-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Bioinformatics Research
2012; 2(3): 21-32
doi: 10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20120203.02
Insilico Analysis of Novel Relb, Rele and Mazf Toxin-Antitoxin Homolog’s from the Genome of Xenorhabdus Nematophila
Jitendra Singh , Ravi Kumar Chaudhary , Pradeep Gautam
School of Biotechnology, Gautam Buddha University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, 201308, India
Correspondence to: Jitendra Singh , School of Biotechnology, Gautam Buddha University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, 201308, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Xenorhabdus nematophila is a motile gram-negative bacteria belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae and is a natural symbiont of a soil nematode of family Steinernematidae. The bacterium is essential for effective killing of the insect host and is required by the nematode to complete its life cycle. X. nematophila can be grown under standard laboratory conditions and known to secrete several extracellular products, which include lipase(s), phospholipase(s), protease(s), and several broad spectrum antibiotics as the bacteria enter the stationary phase of their growth cycle and are believed to be secreted in the insect hemolymph. Recently, the genome of X. nematophila has been completely sequenced and annotated version is available in the NCBI database. In this study we have extensively analyzed bioinformaticaly the genome of X. nematophila with NCBI server (). Our results showed the presence of relB, relE, and mazF toxin-antitoxin homolog’s at different loci in the genome. Later, various genes present in these loci were studied for phylogenetic as well as physiochemical analysis. Promoter analysis of each module has been done to know the various transcription factors involved in their transcription.
Keywords: Toxin-antitoxin system, Putative relB, relE, mazF, genome, phylogenetic analysis, promoter, X. nematophila
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Xenorhabdus nematophila is a motile gram-negative bacteria belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae[1]. It forms symbiotic association in the gut of a soil nematode of family Steinernematidae[2]. All the Xenorhabdus isolates, studied so far have been obtained from nematodes harvested from soil samples. Free-living forms of the bacterium have not yet been isolated from soil or water sources, which suggest that the symbiotic association may be essential for the survival of the bacteria in the environment. The bacteria, in turn, are essential for effective killing of the insect host and are required by the nematode to complete its life cycle[3,4]. X. nematophila can be grown under standard laboratory conditions. Growth in vitro is probably supported by the rich nutrient supply of the laboratory growth media and lack of competition that normally exists in the soil environment. As the bacteria enter the stationary phase of their growth cycle, they secrete several extracellular products, which include lipase(s), phospholipase(s), protease(s), and several broad spectrum antibiotics[5,6] that can be assayed in the culture media.These products are believed to be secreted in the insect hemolymph when the bacteria enter stationary phase conditions. The degradative enzymes break down macromolecules of the insect cadaver to provide the developing nematode with nutrient supply, while the antibiotics suppress contamination of the cadaver by other soil microorganisms. Cytoplasmic inclusion bodies, composed of highly expressed crystalline proteins, are also produced by the bacterium during stationary-phase growth[7]. In general, bacteria exposed to a plethora of environments possess molecular responses that regulate the degradation of defective or unnecessary proteins and mRNA molecules. These defective unnecessary proteins or mRNA molecules proves burden during nutritional stress which decrease cell survival rate. To get rid of these faulty molecules produced during transcription or translation and to increase cell survival rate during nutritional or antibiotic stress a unique control mechanism is operated that help prokaryotes to cope with these unfavourable conditions. This control mechanism consist of two components together known as toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules and these modules form a non toxic complex in a favourable condition[8,9] while on the other hand modulate the global levels of transcription and replication during exposure of nutritional stress or antibiotic stress due to over expression of toxic component.Generally in prokaryote TA modules codes for two components and they are of three types: in type I TA module, the antitoxin are small antisense RNAs that repress translation of the toxin genes[10,11] whereas in type II the antitoxin are proteins in nature and combine with and neutralize the toxin[12]. Type III encodes a small RNA antitoxin that combines with and neutralise toxin protein[13]. Toxin- antitoxin (TA) systems or modules are broadly distributed in prokaryotes in multiple copies[14,15] and all TA operons are auto -regulated at the level of transcription by the antitoxins in which antitoxin component neutralizes its cognate toxin[16]. For example, the relBE and mazEF TA systems are global inhibitors of translation and cleave mRNA during amino acid starvation that leads to the reduction of post starvation rate of translation[17-19]. Moreover, these systems also enhance relative competitiveness of alternative sigma factors (σ) or transcription factors to prioritize transcription of stress related genes[20,21]. Since E. coli TA modules are involved in the survival of E. coli following stress conditions therefore, it could be possible that similar kind of survival mechanism exist in X. nematophila which protects bacterium during its stressfull life cycle inside the insect hemolymph or in insect carcass (due to exponential growth of bacterium which leads to nutrient deprivation). Therefore, it is necessary to study toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules of X. nematophila in detail. Recently, the genome of X. nematophila has been sequenced, annotated and available in NCBI database. Moreover, so far not a single toxin- antitoxin (TA) module from X. nematophila has been reported. Therefore, this gave us opportunity to extensively search X. nematophila genome bioinformatically with NCBI server () for the identification of such toxin-antitoxin modules. In this study we have identified three putative TA modules such as relB, relE and mazEF, in the genome of X. nematophila. Interestingly, in our case relBE module is divided into two separate modules relB and relE, and they are located very far from each other in genome, each having their own toxin and antitoxin components respectively. Molecular weights as well as isoelectric point of each toxin and antitoxin proteins have been identified with Expasy server (www.expasy.ch) which suggests that all the three novel identified TA modules in this study belongs to Type II toxin-antitoxin category. Extensive promoter analysis is done with BPROM () to dissect the role various transcription factor (s) which control the transcription of such novel identified putative toxin-antitoxin modules in X. nematophila.
2. Methods
2.1. Identification and Genetic Organization of Putative TA Modules
- Complete genome sequence of X. nematophila ATCC 19061 was available in NCBI server () in two different databases; INSDC database with accession number and RefSeq database with accession number . The entire genome sequence of X. nematophila was downloaded from the Refseq database due to its nonredundant nature and was analyzed bioinformatically for the presence of relB, relE and mazF homolog’s. Indentified operons coding these toxin-antitoxin modules were downloaded and analyzed with ORF (Open Reading Frame finder) finder software from NCBI server. (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html)
2.2. Protein -Protein Blast
- Protein databank was searched by protein-protein blast performed with putative toxin-antitoxins encoded by the various operon from the genome of X. nematophila using NCBI server ()
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
- Different annotated protein sequences were mutiple aligned and phylogenetic trees were constructed by using CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software.
2.4. Physiochemical Properties
- All the physiochemical properties of putative toxin- antitoxin proteins have been determined by Expasy server ()
2.5. Promoter Analysis
- Identification of putative promoter associated with ORFs were determined by software BPROMO (. com)
2.6. Genomic DNA Isolation
- X. nematophila culture was inoculated from glycerol stock in 50 ml and grown overnight at 28℃, 200 rpm. Overnight grown culture was pelleted down by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4℃. The pellet was resuspended in 4 ml TE buffer pH8 (10 mM Tris HCl, 1mM EDTA) and 0.5 ml of 10% SDS was added. 30 μl of proteinase K (20mg/ml) was added to the resuspended culture and incubated at 37℃ for one hour. After complete lysis of the cells, 1 ml of 5 M NaCl was added and mixed gently. 750 μl CTAB NaCl mixture was added to the lysate and incubated at 65℃ for 20 minutes. Later equal volume of chloroform: Isoamyl alcohol mix (approax 7.5ml) was added and mixed gently. It was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm at 4℃ for 30 minutes. To the aqueous phase containing genomic DNA, 12.5 μl of RNase (2mg/ml) was added. The supernatant was incubated at 37℃ for one and half hours; equal volume of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol mixture was added and mixed properly. The tubes were centrifuged at 12,000 rpm, for 30 minutes at 4℃. The supernatant was again extracted with equal volume of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol mixture. The supernatant (aqueous phase) was collected in korex tube and 0.6 volume of isopropanol was added and mixed properly. korex tube was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 20 minutes at 4 ℃. The pellet was washed with 70 % ethanol and kept for drying in room temperature. Finally the pellet was dissolved in 0.5 ml autoclaved water and run on 0.8 % agarose gel.
2.7. Amplification of putative mazF, relB and relE operon by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) from genome
- The DNA sequence encoding mazF and its putative antitoxin mazE respectively were obtained by PCR amplification using genomic DNA as template (Denaturation at 94ºC for 30 sec, annealing at 60ºC for 30 sec and extension at 68ºC for 50 sec, total 30 cycles) for cloning with primer pair JSR1 and JSR2. Sequence encoding relB antitoxin and its putative toxin respectively were obtained by PCR amplification using genomic DNA as template (Denaturation at 94ºC for 30 sec, annealing at 60ºC for 30 sec and extension at 68ºC for 50 sec, total 30 cycles) for cloning with primer pair JSR6 and JSR7. Sequence encoding relE and its putative antitoxin respectively were obtained by PCR amplification using genomic DNA as template (Denaturation at 94ºC for 30 sec, annealing at 60ºC for 30 sec and extension at 68ºC for 50 sec, total 30 cycles) for cloning with primer pair JSR11 and JSR12.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Genetic Organization of relB, relE, and mazF Homolog’s
- Complete genome of X. nematophila was analyzed bioinformatically for the identification for toxin-antitoxin homologs. We have identified three loci corresponding to three different toxin-antitoxin modules. mazF toxin homolog along with gene encoding a hypothetical protein was located in operon consist of 530bp, annotated as “XCN_1operon0855” which lies between 4269050-4269581 bp of X. nematophila genome as shown in Figure 1 (a). Whereas, relB antitoxin homolog along with part of Qin prophage system was located as a part of operon “XCN_1operon0367” consist of 3278 bp which lies between 1841962-1845241 bp of X. nematophila genome in the complement orientation as shown in Figure 1(b). Interestingly, relE toxin homolog along with stability protein gene stbD was located in separate operon consist of 526 bp, annotated as “XCN_1operon0557” which lies between 2939581-2940108 bp of X. nematophila genome as shown in Figure 1 (c). Therefore, in our case relB and relE homologs were located separately in genome rather than forming usual single relBE toxin-antitoxin module as present in other prokaryotic system[17]. All operons were further analyzed with ORF (Open Reading Frame Finder).
3.2. Analysis by ORF Finder (Open Reading Frame Finder) and Identification of Protein Families
- All three identified operons were analyzed by ORF finder. First operon “XCN_1operon0855” encoded two different genes, first gene correspond to a hypothetical protein of 52 amino acids, where as second gene corresponds to MazF toxin protein of 125 amino acids. Their corresponding protein sequences were deduced by ORF finder. Protein-protein blast with hypothetical protein encoded by first gene of operon did not show any conserved domain. Interestingly, it showed 58% identity with MazE antitoxin protein from vibrio cholerae 1587 (Accession no. ). Therefore, we have designated this hypothetical protein from X. nematophila as putative MazE antitoxin. Similarly, protein-protein blast with MazF toxin protein encoded by the second gene showed a conserved domain in its N’ terminal belonging to PemK superfamily as shown in Figure 2. Blast results showed that MazF toxin protein from X. nematophila was 75% identical with MazF toxin protein from Photobacterium profundum SS9 (Accession no. ). Second operon “XCN_1operon0367” which encoded four different genes but they are in a complement orientation. First gene of an operon corresponds to a RelB antitoxin protein of 84 amino acids, where as second gene corresponds to Qin prophage system coding for 57 amino acids. Third and fourth gene codes for uhpB and upbC gene respectively. uhpC codes for sensory histidine kinase which is part of the two-component regulatory system with UphA whereas, uhpB codes for a membrane protein. All the corresponding protein sequences encoded by four genes were deduced by ORF finder. Protein-protein blast with RelB antitoxin protein showed a conserved domain belonged to RelB superfamily as shown in Figure 3 (a). Blast results showed its similarity with RelB antitoxin protein from Photorhabdus luminesense subs laumondii TT 01 (Accession no. ) with 89% identity. Similarly, protein-protein blast with Qin prophage system protein encoded by the second gene showed 81% identity with hypothetical protein YE0510A from Yersinia enterocolitica subsp enterocolitica 8081 (Accession no ) and 71% identity with RelE toxin protein from Photorhabdus asymbiotica subsp. asymbiotica ATCC 43949. We have designated this protein as putative toxin. Blast results showed that putative toxin encoded by second gene of operon have a conserved domain at N’ terminal which belonged to plasmid stability super family as showed in Figure 3 (b). Although putative toxin was encoded by genome but it belonged to plasmid stability family, this could be possible only due to the horizontal gene transfer, commonly present in the prokaryotic system. Third operon “XCN_1operon0557” encoded two different genes in complement orientation, first gene corresponding to a stability protein StbD of 83 amino acids, where as second gene corresponds to RelE protein of 94 amino acids. Their corresponding protein sequences were deduced by ORF finder. Protein-protein blast with stability protein StbD encoded by first gene of operon showed a conserved domain at its N’ terminal belonged to PhdYefM antitoxin superfamily as shown in Figure 4 (a). Blast result showed that stability protein StbD from X. nematophila is 84% identical with Stability protein StbD (Antitoxin) from Escherichia coli ED1a (Accession no. ). Therefore, we have designated this protein as putative antitoxin. However, protein-protein blast with RelE protein showed a conserved domain at its N’ terminal belonged to plasmid stability superfamily as shown in Figure 4 (b). Blast result showed that RelE protein from X. nematophila is 73% identical with stability protein StbE from Edwardsiella ictaluri 93-146 () and 71% identical with toxin component of toxin-antitoxin sytem of RelE family from Edwardsiella tarda ATCC 23685 (Accession no ). In this case also RelE was encoded by genome but it belonged to a plasmid superfamily, again it is an example of horizontal gene transfer.
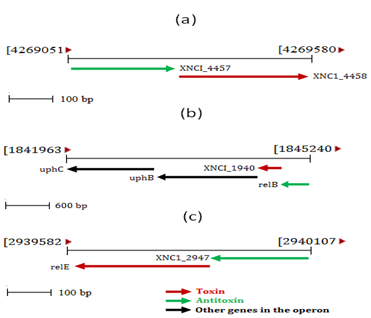 | Figure 1. Genetic organization of (a) mazF toxin homolog and gene encoding hypothetical protein (b) relB antitoxin homolog and gene encoding Qin prophage protein system (c) relE toxin homolog and gene encoding stability protein StbD in the genome of Xenorhabdus nematophila. |
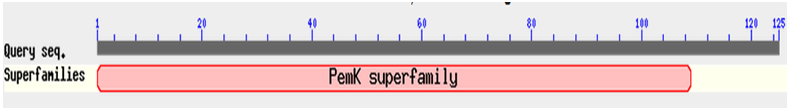 | Figure 2. N’ terminal conserved domain of MazF toxin protein belonged to PemK superfamily from X. nematophila determined by protein-protein blast |
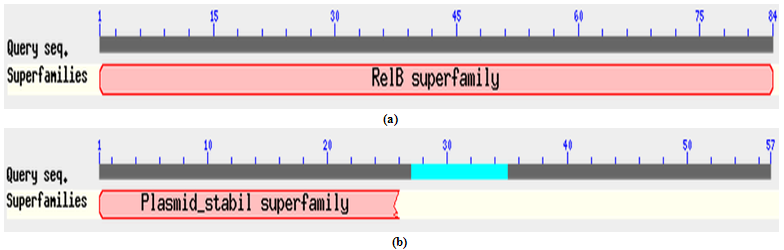 | Figure 3. (a) Conserved domain of RelB protein belonged to RelB super family and (b) N’ terminal of putative toxin belonged to plasmid stability super family from X. nematophila determined by protein-protein blast |
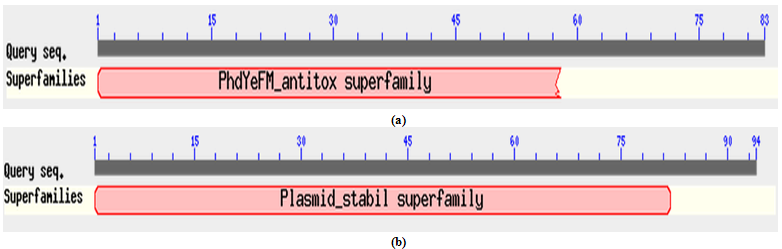 | Figure 4. (a) N’ terminal conserved domain of putative antitoxin belonged to stability protein StbD and (b) Conserved domain of RelE protein belonged to plasmid stability from X. nematophila determined by protein-protein blast |
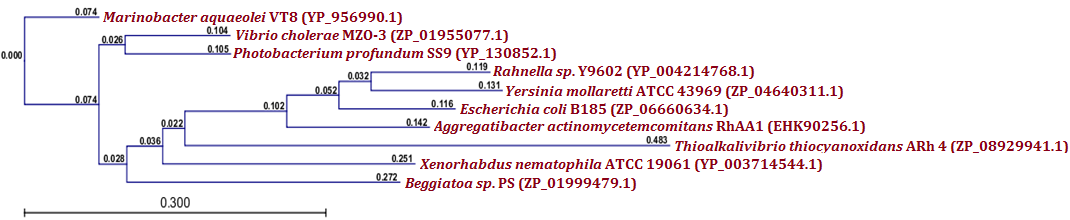 | Figure 5.(a) Phylogenetic analysis of MazF toxin protein from X. nematophila. Phylogenetic tree constructed based on the amino acid sequence of similar toxins from other bacteria. Sequences were multiple aligned by using CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software. Gene accession numbers for the various proteins were as follows: Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061 (YP_003714544.1), Photobacterium profundum SS9 (YP_130852.1), Vibrio cholerae MZO-3 (ZP_01955077.1), Marinobacter aquaeolei VT8 (YP_956990.1), Yersinia mollaretii ATCC 43969 (ZP_04640311.1), Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans RhAA1 (EHK90256.1), Beggiatoa sp. PS (ZP_01999479.1), Rahnella sp. Y9602 (YP_004214768.1), Thioalkalivibrio thiocyanoxidans ARh 4 (ZP_08929941.1) Escherichia coli B185 (ZP_06660634.1). CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software was used to construct the phylogenetic tree |
 | Figure 5.(b) Phylogenetic analysis of putative MazE antitoxin protein from X. nematophila. Phylogenetic tree constructed based on the amino acid sequence of similar antitoxins from other bacteria. Sequences were multiple aligned by using CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software. Gene accession numbers for the various proteins were as follow: Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061(YP_003714543.1), Vibrio cholerae 1587(ZP_01950607.1), Vibrio vulnificus(YP_001393092.1), Photobacterium profundum SS9(YP_130851.1), Photobacterium profundum SS9(AAG34554.1). CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software was used to construct the phylogenetic tree |
 | Figure 6.(a) Phylogenetic analysis of relB antitoxin protein from X. nematophila. Phylogenetic tree constructed based on the amino acid sequence of antitoxins from other bacteria. Sequences were multiple aligned by using CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software. Gene accession numbers for the various proteins were as follows: Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061 (YP_003712183.1), Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii TTO1 (NP_927617.1), Yersinia enterocolitica subsp. enterocolitica 8081 (YP_001004870.1), Candidatus Regiella insecticola LSR1 (ZP_07396152.1), Escherichia coli E22 (ZP_03046989.1),Providencia rustigianii DSM 4541 (ZP_05972866.2), Commensalibacter intestini A911 (ZP_09013002.1), Salmonella enterica subsp. arizonae serovar 62:z4,z23:-- str. RSK2980 (YP_001572182.1), Pantoea sp. SL1_M5 (ZP_09512769.1), Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans RhAA1 (EHK91012.1) CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software was used to construct the phylogenetic tree |
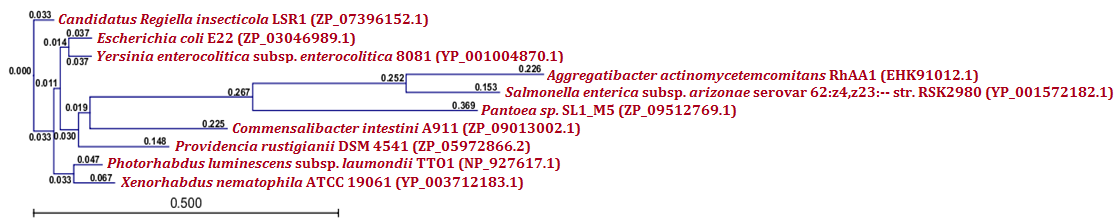 | Figure 6.(b) Phylogenetic analysis of putative toxin protein from X. nematophila. Phylogenetic tree constructed based on the amino acid sequence of antitoxins from other bacteria. Sequences were multiple aligned by using CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software. Gene accession numbers for the various proteins were as follows: Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061 (YP_003712183.1), Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii TTO1 (NP_927617.1), Yersinia enterocolitica subsp. enterocolitica 8081 (YP_001004870.1), Candidatus Regiella insecticola LSR1 (ZP_07396152.1), Escherichia coli E22 (ZP_03046989.1),Providencia rustigianii DSM 4541 (ZP_05972866.2), Commensalibacter intestini A911 (ZP_09013002.1), Salmonella enterica subsp. arizonae serovar 62:z4,z23:-- str. RSK2980 (YP_001572182.1), Pantoea sp. SL1_M5 (ZP_09512769.1), Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans RhAA1 (EHK91012.1) CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software was used to construct the phylogenetic tree |
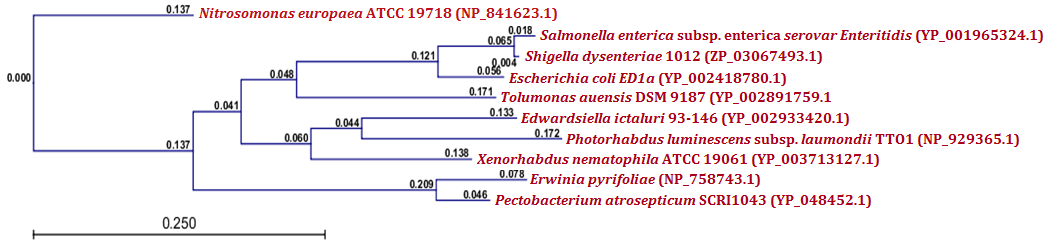 | Figure 7.(a) Phylogenetic analysis of RelE toxin protein. Phylogenetic tree constructed based on the amino acid sequence of toxins from other bacteria Sequence were aligned by using CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software. Gene accession numbers for the various proteins were as follows: Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061 (YP_003713127.1), Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii TTO1 (NP_929365.1), Edwardsiella ictaluri 93-146 (YP_002933420.1), Escherichia coli ED1a (YP_002418780.1), Shigella dysenteriae 1012 (ZP_03067493.1), Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis (YP_001965324.1), Tolumonas auensis DSM 9187 (YP_002891759.1), Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 (YP_048452.1), Erwinia pyrifoliae (NP_758743.1), Nitrosomonas europaea ATCC 19718 (NP_841623.1). CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software was used to construct the phylogenetic tree |
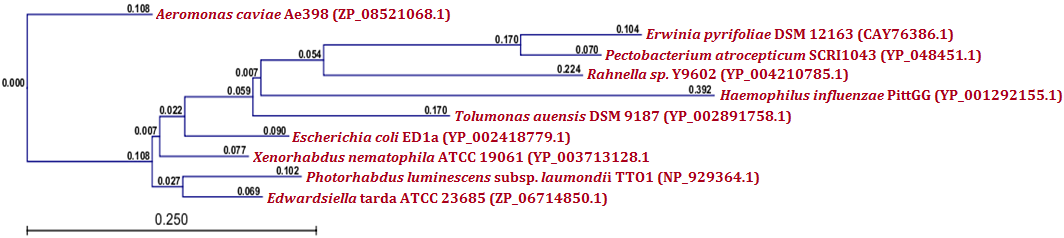 | Figure 7.(b) Phylogenetic analysis of RelE antitoxin protein. Phylogenetic tree constructed based on the amino acid sequence of antitoxins from other bacteria. Sequence were aligned by using CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software. Gene accession numbers for the various proteins were as follows: Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061 (YP_003713128.1), Edwardsiella tarda ATCC 23685 (ZP_06714850.1), Escherichia coli ED1a (YP_002418779.1), Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii TTO1 (NP_929364.1), Aeromonas caviae Ae398 (ZP_08521068.1), Tolumonas auensis DSM 9187 (YP_002891758.1), Rahnella sp. Y9602 (YP_004210785.1), Haemophilus influenzae PittGG (YP_001292155.1), Erwinia pyrifoliae DSM 12163 (CAY76386.1), Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 (YP_048451.1). CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software was used to construct the phylogenetic tree |
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of MazF, RelB and RelE
- Protein-protein blast with MazF, RelB and RelE showed similar proteins from other bacteria. All such similar protein sequences were downloaded, multiple aligned and phylogenetically analyzed with CLC Genomics Workbench (version 4.9) software. Phylogenetic analysis of MazF toxin of X. nematophila revealed that it formed a distinct branch from the toxins of other bacteria as shown in Figure 5 (a). Although, toxin of Photobacterium profundum S99 which showed maximum identity with MazF of X. nematophila was located phylogenetically very far from X. nematophila, it also formed a first distinct cluster with toxin of Vibrio cholerae MZO-3. Toxins from other bacteria such as Rahnella sp. Y9602 and Yersinia mollaretii ATCC 43969 formed their own second cluster where as toxins from Escherichia coli B185, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans RhAA1 and Thioalkalivibrio thiocyanoxidans ARh 4 lies between first cluster and X. nematophila ATCC 19061. Toxin of Marinobacter aquaeolei VT8 was separated from these two clusters in the very beginning however, toxin of Beggiatoa sp. PS was separated from second cluster just before toxin of X. nematophila ATCC 19061. As far as putative antitoxin MazE from X. nematophila ATCC 19061 is concerned, it was separated phylogenetically far from the antitoxin of Vibrio cholerae 1587 in very beginning as shown in figure 5 (b). However, antitoxin from two Photobacterium profundum S99 species formed a distinct cluster from the putative antitoxin MazE of X. nematophila whereas, antitoxin of Vibrio vulnificus was located between these two.Phylogenetic analysis of RelB antitoxin from X. nematophila ATCC 19061 revealed that there were two distinct clusters formed by similar antitoxins from other bacteria. Although X. nematophila ATCC 19061 is very close to Photorhabdus, its RelB antitoxin forms a unique evolutionary branch. Antitoxin of Escherichia coli H120 was separated in the very beginning from two main clusters however; antitoxin of Photorhabdus asymbiotica subsp. asymbiotica ATCC 43949 formed a separate first cluster along with antitoxins from Yersinia enterocolitica subsp. enterocolitica 8081 and Candidatus Regiella insecticola LSR1 which was far apart from antitoxin of X. nematophila ATCC 19061. Antitoxin of Commensalibacter intestini A911 formed a separate branch which was phylgenetically close to antitoxins of X. nematophila ATCC 19061 as well as of Providencia rustigianii DSM 4541. Antitoxin of Erwinia pyrifoliae Ep1/96 lies between antitoxin of Providencia rustigianii DSM 4541 and second cluster formed by antitoxins from Pseudomonas fluorescens WH6, and Shigella dysenteriae 1012 as shown in figure 6 (a). Phylogenetic studies with putative toxin of X. nemtophila ATCC 19061 revealed that it was very close to toxin of Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii TTO1 and both formed a unique cluster separated from the other two clusters formed by toxins from other bacteria. Toxin of Candidatus Regiella insecticola LSR1 was separated in very beginning from the putative toxin of X. nemtophila ATCC 19061 whereas, cluster formed by toxins from Escherichia coli E22 and Yersinia enterocolitica subsp. enterocolitica 8081 lies at distal end however, branch formed by the toxins from Providencia rustigianii DSM 4541 and Commensalibacter intestini A911 located at the proximal to putative toxin of X. nemtophila ATCC 19061. Toxin of Pantoea sp. SL1_M5 was located between toxin of Commensalibacter intestini A911 and third cluster formed by toxins from Salmonella enterica subsp. arizonae serovar 62:z4,z23:-- str. RSK2980 and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans RhAA1 as shown in Figure 6 (b).Phylogenetic analysis of RelE toxin of Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061 revealed that there were three distinct clusters formed by toxins from other bacteria as shown in figure 7 (a). Toxin of Nitrosomonas europaea ATCC 19718 was separated in the very beginning from toxin of Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061. Although Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061 is very close to Photorhabdus but its toxin formed unique evolutionary branch which was separated from distinct cluster formed by toxins from Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii TTO1 and Edwardsiella ictaluri 93-146. Second cluster formed by toxins from Erwinia pyrifoliae and Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 lies proximal to Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061 toxin, whereas thirds cluster formed by toxins from Escherichia coli ED1a, Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis and Shigella dysenteriae 1012 located at distal end whereas, toxin of Tolumonas auensis DSM 9187 was located between second and third cluster as unique branch.Phylogenetic studies with putative antitoxin of Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061 revealed that it was very close to antitoxin of Escherichia coli ED1a but were separated from each other as distinct branches of phylogenetic tree. Antitoxin of Aeromonas caviae Ae398 was separated in very beginning from putative antitoxin of Xenorhabdus nematophila ATCC 19061. Antitoxins from closely related bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii TTO1 (NP_929364.1) and Edwardsiella tarda ATCC 23685 formed separate cluster which was located proximal to putative antitoxin of X. nematophila ATCC 19061, whereas cluster formed by antitoxins from Erwinia pyrifoliae DSM 12163 along with Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 formed a cluster which was located at distal position to a branch formed by putative antitoxin of X. nematophila ATCC 19061. Antitoxins from Rahnella sp. Y9602, Haemophilus influenzae PittGG and Tolumonas auensis DSM 9187 had their own separate branches between antitoxin of Escherichia coli ED1a and a cluster formed by antitoxins from Erwinia pyrifoliae DSM 12163 and Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 as shown in Figure 7 (b).
3.4. Physiochemical Properties
- Toxin–antitoxin are usually transcribed together to form complex, so that the detrimental effect of the toxin part is neutralised by its counter antitoxin. Therefore, to form a tight complex in physiological conditions, pI of the individual proteins play a major role. Interaction between two proteins is depends upon the net charge at the particular pH, and larger the difference between pI, more ionic interaction will occurs between them. Therefore, the physiochemical properties of putative toxin-antitoxin proteins have been determined by Expasy server () which showed that MazF toxin had pI of 8.73 with molecular weight of 13665.03 Da whereas its putative antitoxin MazE had pI 4.41 with molecular weight 5672.30 Da. RelB antitoxin had pI of 9.52 with molecular weight of 6973.13 Da where as its putative antitoxin had pI 4.93 with molecular weight of 9831.21 Da. RelE toxin had pI of 9.71 with molecular weight of 9140.29 Da whereas its putative antitoxin had pI 4.17 with molecular weight of 58950.57 Da. All the above differences between pI of individual toxin and antitoxin pair will direct them to form a complex.
3.5. Promoter Analysis
- DNA sequences from upstream region of all three operons were downloaded from genome database and putative promoters were determined by BPROM software ().
3.5.1. mazF Promoter Analysis
- 170 bp upstream region of mazE were analyzed. It contained putative -10 and -35 promoter like elements. In this upstream region of mazE, CpxR and RpoH3 binding sequences were observed as shown in Figure 8. RpoH (σ32) is the heat shock sigma factor which turns on when exposed to heat. Three types of σ32-type transcription factors are known which codes three proteins named as RpoH1, RpoH2 and RpoH3[22,23]. This rpoH3 is the central gene that is flanked by rag (rpoH3-associated) genes and is arranged as ragABrpoH3ragCD on the chromosome of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. In this unique gene cluster, the first two genes code for a classical two-component regulatory system with an unknown function[22] while last two genes show maximum sequence similarity to heavy metal or multidrug efflux pumps of the RND (Resistance/Nodulation/cell Division)- MFP (Membrane Fusion Protein) family. The functional role and the specificity of rpoH3 transcription factor to its promoter is not well known. CpxR (cytoplasmic response regulator) and membrane-localized sensory histidine kinase (HK) CpxA are the key constituents of typical two- component regulatory system which are responsible to sense envelope stress. Response is mediated by a membrane- localized sensory histidine kinase (HK) CpxA and the cytoplasmic response regulator CpxR (RR). Autophosphorylation occurs at conserved histidine residue of CpxA as a response to envelope stress. The subsequent photophosphorylation of CpxR occurs at its conserved aspartate residue[24]. CpxR, after photophosphorylation, acts as transcriptional activator of those genes that are involved in protein folding and degradation in the bacterial envelope[25-27]. From these information’s, we inferred that putative maEF toxin- antitoxin module could be transcribed under unfavourable conditions such as physical or chemical stress.
3.5.2. relB Promoter Analysis
- 294 bp upstream region of relB were analyzed. It contained putative -10 and -35 promoter elements. In upstream region of relB, overlapping RpoD16, LexA, and ArgR binding sequences were observed above -35 regions whereas, RpoD18 binding sequence was overlapping with -10 region. Fis binding sequence was also observed below -10 region as shown in Figure 9. rpoD transcription factor was named as sigma factor-70 (σ70).
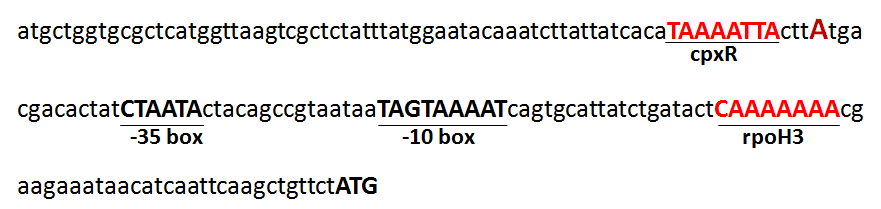 | Figure 8. 170 bp nucleotide sequence of upstream region of mazF operon showing -10, and -30 promoter like elements along with CpxR and RpoH3 binding sequences |
 | Figure 9. 294 bp nucleotide sequence of upstream region of relB operon showing -10, and -30 promoter like elements along with RpoD16, RpoD18, LexA, ArgR and Fis binding sequences |
3.5.3. relE Promoter Analysis
- 80 bp upstream region of relE operon were also analysed. It contained putative -10 and -35 promoter elements. In upstream region of relE, RpoH2 overlapping with -35 towards -10 region where as FUR overlaps RpoH2 towards -10 region as shown in Figure 10. RpoH2 is an alternative sigma factor. All organisms react to heat stress with the expression of heat-shock genes in order to cope with accumulating unfolded proteins. In Escherichia coli, heat-shock response is initiated at the transcriptional level by an alternative sigma factor s32 (RpoH). During heat stress, RpoH associates with RNA polymerase (RNAP) and initiates transcription of the heat-shock regulon, coding mainly for molecular chaperones and proteases. The transient induction of heat-shock response is tightly controlled by a regulatory feedback loop coupling the amount of heat-shock proteins to the cellular protein folding state. The transcriptional activator FUR, for "Ferric Uptake Regulation," is capable of controlling its own synthesis[52-55] and controls the transcription of genes involved in iron homeostasis[52,54,56-64] and a minor sigma factor that initiates transcription of ferric citrate transport genes in response to the presence of periplasmic iron(III) dicitrate[52,59,65]. This regulator also participates in the regulation of transcription of many other genes involved in different cellular functions: flagellum chemotaxis[66], methionine biosynthesis[66], acid and oxidative stresses[57,67] metal ion stress[66,68-70] resistance to cobalt and nickel[71], the tricarboxylic acid cycle[72,73], glycolysis and gluconeogenesis[57], respiration[66,72,73], porins[73], purine metabolism[66], 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate biosynthesis phage DNA packaging[57], etc. Therefore, it is quite possible that relE operon could be activating during the heat, oxidative and metal ion stress conditions.
 | Figure 10. 80 bp nucleotide sequence of upstream region of relE operon containing -10, and -30 promoter like elements along with rpoH2 and Fur binding sequences |
3.6 Genomic DNA and PCR amplification
- Genomic DNA was isolated from the X. nematophila as protocol described in method and shown in figure 10 (A). 530 bp DNA fragment encoding mazF and its putative antitoxin mazE respectively were obtained by PCR amplification using genomic DNA as template as shown in lane 1 figure 11 (B). Whereas, 417 bp DNA fragment encoding relB and its putative toxin were obtained by PCR amplification using genomic DNA as template as shown in lane 2 figure 11 (B) and 526 bp DNA fragment encoding relE and its putative antitoxin were obtained by PCR amplification as shown in lane 3 figure 11 (B).
 | Figure 11. (A) Genomic DNA isolation from X. nematophila. Lane 1, 2 and 3 genomic DNA at 3µg, 4 µg and 5 µg concentration. (B) PCR amplification of mazF, relB and relE operon using genomic DNA as template. Lane M, 100bp ladder; lane 1, 506 bp mazF operon; lane 2, 416bp relb operon; and lane 3, relE 526bp operon |
4. Conclusions
- In general, bacteria exposed to various unfavourable conditions possess molecular responses that regulate the degradation of defective or unnecessary proteins and mRNA molecules. One well-described quality control mechanism of Escherichia coli involves toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules. TA modules have been associated with bacterial programmed cell death (PCD) and programmed cell survival (PCS) or persistence[74-76] under various unfavourable conditions which could be physical, chemical or nutrient depleted condition. Since, X. nematophila which protects itself during stressed life cycle inside insect hemolymph or in insect carcass (due to exponential growth of bacterium which leads to nutrient deprivation) therefore, role of toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules in X. nematophila cannot be ruled out. With this background recently sequenced and annotated genome of X. nematophila has been studied bioinformatically for the identification of putative toxin-antitoxin modules in its genome. Three such modules mazF, relB and relE has been identified and studied in detail. Genomic organization revealed that mazF toxin module is located in “XCN_1operon0855” operon in a downstream position to a hypothetical protein. Protein-protein blast of MazF and hypothetical protein showed their similarity with MazF toxin from Photobacterium profundum SS9 (Accession no. ) and MazE antitoxin protein from vibrio cholerae 1587 (Accession no. ) respectively. Therefore, hypothetical protein from X. nematophila was designated as putative MazE antitoxin. Difference in their individual pI’s (MazF toxin: pI 8.73 and putative MazE antitoxin: pI 4.41) will tend them to form complex in physiological conditions. Therefore, we can presume that in X. nematophila mazF and mazE will form a putative mazEF toxin-antitoxin module. From the predicted promoter analysis, due to the presence of RpoH3 and CpxrR, we inferred that transcription of mazF and putative mazE will occur either under different environmental conditions such as high temperature or envelope stress. Similarly, second operon “XCN_1operon0367” encodes four genes in complement orientation. First gene of this operon encodes for RelB antitoxin which showed similarity with RelB antitoxin protein from Photorhabdus luminesense subs laumondii TT 01 (Accession no. ) where as second gene encode putative toxin part of Qin prophage toxin-antitoxin component system. Protein-protein blast with toxin protein showed its 81% identity with hypothetical protein YE0510A from Yersinia enterocolitica subsp enterocolitica 8081 (Accession no ) and 71% identity with RelE toxin protein from Photorhabdus asymbiotica subsp. asymbiotica ATCC 43949. In this case also difference in individual pI (Putative toxin: pI 9.52 and RelB antitoxin: pI 4.41) will tend them to form complex in physiological conditions. From predicted promoter analysis, presence of RpoD3, LexA, ArgR and Fis indicates that transcription of relB and its putative toxin will occur either under SOS conditions and might be tightly regulated. Therefore, we can presume that in X. nematophila gene encoding putative toxin and relB will form a novel toxin-antitoxin module. However, in other bacteria toxin component of this kind of module is denoted as relE[17,19]. Interestingly, in X. nematophila genome relE gene was located separately at operon “XCN_1operon0557” which encode two different genes in complement orientation. Protein-protein blast with putative stability protein StbD, encoded by first gene showed a conserved domain at its N’ terminal belonged to PhdYefM antitoxin superfamily. Therefore, putative StbD from X. nematophila is similar to Stability protein StbD (Antitoxin) from Escherichia coli ED1a (Accession no. ). Protein-protein blast with protein encoded by second gene relE from X. nematophila showed 73% identity with stability protein StbE from Edwardsiella ictaluri 93-146 () and 71% identity with toxin component of toxin-antitoxin sytem of RelE family from Edwardsiella tarda ATCC 23685 (Accession no ). Therefore, putative StbD antitoxin will form a pair with RelB toxin, which could be a novel toxin-antitoxin module in X. nematophila. In this case due to the differences in individual pI’s (Putative RelE toxin: pI 9.71 and putative antitoxin StbD: pI 4.17) they will form complex in physiological conditions. Predicted promoter revealed the presence of signature sequences for the binding of rpoH, which indicate transcription from this promoter under heat shock conditions. Apart from rpoH presence of FUR signature sequences revealed its transcription under iron regulated conditions. Therefore, in the end we conclude that in X. nematophila we have identified three novel toxin-antitoxin modules from its genome and their existence is proved with the assistance of wet lab experiments.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- We thank Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India for the financial support for this study.
References
| [1] | Boemare, N. E., and Akhrust, R. J. 1988. Biochemical and physiological characterization of colony form variants in Xenorhabdus ssp.[Enteriobacteriaceae]. J. Gen. Microbiol. 134: 751-761. |
| [2] | Herbert, E. E., and Goodrich-Blair, H. 2007. Friends and foes: Two faces of Xenorhabdus nematophila. Nature review. Micro. 5(8): 634-646. |
| [3] | Akhurst, R. J. 1993. Bacterial symbionts of entomopathogenic nematodes—the power behind the throne, pp. 127–136. In R. Bedding, R. Akhurst, and H. Kaya (ed.), Nematodes and the biological control of insect pests. CSIRO Publications, Melbourne, Australia. |
| [4] | Kaya, H. K., and Gaugler, R. 1993. Entomopathogenic nematodes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 38: 181–206. |
| [5] | Akhurst, R. J. 1982. Antibiotic activity of Xenorhabdus spp. bacteria symbiotically associated with insect pathogenic nematodes of the families Heterorhabditae and Steinernematidae. J. Gen. Microbiol. 128(12): 3061-3065. |
| [6] | Nealson, K. H., Schmidt, T. M., and Bleakley, B. 1990. Physiology and biochemistry of Xenorhabdus, p. 271–284. In R. Gaugler and H. Kaya (ed.), Entomopathogenic nematodes in biological control. CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, Fla. |
| [7] | Couche, G. A., and Gregson, R. P. 1987. Protein inclusions produced by the entomopathogenic bacterium Xenorhabdus nematophilus subsp. nematophilus. J. Bacteriol. 169(11):5279–5288. |
| [8] | Gotfredsen, M. & Gerdes, K. 1998. The Escherichia coli relBE genes belong to a new toxin–antitoxin gene family. Mol. Microbiol. 29(4), 1065–1076 |
| [9] | Galvani, C., Terry, J. & Ishiguro, E. E. 2001. Purification of the RelB and RelE proteins of Escherichia coli: RelE binds to RelB and to ribosomes. J. Bacteriol. 183(8), 2700–2703 |
| [10] | Fozo, E. M., Hemm, M. R., Storz, G. 2008. Small toxic proteins and the antisense RNAs that repress them. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72: 579–589. |
| [11] | Gerdes, K., Wagner, E. G. 2007. RNA antitoxins. Curr Opin Microbiol 10(2): 117–124. |
| [12] | Gerdes, K, Christensen SK, Løbner-Olesen , A. 2005. Prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin stress response loci. Nat Rev Microbiol 3(5): 371–382. |
| [13] | Fineran P. C., et al. (2009) The phage abortive infection system, ToxIN, functions as a protein-RNA toxin-antitoxin pair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(3): 894–899. |
| [14] | Fozo, E. M., Makarova, K. S., Shabalina, S. A., Yutin, N., Koonin, E. V., Storz, G. June 2010. "Abundance of type I toxin–antitoxin systems in bacteria: searches for new candidates and discovery of novel families". Nucleic Acids Res. 38(11): 3743 -59. |
| [15] | Gerdes K, Wagner EG April 2007. "RNA antitoxins".Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 10(2): 117–24. |
| [16] | Masuda, Y., Miyakawa, K., Nishimura, Y. & Ohtsubo, E. 1993. chpA and chpB, Escherichia coli chromosomal homologs of the pem locus responsible for stable maintenance of plasmid R100. J. Bacteriol. 175(21), 6850–6856. |
| [17] | Christensen, S. K. & Gerdes, K. 2003. RelE toxins from bacteria and Archaea cleave mRNAs on translating ribosomes, which are rescued by tmRNA. Mol. Microbiol. 48, 1389–1400. |
| [18] | Christensen, S. K., Pedersen, K., Hansen, F. G. & Gerdes, K. 2003. Toxin–antitoxin loci as stress-responseelements: ChpAK/MazF and ChpBK cleave translated RNAs and are counteracted by tmRNA. J. Mol. Biol. 332(4), 809–819. |
| [19] | Christensen, S. K. & Gerdes, K. 2004. Delayed-relaxed response explained by hyperactivation of RelE. Mol. Microbiol. 53(2), 587–597. |
| [20] | Jishage, M., Kvint, K., Shingler, V. & Nystrom, T. 2000. Regulation of factor competition by the alarmone ppGpp. Genes Dev. 16(10), 1260–1270. |
| [21] | Laurie, A. D. et al. 2003. The role of the alarmone (p)ppGpp in competition for core RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 278(3), 1494–1503. |
| [22] | Narberhaus, F., Krummenacher, P., Fischer, H. M. & Hennecke, H. 1997. Three disparately regulated genes for s32-like transcription factors in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol. Microbiol. 24(1),93-104. |
| [23] | Narberhaus, F., Kowarik, M., Beck, C. & Hennecke, H. 1998. Promoter selectivity of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum RpoH transcription factors in vivo and in vitro. J. Bacteriol. 180(9), 2395-2401. |
| [24] | Raivio, T., and T. Silhavy. 1997. Transduction of envelope stress in Escherichia coli by the Cpx two- component system. J. Bacteriol. 179(24):7724-7733. |
| [25] | Danese, P. N., and T. J. Silhavy. 1997. The sigma(E) and the Cpx signal transduction systems control the synthesis of periplasmic protein-folding enzymes in Escherichia coli. genes and development. 11(9):1183-93. |
| [26] | Dartigalongue, C., and S. Raina. 1998. A new heat-shock gene, ppiD, encodes a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase required for folding of outer membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. embo journal. 17(14): 3968-80. |
| [27] | Pogliano, J., A. S. Lynch, D. Belin, E. C. Lin, and J. Beckwith. 1997. Regulation of Escherichia coli cell envelope proteins involved in protein folding and degradation by the Cpx two-component system. genes and development. 11(9): 1169-82. |
| [28] | 'Ari R 1985. "The SOS system." Biochimie 67(3-4); 343-7. |
| [29] | Fernandez De Henestrosa, A. R., Ogi T., Aoyagi, S, Chafin D, Hayes J. J., Ohmori, H, Woodgate, R 2000. "Identification of additional genes belonging to the LexA regulon in Escherichia coli." Mol Microbiol 35(6); 1560-72. |
| [30] | Brent R., Ptashne M. 1980. "The lexA gene product represses its own promoter." Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 77(4); 1932-6. |
| [31] | Chen, Z., Yang, H., Pavletich, N. P. 2008. "Mechanism of homologous recombination from the RecA-ssDNA/dsDNA structures." Nature 453(7194); 489-4. |
| [32] | Cox, M. M. 2007. "Regulation of bacterial RecA protein function." Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 42 (1); 41-63. |
| [33] | Giese, K. C., Michalowski, C. B., Little, J. W. 2008. "RecA-dependent cleavage of LexA dimers." J Mol Biol 377(1); 148-61. |
| [34] | Little, J. W. 1991. "Mechanism of specific LexA cleavage: autodigestion and the role of RecA coprotease." Biochimie 7 (4); 411-21. |
| [35] | Butala, M., Klose D., Hodnik V., Rems A., Podlesek Z., Klare J. P., Anderluh, G., Busby, S. J., Steinhoff, H. J., Zgur-Bertok, D. 2011. "Interconversion between bound and free conformations of LexA orchestrates the bacterial SOS response." Nucleic Acids Res. 39(15): 6546-57. |
| [36] | Mazon G, Erill I, Campoy S, Cortes P, Forano E, Barbe J 2004. "Reconstruction of the evolutionary history of the LexA-binding sequence." Microbiology 150 (Pt 11); 3783-95. |
| [37] | Fogh, R. H., Ottleben G, Ruterjans H, Schnarr M, Boelens R, Kaptein R 1994. "Solution structure of the LexA repressor DNA binding domain determined by 1H NMR spectroscopy." EMBO J 1994; 13(17); 3936-44. |
| [38] | Luo Y, Pfuetzner R. A., Mosimann, S, Paetzel, M., Frey, E. A., Cherney M, Kim B., Little, J. W., Strynadka NC 2001. "Crystal structure of LexA: a conformational switch for regulation of self-cleavage." Cell 106(5); 585-94. |
| [39] | Schnarr, M., Granger-Schnarr, M., Hurstel, S., Pouyet, J. (1988). "The carboxy-terminal domain of the LexA repressor oligomerises essentially as the entire protein." FEBS Lett 234(1); 56-60. |
| [40] | Little, J. W., Mount, D. W., Yanisch-Perron, C. R. (1981). "Purified lexA protein is a repressor of the recA and lexA genes." Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1981; 78(7); 4199-203. |
| [41] | Caldara, M., Charlier, D., Cunin, R. (2006). "The arginine regulon of Escherichia coli: whole-system transcriptome analysis discovers new genes and provides an integrated view of arginine regulation." Microbiology 152(Pt 11); 3343-54. |
| [42] | Lim, D. B., Oppenheim, J. D., Eckhardt, T., Maas, W. K. 1987. "Nucleotide sequence of the argR gene of Escherichia coli K-12 and isolation of its product, the arginine repressor." Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1987; 84(19); 6697-701. |
| [43] | Charlier, D., Roovers, M., Van Vliet, F., Boyen, A., Cunin, R., Nakamura, Y., Glansdorff, N., Pierard, A. 1992. "Arginine regulon of Escherichia coli K-12. A study of repressor-operator interactions and of in vitro binding affinities versus in vivo repression." J Mol Biol 1992; 226(2); 367-86. |
| [44] | Iupakis, A. K., Reitzer, L. 2002. "ArgR-independent induction and ArgR-dependent superinduction of the astCADBE operon in Escherichia coli." J Bacteriol 184(11); 2940-50. |
| [45] | Stirling, C. J., Szatmari, G., Stewart, G., Smith, M. C., Sherratt, D. J. 1988. "The arginine repressor is essential for plasmid-stabilizing site-specific recombination at the ColE1 cer locus." EMBO J 1988; 7(13); 4389-95. |
| [46] | Cho, B. K., Knight, E. M., Barrett, C. L., Palsson, B. O. 2008. "Genome-wide analysis of Fis binding in Escherichia coli indicates a causative role for A-/AT-tracts." Genome Res 18(6): 900-10. |
| [47] | Schneider, R., Lurz, R., Luder, G., Tolksdorf, C., Travers, A., Muskhelishvili, G. 2001. "An architectural role of the Escherichia coli chromatin protein FIS in organising DNA." Nucleic Acids Res 29(24); 5107-14. |
| [48] | Weinstein-Fischer, D., Altuvia, S. 2007. "Differential regulation of Escherichia coli topoisomerase I by Fis." Mol Microbiol 63(4); 1131-44. |
| [49] | Finkel, S. E., Johnson, R. C. 1992. "The Fis protein: it's not just for DNA inversion anymore." Mol Microbiol 6(22); 3257-65. |
| [50] | Travers, A., Schneider, R., Muskhelishvili, G. 2001. "DNA supercoiling and transcription in Escherichia coli: The FIS connection." Biochimie 83 (2); 213-7. |
| [51] | Bradley, M. D., Beach, M. B., de Koning, A. P., Pratt, T. S., Osuna, R. 2007. "Effects of Fis on Escherichia coli gene expression during different growth stages." Microbiology 153 (Pt 9); 2922-40. |
| [52] | Coulton, J. W., Mason, P., Cameron, D. R., Carmel, G., Jean, R., Rode, H. N. 1986. "Protein fusions of beta-galactosidase to the ferrichrome-iron receptor of Escherichia coli K-12." J Bacteriol 1986; 165(1); 181-92. |
| [53] | Chen, Z., Lewis, K. A., Shultzaberger, R. K., Lyakhov, I. G., Zheng M., Doan, B., Storz, G., Schneider, T. D. 2007. "Discovery of Fur binding site clusters in Escherichia coli by information theory models." Nucleic Acids Res 35(20); 6762-77. |
| [54] | Newman, D. L., Shapiro, J. A. (1999). "Differential fiu-lacZ fusion regulation linked to Escherichia coli colony development." Mol Microbiol 33(1); 18-32. |
| [55] | De Lorenzo, V., Herrero, M., Giovannini, F., Neilands, J. B. (1988). "Fur (ferric uptake regulation) protein and CAP (catabolite-activator protein) modulate transcription of fur gene in Escherichia coli." Eur J Biochem 1988; 173(3); 537-46. |
| [56] | Hantke, K. 2001. "Iron and metal regulation in bacteria." Curr Opin Microbiol 4(2); 172-7. |
| [57] | Vassinova, N., Kozyrev, D. 2000. "A method for direct cloning of fur-regulated genes: identification of seven new fur-regulated loci in Escherichia coli." Microbiology 146 Pt 12; 3171-82. |
| [58] | D'Autreaux, B., Touati, D., Bersch, B., Latour, J. M., Michaud-Soret, I. 2002. "Direct inhibition by nitric oxide of the transcriptional ferric uptake regulation protein via nitrosylation of the iron." Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(26); 16619-24. |
| [59] | Angerer, A., Braun, V. 1998. "Iron regulates transcription of the Escherichia coli ferric citrate transport genes directly and through the transcription initiation proteins." Arch Microbiol 1998; 169(6); 483-90. |
| [60] | Kammler, M., Schon, C., Hantke, K. 1993. "Characterization of the ferrous iron uptake system of Escherichia coli." J Bacteriol 1993; 175(19); 6212-9. |
| [61] | Griggs, D. W., Konisky, J. 1989. "Mechanism for iron-regulated transcription of the Escherichia coli cir gene: metal-dependent binding of fur protein to the promoters." J Bacteriol 1989; 171 (2); 1048-52. |
| [62] | Outten, F. W., Djaman, O., Storz, G. 2004. "A suf operon requirement for Fe-S cluster assembly during iron starvation in Escherichia coli." Mol Microbiol 52(3); 861-72. |
| [63] | Sauer, M., Hantke, K., Braun, V. 1990. "Sequence of the fhuE outer-membrane receptor gene of Escherichia coli K12 and properties of mutants." Mol Microbiol 4(3); 427-37. |
| [64] | de Lorenzo, V., Wee, S., Herrero, M., Neilands, J. B. 1987. "Operator sequences of the aerobactin operon of plasmid ColV-K30 binding the ferric uptake regulation (fur) repressor." J Bacteriol 169(6); 2624-30. |
| [65] | Arechaga, I., Miroux, B., Runswick, M. J., Walker, J. E. 2003. "Over-expression of Escherichia coli F1F(o)-ATPase subunit a is inhibited by instability of the uncB gene transcript." FEBS Lett 547(1-3); 97-100. |
| [66] | Stojiljkovic, I., Baumler, A. J., Hantke, K. (1994). "Fur regulon in gram-negative bacteria. Identification and characterization of new iron-regulated Escherichia coli genes by a fur titration assay." J Mol Biol 236(2); 531-45. |
| [67] | Tardat B, Touati D 1993. "Iron and oxygen regulation of Escherichia coli MnSOD expression: competition between the global regulators Fur and ArcA for binding to DNA." Mol Microbiol 1993; 9(1); 53-63. |
| [68] | Patzer, S. I., Hantke, K. 2001. "Dual repression by Fe(2+)-Fur and Mn(2+)-MntR of the mntH gene, encoding an NRAMP-like Mn(2+) transporter in Escherichia coli." J Bacteriol 183(16); 4806-13. |
| [69] | Koch, D., Nies, D. H., Grass, G. 2007. "The RcnRA (YohLM) system of Escherichia coli: A connection between nickel, cobalt and iron homeostasis." Biometals 20(5): 759-71. |
| [70] | Puskarova A., Ferianc, P., Kormanec, J., Homerova, D., Farewell, A., Nystrom, T. 2002. "Regulation of yodA encoding a novel cadmium-induced protein in Escherichia coli." Microbiology 2002; 148 (Pt 12); 3801-11. |
| [71] | Sumi, T., Sekino, H. 2006. "A crossover from metal to plasma in dense fluid hydrogen." J Chem Phys 125(19); 194526. |
| [72] | Tseng, C. P. (1997). "Regulation of fumarase (fumB) gene expression in Escherichia coli in response to oxygen, iron and heme availability: role of the arcA, fur, and hemA gene products." FEMS Microbiol Lett 157(1); 67-72. |
| [73] | Zhang, Z., Gosset, G., Barabote, R., Gonzalez, C. S., Cuevas, W. A., Saier, M. H. (2005). "Functional interactions between the carbon and iron utilization regulators, Crp and Fur, in Escherichia coli." J Bacteriol 187(3); 980-90. |
| [74] | Engelberg-Kulka, H., and Glaser, G. 1999. Addiction modules and programmed cell death and antideath in bacterial cultures. Annu. Rev. Microbiol.53: 43–70. |
| [75] | Amitai, S., Yassin, Y., and Engelberg-Kulka, H. 2004. MazF-mediated cell death in Escherichia coli: a point of no return. J. Bacteriol. 186(24): 8295–8300. |
| [76] | Keren, I., Kaldalu., N., Spoering, A., Wang, Y., and Lewis K. 2004. Persister cells and tolerance to antimicrobials. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 230:13 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML