-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Astronomy
p-ISSN: 2169-8848 e-ISSN: 2169-8856
2013; 2(4): 65-81
doi:10.5923/j.astronomy.20130204.03
Statistical Analysis of Associated and Non Associated Type II Solar Radio Bursts during the Decreasing Phase of Solar Cycle 23
Vijaykumar H Doddamani 1, Raveesha K H 2, K R Subramanian 3
1Dept of Physics, Bangalore University, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
2Dept of Physics, CMR Institute of Technology, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
3Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Correspondence to: Raveesha K H , Dept of Physics, CMR Institute of Technology, Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Type II and Type III bursts are probably the most intensively studied form of radio emission in all of astrophysics. Immense effort has gone into the elucidation of both the observational and theoretical aspects. The bursts have captured the attention of plasma theorists because a considerable body of information exists on the plasma parameters and there is adequate space and time in the solar corona for the evolution of various particle and wave processes. Type II radio bursts are indicative of shock propagation in the corona and inner heliosphere, accompanied by electron acceleration. They are good indicators of shocks that eventually cause sudden commencement of geomagnetic storms. In our work, we have studied the type II bursts and their association with type III bursts during the decreasing phase after the peak phase of solar cycle 23. For the period 2002-2004, type II and type III bursts data of Culgoora observatory is referred. The parameters such as duration drift rate, shock speed, band width of these associated/non associated bursts are compared. Results indicate that except in the case of duration and bandwidth, the above parameters almost remain uniform for associated and non associated type II bursts.
Keywords: Shock Speed, Drift rate, Plasma Frequency, Dynamic Spectrum
Cite this paper: Vijaykumar H Doddamani , Raveesha K H , K R Subramanian , Statistical Analysis of Associated and Non Associated Type II Solar Radio Bursts during the Decreasing Phase of Solar Cycle 23, International Journal of Astronomy, Vol. 2 No. 4, 2013, pp. 65-81. doi: 10.5923/j.astronomy.20130204.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Solar radio bursts were amongst the first phenomena identified as targets for radio astronomy. Solar radio bursts at frequencies below a few hundred MHZ have been extensively studied. Among the 5 types of solar radio bursts, the type ii and type III bursts are most important from the perspective of space weather prediction.Type III bursts are the fast drift bursts which are an attractive tool to investigate fast acceleration processes, which is considered to be the cause of the high exciter velocities. They can be used as natural plasma probes traversing the corona and yielding information about different plasma parameters. Fast drift phenomenon provides an opportunity to study processes of different wave–particle and wave-wave interactions and has stimulated a considerable progress in developing in physical methods for a quantitative investigation. Therefore the type III bursts can be used as tracers of the magnetic field configuration and also other parameters in the coronal and solar wind. The investigation of the interplanetary medium through the analysis of the type III solar radio bursts at long wavelengths can in principle provide information about the structure and properties of active region streamers[8]. The type III phenomenon contains message about the interaction of beam with plasma and so it induced plasma physicists to study the possible mechanisms of such interactions and to study how plasma processes can give rise to the emission of electromagnetic radiation.The main defining characteristic of type III bursts was recognized by Wild[38] and Wild & Mcready[36]; it is that their emission drifts rapidly from high to low frequencies. The drift rate is roughly 100MHz/s in the meter wave range, some 100 times faster than drifting bursts, such as type I chains and type II bursts. Of the various forms of radio burst emissions from the Sun, the type III bursts are most likely to be indicative of the escape of energetic particles from the Sun. These radio bursts exhibit a rapid frequency drift (~80 MHz/s at 100MHz) from high to low frequencies and have been shown to be due to disturbance propagating outward in the solar corona at speeds of ~c/3 (c is velocity of light)[36, 37].Alvarez & Haddock[1] made the suggestion that bursts are caused by streams of electrons. These streams move out through the corona along the open field lines at a speed of about c/3 and their passage sets up plasma oscillations – Langmuir waves then radiate at their characteristic frequency. Because the electron density and consequently the plasma frequency decrease outward from the Sun, the emission frequency of the bursts does likewise. According to plasma hypothesis[38], type III emission at the plasma frequency is given by
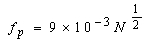 N is the electron density in cm-3It is clear that for the type III bursts extending to low frequencies the exciting agent escapes from the Sun. The nature of the exciting agent has been hypothesized to be both proton[9, 36] and electron streams[37]. There are theoretical grounds for the choice of proton streams as the excitation agent[11]. However, protons of the requisite energy (~50MeV) are rarely observed to be emitted by the Sun, and when they are emitted, they are not necessarily accompanied by type III radio emission but rather by type IV and type[19] raises the possibility that proton flux from a type III burst is too small to be observed above galactic cosmic ray background. Solar electros of ~c/3 velocity (~32keV) energy are frequently observed in the interplanetary medium. Almost every solar electron event of ~40keV is accompanied by such type III burst emission[19]. The plasma hypothesis was confirmed by interferometer measurements of the type III source height at different frequencies which showed successively lower frequencies being emitted from successively greater heights [37]. Interferometerobservations show that the average radial velocity varies from 0.2c to 0.8c between the 60 and 45 MHz plasma levels. Individual type III bursts observed over a frequency range from 200 to 12MHz, i.e. from 0.15Ro to 2Ro above the photosphere, have rift rates which correspond to radial source velocities ~c/3. Wang et al[34] studied type III groups and concluded that type III bursts may be caused by energetic electrons accelerated during a non linear reconnection process in the larger magnetic loop of solar corona. During the reconnection, the magnetic field will become more complex in local smaller area, there will be some explosive and fast instability, such as Tokamak instability, in the smaller area which might case the relevant change in induced electric field and cause acceleration of electrons.The distinguishing characteristic of type III bursts is their harmonic structure; because this has been a subject of controversy and their circular polarization. Harmonic structures are exhibited by a significant proportion of type III bursts at meter and decameter wavelengths. The frequency ratio of harmonic to fundamental averages to 1.8:1 with a range from 1.6:1 to 2.0:1[36]. Type III bursts do not always drift down to very low frequencies. On many occasions bursts observed at metric wavelengths are not observed at decametric wavelengths, and similarly many bursts are not observed at hectometric and kilometric wavelengths which are seen by ground based observations which extend to decametric wavelengths[14]. The reasons for these cutoffs are not well understood. To study the possibility whether the exciting agent is impeded or dispersed in its progress outward through corona, Alvarez, et al[1] studied type III bursts which extend to kilometric wavelengths (frequencies ≤ 0.350MHz at height ≥ 50Ro) and compared them with > 45KeV electron events observed at 1AU.They found that one to one correspondence exists between kilometric wavelength type III burst above a threshold of approximately 10-13 W/m2/Hz and >45Kev observed at 1AU.They concluded that streams of ~10-100keV electrons are the exciting agents for the type III bursts and that ~ 5 x 1032 electrons with energy > 100keV are emitted in a strong type III burst. A problem which remains is to explain the cutoff of many types III bursts before they reach kilometric wavelengths. They observed that such correlation may be due to stopping of the electron beam before it reaches 1AU.The time profiles of the radio emission contain important information about the particle streams and their interaction with the interplanetary medium. A study of the characteristic range of these parameters with distance from Sun can lead to a better understanding of the propagation and interaction of energetic particles in the interplanetary medium, Evans et al[7]. The time profile of type III solar bursts can be used for the determination of the coronal temperature if we assume that the decay of the emission is due to the damping of plasma oscillations by electron-ion collisions[17]. The temperature T is related to the damping constant through the formula
N is the electron density in cm-3It is clear that for the type III bursts extending to low frequencies the exciting agent escapes from the Sun. The nature of the exciting agent has been hypothesized to be both proton[9, 36] and electron streams[37]. There are theoretical grounds for the choice of proton streams as the excitation agent[11]. However, protons of the requisite energy (~50MeV) are rarely observed to be emitted by the Sun, and when they are emitted, they are not necessarily accompanied by type III radio emission but rather by type IV and type[19] raises the possibility that proton flux from a type III burst is too small to be observed above galactic cosmic ray background. Solar electros of ~c/3 velocity (~32keV) energy are frequently observed in the interplanetary medium. Almost every solar electron event of ~40keV is accompanied by such type III burst emission[19]. The plasma hypothesis was confirmed by interferometer measurements of the type III source height at different frequencies which showed successively lower frequencies being emitted from successively greater heights [37]. Interferometerobservations show that the average radial velocity varies from 0.2c to 0.8c between the 60 and 45 MHz plasma levels. Individual type III bursts observed over a frequency range from 200 to 12MHz, i.e. from 0.15Ro to 2Ro above the photosphere, have rift rates which correspond to radial source velocities ~c/3. Wang et al[34] studied type III groups and concluded that type III bursts may be caused by energetic electrons accelerated during a non linear reconnection process in the larger magnetic loop of solar corona. During the reconnection, the magnetic field will become more complex in local smaller area, there will be some explosive and fast instability, such as Tokamak instability, in the smaller area which might case the relevant change in induced electric field and cause acceleration of electrons.The distinguishing characteristic of type III bursts is their harmonic structure; because this has been a subject of controversy and their circular polarization. Harmonic structures are exhibited by a significant proportion of type III bursts at meter and decameter wavelengths. The frequency ratio of harmonic to fundamental averages to 1.8:1 with a range from 1.6:1 to 2.0:1[36]. Type III bursts do not always drift down to very low frequencies. On many occasions bursts observed at metric wavelengths are not observed at decametric wavelengths, and similarly many bursts are not observed at hectometric and kilometric wavelengths which are seen by ground based observations which extend to decametric wavelengths[14]. The reasons for these cutoffs are not well understood. To study the possibility whether the exciting agent is impeded or dispersed in its progress outward through corona, Alvarez, et al[1] studied type III bursts which extend to kilometric wavelengths (frequencies ≤ 0.350MHz at height ≥ 50Ro) and compared them with > 45KeV electron events observed at 1AU.They found that one to one correspondence exists between kilometric wavelength type III burst above a threshold of approximately 10-13 W/m2/Hz and >45Kev observed at 1AU.They concluded that streams of ~10-100keV electrons are the exciting agents for the type III bursts and that ~ 5 x 1032 electrons with energy > 100keV are emitted in a strong type III burst. A problem which remains is to explain the cutoff of many types III bursts before they reach kilometric wavelengths. They observed that such correlation may be due to stopping of the electron beam before it reaches 1AU.The time profiles of the radio emission contain important information about the particle streams and their interaction with the interplanetary medium. A study of the characteristic range of these parameters with distance from Sun can lead to a better understanding of the propagation and interaction of energetic particles in the interplanetary medium, Evans et al[7]. The time profile of type III solar bursts can be used for the determination of the coronal temperature if we assume that the decay of the emission is due to the damping of plasma oscillations by electron-ion collisions[17]. The temperature T is related to the damping constant through the formula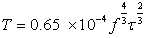 f is the frequency in hertzτ is damping constant in seconds. The frequency drift rate at meter wavelengths according to Alvarez and Haddock (1973) is given by
f is the frequency in hertzτ is damping constant in seconds. The frequency drift rate at meter wavelengths according to Alvarez and Haddock (1973) is given by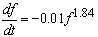 Here f is in MHz and
Here f is in MHz and 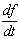 is in MHz/sThe drift rates were converted to velocity by assuming that the bursts propagated along a coronal streamer possessing the density distribution of Newkirk streamer model[25].
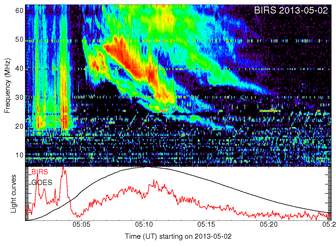
is in MHz/sThe drift rates were converted to velocity by assuming that the bursts propagated along a coronal streamer possessing the density distribution of Newkirk streamer model[25].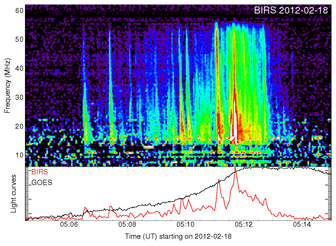 | Figure 1. Typical example of Type III radio burst observed with BIRS observatory on 18/02/2012.The bursts begin at 05:50UT and are observed at till 06:14UT |
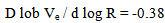 Ve is the exciter speed in terms of velocity of light (Km/s)R is the distance from the Sun in solar RadiiD is the Deceleration in Km/s2The position of type III burst radiation source is determined by the path of the exciting particles in space. Due to the smaller gyro radii, the electrons are forced to follow the magnetic field direction. The starting heights of the type III bursts may not be regarded as the actual heights where the acceleration is initiated; the location of the exciter origin is obscured. Zaitsev[41] concluded that in a spatially bound stream inspite of quasi linear relaxation plasma waves can be generated for a long time owing to faster particles escaping out of the front of the stream.
Ve is the exciter speed in terms of velocity of light (Km/s)R is the distance from the Sun in solar RadiiD is the Deceleration in Km/s2The position of type III burst radiation source is determined by the path of the exciting particles in space. Due to the smaller gyro radii, the electrons are forced to follow the magnetic field direction. The starting heights of the type III bursts may not be regarded as the actual heights where the acceleration is initiated; the location of the exciter origin is obscured. Zaitsev[41] concluded that in a spatially bound stream inspite of quasi linear relaxation plasma waves can be generated for a long time owing to faster particles escaping out of the front of the stream.1.1. Type II Solar Radio Bursts
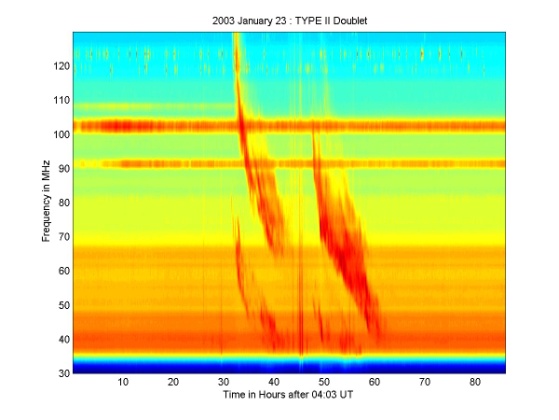
- Payne-Scott observed large outburst of March 08, 1947 from Sun at three frequencies 10, 20 and 60MHz and found that the lower frequency emission was delayed with respect to higher frequencies. The Magneto Hydro Dynamic (MHD) Shock was found to be moving with speed 500-750km/s from higher to lower frequency plasma levels in the corona. Wild and Mcready[38] classified these outbursts as type II radio bursts in contrast to type I storms and the fast drifting type III. All these bursts are due to non thermal electrons and represent energy release in the corona. Type II bursts are the violent eruptions from the Sun that result in shock waves propagating through the corona and interplanetary medium. The origin of the shock waves in the solar corona that manifest themselves as solar type II radio bursts is one of the most important subjects of solar and terrestrial physics. A general picture of emission from type II shocks suggests that the emission mechanism is plasma emission near the fundamental and second harmonic[11, 24]. Langmuir waves are produced by beams produced in the shock. The excited Langmuir waves may be converted into escaping radio waves by non linear wave-wave processes[2, 4, and 11]. The study of type II is thus important for the understanding of the large scale structure and dynamics of the inner heliosphere. Since type II are good indicators of shocks that eventually cause sudden commencement of geomagnetic storms, their study is necessary for space weather predictions.
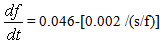 s is the duration in secondsf is the bandwidth in MHz.Statistical studies have shown that duration of type II bursts is about 5-15 minutes. The radio emission is considered to be due to a plasma emission process which involves the following steps.1. An instability condition is set up due to propagation of an exciting agency through the corona resulting in the generation of high frequency plasma waves at the local plasma frequency fp.2. These plasma waves (Langmuir waves) scatter on the background ions resulting in electromagnetic waves of roughly the same frequency which propagate towards the observer and are detected as fundamental emission. Two plasma waves can coalesce resulting in an electromagnetic wave at a frequency 2fp which is observed as harmonic component. The condition for instability is maintained for the duration the agency passes through a given plasma layer. Once the agency leaves the layer, there is no more free energy available so the plasma waves decay to the thermal level and the generation of electromagnetic waves ends. The agency is a shock wave.
s is the duration in secondsf is the bandwidth in MHz.Statistical studies have shown that duration of type II bursts is about 5-15 minutes. The radio emission is considered to be due to a plasma emission process which involves the following steps.1. An instability condition is set up due to propagation of an exciting agency through the corona resulting in the generation of high frequency plasma waves at the local plasma frequency fp.2. These plasma waves (Langmuir waves) scatter on the background ions resulting in electromagnetic waves of roughly the same frequency which propagate towards the observer and are detected as fundamental emission. Two plasma waves can coalesce resulting in an electromagnetic wave at a frequency 2fp which is observed as harmonic component. The condition for instability is maintained for the duration the agency passes through a given plasma layer. Once the agency leaves the layer, there is no more free energy available so the plasma waves decay to the thermal level and the generation of electromagnetic waves ends. The agency is a shock wave. 1.2. Fine Structure in Type II: (Band Splitting)
- In the dynamic structure of type II, the F and H components are composed of two parallel lanes of emission. The frequency separation is about 10% of the central frequency .In the two dimensional images, the lower split bands originate higher in the corona than the upper side band. The band splitting seems to be related to the inhomogenity in the medium. Several studies are being made to find answers to questions on origin height of type II and type III bursts. Dulk et al (1971) pointed out that type II sources often appear in the same regions as the type III sources that precede them in the flash phase and also observed that the type II bursts are occasionally observed at frequencies as low as10MHz. The type II emission is generated behind the shock front-i.e., in the region of enhanced electron density. This means that the electron density of the source as derived from the fundamental frequency of emission does not refer to the undisturbed corona but to temporarily compressed regions. One may therefore expect that at a given frequency type II and type III bursts would be generated at different heights. There is no statistical evidence to support this prediction. This matter requires careful observational investigation since, if established, an equal height for type II and type III bursts may force one to seek type II models in which the radiation is generated ahead of shock front.
1.3. Association between Type II and Type III Radio Bursts
- The association between type II and type III radio bursts are necessary in several aspects. In most of the cases, groups of type III radio bursts occur at the start of a flare. These type III radio bursts in most cases are followed by a type II radio bursts. Type III bursts are fast drifting bursts with duration of few seconds. Type II solar bursts can sometimes occur without preceded by type III radio bursts also. It is interesting to study whether the characteristics of type II bursts associated with type III bursts are different from those which are not associated with type III bursts. This will lead to the understanding of drivers of type II radio bursts. In our work, we have studied the type III bursts and their association with type II bursts. For the period 2002-2004, type III bursts data of Culgoora observatory is referred.
2. Data Selection
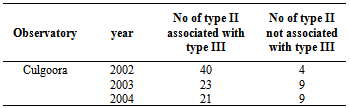
- In this study, we have used the data of type II radio bursts published by Culgoora radio observatory in the Solar Geophysical Data for the period January 2002 to December 2004. In our work, we have studied the type III bursts and their association with type II bursts. We have considered events in which type III and type II bursts are occurring with the time separation less than 30 minutes. A very large number of unclassified types of bursts exists in the decameter range. For our purpose, the bursts have been selected using the following criteria they have to be observed on at least two adjacent frequencies the delay between the bursts observed on the two frequencies must correspond to the normal frequency drift of type III bursts the bursts must be well isolated so that its time profile cannot be the superposition of different emissions. The observing period 2002-2004 being the decreasing phase of Solar cycle 23 close to the peak phase, the activity was moderate. Table 1 summarizes the data set for 2002- 2004.
|
3. Data Analysis
- The radio parameters data for the events considered in our study is given below.

4. Analysis
5. Results and Discussion
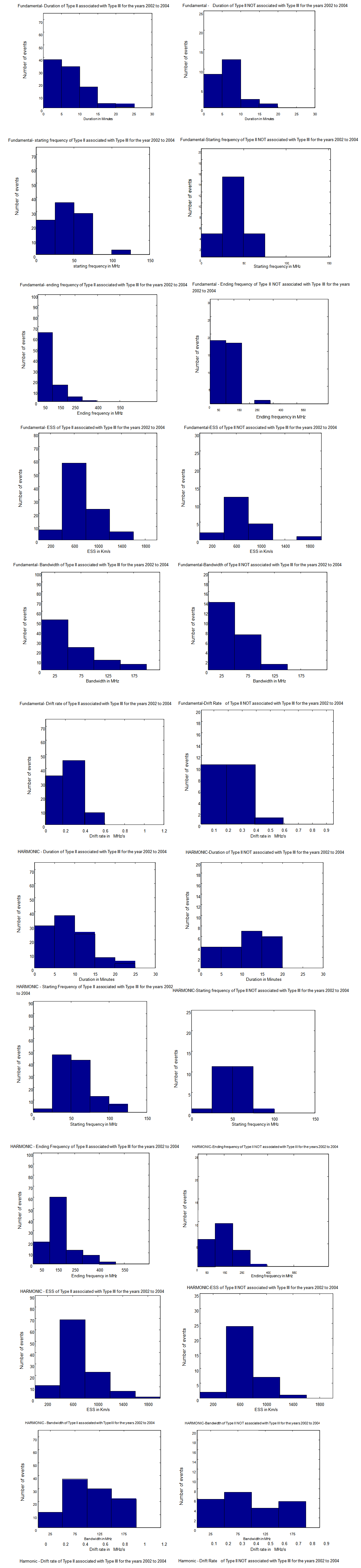
- 1.The time profile of a burst at a given frequency is believed to represent the passage an electron stream through the plasma frequency level and the temperature of the corona at different heights (Aubier et al.1972). The burst duration at each level is believed to be related to the duration of excitation (i.e. the time required for the exciter to cross the level) rather than the response of the medium; it increases with time , which indicates an increase of the exciter length with the distance traversed by the beam due to dispersion(Poquerusse et al.,1984). In the case of fundamental emission, the number of associated type II radio bursts with a duration of 1-5 minutes is almost same as (39 out 92 events) the bursts with duration between 5-10 minutes (32 out of 92 events) and similar pattern is observed with harmonic emissions (30 out of 103 events in the range of 1-5 minutes 36 out of 103 events with duration 5-10 minutes). In the case of type II radio bursts not associated type III radio bursts, 7 out of 22 bursts had the duration in the range 1-5 minutes in the case of fundamental emissions and 4 harmonic emissions had the duration of 1-5minutes. 13 out of 21 bursts had duration in the range 11-20minutes.2. The starting frequencies of majority of associated type II radio bursts lie in the range of 25 to 75 MHz (88 out of 90 events in case of associated fundamental emissions and 90 out of 103 events in case of harmonic events). With Non associated events, a similar pattern was observed (25 out of 25 fundamental bursts and 23 out of 24 harmonic bursts). The ending frequencies are in the range 50-200MHz (86 events out of 91 in associated fundamental events and 80 out of 103 in harmonic events).With non associated bursts, most of the bursts possessed ending frequencies in the range 50-200MHz (20 out of 21 fundamental events and 15 out of 21 harmonic events).3. The Estimated shock speeds (ESS) of associated type II radio bursts are in the range of 400 to 800 km/s in more than half the cases (56 out 94 events). In the case of non associated type II radio bursts also, the ESS is in the range of 400 to 800 km/s in most of the cases (12 out of 19 events). In very few cases, a higher ESS of 2000km/s (1 out of 94 cases including associated and not associated events) is noticed.4. Bandwidth of associated bursts is less than 50 MHz for fundamental emission (in 51 cases out of 90) where as for harmonic emission; it increases up to 100 MHz (50 out of 100 cases). It is observed that bandwidth of equal number of bursts is in the range of 100 – 200MHz. In the case of non associated bursts, 22 out of 23 fundamental bursts had bandwidth in the range of 1-100MHz. Interestingly 13 out of 22 not associated harmonic bursts possessed a bandwidth of 1-100MHz and 9 out of 22 events were in the range 100-200MHz.5. Less half of the associated bursts (36/88) had a drift rate in the range of 0.01-0.099MHz/s where as in 45 out 88 events, the drift rate was in the range 0.1 to 0.4 MHz/s. In 7 cases, it was above 0.4MHz/s. Drift rate of majority of harmonic emissions is in the range 0.1 -0.4 MHz/s (67 out 105 events) and hence is higher than the fundamental emission. In the case of not associated type II bursts, 24 out of 25 fundamental events, the drift rate was in the range of 0.01-0.4MHz/s and 6 out of 12 harmonic events had the drift rate in the range of 0.1 -0.4MHz/s.
6. Conclusions
- Based on association of type II radio bursts and type III radio bursts, the variation in the parameters such as duration , bandwidth, ESS, drift rate of type II radio bursts associated/non associated with type III radio bursts during the decreasing phase after the peak phase (2002 & 2004) of solar cycle 23 are explained. The time structure characteristics of type III radio bursts associated with type II radio burst is carried out. The results of this study have been obtained by an extensive analysis of several data sets. Using the available data we have concluded that:1. Although the sources and origin processes of type II bursts and the type III bursts are different, the plasma parameters remain almost uniform and variation in the plasma parameters of associated and non associated events is very marginal except in the case of duration and bandwidth. The difference in plasma parameters is noticeable in their duration and bandwidth. Relatively higher fraction of non associated type II radio bursts have more duration than the associated type II radio bursts. Also higher fraction of non associated bursts possessed greater bandwidth than the associated bursts. Since the duration of our study and the number of events is not fairly large, this observation needs further examination. 2. The dynamic spectra of events associated with interplanetary solar energetic particles are very complex and rarely show well defined type II bursts i.e. slowly drifting, harmonically-related pairs of narrow bands. The type II features that are observed appear to be composed of limited frequency type III bursts. The dominant feature is overlying wideband type III emission.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Our sincere thanks to the authorities of Culgora observatory for providing the data online. We are deeply indebted to the library authorities of Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore, Bangalore University and CMR Institute of Institute of Technology for providing access to their book facilities. We thank the referee for the constructive suggestions and comments.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML