-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Astronomy
p-ISSN: 2169-8848 e-ISSN: 2169-8856
2021; 10(1): 6-12
doi:10.5923/j.astronomy.20211001.02
Received: Feb. 9, 2021; Accepted: Mar. 9, 2021; Published: Mar. 20, 2021

The Rotational Velocity of Barred Spiral Galaxies in the General Relativity Solution
Adrián G. Cornejo
Electronics and Communications Engineering from Universidad Iberoamericana, Santa Rosa 719, Querétaro, Mexico
Correspondence to: Adrián G. Cornejo , Electronics and Communications Engineering from Universidad Iberoamericana, Santa Rosa 719, Querétaro, Mexico.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This work describes the hypothesis in which the explanation of the rotational velocity of barred spiral galaxies is based on the relativistic solution. Considering a previous relativistic solution for the unbarred spiral galaxies, this solution assumes that the entire spiral galaxy disk would rotate like a rigid (or solid) body. It is considered that both the Solar System and spiral galaxies are behaving like a rigid body in rotation. Then, having both systems the same dynamical behaviour, which can be explained by the same relativistic solution, these two apparently different cases are unified in the same solution. Thus, the stars and gas in the spiral galaxy must be rotating with the system in an almost the same and uniform angular velocity. Nevertheless, according to the Kerr metric for the rotating black hole, at the zone of the bar of barred spiral galaxies, stars and gas must be changing their direction toward the rotation poles of the black hole. On these assumptions, we apply the equation based on the relativistic solution to the barred spiral galaxies. More precisely, we present examples of the rotation curves of unbarred spiral galaxies: NGC 4378 and NGC 4594, and the barred spiral galaxies: Milky Way and, NGC 7541. Comparing our calculations with the observations we find a good approximation.
Keywords: Galaxies: spiral, Kinematics and dynamics, General Theory of Relativity
Cite this paper: Adrián G. Cornejo , The Rotational Velocity of Barred Spiral Galaxies in the General Relativity Solution, International Journal of Astronomy, Vol. 10 No. 1, 2021, pp. 6-12. doi: 10.5923/j.astronomy.20211001.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- One of the problems that classical gravitation theory has had is to justify the large velocities observed for stars and gas in spiral galaxies and how they differ from the rotational velocities of planets. Indeed, precise measurements (with a variety of techniques) of the velocities of stars and gases in spiral galaxies [1,2] make clear that the action of the galaxy on its stars and the gas estimated according to the classical gravitation theory cannot account for the measured velocities, if the gas is assumed to be a stable component of the galaxy, as described by the quasi-stationary density wave theory, which characterizes spirals as rigidly rotating, long-lived patterns (i.e. steady spirals) [3]. Thus, we can consider that in principle, stars and gas in spiral galaxies do not follow a rotational motion as described in classical gravitational theory, so they must obey other considerations to satisfy the observations.The issue is that the classical Newtonian law of gravitation only considers two terms, which are the Newtonian gravity force and the centrifugal force to define the classical total force [4]. Then, it has some limitations proper of this classical theory since it does not consider any other energy or force involved in the rotating systems. This is the reason why is required to add some matter or forces to adjust the calculations to the rotational velocities observed in spiral galaxies, such as the dark matter concept [5], which has not been detected to date, or even develop some adjustments like the proposed in the Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) theory [6,7].On the other hand, the net or absolute total force in the relativistic solution, derived from the General Theory of Relativity (GTR) [8] considers a third term, which includes the force related to the Coriolis force in a rotating system, which is inverse of the distance to the fourth power. This is the main reason why the relativistic solution can be considered to provide an exact solution which does not require any additional matter and does not require any adjustment to fit to the rotational velocities observed in spiral galaxies.Then, based on the relativistic solution to calculate the rotational velocities of unbarred spiral galaxies and their spiral geometry [9], we consider that the rotational velocity of barred spiral galaxies can also be calculated from this relativistic solution. Furthermore, considering the Kerr metric for a rotating black hole, we describe the dynamics and geometry to be applied to the barred spiral galaxies, specifically the dynamic which indicates that gas and matter are carried towards the axial poles defined by the rotating axially-symmetric.A barred spiral galaxy, type as “SB” (spiral, barred) in the Hubble sequence, is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars and gas. For instance, the Milky Way galaxy, where the Solar System is located, is classified as a barred spiral galaxy [10].In this solution, the dynamics of the stars in a spiral galaxy is not exclusively due to the combined gravitational field of all the stars, gas, or any other massive object in the galaxy, but rather considers that the entire galaxy disk moves and rotates as a rigid (or solid) body.Previous works [9,11] show the possibility that both the Solar System and spiral galaxies are behaving like a rigid (or solid) body in rotation. Thus, having both systems the same dynamical behavior, which can be explained by the same relativistic solution, these two apparently different cases are unified in the same solution.This work aims to describe the hypothesis that the explanation of the rotational velocity of some barred spiral galaxies is based on the solution of general relativity. Thus, we revisit the equation that describes the rotational velocity of stars in unbarred spiral galaxies, based on the relativistic solution to be applied to the barred spiral galaxies. In particular, we show examples of the calculated rotation curves of unbarred spiral galaxies NGC 4378 and NGC 4594, and barred spiral galaxies Milky Way and, NGC 7541 (with very different masses and sizes), comparing our calculations with the observations, finding a good approximation.
2. Kerr Metric in the Barred Spiral Galaxies
- The Kerr metric [12] is an exact solution of the Einstein field equations of general relativity that generalizes to a rotating uncharged black hole of the Schwarzschild metric [13]. This metric describes the geometry of empty spacetime around a rotating axially-symmetric black hole of massive resting mass M● with a quasi-spherical event horizon. According to the Kerr metric, a rotating black hole with angular velocity Ω● difference of zero should exhibit frame-dragging [14]. Roughly speaking, this effect predicts that objects coming close to a rotating mass will be entrained to participate in its rotation, because of the swirling curvature of spacetime itself associated with rotating bodies. In the case of a rotating black hole, at close enough distances, all objects, even light, must rotate with the black hole. This region is called the ergosphere. Rotating black holes have surfaces where the metric seems to have apparent singularities; the size and shape of these surfaces would depend on the black hole's mass and angular momentum. The outer surface encloses the ergosphere and has a shape like a flattened sphere. The inner surface marks the event horizon [15] (Figure 1).The Kerr metric has two physically relevant surfaces on which it appears to be singular. The inner surface corresponds to an event horizon like that observed in the Schwarzschild metric; this occurs where the purely radial component grr of the metric goes to infinity. Solving the quadratic equation 1⁄grr = 0 yields the solution:
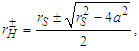 | (1) |
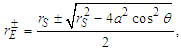 | (2) |
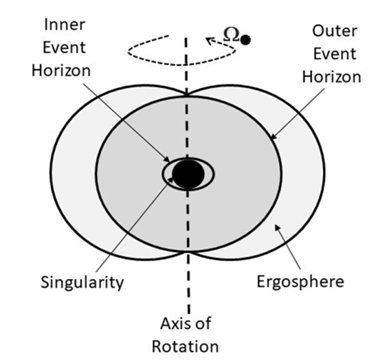 | Figure 1. Kerr metric of a rotating black hole |
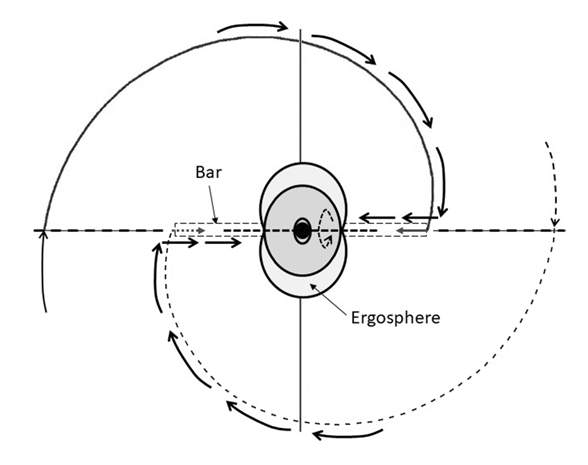 | Figure 2. The dynamics around the Kerr metric of a rotating black hole, and the forming of the bar of a barred spiral galaxy |
3. General Theory of Relativity Solution for the Total Force
- A relativistic solution for the angular movement of the celestial bodies in a rotating system can be determined by a study of the solutions of Einstein’s equations following the standard procedure [16-18]. Thus, the total force for a rotating system is given as
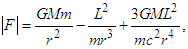 | (3) |
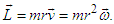 | (4) |
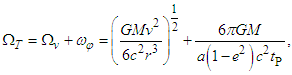 | (5) |
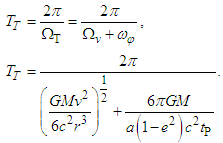 | (6) |
4. Rotational Velocity for Unbarred Spiral Galaxies
- According to this relativistic solution [19], at the stage where the entire spiral galaxy disk rotates like a rigid (or solid) body, the motion of the stars and gas that forms the spiral galaxy should be perceived from Earth as an almost uniform rotation of the galaxy. Considering the third term in Eq. (3), we can reduce common terms, giving
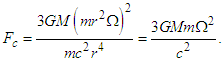 | (7) |
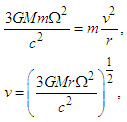 | (8) |
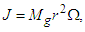 | (9) |
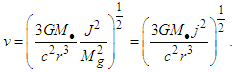 | (10) |
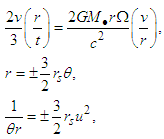 | (11) |
5. Spiral Geometry in Barred Spiral Galaxies
- Considering the Kerr metric for a rotating black hole, specifically the dynamic which indicates that gas and matter are carried from the outside towards the axial poles, following a linear path and forming the bar, we find the geometry of the barred spiral galaxies.According to the Kerr metric, geometry of empty spacetime around a rotating axially-symmetric black hole would form the bar from the spiral towards the axial poles. Thus, from Eq. (11), we define the equation for the geometry of barred spiral galaxies, giving
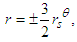 | (12) |
6. Comparison between Calculated and Observed Rotational Velocities in Spiral Galaxies
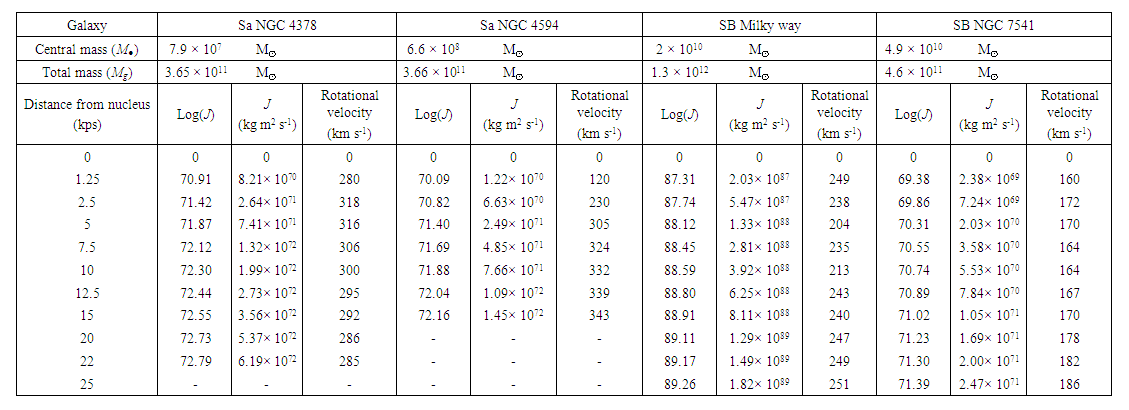
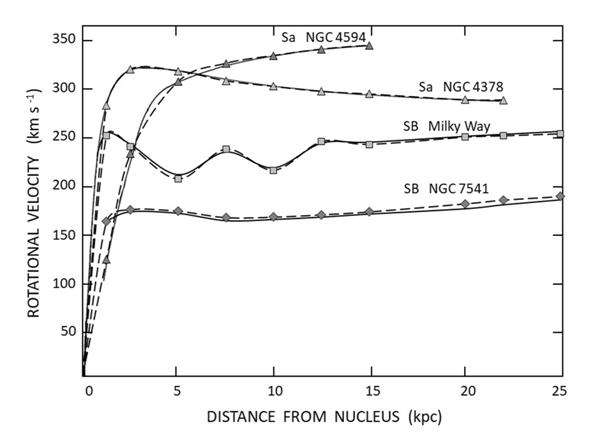
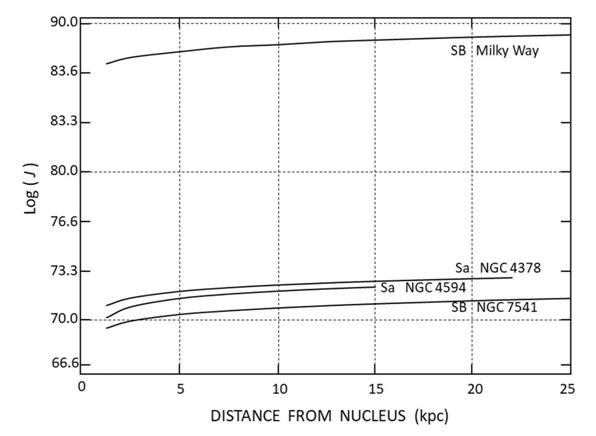
- Our purpose is to calculate the rotational velocity of some unbarred and barred spiral galaxies based on the relativistic solution and assuming their behaviour is like a rigid (or solid) body, plotting the rotation curves with the calculated values and compare them with the observed rotation curves. In particular, we focus on the rotation curves of two spiral Sa and two spiral SB galaxies. More precisely, we take as an example the known rotation curves of the spiral Sa galaxies: NGC 4378 and NGC 4594, and spiral SB galaxies: Milky Way and, NGC 7541, assuming that the only relevant contribution to the movement of their different regions is due to their behaviour as a rigid (or solid) body in rotation and considering only the movements found on the galactic plane. Then, calculation the rotational velocity is given by Eq. (10), considering the known values for each of these four spiral galaxies [23-29]. From this information, it is observed that the nucleus masses of barred spiral galaxies are larger than the nucleus masses of unbarred spiral galaxies. The results are tabulated in Table 1 (Rotational velocities) for each galaxy.
7. Conclusions
- The aim of this work is to describe the hypothesis in which the explanation of the rotational velocity of some unbarred and barred spiral galaxies is based on the general relativity solution. Furthermore, it is considered that both the Solar System and spiral galaxies are behaving like a rigid (or solid) body in rotation. Thus, having both systems the same dynamical behaviour, which can be explained by the same relativistic solution, these two apparently different cases are unified in the same solution. In this work, the relativistic solution of the rotational curves for the unbarred spiral galaxies and the Kerr metric for the rotating black hole are related to the observed bar of the barred spiral galaxies. Then, this work shows the use of Eq. (3) derived from the general relativity solution, applied here to calculate the rotational velocity of some spiral galaxies.Thus, we apply Eq. (10) to describe the rotational velocity of stars and gas in some spiral galaxies based on this solution. We present preliminarily examples of the rotation curves of unbarred spiral galaxies: NGC 4378 and NGC 4594, and barred spiral galaxies: Milky Way and, NGC 7541.Comparing our calculations with the observations we find a good approximation. It is shown that the respective angular momentum for these spiral galaxies has the same almost linear pattern along the different distances from their respective nucleus. One of the significances of this result based on the general relativity solution is that it is possible to fit the known rotation curves of the spiral galaxies without any need of introducing dark matter at all. The next step in proving the galaxy dynamics on the general relativity solution is to make more detailed observations of their angular momentum to confirm if the way in which spiral galaxies rotate is mainly according to rigidly rotating and long-lived patterns, as steady spirals.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The author would like to thank Professor Sergio S. Cornejo for its review and comments for this work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML