-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Astronomy
p-ISSN: 2169-8848 e-ISSN: 2169-8856
2012; 1(5): 105-113
doi: 10.5923/j.astronomy.20120105.05
To Understand the Four Cosmological Interactions
U. V. S. Seshavatharam1, S. Lakshminarayana2
1Honorary faculty, I-SERVE, Alakapuri, Hyderabad, 35, AP, India
2Dept. of Nuclear Physics, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam, 03, AP, India
Correspondence to: U. V. S. Seshavatharam, Honorary faculty, I-SERVE, Alakapuri, Hyderabad, 35, AP, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Within the expanding cosmic Hubble volume, Hubble length can be considered as the gravitational or electromagnetic interaction range. Product of ‘Hubble volume’ and ‘cosmic critical density’ can be called as the “Hubble mass”. The three key assumptions are: 1) within the Hubble volume, each and every point in free space is influenced by the Hubble mass, 2) ‘molar electron mass’ can be considered as the rest mass of a new heavy charged elementary particle and 3) atomic gravitational constant seems to be Avogadro number times the classical gravitational constant. This is a new approach and may be given a chance in understanding the four fundamental cosmological interactions.
Keywords: Hubble Volume, Critical Density, Hubble Mass, Coulomb Mass, Molar Electron Mass, Atomic Gravitational Constant and the CMBR Temperature
Cite this paper: U. V. S. Seshavatharam, S. Lakshminarayana, "To Understand the Four Cosmological Interactions", International Journal of Astronomy, Vol. 1 No. 5, 2012, pp. 105-113. doi: 10.5923/j.astronomy.20120105.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- “Hubble volume” can be considered as a key tool in cosmology and unification. In this paper an attempt is made to understand the basic unified concepts of the four fundamental cosmological interactions. This is a new approach and particle physics and cosmology can be studied in a cohesive mode.
1.1. Basic Assumptions in Particle Cosmology
- With reference to the Mach’s principle[1-6] and the Hubble volume, if “Hubble mass” is the product of cosmic critical density and the Hubble volume[7-9], then it can be assumed that, 1) Within the Hubble volume, each and every point in free space is influenced by the Hubble mass. 2) Within the Hubble volume, the Hubble mass plays a vital role in understanding the properties of electromagnetic and nuclear interactions. 3) Within the Hubble volume, Hubble mass plays a key role in understanding the geometry of the universe. With reference to the Avogadro number[10] and from unification point of view, the utmost fundamental question is: How to understand the origin of “mass” of elementary particles? In this connection it can be assumed that, 1) “Molar electron mass” can be considered as the rest mass of a new heavy charged elementary particle.2) Atomic gravitational constant is Avogadro number times the classical gravitational constant.
2. Key Concepts in Particle Cosmology
- Concept-1: In atomic and nuclear physics, atomic gravitational constant
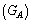 is Avogadro number times the classical gravitational constant
is Avogadro number times the classical gravitational constant 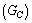 .
. 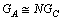 | (1) |
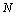 times the classical gravitational constant, atoms are themselves arranged in a systematic manner and generate the “gram mole”. Concept -2: The key conceptual link that connects the gravitational and non-gravitational forces is - the classical force limit
times the classical gravitational constant, atoms are themselves arranged in a systematic manner and generate the “gram mole”. Concept -2: The key conceptual link that connects the gravitational and non-gravitational forces is - the classical force limit 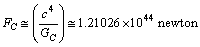 | (2) |
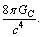 It has multiple applications in Black hole physics and Planck scale physics[16]. It has to be measured either from the experiments or from the cosmic and astronomical observations. Concept -3: Ratio of ‘classical force limit
It has multiple applications in Black hole physics and Planck scale physics[16]. It has to be measured either from the experiments or from the cosmic and astronomical observations. Concept -3: Ratio of ‘classical force limit 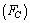 ’ and ‘ weak force magnitude
’ and ‘ weak force magnitude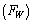 ’ is
’ is 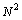 where
where 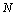 is a large number close to the Avogadro number.
is a large number close to the Avogadro number. 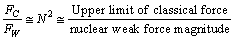 | (3) |
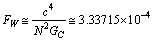 newton. Considering this
newton. Considering this 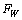 , Higgs fermion and boson masses can be fitted. In this connection please see our earlier published papers[17-21] and application-9 of this paper. Concept-4: In the expanding cosmic Hubble volume,
, Higgs fermion and boson masses can be fitted. In this connection please see our earlier published papers[17-21] and application-9 of this paper. Concept-4: In the expanding cosmic Hubble volume, 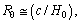 can be considered as the gravitational or electromagnetic interaction range.Concept-5: In the expanding cosmic Hubble volume, characteristic cosmic Hubble mass is the product of the cosmic critical density and the Hubble volume. If the critical density is
can be considered as the gravitational or electromagnetic interaction range.Concept-5: In the expanding cosmic Hubble volume, characteristic cosmic Hubble mass is the product of the cosmic critical density and the Hubble volume. If the critical density is 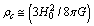 and characteristic Hubble radius is
and characteristic Hubble radius is 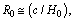 mass of the cosmic Hubble volume is
mass of the cosmic Hubble volume is 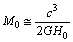 | (4) |
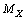 in such a way that, inverse of the fine structure ratio is equal to the natural logarithm of the sum of number of positively and negatively charged
in such a way that, inverse of the fine structure ratio is equal to the natural logarithm of the sum of number of positively and negatively charged 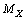 in the Hubble volume. If the number of positively charged particles is
in the Hubble volume. If the number of positively charged particles is 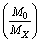 and the number of negatively charged particles is also
and the number of negatively charged particles is also 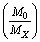 then
then 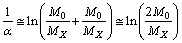 | (5) |
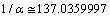 and from the current observations[22,23,24], magnitude of the Hubble constant is,
and from the current observations[22,23,24], magnitude of the Hubble constant is, 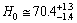 Km/sec/Mpc. Thus
Km/sec/Mpc. Thus 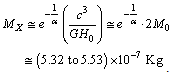 | (6) |
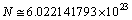 is the Avogadro number and
is the Avogadro number and 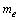 is the rest mass of electron, surprisingly it is noticed that,
is the rest mass of electron, surprisingly it is noticed that, 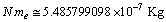 and this is close to the above estimation of
and this is close to the above estimation of 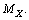 Thus it can be suggested that,
Thus it can be suggested that,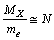 | (7) |
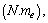 the obtained cosmic Hubble mass is
the obtained cosmic Hubble mass is 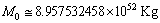 and thus the obtained Hubble’s constant is
and thus the obtained Hubble’s constant is 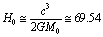 Km/sec/Mpc. Note that large dimensionless constants and compound physical constants reflect an intrinsic property of nature [25,26]. Whether to consider them or discard them depends on the physical interpretations, logics, experiments, observations and our choice of scientific interest. In most of the critical cases, ‘time’ only will decide the issue. The mystery can be resolved only with further research, analysis, discussions and encouragement.Concept -7: For any observable charged particle, there exist two kinds of masses and their mass ratio is
Km/sec/Mpc. Note that large dimensionless constants and compound physical constants reflect an intrinsic property of nature [25,26]. Whether to consider them or discard them depends on the physical interpretations, logics, experiments, observations and our choice of scientific interest. In most of the critical cases, ‘time’ only will decide the issue. The mystery can be resolved only with further research, analysis, discussions and encouragement.Concept -7: For any observable charged particle, there exist two kinds of masses and their mass ratio is  Let this number be
Let this number be 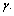 First kind of mass seems to be the ‘gravitational or observed’ mass and the second kind of mass seems to be the ‘electromagnetic’ mass. This idea can be applied to proton and electron. This number is obtained in the following way. In the Planck scale, similar to the Planck mass, with reference to the elementary charge, a new mass unit can be constructed in the following way.
First kind of mass seems to be the ‘gravitational or observed’ mass and the second kind of mass seems to be the ‘electromagnetic’ mass. This idea can be applied to proton and electron. This number is obtained in the following way. In the Planck scale, similar to the Planck mass, with reference to the elementary charge, a new mass unit can be constructed in the following way. | (8) |
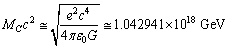 | (9) |
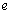 is the elementary charge. How to interpret this mass unit? Is it a primordial massive charged particle? If two such oppositely charged particles annihilate, a large amount of energy can be released. This may be the root cause of cosmic energy reservoir. Such pairs may be the chief constituents of black holes. In certain time interval with a well defined quantum rules they annihilate and release a large amount of energy in the form of
is the elementary charge. How to interpret this mass unit? Is it a primordial massive charged particle? If two such oppositely charged particles annihilate, a large amount of energy can be released. This may be the root cause of cosmic energy reservoir. Such pairs may be the chief constituents of black holes. In certain time interval with a well defined quantum rules they annihilate and release a large amount of energy in the form of 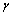 photons. In the Hubble volume, with its pair annihilation, “origin of the CMBR” can be understood. Clearly speaking, gravitational and electromagnetic force ratio of
photons. In the Hubble volume, with its pair annihilation, “origin of the CMBR” can be understood. Clearly speaking, gravitational and electromagnetic force ratio of 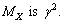
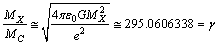 | (10) |
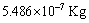 is the observable or gravitational mass of
is the observable or gravitational mass of , then
, then 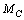 is the electromagnetic mass of
is the electromagnetic mass of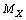 . With reference to the electron rest mass,
. With reference to the electron rest mass, 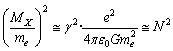 | (11) |
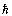 is the quantum of the gravitational angular momentum, then the electromagnetic quantum can be expressed as
is the quantum of the gravitational angular momentum, then the electromagnetic quantum can be expressed as 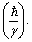 Thus the ratio,
Thus the ratio, 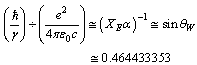 | (12) |
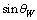 is very close to the weak mixing angleConcept-9: In modified quark SUSY[17,18], if
is very close to the weak mixing angleConcept-9: In modified quark SUSY[17,18], if 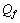 is the mass of quark fermion and
is the mass of quark fermion and 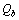 is the mass of quark boson, then
is the mass of quark boson, then 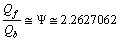 | (13) |
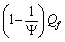 represents the effective quark fermion mass. The number
represents the effective quark fermion mass. The number 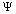 can be fitted with the following empirical relation
can be fitted with the following empirical relation 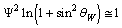 | (14) |
3. To Fit the Rest Masses of Electron, Proton and Neutron
- If
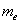 is the light charged elementary particle and
is the light charged elementary particle and 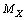 is the heavy charged elementary particle to be detected or observed, it is possible to represent the relation in the following form.
is the heavy charged elementary particle to be detected or observed, it is possible to represent the relation in the following form. 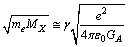 | (15) |
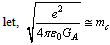 | (16) |
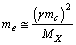 | (17) |
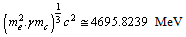 | (18) |
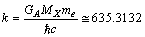 ,
, 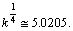 An attempt is made to fit the rest masses of proton and neutron in the following way.
An attempt is made to fit the rest masses of proton and neutron in the following way.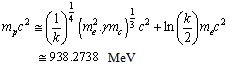 | (19) |
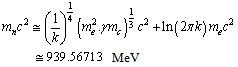 | (20) |
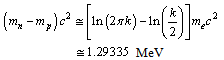 | (21) |
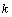 in fitting the nuclear binding energy constants and other areas of physics like strong interaction range, potential energy of electron in hydrogen atom, electroweak physics etc.
in fitting the nuclear binding energy constants and other areas of physics like strong interaction range, potential energy of electron in hydrogen atom, electroweak physics etc. 3.1. To Fit the Nuclear Binding Energy Constants
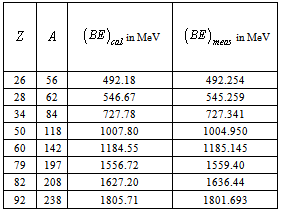
- The semi-empirical mass formula (SEMF) is used to approximate the mass and various other properties of an atomic nucleus[27,28,29]. As the name suggests, it is based partly on theory and partly on empirical measurements. Based on the ‘least squares fit’, volume energy coefficient is
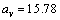 MeV, surface energy coefficient is
MeV, surface energy coefficient is 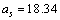 MeV, coulombic energy coefficient is
MeV, coulombic energy coefficient is 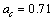 MeV, asymmetric energy coefficient is
MeV, asymmetric energy coefficient is 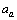 = 23.21 MeV and pairing energy coefficient is
= 23.21 MeV and pairing energy coefficient is 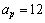 MeV. The semi empirical mass formula is
MeV. The semi empirical mass formula is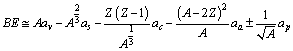 | (22) |
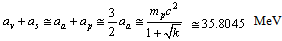 | (23) |
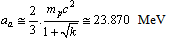 | (24) |
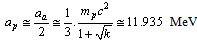 | (25) |
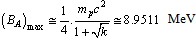 | (26) |
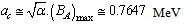 | (27) |
|
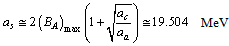 | (28) |
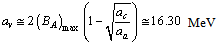 | (29) |
 to
to  nuclear binding energy is calculated and compared with the measured binding energy[30]. Column-3 represents the calculated binding energy and column-4 represents the measured binding energy.
nuclear binding energy is calculated and compared with the measured binding energy[30]. Column-3 represents the calculated binding energy and column-4 represents the measured binding energy.3.2. Proton-nucleon Stability Relation
- It is noticed that
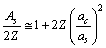 | (31) |
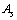 is the stable mass number of
is the stable mass number of 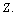 This is a direct relation. Assuming the proton number
This is a direct relation. Assuming the proton number 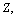 in general, for all atoms, lower stability can be fitted directly with the following relation[27].
in general, for all atoms, lower stability can be fitted directly with the following relation[27]. 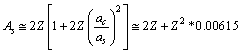 | (32) |
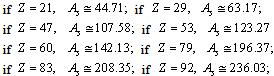 Stable super heavy elements can be predicted with this relation. In between
Stable super heavy elements can be predicted with this relation. In between  to
to  obtained
obtained 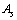 is lower compared to the actual
is lower compared to the actual 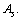 It is noticed that, upper stability in light and medium atoms up to
It is noticed that, upper stability in light and medium atoms up to 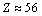 can be fitted with the following relation.
can be fitted with the following relation.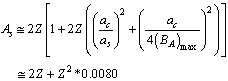 | (33) |
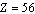 ,obtained upper
,obtained upper 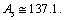 Note that, for
Note that, for 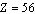 ,actual stable
,actual stable 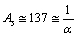 where
where 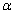 is the fine structure ratio. This seems to be a nice and interesting coincidence. In between 0.00615 and 0.0080, for light and medium atoms up to
is the fine structure ratio. This seems to be a nice and interesting coincidence. In between 0.00615 and 0.0080, for light and medium atoms up to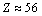 or
or 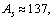 mean stability can be fitted with the following relation.
mean stability can be fitted with the following relation.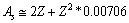 | (34) |
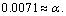 Thus up to
Thus up to 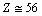 or
or 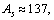 mean stability can be expressed as
mean stability can be expressed as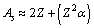 | (35) |
4. To Fit the Rms Radius of Proton
- Let
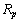 be the rms radius of proton. Define two radii
be the rms radius of proton. Define two radii 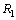 and
and 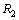 as follows.
as follows. 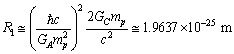 | (36) |
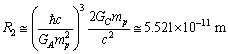 | (37) |
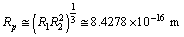 | (38) |
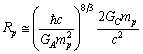 | (39) |
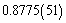 fm. Recent work on the spectrum of muonic hydrogen (an exotic atom consisting of a proton and a negative muon) indicates a significantly lower value for the proton charge radius,
fm. Recent work on the spectrum of muonic hydrogen (an exotic atom consisting of a proton and a negative muon) indicates a significantly lower value for the proton charge radius, 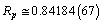 fm and the reason for this discrepancy is not clear. This is 10 times more precise than all the previous determinations[31,32]. Thus from proton rest mass and rms radius,
fm and the reason for this discrepancy is not clear. This is 10 times more precise than all the previous determinations[31,32]. Thus from proton rest mass and rms radius, 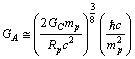 | (40) |
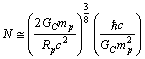 | (41) |
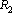 is very close to the Bohr radius of Hydrogen atom. It is very interesting to note that, with
is very close to the Bohr radius of Hydrogen atom. It is very interesting to note that, with 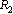 ionic radii of atoms can be fitted very easily as
ionic radii of atoms can be fitted very easily as 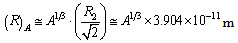 | (42) |
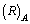 is the ionic radius of mass number
is the ionic radius of mass number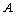 If
If 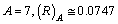 nm, if
nm, if 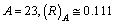 nm and if
nm and if 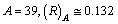 nm. Their corresponding recommended radii are 0.076 nm, 0.102 nm and 0.138 nm respectively[31,32].
nm. Their corresponding recommended radii are 0.076 nm, 0.102 nm and 0.138 nm respectively[31,32]. 5. To Fit the Characteristic Potential Radius of Nucleus 1.4 fm
- It is noticed that, gram mole is a black hole where the operating gravitational constant is
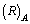 but not
but not 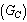 . That means for the simplest case of gram mole of electrons or gram mole of protons, there exist
. That means for the simplest case of gram mole of electrons or gram mole of protons, there exist 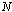 number of electrons or
number of electrons or 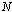 number of protons. Let it follows the concept of Schwarzschild radius. It can be expressed in the following way. Let us define two radii
number of protons. Let it follows the concept of Schwarzschild radius. It can be expressed in the following way. Let us define two radii 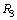 and
and 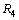 as follows.
as follows.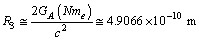 | (43) |
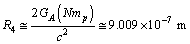 | (44) |
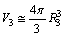 | (45) |
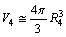 | (46) |
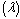 in between
in between 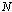 electrons or in between
electrons or in between 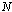 protons, can be obtained as
protons, can be obtained as 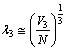 | (47) |
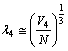 | (48) |
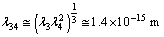 | (49) |
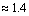 fm. Based on the Yukawa’s Pion exchange model nuclear interaction range is 1.4 fm. Thus if
fm. Based on the Yukawa’s Pion exchange model nuclear interaction range is 1.4 fm. Thus if 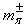 is the charged pion rest mass,
is the charged pion rest mass, 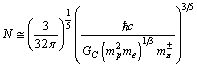 | (50) |
6. Applications of the Proposed Assumptions and Concepts
6.1. Part-1: Applications in Particle and Nuclear Physics
6.1.1. Application-1: The Characteristic Nuclear Charge Radius
- If
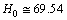 Km/sec/Mpc,
Km/sec/Mpc,  is the characteristic radius of nucleus, it is noticed that,
is the characteristic radius of nucleus, it is noticed that,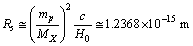 | (51) |
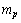 is the proton rest mass. This can be compared with the characteristic charge radius of the nucleus and the strong interaction range.
is the proton rest mass. This can be compared with the characteristic charge radius of the nucleus and the strong interaction range. 6.1.2. Application-2: Scattering Distance between Electron and the Nucleus
- If
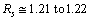 fm is the minimum scattering distance between electron and the nucleus, it is noticed that,
fm is the minimum scattering distance between electron and the nucleus, it is noticed that, 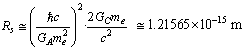 | (52) |
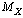 is the molar electron mass. Here it is very interesting to consider the role of the Schwarzschild radius of the ‘electron mass’.
is the molar electron mass. Here it is very interesting to consider the role of the Schwarzschild radius of the ‘electron mass’. 6.1.3. Aplication-3: To fit the charged lepton rest masses
- Muon and tau rest masses can be fitted in the following way[33]. Let
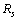 be the characteristic nuclear unit size. The key relation seems to be
be the characteristic nuclear unit size. The key relation seems to be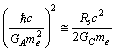 | (53) |
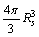 and
and 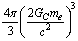 , let
, let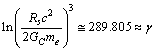 | (54) |
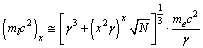 | (55) |
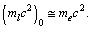 At x = 1,
At x = 1, 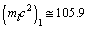 MeV and can be compared with the rest mass of muon (105.66 MeV). At x = 2,
MeV and can be compared with the rest mass of muon (105.66 MeV). At x = 2, 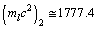 MeV and can be compared with the rest mass of tau (1777.0 MeV). x = 0,1 and 2 can be considered as the 3 characteristic vibrating modes.
MeV and can be compared with the rest mass of tau (1777.0 MeV). x = 0,1 and 2 can be considered as the 3 characteristic vibrating modes. 6.1.4. Aplication-4: Electromagnetic and Strong Interaction Ranges
- For electron, starting from
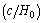 , its characteristic interaction ending range can be expressed as
, its characteristic interaction ending range can be expressed as 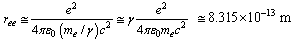 | (56) |
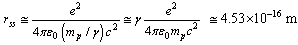 | (57) |
6.1.5. Application-5: Ratio of Electromagnetic and Strong Interaction Ending Range
- Ratio of electromagnetic ending interaction range and strong interaction ending range can be expressed as
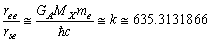 | (58) |
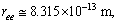
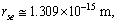
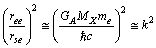 | (59) |
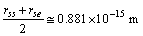 | (60) |
6.1.6. Application-6
- For any elementary particle of charge
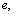 electromagnetic mass
electromagnetic mass 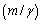 and characteristic radius
and characteristic radius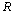 , it can be assumed as
, it can be assumed as 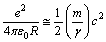 | (61) |
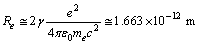 | (62) |
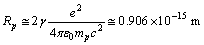 | (63) |
6.1.7. Application-7: Potential Energy of Electron in Hydrogen Atom
- Let
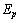 be the potential energy of electron in the Hydrogen atom. It is noticed that,
be the potential energy of electron in the Hydrogen atom. It is noticed that, 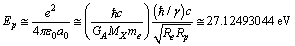 | (64) |
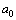 is the Bohr radius[34,35]. With 99.6822% this is matching with
is the Bohr radius[34,35]. With 99.6822% this is matching with 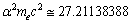 eV. After simplification it takes the following form.
eV. After simplification it takes the following form.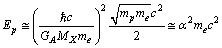 | (65) |
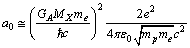 | (66) |
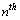 orbit radii can be expressed as
orbit radii can be expressed as 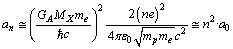 | (67) |
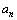 is the radius of
is the radius of 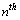 orbit and
orbit and 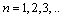 Thus in Hydrogen atom, potential energy of electron in
Thus in Hydrogen atom, potential energy of electron in 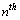 orbit can be expressed as
orbit can be expressed as 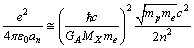 | (68) |
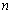 is
is 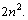 Thus on comparison, it can suggested that,
Thus on comparison, it can suggested that, 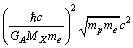 is the potential energy of
is the potential energy of 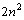 electrons and potential energy of one electron is equal to
electrons and potential energy of one electron is equal to 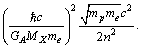
6.1.8. Application-8: Magnetic Moments of the Nucleon
- If
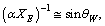 magnetic moment of electron can be expressed as[36,37]
magnetic moment of electron can be expressed as[36,37]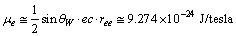 | (69) |
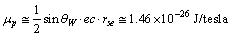 | (70) |
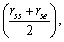 magnetic moment of neutron can be fitted as
magnetic moment of neutron can be fitted as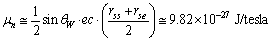 | (71) |
6.1.9. Application-9: To Correlate the Charged Higgs Fermion Mass and the Electron Mass
- If
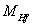 is the charged Higgs fermion, it is noticed that,
is the charged Higgs fermion, it is noticed that,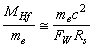 | (72) |
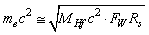 | (73) |
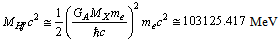 | (74) |
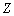 boson of rest energy 91152.53 MeV. Estimated top quark rest energy[17,18] is 182160 MeV and its corresponding boson is 80505.6 MeV. Thus the surprising thing is that, susy boson of the top quark seems to be the electroweak
boson of rest energy 91152.53 MeV. Estimated top quark rest energy[17,18] is 182160 MeV and its corresponding boson is 80505.6 MeV. Thus the surprising thing is that, susy boson of the top quark seems to be the electroweak 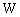 boson. Another interesting idea is that
boson. Another interesting idea is that 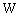 boson and Higgs boson generate a neutral boson of mass 126 GeV. It can be suggested that,
boson and Higgs boson generate a neutral boson of mass 126 GeV. It can be suggested that, 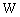 boson pair generates a neutral boson of rest energy 161 GeV.
boson pair generates a neutral boson of rest energy 161 GeV.6.2. Part-2 : Applications in Cosmology
6.2.1. Application-10: To fit the Hubble’s Constant
- Combining the relations (51) and (52) and if
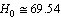 Km/sec/Mpc, it is noticed that,
Km/sec/Mpc, it is noticed that,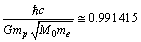 | (75) |
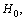 in the presently believed atomic and nuclear physical constants, on the cosmological time scale, there exists one variable physical quantity. ‘Rate of change’ in its magnitude may be a measure of the present cosmic acceleration. Thus independent of the cosmic red shift and CMBR observations, from the atomic and nuclear physics, cosmic acceleration can be verified. Based on the above coincidence, magnitude of the present Hubble’s constant can be expressed as
in the presently believed atomic and nuclear physical constants, on the cosmological time scale, there exists one variable physical quantity. ‘Rate of change’ in its magnitude may be a measure of the present cosmic acceleration. Thus independent of the cosmic red shift and CMBR observations, from the atomic and nuclear physics, cosmic acceleration can be verified. Based on the above coincidence, magnitude of the present Hubble’s constant can be expressed as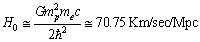 | (76) |
6.2.2. Application-11: Pair Creation of Mc within the Hubble Volume and the CMBR Temperature
- Pair particles creation and annihilation is a characteristic phenomena in `free space’, and is the basic idea of quantum fluctuations of the vacuum. In the expanding universe, from relation (8) by considering the proposed charged
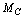 and its pair annihilation as characteristic cosmic phenomena, origin of the isotropic CMB radiation can be addressed. At any time
and its pair annihilation as characteristic cosmic phenomena, origin of the isotropic CMB radiation can be addressed. At any time 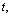 it can be suggested that
it can be suggested that 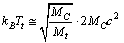 | (77) |
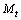 is the cosmic mass at time
is the cosmic mass at time 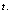 Please note that, at present
Please note that, at present 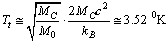 | (78) |
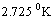 . But it has to be discussed in depth. It seems to be a direct consequence of the Mach's principle.
. But it has to be discussed in depth. It seems to be a direct consequence of the Mach's principle. 6.2.3. Application-12: A Quantitative Approach to Understand the CMBR Radiation
- It is noticed that, there exists a very simple relation in between the cosmic critical density, matter density and the thermal energy density. It can be expressed in the following way. At any time
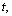
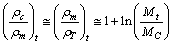 | (79) |
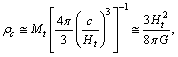
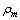 is the matter density and
is the matter density and 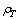 is the thermal energy density expressed in
is the thermal energy density expressed in 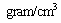 or
or 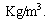 Considering the Planck - Coulomb scale, at the beginning if
Considering the Planck - Coulomb scale, at the beginning if 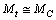
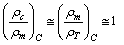 | (80) |
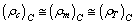 | (81) |
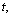
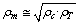 | (82) |
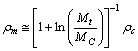 | (83) |
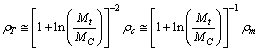 | (84) |
6.3. Present Matter Density of the Universe
- From (76) at present if
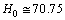 Km/sec/Mpc,
Km/sec/Mpc, 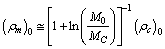 | (85) |
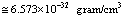 where
where 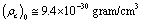 and
and 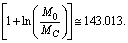 Based on the average mass-to-light ratio for any galaxy[6]
Based on the average mass-to-light ratio for any galaxy[6] 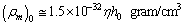 | (86) |
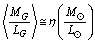 and the number
and the number 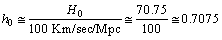 .Note that elliptical galaxies probably comprise about 60% of the galaxies in the universe and spiral galaxies thought to make up about 20% percent of the galaxies in the universe. Almost 80% of the galaxies are in the form of elliptical and spiral galaxies. For spiral galaxies,
.Note that elliptical galaxies probably comprise about 60% of the galaxies in the universe and spiral galaxies thought to make up about 20% percent of the galaxies in the universe. Almost 80% of the galaxies are in the form of elliptical and spiral galaxies. For spiral galaxies, 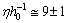 and for elliptical galaxies,
and for elliptical galaxies, 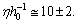 For our galaxy inner part,
For our galaxy inner part, 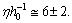 Thus the average
Thus the average 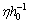 is very close to 8 to 9 and its corresponding matter density is close to
is very close to 8 to 9 and its corresponding matter density is close to 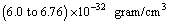 and can be compared with the above proposed magnitude of
and can be compared with the above proposed magnitude of 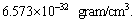
6.4. Present Thermal Energy Density of the Universe
- At present if Km/sec/Mpc,
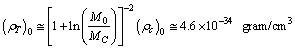 | (87) |
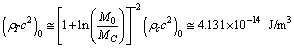 | (88) |
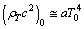 | (89) |
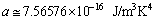 is the radiation energy density constant, then obtained CMBR temperature is,
is the radiation energy density constant, then obtained CMBR temperature is, 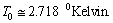 This is accurately fitting with the observed CMBR temperature[24] ,
This is accurately fitting with the observed CMBR temperature[24] , 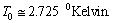 Thus in this way, the present value of the Hubble’s constant and the present CMBR temperature can be co-related with the following trial-error relation.
Thus in this way, the present value of the Hubble’s constant and the present CMBR temperature can be co-related with the following trial-error relation.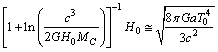 | (90) |
7. Discussion & Conclusions
- String theory or QCD is not in a position to address the basics of cosmic structure[38]. In understanding the basic concepts of unification or theory of every thing, role of dark energy and dark matter is insignificant. Even though string theory was introduced for understanding the basics of strong interaction, its success seems to be a dilemma because of its higher dimensions and the non-coupling of the nuclear and Planck scale. Based on the proposed relations and applications, Hubble volume or Hubble mass, can be considered as a key tool in unification as well as cosmology. From relations (51,52,75), if it is possible to identify the atomic cosmological physical variable, then by observing the rate of change in its magnitude (on the cosmological time scale), the “future” cosmic acceleration can be verified and thus the cosmic geometry can be confirmed from atomic and nuclear physics! Without the advancement of nano- technology or fermi-technology this may not be possible. Not only that, independent of the cosmic red shift and CMBR observations “future” cosmic acceleration can be checked in this new direction. Considering the proposed relations and concepts it is possible to say that there exists a strong relation between cosmic Hubble mass, Avogadro number and unification..
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The first author is indebted to professor K. V. Krishna Murthy, Chairman, Institute of Scientific Research on Vedas (I-SERVE), Hyderabad, India and Shri K. V. R. S. Murthy, former scientist IICT (CSIR) Govt. of India, Director, Research and Development, I-SERVE, for their valuable guidance and great support in developing this subject.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML