-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Astronomy
p-ISSN: 2169-8848 e-ISSN: 2169-8856
2014; 3(2): 31-34
doi:10.5923/j.astronomy.20140302.01
A Lagrangian Solution for the Precession of Mercury’s Perihelion
Adrián G. Cornejo
Electronics and Communications Engineering from Universidad Iberoamericana, Col. Santa Mónica, Querétaro, Mexico
Correspondence to: Adrián G. Cornejo, Electronics and Communications Engineering from Universidad Iberoamericana, Col. Santa Mónica, Querétaro, Mexico.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
A Langrangian solution is proposed for the apsidal precession by considering the precession of a body orbiting and rotating in a rotating reference frame, deriving an analogous equation to the relativistic solution.
Keywords: Rotating Reference Frame, Lagrangian Solutions, General Theory of Relativity, Precession of Mercury’s Perihelion
Cite this paper: Adrián G. Cornejo, A Lagrangian Solution for the Precession of Mercury’s Perihelion, International Journal of Astronomy, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2014, pp. 31-34. doi: 10.5923/j.astronomy.20140302.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The rotating reference frame is a frame that rotates about a spin axis (fixed for simplicity) with a given angular velocity. Formalism to describe a rotating reference frame is commonly given by the Lagrangian mechanics. In this kind of reference frame, an angular velocity of rotation is present in the particles within the rotating reference frame (like the particles in a whirl as described by the fluid mechanics or the particles on a solid body in rotation as described by the classical mechanics). This additional angular velocity in the periodic motion causes a precession towards the sense of rotation, as it is the case of the gyroscope. This effect is also present in some other natural phenomena where a rotating frame is involved, such as the Coriolis effect and the Foucault’s pendulum. However, could this kind of effect also be present in the apsidal precession?A Langrangian solution is proposed for the apsidal precession (like the precession of Mercury’s perihelion) by considering the precession of a body orbiting and rotating in a rotating reference frame, deriving an analogous equation to the relativistic solution.
2. Lagrangian Formulation for the Rotating Reference Frame
- In this section, certain aspects of the rotating reference frame will be reviewed through the general case of a rotating reference frame and a fixed frame where a body is orbiting and rotating about a spin axis [1]. Let us consider the distance from the spin axis to the final position of a point P that according to the fixed frame of reference is the radius vector named rf while some position of the same point according to the rotating reference frame is named r, and
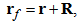 | (1) |
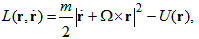 | (2) |
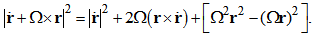 | (3) |
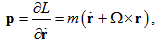 | (4) |
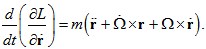 | (5) |
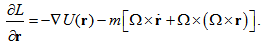 | (6) |
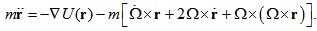 | (7) |
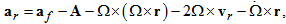 | (8) |
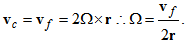 | (9) |
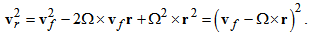 | (10) |
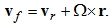 | (11) |
3. Total Energy in the Rotating Reference Frame
- In the rotating coordinate system [5], total energy on the orbital motion is defined as
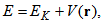 | (12) |
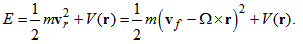 | (13) |
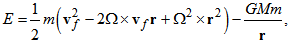 | (14) |
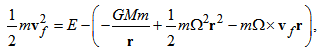 | (15) |
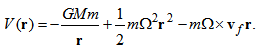 | (16) |
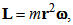 | (17) |
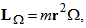 | (18) |
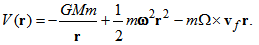 | (19) |
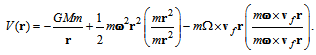 | (20) |
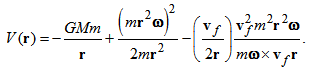 | (21) |
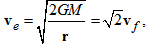 | (22) |
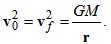 | (23) |
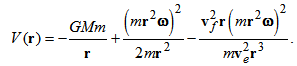 | (24) |
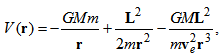 | (25) |
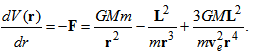 | (26) |
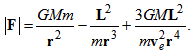 | (27) |
4. The Precession in a Rotating Reference Frame
- Precession results from the angular velocity of rotation and the angular velocity that is produced by the torque. Let us consider that a body in circular orbit at the distance r from a central point. Let us also consider that such a body is in a rotating reference frame where the whole system is rotating with a given angular velocity. In a rotating reference frame, the body orbiting undergoes a precession expressed by the angular velocity of precession ωφ as the described for a gyroscope of radius r in rotation [8], with some equivalences defined as
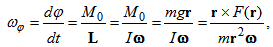 | (28) |
 | (29) |
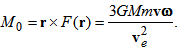 | (30) |
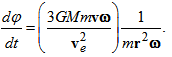 | (31) |
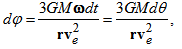 | (32) |
5. Analogous Equation to the Relativistic Solution
- Now, considering a body in elliptical orbit around a central point in a rotating reference frame (Figure 1), distance from the centre changes according to the ellipse, where semi-latus rectum is represented by ρ = a(1 - e2), being a the semi-major axis of the ellipse and e the eccentricity. For an ellipse of zero eccentricity, ρ is tending to the radius r of a circle. Thus, from Eq. (32), the rate of angle of precession dφ for the elliptical motion, while the body moves one revolution (θ completing 2π radians) advancing through an angle is given as
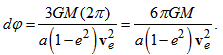 | (33) |
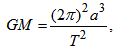 | (34) |
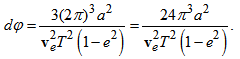 | (35) |
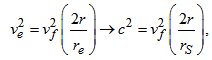 | (36) |
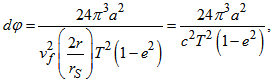 | (37) |
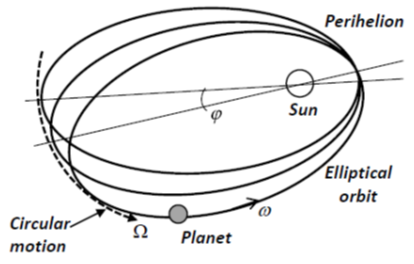 | Figure 1. Precession of Mercury’s perihelion in a rotating reference frame with angular velocity Ω |
6. Conclusions
- This work aims to analyze an alternative way to derive an approximation to the celebrated Einstein solution to predict the precession of Mercury’s perihelion, proposing an equivalent equation derived from the Lagrangian mechanics by considering an additional angular velocity which is included in a rotating reference frame. The here proposed solution for the apsidal precession is equivalent to the precession as described for a gyroscope in rotation, which could indicate that the apsidal precession may be related with this rotational effect.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The author would like to thank Professor Sergio S. Cornejo for the review and comments for this paper.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML