-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Bioinformatics Research
p-ISSN: 2167-6992 e-ISSN: 2167-6976
2012; 2(1): 14-20
doi:10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20120201.03
Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Prediction
Zeinab Abd El Halim, Amr Badr, Khaled Tawfik, Ibrahim Farag
Faculty of computers and information, CairoUniversity, Ahmed Zewiel Street, Giza, Egypt
Correspondence to: Zeinab Abd El Halim, Faculty of computers and information, CairoUniversity, Ahmed Zewiel Street, Giza, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Major Histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules play an essential role in introducing and regulation immune system. The MHC molecules are divided into two classes, class I and class II which are differ in size of their binding pockets. Determining which peptides bind to a specific MHC molecule is fundamental to understanding the basis of immunity, and for the development of vaccines and immunotherapeutic for autoimmune diseases and cancer. Due to the variability of the locations of the class II binding cores, the process for predicting the affinity of these peptides is difficult.This paper investigates a new method for predicting peptides binding to MHC class II molecules and its affinity using genetic algorithms and metaheuristics. The algorithm is based on a fitness function that builds a scoring matrix for all suggested motifs in a specific iteration to test the motif ability to be one of the real motifs in the nature. The genetic algorithmpresented here shows increased prediction accuracy with higher number of true positives and negatives on almost of MHC class II alleles,about 80 percent of peptides were correctly classified when testing dataset from IEDB[26]. Generally, these results indicate that GA has a strong ability for MHC Class II binding prediction.
Keywords: Major Histocompatibility complex (MHC), peptide Binding, Binders, NonBinders, Antigen presenting cells (APCs)
Cite this paper: Zeinab Abd El Halim, Amr Badr, Khaled Tawfik, Ibrahim Farag, Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Prediction, American Journal of Bioinformatics Research, Vol. 2 No. 1, 2012, pp. 14-20. doi: 10.5923/j.bioinformatics.20120201.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Vaccines are the greatest single way for preventing infection diseases, with huge benefits to human wellbeing. Vaccine allows the immune system to develop antibodies and overcome the disease should we become infected with the real disease.Developing a vaccine currently takes a long time but with the interconnectivity of the world there is a mounting fear of a disease quickly spreading as SARS and A (H1N1). To fight this, methods for designing vaccines are researched and implemented.So the accurate and reliable prediction of MHC peptides binding is fundamental to the strong identification of T-cell epitopes and thus a successful design of peptide – protein based vaccine.Predicting the peptides that bind to Major Histocompatibility Complex class II molecules can reduce the number of experiments for identifying T cell and play an important role in the process of designing vaccines.A MHC molecule binds peptide that derived from an antigen, and then displays it on the cell surface for T cells recognition[10]. Thus determining which peptides bind to a specific molecule is important for treatment of autoimmune diseases and cancer. MHC molecules are classified into two major classes and MHC alleles are grouped according totheir structure. For class I MHC alleles, the binding groove is closed at both ends, making it possible to predict exactly which residues is positioned in the binding groove. For class II MHC molecules, the binding groove is open at both ends, allowing peptides longer than 9-mers to bind[1]. However, it has been reported that a 9-mer core region is essential for MHC II binding. Because the precise location of the 9-mer region of the MHC II binding peptides is unknown, predicting MHC II binding peptides tends to be more challenging than MHC I binding peptides. Some of this reasons are: the variable length of binding peptides, the undermined core regions for individual peptides, the number of amino acids admissible as primary anchors and the experimental and reporting errors that depending on different methods[1].Despite of the variability of the length of MHC II binding peptides, many computational methods exits and can be divided into two approaches: sequence based approach and structure based approach[15,17]. Peptide binding to MHC is allele specific and by looking at frequencies of different amino acids in different positions for a large number of known binders, sequence motifs can be seen. An example of sequence based approach is to create a scoring matrix for a specific MHC type and this can be done by looking at frequencies of different amino acids in different positions in the peptide. Another approach for prediction is based on structural information or crystal structure about MHC-peptide complexes and evaluates how well a new peptide fits in the binding groove of a MHC molecule[6].Prediction has also been made by using machine learning approaches such as artificial neural network (ANN) and Hidden Markov Model (HMM)[3,4]. Each of all prediction methods has its pros and cons.This papershows an ideal prediction method which would integrate the strengths of these individual methods while minimizing their disadvantages.The aim of this paper is to predict MHC binding peptides and its affinity cores using genetic algorithms and metaheuristics. A genetic algorithm is an approach to solving certain kinds of search and optimisation problems, this approach involves maintaining a population of possibility solutions and then generating new solutions by the use of genetic operators such as reproduction, crossover and mutation[10]. A fitness function is a measure of the quality of the solution so as the genetic algorithm proceeds the binding matrices improve. In this project sequence data of peptides that bind different MHC types can be extracted from public databases. The sequences can then be trained in MHCPEP dataset[5]. The input will be a peptide sequences and the output will be yes or no (1 or 0) yes for each binder and no for each nonbinder. The genetic algorithm will then be able to predict if a peptide binds or not given its sequence.After that a comparative study done between the output of the genetic algorithm and the output of the test dataset (IEDB)[26,27]. The next step is to predict the best 9’s through binder’s classifier. The last step is to determine the accuracy of the algorithm. This paper also combined the results of experimental studies to represent the accuracy and utility of genetic algorithm in the prediction of peptide MHC II binding. These results are expected to be of practical interest to immunologists for efficient identification of peptides as candidates for immunotherapy.
2. Materialsand Methods
2.1. Data Collection
- The data sets used for training and testing for binders and non-binders (BNB) were obtained from MHCBN (Bhasinet al., 2003), MHCPEP (Brusicet al., 1998b), and IEDB (Peters B, et al. 2005) for testing and predicting binding affinity (9-mers).The MHCBN is a curated database consisting of detailed information about Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) binding, non-binding peptides and T cell epitopes. The MHCBNdatabase provides information about peptides interaction with TAP and MHC linked autoimmune diseases [16].MHCPEP is a curated database comprising over 13000 peptide sequences for MHC molecules. Entries are compiled from published reports as well as from direct submission of experimental data. Each entry contains the source protein (when known), an estimate of binding affinity and critical anchor residues (if identified), and is fully referenced[5].IEDB (Immune Epitopes Database) provides a catalog of experimentally characterized B and T cell epitopes, as well as data on Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) binding[26,27]. The IEDB database covers 99% of all publicly available information on peptide epitopes. With respect to MHC II the IEDB database provides a tool that employs a consensus approach to predict MHC class II epitopes and its 9-mers based upon different methods such as Sturniolo, ARB, and SMM_align[13].In this study the MHCBN and MHCPEP are used as training datasets, these datasets contains many unique peptides known to bind or not bind to the MHC II molecules. The lengths of the peptides vary from 9 to 30 amino acids and have an average length of 15 amino acids.The structure of the peptides is a line containing the amino acids of the actual peptide; the first five peptides on the training dataset are shown below.AAPYEKEVPLSALTNILSAQLAEALERMFLSFPTTKTHLAGMGWAGWLLSPRGSAAGFKGEQGPKGRPSWGPTDPRRRSRAThe IEDB is used as a testing dataset to evaluate the predictive performance of the genetic algorithm which used in this project. The output of this dataset is a table with many rows; each row corresponds to one peptide prediction. The columns contain the allele the prediction was made for, the position of the peptide in the input sequences, the core sequence, the predicted score and percentile rank for ARB, combinatorial library, SMM_align and Sturniolo. The last column is percentile rank for the consensus method such that top percentile means good binders.
2.2. Predictive Model (Algorithm)
- A Genetic algorithm can be defined as a search heuristic that mimics the process of natural evolution. Genetic algorithms belong to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA) which generate solutions to optimization problems using techniques inspired by natural evolution, such as inheritance, mutation, selection, and crossover.A GA that presented in this paper consists of 4 steps as follow:(1). Representing input variables as individuals or chromosomes in population.(2). Formulating the fitness (objective function) to evaluate individuals.(3). Generating a new population by genetic operations (selection, crossover, and mutation) on the current population.(4). Determining if the population has reached the optimal fitness.The fitness function presented in this paper should produce a score for each peptide input evaluating how good the input is, the input consists of a number of sequences of amino acids.Given a dataset containing n peptides, S1, S2, … Sn, the main goal of the genetic algorithm is to find the optimal alignment of the peptides to get a corresponding core of the motif(best 9mer) from each peptide. Each peptide is a sequence of amino acids and there are 20 different amino acids identified by a roman character in the alphabet ∑.Example of input peptides can be seen in the following figure 1.
 | Figure 1. Example of 5 Peptides Represented as Sequences of Amino Acids, The Highlighted Amino Acids in Each Peptide is The 9 mers which the Algorithm Should Determine and This is Called a Motif |
 | (1) |
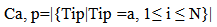 | (2) |
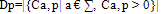 | (3) |
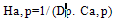 | (4) |
 | (5) |
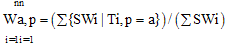 | (6) |
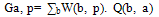 | (7) |
 | (8) |
2.3. The Parts of the Genetic Algorithm
- A genetic algorithm consists of three main functions; Selection, Crossover and Mutation. These functions are used to convert an old generation of chromosomes into a new generation that fit the requirements of the fitness function.The Selection process is responsible for selecting which chromosomes in the current generation are to be used in the new generation and which will be forgotten. The type of selection process used in this project is the Roulette selection.
 | (9) |
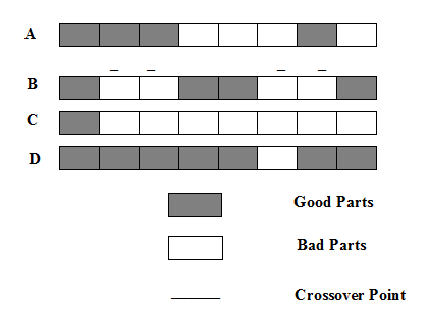 | Figure 3. Crossover performed on the chromosomes A and B with the crossover points marked by the sign _ results in the chromosomes C and D |
 | Figure 4. Shift Mutation is performed in the chromosome leading to leave the mutated amino acids to a large extent more different from its main shape (replicated from) |
2.4. Evaluation
- Evaluation done using the AUC (Area under Curve) gives a value indicating how much deference between the results of the algorithm and the real results that got from the labs. The evaluation starts after testing using IEDB dataset to know the binders, nonbinder, the output from the IEDB is to say if the peptide binds or not and with what value?. In the AUC if the peptide binds it is said to be positive and represented as T and if it does not bind it is said to be negative and represented as N. And there are 4 categories:TP: if a positive peptide is predicted to be binding it is considered a true positive.FN: if a negative peptide is predicted to be binding it is considered a false negative.TN: if a negative peptide is predicted not to be binding, it is considered a true negative.FP: if a positive peptide is predicted not to be binding it is considered a false positive.After the previous step of classification, the total number of actual positive peptides can be calculated as P=TP+FN and the total number of negative peptides calculated as N=FP+TN. After that the TP_Rate and FP_Ratecan be calculated as follow:A good prediction would be indicated by the point (0, 1). The TP_Rate=1 means that the number of positives correctly classified is equal to the number of positives (TP=P).The worst prediction is located in (1,0) as this means that none of the positives has been correctly classified and all the negatives has been incorrectly classified. GA applied in this paper predicts binding peptides affinity with high accuracy; about 80 percent of peptides were correctly classified.
3. Results
- The GA was applied to derive a position specific scoring matrix for predicting MHC-II binding affinities for the alleles in the dataset. The predictive performance of the GA was tested on IEDB datasetand compared with Gibbs sampler and SVRMHC method[28]. The binding of a peptide was calculated as the score of the highest scoring 9mer sub peptide.The predictive performance of the different methods was measured in terms of the area under the curve (AUC) [19].
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4. Discussion
- Determining which peptides bind a particular MHC molecule important for understanding the basis of immune responses, and has potential applications in the design of peptide vaccines and other issues. Tools to facilitate prediction of peptide MHC binding have practical utility in minimising the number of binding experiments in the laboratory. Many methods were implemented to do this job as predicting peptides binding to MHC class I and II and each one has its own performance and major. In this contribution to the field, GA used and a fitness function was developed for binding several MHC molecules using peptide data and other techniques required and used as classifier systems.The main objective of this paper was to design a method for the prediction of MHC class II- binding peptides that could integrate experimental data and expert knowledge with the search and classification tools of the information science to be able to design vaccines for critical diseases like cancer. The results indicate that GA and its fitness function discussed in this paper succeeded in achieving this objective.GA predictions of peptides binding to MHC-II alleles are as good as or better than alternative methods.Peptides are typically longer than the core motif, and correct alignment is a key for obtaining good prediction performance.Prediction of MHC class II peptides is a difficult task, and the prediction accuracy of the method described is good.As the genetic algorithm is as good as the Gibbs sampler and its ability to predict is very good, but the fitness function used here is simpler than the one used by the Gibbs sampler. However tests of the fitness function performed has shown that the fitness functions are identical with some exceptions like using Henikoff and Henikoff sequence weighting and the training and testing datasets. The following figure shows the comparable values for AUC between Genetic Algorithm and Gibbs sampler.
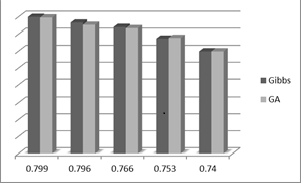 | Figure 5. AUC values for Gibbs sampler & Genetic algorithm |
5. Conclusions
- This paper presents a Genetic algorithm for predicting peptides binding to MHC class-II molecules and finding its motifs. GA has successfully designed in modules to make it easy to change the types of elements (mutation, selection, etc.) and implementedin a simple way to optimise the fitness function. The problem of this paper was written using mathematical notation in order to clarify what has to be calculated. The experiment shows that the proposed GA is better than earlier methods in predicting binding sites on most alleles of class II MHC IEDB dataset. This shows the applicability of GA methodology to find binding motifs in a wide range of MHC alleles and thus can help biologists in designing vaccines for autoimmune diseases and cancer.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML