-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Astronomy
2012; 1(3): 38-43
doi: 10.5923/j.astronomy.20120103.01
On Multiple Type II Bursts and Coronal Mass Ejections
Joginder Sharma 1, Nishant Mittal 1, 2, Udit Narain 1, 3
1Astrophysics Research Group, Dept. of Physics, Meerut College Meerut, 250001, India
2Dept. of Physics, IIMT Engineering College, Meerut, 250001, India
3Dept. of Physics, FIT Engineering College, Mawana Road, Meerut, 250001, India
Correspondence to: Joginder Sharma , Astrophysics Research Group, Dept. of Physics, Meerut College Meerut, 250001, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
We have investigated 42 multiple type II events observed during the period 1997-2007 for the complete solar cycle 23 recorded by WAVES/WIND instrument and point out that the average speed of associated CMEs is 1311 km/s and 57% of CMEs have their widths larger than 200 degree or they are halo CMEs. The mean of starting and ending frequencies is 9.09 MHz and 1.82 MHz, respectively. The linear correlation factor is 0.052 which implies that starting and ending frequencies have no correlation.
Keywords: Sun, Coronal Mass Ejections, Radio Burst, Solar Cycle
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- First of the observations of type II bursts occurring in non thermal solar radiation were reported by[1]. Type II burst appears as an emission band slowly drifting from high to low frequencies in dynamic radio spectra, in contrast to the type I storms and the fast drifting type III bursts. Type IV bursts from moving and stationary coronal structures and type V bursts, a variant of type III bursts, were subsequently added to the types of radio bursts. These bursts are interpreted as the radio signature of shock waves in the solar corona. Such shock waves can be generated by flares and/ or coronal mass ejections[2, 3, 4].The type II bursts are signatures of violent eruptions from the Sun that result in shock waves propagating through the corona and the interplanetary (IP) medium. The study of type II bursts is thus important for the understanding of the large scale structures and dynamics of the inner heliosphere.More often than not, the appearance of type II radio bursts is preceded by groups of bursts of the type III family. The dynamic spectra of the onset of the type III activity seems to be in the same spectral range as the backward extrapolated type II lanes.[5] named this type of event compound and concluded that both the type III and type II originated from a common source.[6] reported two more spectral features physically related to the type II exciter; the type II precursor which consists of fast drift bursts or pulsations with a restricted bandwidth near the spectral range of the backward extrapolated type II lanes; the arc consists of a series of narrow band bursts immediately preceding the type II onset. It has an inverted U- shaped envelope, hence its name. The relationship of type II bursts with CMEs has been explored by[7, 8, 9, 10, and 11]; using the uniform and extended high quality data on radio bursts from WIND/WAVES and CMEs from SOHO/LASCO, have studied the properties of the radio rich CMEs which produce type II i.e. decametric - hectomatric or DH radio bursts. These DH CMEs are relatively faster and wider than the normal CMEs. These special characteristics of radio-rich CMEs could be used to identify the population of geoeffective CMEs, which are quite relevant to space weather. Like type III radio bursts which sometimes occur in groups, type II radio bursts can also occur in multiples.[12] were the first to report multiple type II bursts and to suggest that they were due to a single shock intersecting different coronal structures. Most of the type II bursts have fundamental and harmonic signatures in the dynamic spectrum. As reported by[12 and 13], a multiple type II burst consists of multiple bands in the dynamic spectrum. These bands often have different frequency drift rates or are significantly displaced in frequency in a manner different from the normal fundamental harmonic or split band relationships[14]. The presence of these multiple bands may indicate the interaction of a single shock front with different coronal structures. Alternatively, the various bands may indicate successive shocks. Thus the study of multiple type II shocks and their physical origin is of great interest.The study of multiple types II bursts is rare.[12] Reported that nearly 20% of all the type II is multiple types II.[15 and 16] made a detailed analysis of multiple type II radio bursts observed by culgoora radio spectrograph from January 1997 to July 2003, and concluded that the probability of observing the multiple types II is higher when the strength of the flare is high, and the width of the CMEs is large. The results are also discussed with a focus on the various possibilities on the origin of multiple types II bursts. Prakash et al have[17] investigated the properties of type II burst pairs (m-and DH type IIs) associated with flares and CMEs during the period 2000 to 2005. They concluded that the difference between class I and II events in durations and starting frequencies of type IIs is insignificant. However, most of the class I DH- type IIs start below 14 MHz, whereas class II events are already present at 14 MHz which is the WAVES upper starting frequency. The different components in a multiple type II event might be assumed to be generated by a single shock traveling through different coronal structures. It may be said that the flares and CMEs (front or flank) both might be the source of multiple type II bursts.Here we extend the aforesaid studies from 1997 to 2007 that is for the complete solar cycle 23, in view of its importance to space weather related problems.
2. Data Selection, Analysis and Results
- A list of all solar type II and IV radio bursts recorded by WAVES/WIND instrument has been obtained from the online catalog available athttp://www-lep.gsfc.nasa.gov/waves/waves.html. A total of 510 events were recorded by WAVES/WIND instrument in the period 1997-2007 for the complete solar cycle 23, of which 468 events were type II bursts. Out of which 42 events have multiple tones and are said to be multiple type II bursts. CME data has been taken from the website http://cdaw.gsfc.nasa.gov.nasa.gov/cmelist . Different observatories use different density models, for the calculation of the estimated shock speeds and different methods to determine the characteristics of the bursts. As already pointed out our study considers the bursts observed by WAVES/WIND instrument. In the following Table 1 we exhibit starting, ending frequencies, CMEs speeds and band width. For convenience, on line data is exhibited in table 2, as appendix.
2.1. Life Time
- Figure 1 shows distribution of life times of multiple type II radio bursts. The life time of bursts varies from 1 to 1437 minutes, and the mean value is 272 min.
2.2. Start Frequency
- The histogram of the starting frequency is shown in figure 2. The start frequency for most of the multiple type II lies in the range of 1- 14 MHz. The mean of starting frequency is 9.09 MHz with a standard deviation of 5.62 MHz.
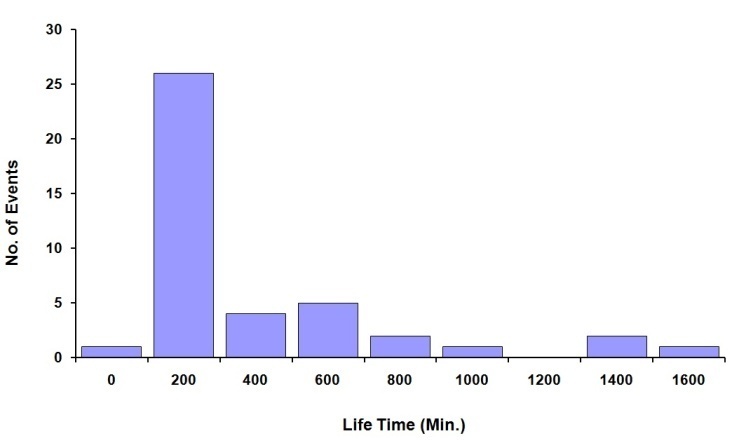 | Figure 1. Distribution of life times of multiple type II radio bursts |
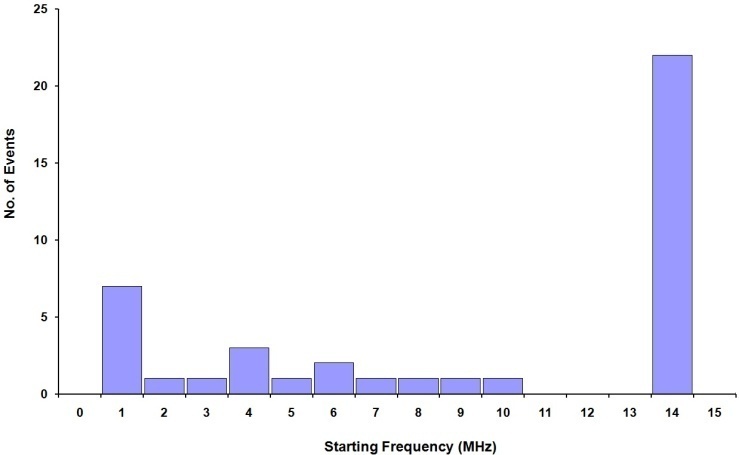 | Figure 2. Shows the starting frequency of 42 multiple type II bursts |
2.3. End Frequency
- The distribution of the end frequencies of type II bursts is shown in figure 3. The end frequency varies from 1 to 10 MHz with most of its value lying around 1 MHz. The average end frequency is 1.82 MHz.
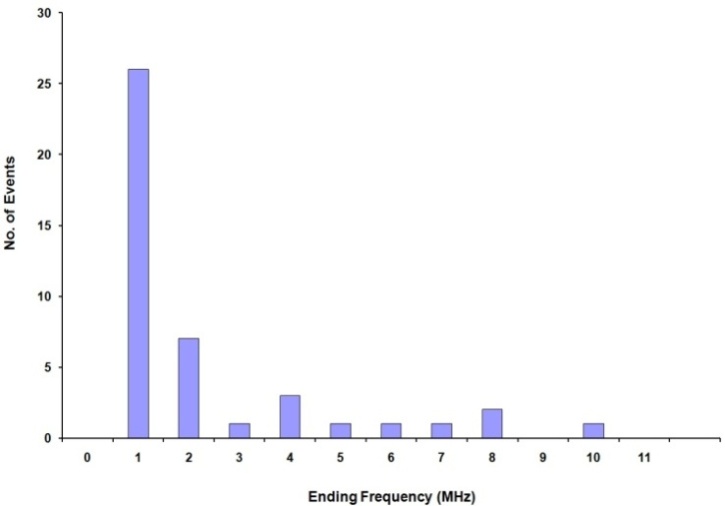 | Figure 3. Shows the ending frequency of 42 multiple types II bursts |
2.4. Band Width
- Figure 4 shows the histogram of bandwidths (difference of start and end frequencies). The band width varies from 0.08 to 13.96 MHz, and the average band width is 7.27 MHz.
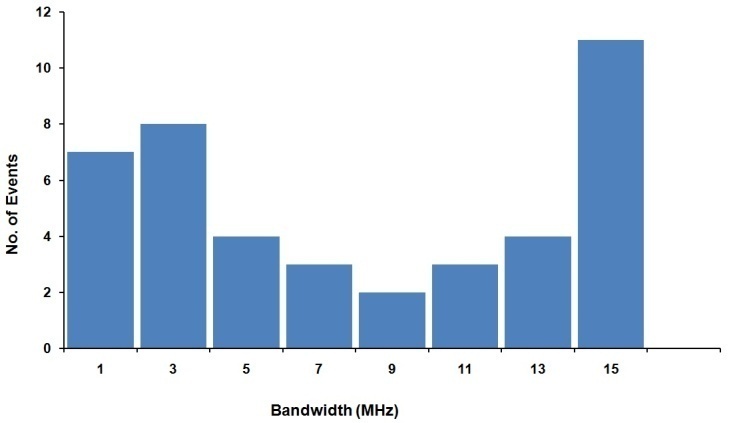 | Figure 4. histogram showing the distribution of bandwidth of 42 multiple types II bursts |
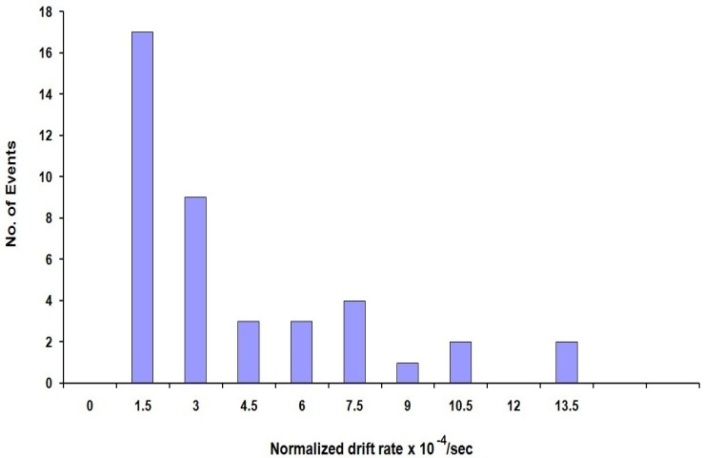 | Figure 5. Distribution of normalized drift rates of type II radio bursts |
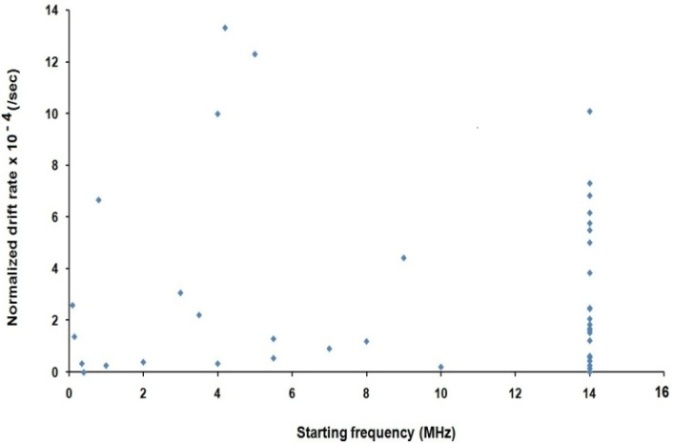 | Figure 6. The scatter plot of the start frequency of type II bursts and their normalized drift rates |
2.5. Drift Rate
- The drift rate is determined from the starting and ending frequencies, and the time duration of type II bursts[18] given by the following relation;
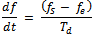 where Td is the time duration between the start and end. fs and fe are starting and ending frequencies, respectively.The normalized drift rate is denoted by
where Td is the time duration between the start and end. fs and fe are starting and ending frequencies, respectively.The normalized drift rate is denoted by 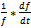 [16]. These rates have been determined and shown in figure 5. The mean normalized drift rate is 3.23*10-4 sec-1.Figure 6 shows scatter plot between the start frequency of type II bursts and their normalized drift rate. Here the linear correlation coefficient r = 0.034 which implies very poor correlation.
[16]. These rates have been determined and shown in figure 5. The mean normalized drift rate is 3.23*10-4 sec-1.Figure 6 shows scatter plot between the start frequency of type II bursts and their normalized drift rate. Here the linear correlation coefficient r = 0.034 which implies very poor correlation.2.6. Drift velocity
- The type II shock velocities Vdrift are determined from the normalized drift rate by using the relation[19].
 where f is the frequency in MHz and Vdrift is in solar radii per second. Here radial propagation of the MHD shocks and emission at the first harmonic of the local Langmuir frequency is assumed.The velocities of CMEs in km/s (VCME) versus drift velocities of associated type II bursts (V drift) in km/s are exhibited in figure 7. Here we compare velocities of CMEs with associated type II drift velocities. In order to account for all errors in the estimation of speeds, following[20], we assume that a velocity ratio in the range 0.5-2 gives type II MHD shock which originates in the CME front. Only 9 of the CMEs associated with type II bursts come in this category.
where f is the frequency in MHz and Vdrift is in solar radii per second. Here radial propagation of the MHD shocks and emission at the first harmonic of the local Langmuir frequency is assumed.The velocities of CMEs in km/s (VCME) versus drift velocities of associated type II bursts (V drift) in km/s are exhibited in figure 7. Here we compare velocities of CMEs with associated type II drift velocities. In order to account for all errors in the estimation of speeds, following[20], we assume that a velocity ratio in the range 0.5-2 gives type II MHD shock which originates in the CME front. Only 9 of the CMEs associated with type II bursts come in this category. 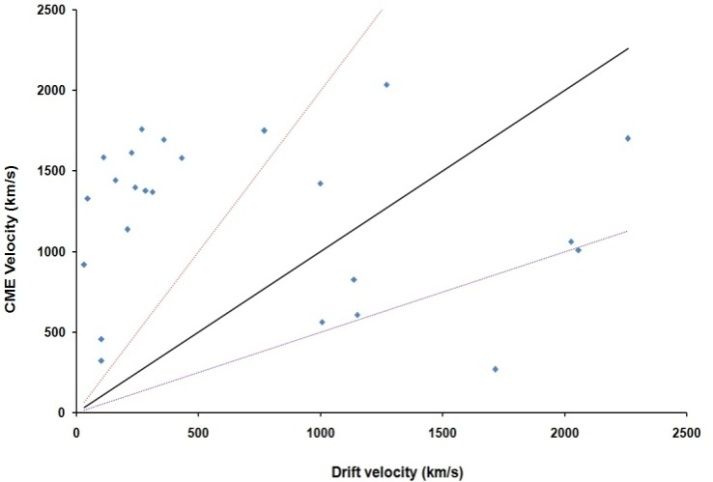 | Figure 7. Shows the distribution of CMEs velocities and drift velocities of multiple type II radio bursts |
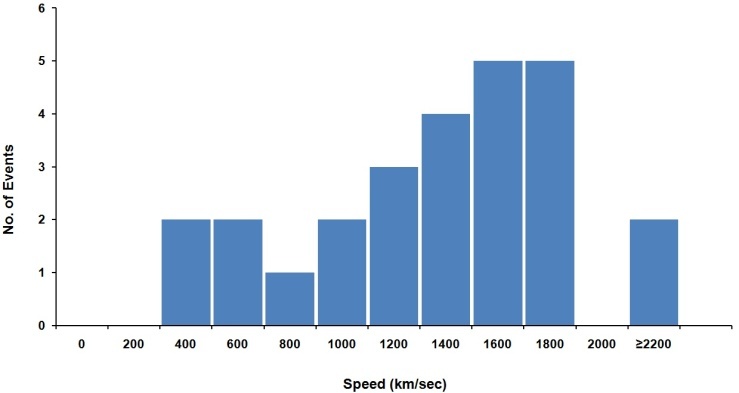 | Figure 8. Shows the speeds of CMEs associated with multiple types II bursts |
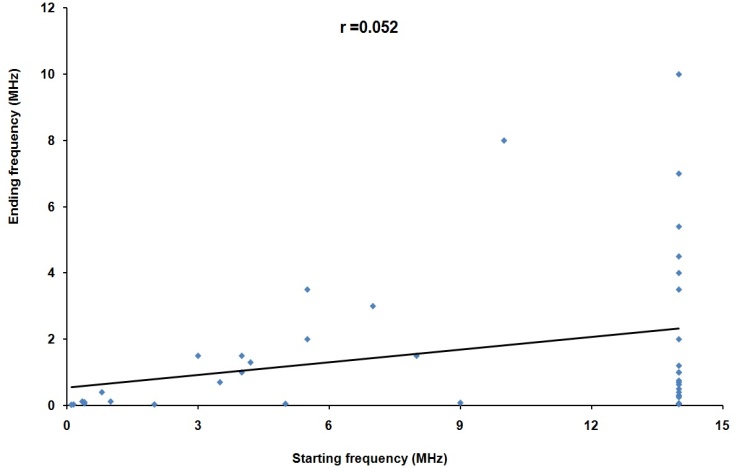 | Figure 9. Scatter plot of ending and starting frequencies of 42 multiple types II bursts |
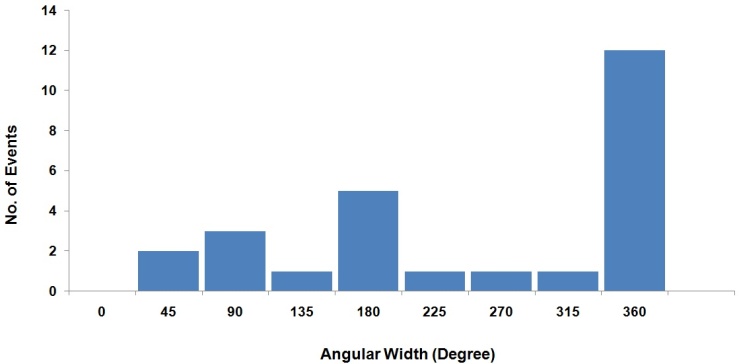 | Figure 10. Distribution of angular width of CMEs associated with multiple type II bursts |
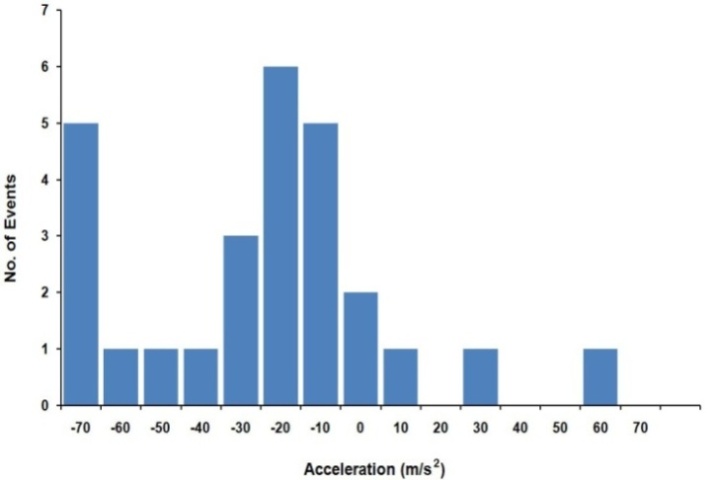 | Figure 11. Distribution of acceleration of CMEs associated with type II bursts |
3. Discussion and Conclusions
- We have analysed the characteristics of type II bursts and associated CMEs. Our analysis shows that most of the multiple type II bursts have life time around 200 min, the start frequencies around 14 MHz (see, e.g. Fig. 2 ) and ending frequencies around 1MHz (Fig 3). The starting frequencies peak at about 14 MHz, whereas the ending frequency peaks at about 1MHz, the number of events decreases when the frequency increases. The relatively high values of starting frequencies may be due to flare blast wave.The normalized drift rates of many of type II bursts are around 1.5*10-4/sec. (cf. Fig, 5). These drift rates and starting frequencies seem to be uncorrelated, the correlation coefficient r = 0.034 (cf. Fig. 6). The starting and ending frequencies also seem to have no correlation, the correlation coefficient r = 0.052 (cf. Fig 9). This is in contradiction to[16].Most of the CMEs associated with type II bursts are halo CMEs (Fig 10) with negative acceleration around – 20 m/s2 (Fig. 11) which is two times that reported by[16].Figure 7 shows that only 7 of the type II MHD shocks originate in the CME front, the remaining may correspond to CME flank.The association of type II bursts with flares will be the subject matter of our next article.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors are thankful to Meerut College, IIMT Engg. College and FIT Engg. College, Meerut authorities for their cooperation. The authors are thankful to IUCAA, Pune and HRI, Allahabad for their financial assistance. They are also thankful to SOHO/LASCO catalogue and WIND/WAVES data system for providing their data.
Appendix
- WIND/WAVES, SOHO/LASCO observationsTable-2 provides a brief summary of multiple type II bursts and corresponding CMEs during the study period. Column 1 give the date of events, start time, end time and frequency range are given by column 2,3, and 4 respectively. Column 5,6 and 7 gives the CMEs time, speed and width respectively from the SOHO/LASCO lists.
|
References
| [1] | Wild J.P., Mc Cready L., Austr. J. Sci. Res. Ser. A, 3, 387 (1950) |
| [2] | Roberts J A., Austr. J. Phys. 12, 327 (1959). |
| [3] | Wild J.P., Smerd S. F., ARA& A, 10, 159 (1972). |
| [4] | Smerd S F., Sheridan K.V., Stewart R.T.,Apj lett. 16,23 (1975) |
| [5] | Wild J.P., Smered S.F.,&Weiss, A A., AR A&A. 1, 291, (1963). |
| [6] | Klassen A., Aurass H., Klein K L., Hoffman, A., & Mann G., A&A, 343,287 (1999). |
| [7] | Kahler, S W., Sheeley, N R,. Jr, Koomen M J and Michels, D.J., Sol. Phy. 93, 133 (1984). |
| [8] | Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A. and Bougeret, J.L., In; Solar terrestrial magnetic and space environment, Eds; Wang, H, N., Xie, R, L., 6, 173, (2002). |
| [9] | Gopalswamy, N., Aguilar-Rodriques, E., Yashiro S., Nunes, S., Kaiser, M. L., Howard, R, A., JGR 110, A12S07, (2005). |
| [10] | Gopalswamy N., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Aguilar- Rodriques, E., Kaiser, M. L., Howard, R. A., Bougeret, J L., Astrophys. J. 674, 560 (2008). |
| [11] | Sharma J., Mittal N., Tomar, V., and Narain, U., Astrophys. Space Sci., 317, 261, (2008). |
| [12] | Robinson R.D and Sheridan, K V., Proc. Astron. Soc. Aust. 4, 392, (1982) |
| [13] | Geregly T.E., Kundu, M R., Wu, S. T., Dryer M., Smith, Z. K., and Stewart, R.T., Adv. Space Res. 4(7), 283 (1984). |
| [14] | Vrsnak, B., Magdalenic, J., and Aurass, H., Solar Physics, 202, 319 (2001). |
| [15] | Shanmugaraju, A., Moon V. J., Cho, K. S., Kim V. H., Dryer. M., and Umapathy. S., Solar phy. 232, 87, (2005) |
| [16] | Subramanian K R and Ebenzer E, A & A 451, 683 (2006). |
| [17] | Prakash O., Umapathy S.,. Shanmugaraju. A., Pappa Kalaivani. P. and Vrsnak B., Solar Phys, 266; 135 (2010). |
| [18] | Prakash, O., Umapathy, S., Shanmugaraju, A. and Vrsnak, B., Solar Physics, 258, 105, (2009) |
| [19] | Caroubalos C et al., A & A 413, 1125, (2004) |
| [20] | Classen, H. T.; Aurass, H., Astronomy and Astrophysics, 384, 1098, (2002) |
| [21] | Mittal, N. and Narain, U., New Astronomy, 14 (3), 341, (2009) |
| [22] | Mittal. N., Sharma J., Tomar, V., and Narian U., Planetary and Space Sci., 57, 53, (2009). |
| [23] | http://cdaw.gsfc.nasa.gov/CME_list/radio/waves_type2.html |
| [24] | http://www-lep.gsfc.nasa.gov/waves/waves.html |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML