simultaneous identification of DNA copy number alternations on a human genome. The statistical CBS method used to identify chromosomal regions that have been gained or lost and the statistical Bayesian approach of HMM procedure formulates the analysis of array CGH of human HCC in order to detect the chromosomal aberrations; amplifications or deletions. The procedures starts with loading the array CGH data of hepatocellular carcinoma, and then apply the CBS and Bayesian HMM algorithms individually to analyse 35 samples from human chromosomes 1, 4, 13, 16, 17 and 20 of the hepatocellular carcinoma array CGH data, and finally compare results of the two algorithms.The CBS method provides a natural way to segment the chromosome into contiguous regions and bypasses parametric modelling of the data with its use of a permutation reference distribution.It is starts with the whole chromosome and segments it recursively by testing for change points; it stops when none can be found in any of the segments[23]. It recursively detects pairs of change points to identify chromosomal segments with altered copy numbers, Once the chromosome is partitioned, the change points on array-CGH data and copy numbers of the segments can be estimated[24].The likelihood function of HMM can use the objective decision rules based on posterior probabilities to detect CNA, unlike CBS which is purely segmentation method.Bayesian HMM is applied by initializing the model parameters, determine the prior distribution, generating the posterior samples, then posterior inference to compute the probabilities of each state and at last classify array CGH profiles. Results obtained by the two statistical approaches are compared to identify genome-wide alternations in copy number from the genomic data; the overall process is shown in figure 2.
2.1. Loading the Array CGH Data of HCC
- Array-based CGH is an accurate technique to predict DNA copy number variations across the genome. The DNA clones of both test and reference samples are first hybridized to mapped array fragments. Then, log2 intensity ratios of test to reference provide useful information about genome- profiles in copy number. Array-CGH measures the relative copy number of the tumour (T) against reference(R) genomic DNA, which is reflected in its log2 T/R ratio. In an ideal situation, the log2 ratio of normal clones is log2 (2/2) = 0, single copy losses is log2 (1/2) = -1, and single copy gains is log2 (3/2) = 0.58. Multiple copy gains or amplifications would have values of log2 (4/2), log2 (5/2), and so on. Loss of either copies, or a deletion would correspond to the value of -inf. There is a dependent relation between the log2 ratios of neighbouring clones. These dependencies require the use of efficient statistical methods like circular binary segmentation and Bayesian HMM as in this paper to characterize the genomic profiles. The data used in this study is the array CGH profiles of 35 hepatocellular carcinoma samples of human chromosomes 1, 4, 13, 16, 17 and 20 to compare the normal versus tumour DNA (hepatocellular carcinoma). It provides a whole-genome screening of DNA-copy number changes by array-based or matrix comparative genomic hybridization (a-CGH). Tumour DNA labelled in Cy3 and pooled DNA of lymphocytes from healthy donors labelled in Cy5[1816105025].The data of normalized log2 based intensity ratios were stored in Excel files and are available at[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo].
2.2. Circular Binary Segmentation (CBS)
- A number of 35 samples of human chromosomes 1, 4, 13, 16, 17 and 20 from HCC patients are analysed using MATLAB by identifying change-points that will partition each chromosome into segments. Once the chromosome is partitioned, we can estimate the copy numbers of the segments with the help of additional information such as the ploidy of the chromosome to estimate the locations of copy number aberrations, Designated by Zij as shown in Equation (1):
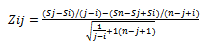 | (1) |
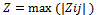 | (2) |
2.3. Bayesian HMM
- The Bayesian HMM approach of a Metropolis-within- Gibbs algorithm is used to generate posterior samples of the parameters[26-27].Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is useful in different kinds of situations especially in Bayesian algorithm. This technique used to receive samples from a multivariate distribution when it is infeasible to simulate from the distribution directly. Instead one simulates samples from a Markov chain whose stationary distribution is the desired distribution. Discarding the first simulations as burn in, it is possible to assume that the simulations are samples from the required multivariate distribution[28].To analyse the a-CGH data of HCC with the Bayesian HMM approach, we need to initialize the parameters. The model parameters are divided into four blocks. The algorithm iteratively generates each of the four blocks based on the remaining blocks and the data. We need to define the number of states of 4 as follows:S1= copy number loss state.S2= copy number neutral state.S3= single copy gain state. S4= amplification (multiple gain) state.The mu is an unknown parameter for each state with this constraint[26]:µ1<µ2<µ3<µ4The priors for mean copy number changes are:μ1 ∼N (−1, τ21) · I (μ1 <- ε) where ε >0, for the mean μ1 corresponding to copy number losses.μ2 ∼N (0, τ22)· I (−ε<μ2 <ε), for the copy-neutral state.μ3 ∼N (.58, τ2)· I (ε<μ3 < .58), for single-copy gains.[μ4 | μ3, σ3] ∼N (1, τ24) · I (μ4 >μ3 + 3σ3), for multiple-copy gains (amplification).Also, the number of Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) iterations is defined to be 100. The chromosome-specific hyper parameters are the transition probability matrix A, means {μ1, μ2, μ3, μ4}, and error variances {σ1, σ2, σ3, σ4}. The hyper parameters of the prior distributions for the four states are determined as[-1, 0, 0.58, 1], and the parameter ε which determines constrains of the means is set as ε = 0.1.The Bayesian approach assumes priors for all unknown parameters. As the meaning of the copy number states S1, S2, S3 and S4 are well defined before; this will make the use of informative priors based on the knowledge of array CGH data more facilitated[26]. The error variance ơ for the four states is determined by sampling from ɤ distribution with prior scale parameter α and β. The means for the four states are determined by sampling from truncated normal distribution between the lower and upper bounds of the means. Independent Dirichlet priors for the rows of the stochastic 4x4 transition probability matrix are assumed and the stochastic prior transition matrix A from the Dirichlet distributions is also generated. The transition matrix has a unique stationary distribution PI. This stationary distribution is an eigenvector of the transition matrix associated with the eigenvalue 1. So, the prior stationary distribution PI and then the initial emission matrix B are generated. Decode initial hidden states of the clones using a stochastic forward- backward algorithm[27]. For each MCMC iteration, the four blocks of parameters are generated as in[26], block B1 is updated using a Metropolis-Hastings step to generate the transition matrix, block B2 the copy number states is updated using a stochastic forward propagate backward sampling algorithm, block B3 is updated by computing the posterior mean mu distributions of the four states to generate the error variance ơ, and lock B4 is updated to generate sigmas distributions.For each MCMC iteration, the generated states can be classified as focal aberrations, transition points, amplifications, outliers and whole chromosomal changes [26].
2.4. Implementation
- This work is written in the MATLAB language and has been tested on the WINDOWS platform with MATLAB version 7.0 and its powerful Bioinformatics Toolbox.
3. Results and Discussion
- The development and progression of cancer diseases characterizes the genomic instability that frequently resulting in genomic alternations including chromosome aberrations of DNA copy number gains or losses. The study at hands uses each CBS and Bayesian HMM to identify genome wide alternations in copy number from the array CGH data of HCC. Array CGH was constructed to detect DNA copy-number variations across a whole genome. Circular binary segmentation (CBS) approach is performed on array-based comparative genomic hybridization (a-CGH) data to determine the copy number alteration segments and change points. Also, Bayesian statistical approach depending on Hidden Markov Model (HMM) is used to analyse array CGH data in order to detect copy number variations; loss or gain, identifying localized amplifications and deletions. The array CGH data of 35 samples from human chromosomes 1, 4, 13, 16, 17 and 20 of human HCC is first downloaded from GEO in the form of excels files and loaded. Each measurement in array CGH data is the log ratio of two raw measurements, red and green, which we denote by log(R/G). Figure 3, shows a plot the log2 ratio data of chromosome 1 from sample (GSM207013), then CBS method is performed to segment the chromosome and the ideogram for specific chromosome of Homo sapiens is added. Figure 4, shows that there is gain detected in chromosome 1 in the region from 1q21 to 1q22 which contains the tumor suppressors gens JTB, SHC1, CCT3and COPA[29]. We validated CBS model on chromosome 1 and it was detected in 63% of HCC cases[24].
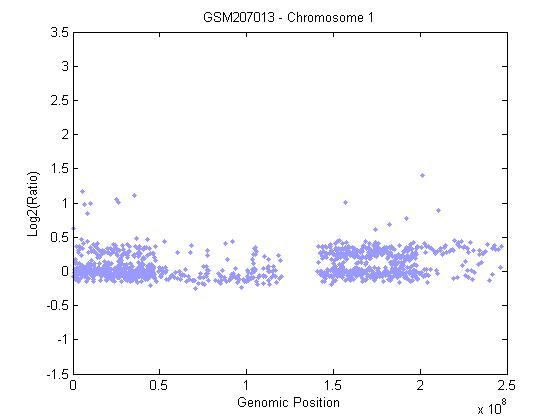 | Figure 3. Array CGH profiles of chromosome 1 |
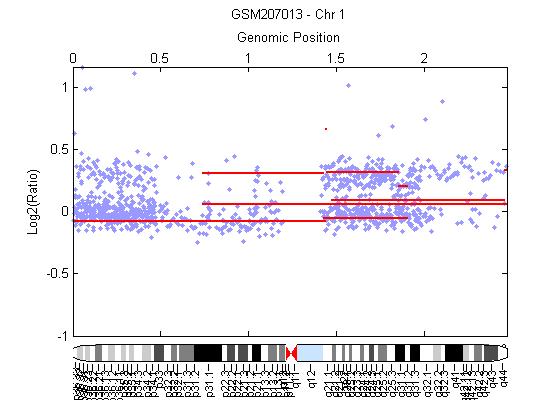 | Figure 4. Chromosome 1 segmented by CBS and has gain represented by red horizontal line in region 1q21-1q22 |
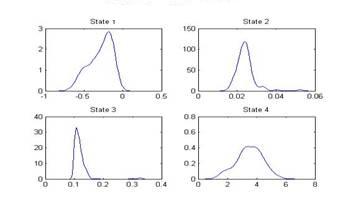 | Figure 5. Distribution of Mu of states |
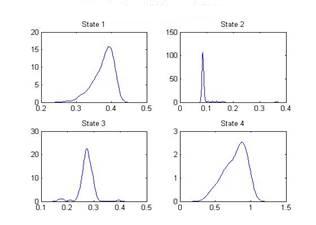 | Figure 6. Distribution of sigma of states |
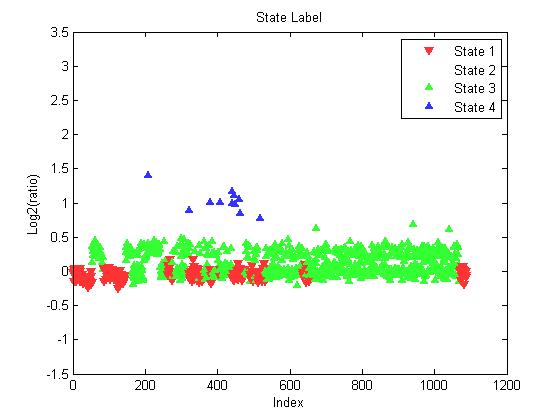 | Figure 7. State label for each clone on chromosome (1) of sample GSM207013 |
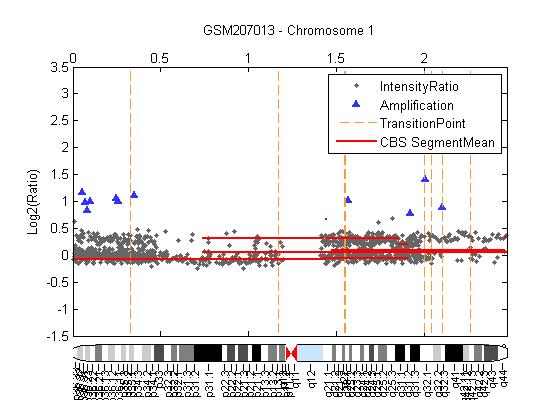 | Figure 8. The segment means polled by red horizontal line from the CBS procedure with HMM algorithm the broken red vertical lines represent transition points, High-level amplifications indicated by ∆ |
4. Conclusions
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a malignant tumour of the liver. Liver cirrhosis is the most important leading causes of HCC, Diagnosis of HCC patient are difficult, because the difficulty of detecting HCC at its early stage. Newly developed of a-CGH enable simultaneous measurement of copy number at thousands of sites in a genome, it is provides much useful information about changes in copy number.Identifying abnormal chromosomal regions and studying genes located in these regions can help to understand better the hepatocarcinogenesis using two statistical approaches named Circular Binary Segmentation (CBS) and Bayesian HMM for analysing array CGH data , we detected and characterized genome-wide copy number alterations on more than one thousand clones arising from several chromosomes. Result revealed that Bayesian HMM algorithm can identify high-level amplification regions, but CBS failed to detect any region of amplifications and Bayesian HMM are preferred because it is coherent way of incorporating all sources of information and of treating missing data, and it is ability to quantify numerically uncertainties in all unknowns, so Bayesian HMM is a powerful technology that provieds more information about the development of HCC, which may provide better diagnosis and prognosis of HCC .
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML