-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Astronomy
2012; 1(2): 20-37
doi: 10.5923/j.astronomy.20120102.02
The Primordial Cosmic Black Hole and the Cosmic Axis of Evil
U. V. S. Seshavatharam
Honorary faculty, I-SERVE, Alakapuri, Hyderabad-35, AP, India
Correspondence to: U. V. S. Seshavatharam, Honorary faculty, I-SERVE, Alakapuri, Hyderabad-35, AP, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Based on the big bang concepts- in the expanding universe, ‘rate of decrease in CMBR temperature’ is a measure of the cosmic ‘rate of expansion’. Modern standard cosmology is based on two contradictory statements. They are - present CMBR temperature is isotropic and the present universe is accelerating. In particle physics also, till today there is no practical evidence for the existence of ‘dark matter’ and ‘dark energy’. Astronomers are puzzled by the announcement that the masses of the largest objects in the Universe appear to depend on which method is used to weigh them. Recent observations and discussions at Astrophysics Research Institute (ARI) supported by the Royal Astronomical Society create new thoughts on the existence of the ‘cosmic axis of evil’. In this connection an attempt is made to study the universe with a closed and growing model of cosmology. If the primordial universe is a natural setting for the creation of black holes and other non-perturbative gravitational entities, it is also possible to assume that throughout its journey, the whole universe is a primordial (growing and rotating) cosmic black hole. Planck particle can be considered as the baby universe.
Keywords: Cosmic Axis of Evil, Rate of Decrease in CMBR Temperature, Rate of Increase in Cosmic Red Shift, Classical Limit of Force, Classical Limit of Power, Primordial Cosmic Black Hole, Light Speed Rotation, Planck Scale, Unruh Effect
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Based on the big bang concepts- in the expanding universe, ‘rate of decrease in CMBR temperature’ is a measure of the cosmic rate of expansion’. Modern standard cosmology is based on two contradictory statements. They are - present CMBR temperature is isotropic and the present universe is accelerating. In particle physics also, till today there is no practical evidence for the existence of ‘dark matter’ and ‘dark energy’. Astronomers are puzzled by the announcement that the masses of the largest objects in the Universe appear to depend on which method is used to weigh them. Recent observations and discussions at Astrophysics Research Institute (ARI) supported by the Royal Astronomical Society create new thoughts on the existence of the ‘cosmic axis of evil’. In this connection, in this paper - an attempt is made to study the universe with a closed and growing model of cosmology. Please see the appendix on the ‘cosmic axis of evil’.
2 About the Existence and Growth of the Galactic Central Black Holes
- If the interior geometry of a black hole is a space-like region in which all world lines terminate at the black hole singularity, then thinking about the formation and existence of “massive black” holes seems to be un-physical. But the modern astronomical and galactic observations strongly reveal that every galaxy constitutes a heavy massive central black hole! If this is really true, then the fundamental question to be answered is: Which is primordial, either ‘the whole galaxy’ or ‘the galactic central black hole’? Initially astrophysicists attempted to explain the presence of these galactic central black holes by describing the evolution of galaxies as gathering mass until black holes form at their centre but further observation demanded that the galactic central black hole co-evolved with the galactic bulge plasma dynamics and the galactic arms. Very recently, on 23 March 2012, astronomers have put forward a new theory for the growth of the galactic central black holes[1].To resolve these sensitive problems some scientists say: existence of a black hole is controversial. All these ideas are purely theoretical. Here it is very important to note that physics works on physical constants and runs on mathematical equations. The combination of the observed and well believed physical constants play a vital role in understanding many physical phenomena. Their combination generates some special and strange constants which are natural, unbelievable and immeasurable. The formation of black holes, planck mass etc can be understood with those fundamental and compound physical constants.
2.1. The two strange compound physical constants
- It is noticed that
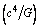 is the classical limit of force and
is the classical limit of force and  is the classical limit of power. For any rotating celestial body, the 3 critical conditions are: magnitude of ‘kinetic energy’ never crosses ‘rest energy’, magnitude of ‘torque’ never crosses ‘potential energy’ and magnitude of mechanical power never crosses
is the classical limit of power. For any rotating celestial body, the 3 critical conditions are: magnitude of ‘kinetic energy’ never crosses ‘rest energy’, magnitude of ‘torque’ never crosses ‘potential energy’ and magnitude of mechanical power never crosses  . With these conditions, mathematical complexity involved in GTR and black hole physics can be simplified. Now this is the time to re-examine the foundations of modern black hole physics. Planck mass can be derived very easily. Light speed rotating black hole’s formation can be understood. GTR and quantum mechanics can be coupled in a unified manner. Rotating black hole temperature formula can be derived very easily.One such fundamental and unbelievable compound physical constant is
. With these conditions, mathematical complexity involved in GTR and black hole physics can be simplified. Now this is the time to re-examine the foundations of modern black hole physics. Planck mass can be derived very easily. Light speed rotating black hole’s formation can be understood. GTR and quantum mechanics can be coupled in a unified manner. Rotating black hole temperature formula can be derived very easily.One such fundamental and unbelievable compound physical constant is 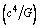 where
where 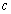 the speed of light is and
the speed of light is and 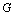 is the gravitational constant. The more surprising and strange thing is that its dimensions are identical to the dimensions of ‘force’. Its magnitude is
is the gravitational constant. The more surprising and strange thing is that its dimensions are identical to the dimensions of ‘force’. Its magnitude is 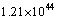 Newton. This is a very big magnitude and cannot be measured in laboratory experiments. The most unfortunate thing is that it appears in general theory of relativity in inverse form as
Newton. This is a very big magnitude and cannot be measured in laboratory experiments. The most unfortunate thing is that it appears in general theory of relativity in inverse form as 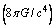 . It can be considered as the ultimate force in true unification. The only way is to implement it in fundamental physics. Another fundamental and unbelievable compound physical constant is
. It can be considered as the ultimate force in true unification. The only way is to implement it in fundamental physics. Another fundamental and unbelievable compound physical constant is  The more surprising and strange thing is that its dimensions are identical to the dimensions of ‘power’. Its magnitude is
The more surprising and strange thing is that its dimensions are identical to the dimensions of ‘power’. Its magnitude is 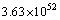 J/sec. This is also a very big magnitude and cannot be measured in laboratory experiments. Whether to consider them or discard them - depends only on our choice of scientific interest. Considering these two compound physical constants, Planck scale can be constructed. Without considering the complicated mathematical equations of GTR, black hole radius can be obtained. Combining them with some of the classical and quantum laws of physics, some miracles can be done.
J/sec. This is also a very big magnitude and cannot be measured in laboratory experiments. Whether to consider them or discard them - depends only on our choice of scientific interest. Considering these two compound physical constants, Planck scale can be constructed. Without considering the complicated mathematical equations of GTR, black hole radius can be obtained. Combining them with some of the classical and quantum laws of physics, some miracles can be done.3. Disclosure
- Most of the information included in this article has been previously published[2] in the paper “Physics of Rotating and Expanding Black Hole Universe”, Progress in Physics, vol. 2, pp. 7-14, April, 2010. The main concepts of the paper were: ‘rate of decrease in CMBR’ temperature is a measure of cosmic ‘rate of expansion’ and throughout its journey, universe is an expanding and (light speed) rotating black hole[3]. This article is its revised version. In this article it is suggested that universe can be considered as the primordial cosmic black hole.Existence of dark matter, dark energy, inflation and the accelerating universe - these four concepts are having only indirect support and can be considered as ‘enigmatic concepts’. Their root was originated in 1929 from Edwin Hubble’s incomplete interpretations[4,5]. For the same observations it is also possible to reinterpret as: ‘rate of increase in red shift’ is a measure of cosmic rate of expansion. With this idea, automatically a closed expanding and rotating model of universe comes into picture. With the above four enigmatic concepts (directly and indirectly) GTR is losing its original identity from the rest of the physics world. But this is the time to think about the unification of GTR and quantum mechanics. In this critical situation, one very interesting theoretical idea is - now a days to understand the origin of dark matter and galaxy growth, physicists are focusing their concentration on primordial cosmic black holes. One interesting observation is: central galactic black holes are spinning close to speed of light[6]. Even though these two are also enigmatic concepts, GTR and quantum mechanics can be studied in a unified manner.Published papers[7-10] clearly indicate that, current cosmological observations can be understood with the black hole concepts and the possibility of a model of black hole cosmology is not far away from reality. Interesting research work on black hole cosmology can be seen in physics literature[11-15].
4. Light Speed Rotation - An Unified Enigmatic Concept
- All these enigmatic concepts can be unified into one enigmatic concept. That is - light speed rotation[16,17]. Its important and immediate applications are 1. Classical limits of force and power can be generated.2. GTR and quantum mechanics can be studied in a unified manner.3. Origin of the Planck scale can be understood.4. A closed rotating and expanding model of the universe can be developed.5. The two experimental numbers CMBR temperature and cosmic expansion rate can be interrelated in a unified way.6. Finally a unified black hole model of cosmology can be developed.
5. Deduction of the Classical Limits of Force and Power
- Special theory of relativity says that light speed is the maximum speed that a material particle can move with. It is the natural speed with which photon or electromagnetic signal travels in free space. Till today there is no explanation for this characteristic speed limit. Throughout the cosmic evolution whether the speed limit is constant or changing? is also an answerless question. It is an accepted and universal idea that ‘gravity’ and ‘gravitational radiation’ also propagates with speed of light.Dimensionally and physically a characteristic force form can be obtained with speed of light
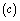 and Newton’s gravitational constant
and Newton’s gravitational constant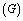 . It can be expressed as
. It can be expressed as 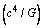 . It can be considered as the ‘classical limit’ of ‘force’[18-21]. It represents the maximum ‘gravitational force of attraction’ and maximum ‘electromagnetic force’. It plays an important role in ‘unification’ scheme. It is the origin of “Planck scale”. It is the origin of ‘Quantum gravity’. Similar to this ‘classical force’, classical limit of ‘power’ can be given by
. It can be considered as the ‘classical limit’ of ‘force’[18-21]. It represents the maximum ‘gravitational force of attraction’ and maximum ‘electromagnetic force’. It plays an important role in ‘unification’ scheme. It is the origin of “Planck scale”. It is the origin of ‘Quantum gravity’. Similar to this ‘classical force’, classical limit of ‘power’ can be given by  . It plays a crucial role in ‘gravitational radiation’. It represents the ‘maximum limit’ of ‘mechanical’ or ‘electromagnetic’ power and ‘radiation power’.
. It plays a crucial role in ‘gravitational radiation’. It represents the ‘maximum limit’ of ‘mechanical’ or ‘electromagnetic’ power and ‘radiation power’. 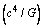 can be derived based on ‘Newton’s law of gravitation’ and ‘constancy of speed of light’. In Sun-Planet system, from Newton’s law of gravitation,
can be derived based on ‘Newton’s law of gravitation’ and ‘constancy of speed of light’. In Sun-Planet system, from Newton’s law of gravitation,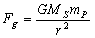 | (1) |
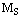 = mass of sun,
= mass of sun, 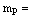 mass of planet and
mass of planet and 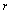 = distance between them. Centripetal force on planet is,
= distance between them. Centripetal force on planet is,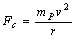 | (2) |
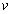 = orbiting velocity of planet. Eliminating
= orbiting velocity of planet. Eliminating 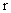 from equation (2), force of attraction between sun-planet can be given as,
from equation (2), force of attraction between sun-planet can be given as,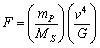 | (3) |
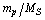 ) is a ratio, (
) is a ratio, (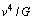 ) must have the dimensions of ‘force’. Following the ‘constancy of speed of light’, a force of the form,
) must have the dimensions of ‘force’. Following the ‘constancy of speed of light’, a force of the form, 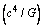 can be constructed. This can be considered as the upper limit or magnitude of any force. Nature of the force may be mechanical or electromagnetic or gravitational. Note that in GTR this force appears in an inverse form[22] as
can be constructed. This can be considered as the upper limit or magnitude of any force. Nature of the force may be mechanical or electromagnetic or gravitational. Note that in GTR this force appears in an inverse form[22] as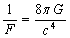 | (4) |
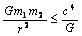 | (5) |
 are any 2 massive bodies and
are any 2 massive bodies and  is distance between them. Then minimum distance between the 2 bodies can be obtained as
is distance between them. Then minimum distance between the 2 bodies can be obtained as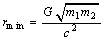 | (6) |
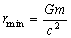 | (7) |
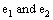 can be expressed as
can be expressed as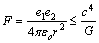 | (8) |
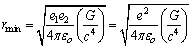 | (9) |
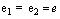 Charged particle’s space-time curvature can be understood from this expression. With this idea GTR can be applied to charged elementary particles easily. Not only that this method simply and directly leads to Planck scale and grand unification or TOE. Grand unification assumes that in the past the observed 4 fundamental interactions are same and having the same strength. Magnitude of the force at that time can be taken as
Charged particle’s space-time curvature can be understood from this expression. With this idea GTR can be applied to charged elementary particles easily. Not only that this method simply and directly leads to Planck scale and grand unification or TOE. Grand unification assumes that in the past the observed 4 fundamental interactions are same and having the same strength. Magnitude of the force at that time can be taken as 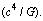 With a suitable proportionality ratio quark confinement can be understood as a charged space-time curvature. Clearly speaking ‘gravity’ can be implemented very easily in nuclear and quark physics[23-26]. From quantum mechanics
With a suitable proportionality ratio quark confinement can be understood as a charged space-time curvature. Clearly speaking ‘gravity’ can be implemented very easily in nuclear and quark physics[23-26]. From quantum mechanics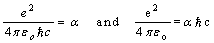 | (10) |
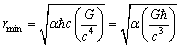 | (11) |
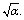
6. To Derive the Planck Scale
- Assume that 2 Planck particles having mass
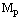 moving in opposite direction and coming closer and closer. At some minimum distance their magnitude of gravitational force of attraction approaches
moving in opposite direction and coming closer and closer. At some minimum distance their magnitude of gravitational force of attraction approaches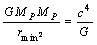 | (12) |
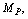
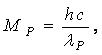 | (13) |
 | (14) |
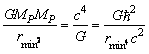 | (15) |
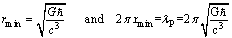 | (16) |
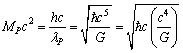 | (17) |
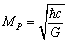 | (18) |
6.1. The planck mass & the coulomb mass
- With this classical limit of force
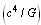 , similar to the Planck mass-energy ‘coulomb mass-energy’ can expressed as
, similar to the Planck mass-energy ‘coulomb mass-energy’ can expressed as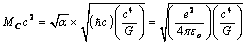 | (19) |
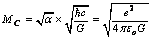 | (20) |
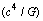 is the classical limit of force. How to interpret this mass unit? Is it a primordial massive charged particle? If 2 such oppositely charged particles annihilates, a large amount of energy can be released. Considering so many such pairs annihilation hot big bang or inflation can be understood. This may be the root cause of cosmic energy reservoir. Such pairs may be the chief constituents of black holes. In certain time interval with a well defined quantum rules they annihilate and release a large amount of energy in the form of
is the classical limit of force. How to interpret this mass unit? Is it a primordial massive charged particle? If 2 such oppositely charged particles annihilates, a large amount of energy can be released. Considering so many such pairs annihilation hot big bang or inflation can be understood. This may be the root cause of cosmic energy reservoir. Such pairs may be the chief constituents of black holes. In certain time interval with a well defined quantum rules they annihilate and release a large amount of energy in the form of 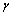 photons[27].It is widely accepted that charged leptons, quarks, and baryons all these comes under matter or mass carriers and photons and mesons comes under force carriers. If so what about this new mass unit? Is it a fermion? Or is it a boson? Or Else is it represents a large potential well in the primordial matter or mass generation program? Is it the mother of magnetic monopoles? Is it the mother of all charged particles? By any suitable proportionality ratio or with a suitable scale factor if one is able to bring down its mass to the observed particles mass scale, very easily a grand unified model can be developed.
photons[27].It is widely accepted that charged leptons, quarks, and baryons all these comes under matter or mass carriers and photons and mesons comes under force carriers. If so what about this new mass unit? Is it a fermion? Or is it a boson? Or Else is it represents a large potential well in the primordial matter or mass generation program? Is it the mother of magnetic monopoles? Is it the mother of all charged particles? By any suitable proportionality ratio or with a suitable scale factor if one is able to bring down its mass to the observed particles mass scale, very easily a grand unified model can be developed.7. Light Speed Rotating Black Holes: the Special Holes
- Origin of ‘rotating black hole’ formation can be understood with the classical power limit
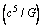 and
and  within 3 steps. For any rotating celestial body assume that,
within 3 steps. For any rotating celestial body assume that,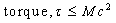 | (21) |
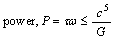 | (22) |
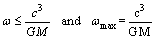 | (23) |
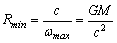 | (24) |
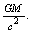 Clearly speaking this proposal is entirely different from the existing concepts of General theory of relativity. It is not speaking about the gravitational collapse of stars or space-time curvature or singularity. Now this is the time to re-examine the foundations of modern black hole physics. It can be suggested that, the subject of ‘black hole physics’ has to be studied in a new direction. If the concept of ‘Schwarzschild radius’ is believed to be true, for any rotating celestial body or black hole of rest mass
Clearly speaking this proposal is entirely different from the existing concepts of General theory of relativity. It is not speaking about the gravitational collapse of stars or space-time curvature or singularity. Now this is the time to re-examine the foundations of modern black hole physics. It can be suggested that, the subject of ‘black hole physics’ has to be studied in a new direction. If the concept of ‘Schwarzschild radius’ is believed to be true, for any rotating celestial body or black hole of rest mass 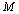 the critical conditions can be stated as follows.1. Magnitude of ‘kinetic energy’ never crosses ‘rest energy’.2. Magnitude of ‘torque’ never crosses ‘potential energy’ and3. Magnitude of mechanical power never crosses
the critical conditions can be stated as follows.1. Magnitude of ‘kinetic energy’ never crosses ‘rest energy’.2. Magnitude of ‘torque’ never crosses ‘potential energy’ and3. Magnitude of mechanical power never crosses  Based on the Viral theorem, potential energy is twice of kinetic energy and hence
Based on the Viral theorem, potential energy is twice of kinetic energy and hence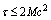 . In this way factor 2 can be obtained easily from equations (21), (22) and (23). Not only that special theory of relativity, classical mechanics and general theory of relativity can be studied in a unified way. Such light speed rotating black holes may be called as ‘special holes’.
. In this way factor 2 can be obtained easily from equations (21), (22) and (23). Not only that special theory of relativity, classical mechanics and general theory of relativity can be studied in a unified way. Such light speed rotating black holes may be called as ‘special holes’.8. Derivation for Black Hole Temperature
- Dr. Stephen Hawking[30] says- “The main difficulty in finding a theory that unifies gravity with the other forces is that general relativity is a “classical” theory; that is, it does not incorporate the uncertainty principle of quantum mechanics. On the other hand, the other partial theories depend on quantum mechanics in an essential way. A necessary first step, therefore, is to combine general relativity with the uncertainty principle. As we have seen, this can produce some remarkable consequences, such as black holes not being black, and the universe not having any singularities but being completely self-contained and without a boundary”.“Einstein’s general theory of relativity seems to govern the large-scale structure of the universe. It is what is called a classical theory; that is, it does not take account of the uncertainty principle of quantum mechanics, as it should for consistency with other theories. The reason that this does not lead to any discrepancy with observation is that all the gravitational fields that we normally experience are very weak. However, the singularity theorems discussed earlier indicate that the gravitational field should get very strong in at least two situations, black holes and the big bang. In such strong fields the effects of quantum mechanics should be important. Thus, in a sense, classical general relativity, by predicting points of infinite density, predicts its own downfall, just as classical (that is, non quantum) mechanics predicted its downfall by suggesting that atoms should collapse to infinite density. We do not yet have a complete consistent theory that unifies general relativity and quantum mechanics, but we do know a number of the features it should have”.A black hole of mass
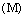 having size,
having size, 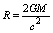 rotates with an angular velocity
rotates with an angular velocity 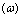 and rotational speed
and rotational speed 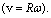 Assume that, its temperature
Assume that, its temperature 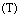 is inversely proportional to its rotational time period
is inversely proportional to its rotational time period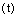 . Keeping Law of uncertainty in view, assume that,
. Keeping Law of uncertainty in view, assume that,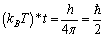 | (25) |
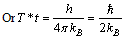 | (26) |
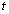 = rotational time period and
= rotational time period and 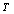 = Temperature,
= Temperature, 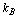 = Boltzmann’s radiation constant,
= Boltzmann’s radiation constant, 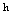 = Planck’s constant and
= Planck’s constant and 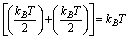 is the sum of kinetic and potential energies of a particle in any one direction. We know that,
is the sum of kinetic and potential energies of a particle in any one direction. We know that,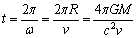 | (27) |
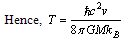 | (28) |
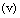 approaches light speed
approaches light speed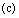 , then temperature reaches to maximum. Here author’s humble appeal is: force limit
, then temperature reaches to maximum. Here author’s humble appeal is: force limit 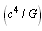 keeps the black hole ‘stable or rigid’ even at light speed rotation.
keeps the black hole ‘stable or rigid’ even at light speed rotation.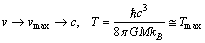 | (29) |
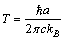 | (30) |
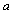 is the local acceleration. If one is willing to replace the ‘linear acceleration’ with the ‘angular acceleration’ of the rotating black hole, then ‘black hole temperature’ comes into picture.
is the local acceleration. If one is willing to replace the ‘linear acceleration’ with the ‘angular acceleration’ of the rotating black hole, then ‘black hole temperature’ comes into picture.8.1. Hawking’s Black hole temperature formula demands light speed rotation
- From the above discussion it is very clear that, origin of Hawking radiation is possible in another way also. But it has to be understood more clearly. Information can be extracted from a black hole, if it rotates with “light speed”. If a black hole rotates at ‘light speed’, photons or elementary particles can escape from its ‘equator only’ with light speed and in the direction of black hole rotation and this seems to be a signal of “Black hole radiation” around the black hole equator. With this idea origin of cosmic rays can also be understood. Please note that, not only at the black hole equator, Hawking radiation can take place at the event horizon of the black hole having a surface area. This equation (29) is identical to the famous expression derived by Hawking. Since the black hole temperature formula is accepted by the whole science community, author humbly requests the modern scientists to kindly look into this major conceptual clash at utmost fundamental level.Temperature of any black hole is very small and may not be found experimentally. But this idea can successfully be applied to the Universe! By any reason if it is assumed that, Universe is a black hole, then it seems to be surprising that, temperature of a stationary cosmic black hole is “zero”. Its temperature increases with increase in its rotational speed and reaches to maximum if the rotational speed of the cosmic black hole approaches ‘light speed’. This is the essence of cosmic black hole rotation. CMBR temperature demands the existence of “cosmic rotation”. This is the most important point to be noted here.
8.2. Planck particle and its light speed rotation
- If Planck particle or Planck photon follows strong gravity and rotates at light speed, obtained Planck mass,
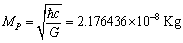 | (31) |
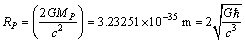 | (32) |
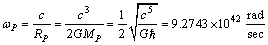 | (33) |
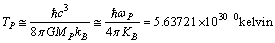 | (34) |
9. GTR, Planck Mass and the CMBR Temperature
- Let us assume that present universe is a point particle having mass
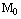 . Assume that gravitational force of attraction between the point universe mass and the Planck photon (the baby universe mass) is equal to
. Assume that gravitational force of attraction between the point universe mass and the Planck photon (the baby universe mass) is equal to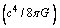 . Author humbly say- this simple assumption unifies GTR, quantum mechanics, planck scale, big bang cosmology and Hubble’s observations.
. Author humbly say- this simple assumption unifies GTR, quantum mechanics, planck scale, big bang cosmology and Hubble’s observations.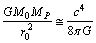 | (35) |
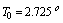 Kelvin. Surprisingly it is noticed that, above assumption is satisfied at the following 2 conditions.
Kelvin. Surprisingly it is noticed that, above assumption is satisfied at the following 2 conditions.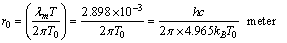 | (36) |
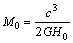 | (37) |
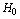 is the present cosmic expansion rate index[32,33]. Above expression can be expressed as
is the present cosmic expansion rate index[32,33]. Above expression can be expressed as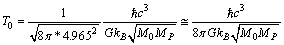 | (38) |
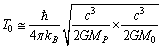 | (39) |
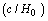 is the characteristic length of the universe and is called as the Hubble radius. Not only that Hubble volume
is the characteristic length of the universe and is called as the Hubble radius. Not only that Hubble volume 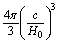 represents the characteristic and observable volume of the universe. It is defined and accepted that
represents the characteristic and observable volume of the universe. It is defined and accepted that 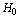 value changes with time. Cosmic temperature also changes with time. By any chance if one is able to consider
value changes with time. Cosmic temperature also changes with time. By any chance if one is able to consider 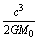 as the present angular velocity,
as the present angular velocity, 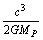 as the Planck photon angular velocity then above relation can be expressed as
as the Planck photon angular velocity then above relation can be expressed as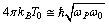 | (40) |
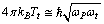 | (41) |
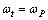 . Hence
. Hence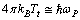 | (42) |
10. Modified Hubble’s Law
- Ever since the late 1920’s, when Edwin Hubble discovered a simple proportionality between the red shifts in the light coming from nearby galaxies and their distances, we have been told that the Universe is expanding. Hubble found the recession speed
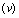 of a nearby galaxy was related to its radial distance
of a nearby galaxy was related to its radial distance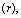
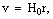 where
where 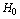 is the constant of proportionality[4]. This relationship- dubbed the Hubble law- has since been strengthened and extended to very great distances in the cosmos. This was the incomplete interpretation that changed the destiny of the modern cosmology. Based on this interpretation modern cosmologists arrived at the conclusion that - at present, universe is flat and is accelerating. Nowadays it is considered to be well established in the expanding big bang universe. Hubble initially interpreted his red shifts as a Doppler effect, due to the motion of the galaxies as they receded for our location in the Universe. He called it a ‘Doppler effect’ as though the galaxies were moving ‘through space’; that is how some astronomers initially perceived it. This is different to what has now become accepted but observations alone could not distinguish between the two concepts.Later in his life Hubble varied from his initial interpretation[5] and said that the Hubble law was due to a hitherto undiscovered mechanism, but not due to expansion of space - now called cosmological expansion. In this connection, author humbly says - there was something wrong and missing in Hubble’s interpretation. For the same observations it can also be possible to state that, in a closed and expanding universe, from and about the cosmic centre, rate of increase in galaxy red shift is a measure of cosmic rate of expansion. This statement includes 3 points.1. Light from the galaxy travels opposite to the direction of cosmic expansion and shows red shift and thus red shift is a measure of galaxy distance from the cosmic centre.2. In the expanding universe, increase in red shift is instantaneous due to instantaneous increase in galaxy distance (which is due to instantaneous increase in cosmic volume).3. Rate of increase in red shift indicates the cosmic rate of expansion.
is the constant of proportionality[4]. This relationship- dubbed the Hubble law- has since been strengthened and extended to very great distances in the cosmos. This was the incomplete interpretation that changed the destiny of the modern cosmology. Based on this interpretation modern cosmologists arrived at the conclusion that - at present, universe is flat and is accelerating. Nowadays it is considered to be well established in the expanding big bang universe. Hubble initially interpreted his red shifts as a Doppler effect, due to the motion of the galaxies as they receded for our location in the Universe. He called it a ‘Doppler effect’ as though the galaxies were moving ‘through space’; that is how some astronomers initially perceived it. This is different to what has now become accepted but observations alone could not distinguish between the two concepts.Later in his life Hubble varied from his initial interpretation[5] and said that the Hubble law was due to a hitherto undiscovered mechanism, but not due to expansion of space - now called cosmological expansion. In this connection, author humbly says - there was something wrong and missing in Hubble’s interpretation. For the same observations it can also be possible to state that, in a closed and expanding universe, from and about the cosmic centre, rate of increase in galaxy red shift is a measure of cosmic rate of expansion. This statement includes 3 points.1. Light from the galaxy travels opposite to the direction of cosmic expansion and shows red shift and thus red shift is a measure of galaxy distance from the cosmic centre.2. In the expanding universe, increase in red shift is instantaneous due to instantaneous increase in galaxy distance (which is due to instantaneous increase in cosmic volume).3. Rate of increase in red shift indicates the cosmic rate of expansion.10.1. Cosmic acceleration, rate of decrease in CMBR temperature, isotropy and rotation
- 1. After the big bang, since 5 billion years if universe is “accelerating” and at present dark energy is driving it- right from the point of big bang to the visible cosmic boundary in all directions, thermal photon wavelength must be stretched instantaneously and continuously from time to time and cosmic temperature must decrease instantaneously and continuously for every second. This is just like “rate of stretching of a rubber band of infinite length”. Note that photon light speed concept is not involved here. Against to this idea since 1992 from Cobe satellite’s CMBR data reveals that cosmic temperature is practically constant at
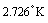 . This observational clash clearly indicates that something is going wrong with accelerating model. Moreover the standard model predicts that the cosmic background radiation should be cooling by something like one part in
. This observational clash clearly indicates that something is going wrong with accelerating model. Moreover the standard model predicts that the cosmic background radiation should be cooling by something like one part in 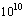 per year. This is at least 6 orders of magnitude below observable limits. Such a small decrease in cosmic temperature might be the result of cosmic “slowing down” rather than cosmic acceleration. Technically from time to time if we are able to measure the changes in cosmic temperature then ‘rate of decrease’ in cosmic temperature will give the ‘rate of increase’ in cosmic expansion accurately. Author humbly requests the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) to launch a satellite for measuring the ‘rate of decrease’ in CMBR temperature.2. Based on this analysis if “cosmic constant temperature” is a representation of “isotropy” it can be suggested that at present there is no acceleration and there is no space expansion and thus universe is static. From observations it is also clear that universe is homogeneous in which galaxies are arranged in a regular order and there is no mutual attraction in between any two galaxies. Not only that Hubble’s observations clearly indicate that there exists a linear relation in between galaxy distance and galaxy speed (which might be a direct consequence of “cosmic rotation” with “constant speed”). This will be true if it is assumed that “rate of increase in red shift” is a measure of cosmic “rate of expansion”. Instead of this in 1929 Hubble interpreted that “red shift” is a measure of cosmic “expansion”. This is the key point where Einstein’s static universe was discarded.3. At present if universe is isotropic and static how can it be stable? The only one solution to this problem is “rotation with constant speed”. If this idea is correct, universe seems to follow a closed model. At present if universe rotates as a rigid sphere with constant speed then galaxies will revolve with speeds proportional to their distances from the cosmic axis of rotation. Hence the Hubble’s law must be re-interpreted as “at present as galaxy distance increases its revolving speed increases”. If so
per year. This is at least 6 orders of magnitude below observable limits. Such a small decrease in cosmic temperature might be the result of cosmic “slowing down” rather than cosmic acceleration. Technically from time to time if we are able to measure the changes in cosmic temperature then ‘rate of decrease’ in cosmic temperature will give the ‘rate of increase’ in cosmic expansion accurately. Author humbly requests the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) to launch a satellite for measuring the ‘rate of decrease’ in CMBR temperature.2. Based on this analysis if “cosmic constant temperature” is a representation of “isotropy” it can be suggested that at present there is no acceleration and there is no space expansion and thus universe is static. From observations it is also clear that universe is homogeneous in which galaxies are arranged in a regular order and there is no mutual attraction in between any two galaxies. Not only that Hubble’s observations clearly indicate that there exists a linear relation in between galaxy distance and galaxy speed (which might be a direct consequence of “cosmic rotation” with “constant speed”). This will be true if it is assumed that “rate of increase in red shift” is a measure of cosmic “rate of expansion”. Instead of this in 1929 Hubble interpreted that “red shift” is a measure of cosmic “expansion”. This is the key point where Einstein’s static universe was discarded.3. At present if universe is isotropic and static how can it be stable? The only one solution to this problem is “rotation with constant speed”. If this idea is correct, universe seems to follow a closed model. At present if universe rotates as a rigid sphere with constant speed then galaxies will revolve with speeds proportional to their distances from the cosmic axis of rotation. Hence the Hubble’s law must be re-interpreted as “at present as galaxy distance increases its revolving speed increases”. If so 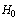 shall turn out to be the present angular velocity. In this way cosmic stability and homogeneity can be understood.4. This “constant speed cosmic rotation” can be extended to the big bang also. As time passes while in constant speed of rotation somehow if the cosmic sphere expands then “galaxy receding” as well as “galaxy revolution” both will come into picture. In the past while in constant speed of rotation at high temperatures if expansion is rapid for any galaxy (if born) receding is rapid and photon from the galaxy travels towards the cosmic centre in the opposite direction of space expansion and suffers a continuous fast rate of stretching and there will be a continuous fast rate of increase in red shift. At present at small temperatures if expansion is slow galaxy receding is small and photon suffers continuous but very slow rate of stretching and there will be a continuous but very slow rate of increase in red shift i.e. red shift practically remains constant. From this analysis it can be suggested that rate of decrease in cosmic temperature or rate of increase in red shift will give the rate of cosmic expansion. In the past we have galaxy receding and at present we can have galaxy revolution. By this time at low temperature and low angular velocity, galaxies are put into stable orbits.
shall turn out to be the present angular velocity. In this way cosmic stability and homogeneity can be understood.4. This “constant speed cosmic rotation” can be extended to the big bang also. As time passes while in constant speed of rotation somehow if the cosmic sphere expands then “galaxy receding” as well as “galaxy revolution” both will come into picture. In the past while in constant speed of rotation at high temperatures if expansion is rapid for any galaxy (if born) receding is rapid and photon from the galaxy travels towards the cosmic centre in the opposite direction of space expansion and suffers a continuous fast rate of stretching and there will be a continuous fast rate of increase in red shift. At present at small temperatures if expansion is slow galaxy receding is small and photon suffers continuous but very slow rate of stretching and there will be a continuous but very slow rate of increase in red shift i.e. red shift practically remains constant. From this analysis it can be suggested that rate of decrease in cosmic temperature or rate of increase in red shift will give the rate of cosmic expansion. In the past we have galaxy receding and at present we can have galaxy revolution. By this time at low temperature and low angular velocity, galaxies are put into stable orbits.10.2. Cosmic closed model and rotation
- In our daily life generally it is observed that, any animal or fruit or human being (from birth to death) grows with closed boundaries (irregular shapes also can have a closed boundary). An apple grows like an apple. An elephant grows like an elephant. A plant grows like a plant. A Human grows like a human. Throughout their life time, they won’t change their respective identities. These are observed facts. From these observed facts it can be suggested that, “growth” or “expansion” can be possible with a closed boundary. By any reason, if the closed boundary is opened it leads to ‘destruction’ rather than ‘growth or expansion’. Rotation is an universal phenomenon[34-43] in any closed model.
10.3. Universe - the primordial black hole
- Thinking that nature loves symmetry, in a heuristic approach in this paper author assumes that, throughout its life time, universe is a black hole. Even though it is growing, at any time it is having a closed boundary and thus it retains her identity as a black hole forever. The subject of black hole cosmology is not new. Note that universe is an independent body. It may have its own set of laws. If universe is having ‘no black hole structure’, any massive body (which is bound to the universe) may not show a ‘black hole structure’. i.e ‘Black hole structure’ may be a sub set of ‘cosmic structure’. A recent observation indicates that, black holes are spinning close to speed of light[6]. For any astrophysical body its size is minimal if it follows strong gravity. Being an astrophysical body at any time to have a minimum size of expansion- universe will follow strong gravity. Following a closed model if universe grows in mass and size it is natural to say that as time is passing cosmic black hole is “growing or expanding”.Clearly and strictly speaking there was no big bang at all. Highly dense, hot and tiny Planck particle (the baby universe) was rotating with light speed and high angular velocity. Why, how and when the Planck particle was born? is a trillion dollar question to be answered. As time is passing, forever rotating at light speed the baby universe starts growing with decreasing temperature, decreasing angular velocity, increasing size and increasing mass. At what rate the changes are occurring? is a fundamental question to be answered. By observations and suitable analysis it is possible. The utmost fundamental question to be answered is -- is planck particle a black hole? If it is a really a black hole certainly it possess an intrinsic or a characteristic (high) temperature. Keeping this idea in mind if one proceeds further, concepts of isotropy, homogeneity can be answered very easily. Inflation hypothesis can be eliminated. A unified model of black hole cosmology can be developed. But the subject of black holes is still under development. So many doubts and conflicts are there about the formation and growth of galactic central black holes and galaxy as a whole[44,45].
11. Growth of the Galactic Central Black Holes
- Now as recently reported at the American Astronomical Society a study using the Very Large Array radio telescope in New Mexico and the French Plateau de Bure Interferometer has enabled astronomers to peer within a billion years of the big bang and found evidence that black holes were the first that leads galaxy growth[44]. The implication is that the black holes started growing first. Initially astrophysicists attempted to explain the presence of these black holes by describing the evolution of galaxies as gathering mass until black holes form at their centre but further observation demanded that the galactic central black hole co-evolved with the galactic bulge plasma dynamics and the galactic arms. This clearly suggests that1. Galaxy constitutes a central black hole.2. The central black hole grows first and3. Star and galaxy growth goes parallel or later to the central black holes growth.The fundamental questions are1. If “black hole” is the result of a collapsing star, how and why a stable galaxy contains a black hole at its centre?2. Where does the central black hole comes from?3. How the galaxy centre will grow like a black hole?4. How its event horizon exists with growing?If these are the observed and believed facts - not only for the author- this is a big problem for the whole science community to be understood. Anyhow, the important point to be noted here is that “due to some unknown reasons galactic central black holes are growing”! In this critical situation, these day’s scientists are seriously thinking about the origin and growth of primordial black holes[7].
11.1. New theory for Black Hole’s growth
- Very recently astronomers have put forward a new theory[1] about why black holes become so hugely massive - claiming some of them have no 'table manners', and tip their 'food' directly into their mouths, eating more than one course simultaneously. Professor Andrew King from the Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, said: “Almost every galaxy has an enormously massive black hole in its centre. Our own galaxy, the Milky Way, has one about four million times heavier than the sun. But some galaxies have black holes a thousand times heavier still. We know they grew very quickly after the Big Bang”. “These hugely massive black holes were already full--grown when the universe was very young, less than a tenth of its present age”. Black holes grow by sucking in gas. This forms a disc around the hole and spirals in, but usually so slowly that the holes could not have grown to these huge masses in the entire age of the universe. ‘We needed a faster mechanism’, says Chris Nixon, also at Leicester, “so we wondered what would happen if gas came in from different directions”.Nixon, King and their colleague Daniel Price in Australia made a computer simulation of two gas discs orbiting a black hole at different angles. After a short time the discs spread and collide, and large amounts of gas fall into the hole. According to their calculations black holes can grow 1,000 times faster when this happens. “If two guys ride motorbikes on a Wall of Death and they collide, they lose the centrifugal force holding them to the walls and fall”, says King. The same thing happens to the gas in these discs, and it falls in towards the hole. This may explain how these black holes got so big so fast. “We don't know exactly how gas flows inside galaxies in the early universe”, said King, “but I think it is very promising that if the flows are chaotic it is very easy for the black hole to feed”. Their research is due to published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. The research was funded by the UK Science and Technology Facilities Council.
11.2. The primordial black holes
- A primordial black hole is a hypothetical type of black hole that is formed not by the gravitational collapse of a large star but by the extreme density of matter present during the universe’s early expansion. One way to detect primordial black holes is by their Hawking radiation. Stephen Hawking theorized in 1974 that large numbers of such smaller primordial black holes might exist in the Milky Way in our galaxy’s Halo region. All black holes are believed by many theorists to emit Hawking radiation at a rate inversely proportional to their mass. Since this emission further decreases their mass, black holes with very small mass would experience runaway evaporation, creating a massive burst of radiation at the final phase, equivalent to millions of one-megaton hydrogen bombs exploding. This explanation is, however, considered unlikely. Other problems for which primordial black holes have been suggested as a solution include the dark matter problem, the cosmological domain wall problem and the cosmological monopole problem. Primordial black holes in the mass range
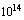 kg to
kg to 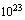 kg may also have contributed to the later formation of galaxies. This is due to the possibility that at this low mass they would behave as expected of other particle candidates for dark matter. As of today there is no solid evidence for the existence of PBHs, but their presence would be very difficult to detect even if they constitute the bulk of the dark matter. A black hole with a mass of about
kg may also have contributed to the later formation of galaxies. This is due to the possibility that at this low mass they would behave as expected of other particle candidates for dark matter. As of today there is no solid evidence for the existence of PBHs, but their presence would be very difficult to detect even if they constitute the bulk of the dark matter. A black hole with a mass of about 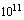 kg would have a lifetime about equal to the age of the universe. Based on the present theoretical works, expected mass of the non-evaporating PBHs ranges from
kg would have a lifetime about equal to the age of the universe. Based on the present theoretical works, expected mass of the non-evaporating PBHs ranges from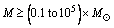 . PBHs with masses
. PBHs with masses 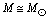 may form during the QCD (quark-hadron) phase transition at
may form during the QCD (quark-hadron) phase transition at 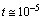 seconds, or PBHs with mass
seconds, or PBHs with mass 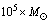 may form during the
may form during the 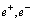 annihilation era. If universe is natural setting for the origin of primordial black holes- to understand the cosmological observations and black hole physics in a unified manner, it can be assumed that, right from the beginning to the present state, whole universe is a primordial black hole.
annihilation era. If universe is natural setting for the origin of primordial black holes- to understand the cosmological observations and black hole physics in a unified manner, it can be assumed that, right from the beginning to the present state, whole universe is a primordial black hole.11.3. The Cosmological Principle and the Closed Expanding Universe
- It may be a flat universe or closed universe, why universe is/was filled with thermal bath? is a million dollar question. If it is a black hole this question can be answered partially. The cosmological principle states that at any given cosmic time universe is homogeneous and isotropic. Compared to a flat model, isotropy is more natural in a closed expanding universe. Considering the closed expanding universe this can be very easily understood. In a closed expanding universe the utmost important and interesting point is that as the closed universe is expanding its thermal waves are stretched by the closed cosmic boundary in opposite directions simultaneously. As long as the closed universe is expanding instantaneously thermal waves undergo continuous stretching and results in instantaneous isotropy or thermal equilibrium. This is just like stretching of a rubber band with both the hands in opposite directions.In a flat universe there exists no working boundary and hence stretching of the thermal waves in opposite directions may not be possible instantaneously. Hence isotropy or thermal equilibrium cannot be maintained instantaneously in a flat model. Even the possibility of a proper physical coupling or contact in between the thermal bath and the flat cosmic volume is doubtful. Inflation may be required in a flat model but not required for the closed expanding model. Even in particle physics also there is no clear and solid mechanism for the initiation of inflation. More over inflation or exponential expansion of cosmic space violates the constancy of speed of light. Please note that at present there is no fundamental theory for the inflationary universe. With this discussion any one can confidently say that - the notion of ‘flat accelerating universe’ is incorrect. Note that present ‘accelerating model’ and ‘dark energy’ both are the consequences of ‘flat model’[46-48]. Hence their survival seems to be ad-hoc and uncertain[49-52].The new SNe distance determinations do not state that the expansion of the universe is accelerating or that there is some kind of “antigravity” effect, or that there is some new substance. The data only forces the conclusion that there is a problem in the purely Hubble conception of the cosmos or at least in the Hubble-based method of determining the distance to distant objects. Present observational or experimental data indicates that cosmic microwave back ground radiation temperature is 2.725
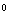 Kelvin[53]. It is very uniform up to several mega parsecs from Earth and so smooth to one part in 100000.
Kelvin[53]. It is very uniform up to several mega parsecs from Earth and so smooth to one part in 100000.12. The ‘Black Hole Cosmology’
- Concept of ‘cosmic rotation’ is not new. The subject of cosmic strong gravity is also not new. The only ad-hoc and speculative idea (from accelerating model point of view but not from the black hole physics point of view) of this model is – ‘cosmic light speed rotation’. Till today there is no explanation for ‘constancy of speed of light’. Recent observations indicate that galactic central black holes are spinning close to the speed of light! Really this is a surprise. Not only that present observations confirms that the galactic central black holes co-evolved with the galactic bulge plasma dynamics and the galactic arms. With these fascinating observations one cannot say that, the idea of ‘cosmic light speed rotation’ is a speculative concept in fundamental physics. It will be a very interesting and challenging task for a mathematician or physicist to describe the light speed cosmic ‘space rotation’. Compared to the other models of cosmology like hot big bang, inflation, accelerating universe, this model is free from speculative concepts like exponential expansion, hot big bang and dark energy. From fundamental physics point of view really and certainly these are speculative concepts. In real life or at least in a laboratory one cannot experience these concepts, whereas the ‘concept of light speed’ is an observable and measurable one.In grand unification program physicists and mathematicians often use the concept of ‘n’ dimensions. This idea is highly speculative compared to the proposed ‘cosmic light speed rotation’. To unify 2 interactions if 5 dimensions are required, for unifying 4 interactions 10 dimensions are required. For 3+1 dimensions if these exist 4 (hitherto observed) interactions, for 10 dimensions these may exist 10 (observable) interactions. To unify 10 interactions 20 dimensions are required. It seems this is a mathematical problem rather than a serious fundamental physical problem. Applying this idea to cosmology some people say there exists other universes in n-dimensions. But what to do with these unknown and hiding dimensions and universes. In 3+1 if there exists space, ether, gravitational radiation, dark matter and dark energy etc in n- new dimensions there may exist a number of new and strange things. The surprising and compromising statement is that: n - new dimensions curl up in ordinary 3+1 dimensions. Even though it is very interesting, from fundamental physics point of view this ‘n’ dimensions’ concept is highly speculative. Till today no single new physical property was defined in ‘n’ extra dimensions.In this sensitive and mysterious issue author’s humble appeal is: first let us find the primitive, natural and universal physical limits that may exist in the universal physics lab. With their implementation existing physical concepts and physical equations can be simplified and physical models can be refined.
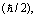 force
force 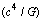 and power
and power 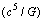 are really the utmost fundamental tools of black hole physics and ‘black hole cosmology’. To proceed further, it is a must to show that,1. There is a fundamental flaw in the basics of modern flat cosmology. It goes back to 1929 Hubble’s interpretation of galactic red shift data. It’s correct interpretation is: ‘rate of increase’ in red shift is a measure of cosmic rate of expansion.2. Rate of decrease in CMBR temperature is a measure of cosmic rate of expansion. ‘Cosmic isotropy’ and ‘cosmic acceleration’ both are inversely proportional to each other.3. Dimensions of Hubble’s constant are ‘radian/sec’ but not ‘1/sec’. This is very simple and brings cosmic rotation into picture.4. Universe follows a closed expanding boundary. Best example is: ‘Apple grows like an apple’ with closed expanding/growing boundary. Rotation will make the closed expanding universe stable.5. At any time, strong gravity plays an interesting role in minimizing the (expanding) cosmic size.6. Large cosmic time and smooth cosmic expansion play an interesting role in the evolution of fundamental particles.
are really the utmost fundamental tools of black hole physics and ‘black hole cosmology’. To proceed further, it is a must to show that,1. There is a fundamental flaw in the basics of modern flat cosmology. It goes back to 1929 Hubble’s interpretation of galactic red shift data. It’s correct interpretation is: ‘rate of increase’ in red shift is a measure of cosmic rate of expansion.2. Rate of decrease in CMBR temperature is a measure of cosmic rate of expansion. ‘Cosmic isotropy’ and ‘cosmic acceleration’ both are inversely proportional to each other.3. Dimensions of Hubble’s constant are ‘radian/sec’ but not ‘1/sec’. This is very simple and brings cosmic rotation into picture.4. Universe follows a closed expanding boundary. Best example is: ‘Apple grows like an apple’ with closed expanding/growing boundary. Rotation will make the closed expanding universe stable.5. At any time, strong gravity plays an interesting role in minimizing the (expanding) cosmic size.6. Large cosmic time and smooth cosmic expansion play an interesting role in the evolution of fundamental particles.12.1. Proposed five assumptions
- Starting from the Planck scale, at any time
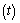 ,1. The universe can be treated as a rotating and growing black hole.2. With increasing mass and decreasing angular velocity, the universe is always rotating with speed of light.3. Without ‘cosmic rotation’ there is no ‘cosmic temperature’. Cosmic temperature follows Hawking black hole temperature formula where mass is equal to the geometric mean of the planck mass and the cosmic mass.4. ‘Rate of decrease’ in CMBR temperature is a measure of cosmic ‘rate of expansion’.5. Space, time and matter are the immediate and parallel results of cosmic expansion.
,1. The universe can be treated as a rotating and growing black hole.2. With increasing mass and decreasing angular velocity, the universe is always rotating with speed of light.3. Without ‘cosmic rotation’ there is no ‘cosmic temperature’. Cosmic temperature follows Hawking black hole temperature formula where mass is equal to the geometric mean of the planck mass and the cosmic mass.4. ‘Rate of decrease’ in CMBR temperature is a measure of cosmic ‘rate of expansion’.5. Space, time and matter are the immediate and parallel results of cosmic expansion.12.2. The cosmic critical density and its dimensional analysis
- Assume that, a planet of mass
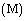 and size
and size 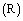 rotates with angular velocity
rotates with angular velocity 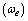 and linear velocity
and linear velocity 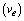 in such a way that, free or loosely bound particle of mass
in such a way that, free or loosely bound particle of mass 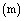 lying on its equator gains a kinetic energy equal to potential energy as,
lying on its equator gains a kinetic energy equal to potential energy as,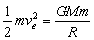 | (43) |
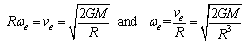 | (44) |
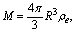
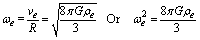 | (45) |
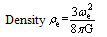 | (46) |
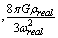 may have some physical meaning. The most important point to be noted here, is that, as far as dimensions and units are considered, from equation (46), it is very clear that, proportionality constant being
may have some physical meaning. The most important point to be noted here, is that, as far as dimensions and units are considered, from equation (46), it is very clear that, proportionality constant being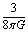 ,
,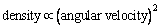 Equation (46) is similar to the “flat model concept” of the cosmic “critical density”
Equation (46) is similar to the “flat model concept” of the cosmic “critical density”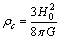 | (47) |
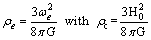 | (48) |
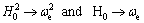 | (49) |
12.3. Planck scale and cosmic black hole temperature
- At any time
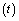 from assumption (1) based on black hole concepts, if mass of the universe is
from assumption (1) based on black hole concepts, if mass of the universe is 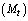 size of the cosmic black hole can be given by
size of the cosmic black hole can be given by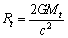 | (50) |
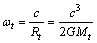 | (51) |
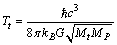 | (52) |
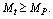 From equations (51) and (52)
From equations (51) and (52)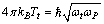 | (53) |
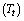 is known
is known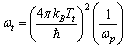 | (54) |
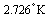 in equation (54) we get present cosmic angular velocity
in equation (54) we get present cosmic angular velocity 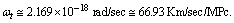 Numerically this obtained value is very close to the measured value of Hubble’s constant
Numerically this obtained value is very close to the measured value of Hubble’s constant 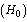 Not only that this proposed unified method is qualitatively and quantitatively simple compared with the “cosmic red shift” and “galactic distance” observations. This procedure is error free and is reliable. Author requests the science community to kindly look into this kind of rotating and growing universe models. If this procedure is really true and applicable to the expanding universe then accelerating model, dark matter and dark energy becomes ad-hoc concepts.
Not only that this proposed unified method is qualitatively and quantitatively simple compared with the “cosmic red shift” and “galactic distance” observations. This procedure is error free and is reliable. Author requests the science community to kindly look into this kind of rotating and growing universe models. If this procedure is really true and applicable to the expanding universe then accelerating model, dark matter and dark energy becomes ad-hoc concepts.12.4. Cosmic mass density and baryon-photon number density ratio
- With this model empirically it is noticed that, mass density
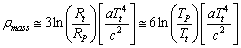 | (55) |
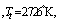
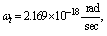
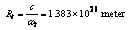 and
and 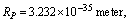 present mass density is
present mass density is 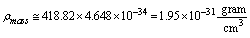 . This is very close to the observed mater density[54] of the universe
. This is very close to the observed mater density[54] of the universe 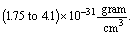 If this idea is true the proposed term
If this idea is true the proposed term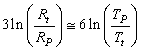 | (56) |
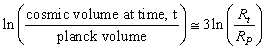 | (57) |
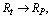 and
and 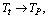 the term
the term 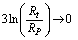 and mass density at Planck time approaches zero. Conceptually this supports the big bang assumption that “at the time of big bang matter was in the form of radiation”. Not only that as cosmic time increases mass density gradually increases and thermal density gradually decreases.Using this term and considering the present CMBR temperature baryon-photon number density ratio can be fitted as follows.
and mass density at Planck time approaches zero. Conceptually this supports the big bang assumption that “at the time of big bang matter was in the form of radiation”. Not only that as cosmic time increases mass density gradually increases and thermal density gradually decreases.Using this term and considering the present CMBR temperature baryon-photon number density ratio can be fitted as follows.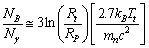 | (58) |
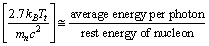 | (59) |
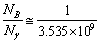 | (60) |
12.5. The 2 real densities
- Since the cosmic black hole always follows closed model and rotates at light speed, at any time size of cosmic black hole is
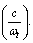 It’s density =
It’s density = 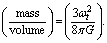 It is no where connected with “critical density” concepts. It is noticed that
It is no where connected with “critical density” concepts. It is noticed that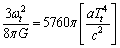 | (61) |
12.6. Origin of the cosmic red shift, galaxy receding and galaxy revolution
- As the cosmic sphere is expanding and rotating galaxies receding and revolving from and about the cosmic axis. As time passes photon from the galaxy travels opposite to the direction of expansion and reaches to the cosmic axis or centre. Thus photon shows a red shift about the cosmic centre. If this idea is true cosmic red shift is a measure of galactic distances from the cosmic axis of rotation or centre. Galaxy receding is directly proportional to the rate of expansion of the rotating cosmic sphere as a whole. In this scenario for any galaxy continuous increase in red shift is a measure of rapid expansion and “practically constant red shift” is a measure of very slow expansion. That is change in galaxy distance from cosmic axis is practically zero. At any time
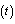 it can be defined as, cosmic red shift
it can be defined as, cosmic red shift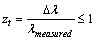 | (62) |
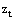 is very small this definition is close to the existing red shift definition
is very small this definition is close to the existing red shift definition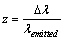 | (63) |
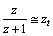 | (64) |
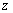 is very small. Note that at Hubble’s time the maximum red shift observed was,
is very small. Note that at Hubble’s time the maximum red shift observed was, 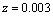 which is small and value of
which is small and value of 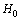 was 530
was 530 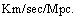 By Hubble’s time equation (62) might had been defined in place of equation (63). But its not happened so! When rate of expansion is very slow, i.e. at present, based on
By Hubble’s time equation (62) might had been defined in place of equation (63). But its not happened so! When rate of expansion is very slow, i.e. at present, based on 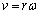 concepts
concepts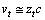 | (65) |
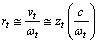 | (66) |
13. The Present Cosmic Time
- 1. Time required to complete one radian is
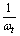 where
where 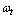 is the angular velocity of the universe at time
is the angular velocity of the universe at time 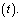 At any time this is not the cosmic age. If at present,
At any time this is not the cosmic age. If at present, 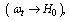 it will not represent the present age of the universe.2. Time required to complete one revolution is
it will not represent the present age of the universe.2. Time required to complete one revolution is 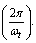 3. Time required to move from Planck volume to existing volume = present cosmic age. How to estimate this time? Author suggests a heuristic procedure in the following way.
3. Time required to move from Planck volume to existing volume = present cosmic age. How to estimate this time? Author suggests a heuristic procedure in the following way.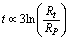 | (67) |
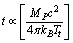 | (68) |
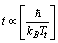 | (69) |
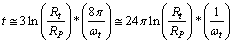 | (70) |
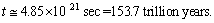 After simplification, this relation takes the following form.
After simplification, this relation takes the following form.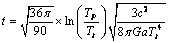 | (71) |
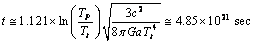 | (72) |
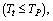 and interesting idea is that if
and interesting idea is that if 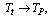 the term,
the term, 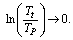 It indicates that, unlike the planck time, here in this model cosmic time starts from zero seconds. This idea is very similar to the birth of a living creature. How and why, the living creature has born? - This is a fundamental question to be investigated by the present and future mankind. In the similar way, how and why, the “planck particle” born? has to be investigated by the present and future cosmologists. Proposed time is 9400 times of
It indicates that, unlike the planck time, here in this model cosmic time starts from zero seconds. This idea is very similar to the birth of a living creature. How and why, the living creature has born? - This is a fundamental question to be investigated by the present and future mankind. In the similar way, how and why, the “planck particle” born? has to be investigated by the present and future cosmologists. Proposed time is 9400 times of 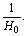 With this large time “smooth cosmic expansion” can be possible. Inflation, magnetic monopoles problem and super novae dimming can be understood by a “larger cosmic time and smooth cosmic expansion”. One second after the birth of planck particle,
With this large time “smooth cosmic expansion” can be possible. Inflation, magnetic monopoles problem and super novae dimming can be understood by a “larger cosmic time and smooth cosmic expansion”. One second after the birth of planck particle, 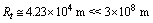 and is less than one light second. Please see the following table-1.
and is less than one light second. Please see the following table-1.
|
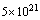 sec[55]. Here error is 3 %. Really this is a miracle. This may be a coincidence also. The interesting question is -- why and how the ancient Indians obtained that number? If so the interesting thing is that 1.7 days of lord Brahma is roughly matching with the current estimations of cosmic age!
sec[55]. Here error is 3 %. Really this is a miracle. This may be a coincidence also. The interesting question is -- why and how the ancient Indians obtained that number? If so the interesting thing is that 1.7 days of lord Brahma is roughly matching with the current estimations of cosmic age!14. Conclusions
- In cosmology, one should not forget the history of the unexpected discovery of the famous CMBR temperature and the famous Einstein’s ‘lambda’ term. The subjects of cosmology and black hole physics are still very much open. Any thing may happen at any time. A debate is well going on the ‘existence’ and ‘growth’ of black holes’[1,44,45,56-58]. Proposed classical limits can be given a chance in fundamental and unified physics. Author showed the different applications of force
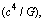 and power
and power 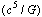 in astrophysics. With these 2 expressions or limits, mathematical complexity in GTR can be resolved. Not only that, force
in astrophysics. With these 2 expressions or limits, mathematical complexity in GTR can be resolved. Not only that, force 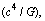 plays a crucial role in grand unification and power
plays a crucial role in grand unification and power 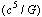 plays a crucial role in gravitational radiation. Even though detection of primordial cosmic black holes is very difficult, their direct effects are best seen in the form of old and new galaxies and their fast spinning galactic centres. Recent observations reveal that galactic central black holes are spinning close to speed of light. Another debate is well going on the ‘cosmic acceleration’, the existence of ‘dark matter’ and ‘dark energy’. Compared to dark matter and dark energy, a primordial cosmic black hole connects GTR, quantum mechanics and cosmology in a unified manner. Thinking positively, from its birth to its present state, universe can be considered as a growing and rotating primordial black hole. Constant ‘light speed rotation’ maintains its stability and rate of decrease in temperature indicates its growth or expansion rate. Now this is the time to search for the primordial cosmic axis. Please see the appendix on the cosmic ‘axis of evil’.
plays a crucial role in gravitational radiation. Even though detection of primordial cosmic black holes is very difficult, their direct effects are best seen in the form of old and new galaxies and their fast spinning galactic centres. Recent observations reveal that galactic central black holes are spinning close to speed of light. Another debate is well going on the ‘cosmic acceleration’, the existence of ‘dark matter’ and ‘dark energy’. Compared to dark matter and dark energy, a primordial cosmic black hole connects GTR, quantum mechanics and cosmology in a unified manner. Thinking positively, from its birth to its present state, universe can be considered as a growing and rotating primordial black hole. Constant ‘light speed rotation’ maintains its stability and rate of decrease in temperature indicates its growth or expansion rate. Now this is the time to search for the primordial cosmic axis. Please see the appendix on the cosmic ‘axis of evil’.Acknowledgements
- Author is indebted to Prof. K. V. Krishna Murthy, Chairman, Institute of Scientific Research on Vedas (I- SERVE), Hyderabad, India, Shri K. V. R. S. Murthy, former scientist IICT (CSIR) Govt. of India and Director (R&D), (I-SERVE), Hyderabad, India, professor S. Lakshminarayana, Dept. of Nuclear physics, Andhra university, India and Dr. Sankar Hazra, PIRT-CMS, Kolkata, for their valuable guidance and great support in developing this subject.
Appendix
- The cosmic ‘axis of evil’In 1997 Nodland and Ralston reported to have discovered a cosmic axis. The cosmic “axis of evil” is a name astrophysicists are giving to a newly discovered feature of our universe: a spiral pattern imprinted on radiation left over from the big bang. It has long been thought that matter is uniformly distributed throughout space, with no particular preference in any direction. Now there is new evidence (New Scientist, April 13, 2007) suggesting that the entire structure of the universe has the orientation of a corkscrew pattern: over 300 quasars fit into this overall whole twisting structure. Data from 1660 spiral galaxies also show the same overall orientation. If such a thing is true it would suggest that directionality, or anisotropy, rather than isotropy is the basis for galactic organization at the largest scale. Thus, the whole universe may in fact be based on spiral geometry, rather than being evenly spread out and uniform in all directions.Astronomers reveal a cosmic ‘axis of evil’- news from Royal Astronomical Society, 2011 June 30Astronomers are puzzled by the announcement that the masses of the largest objects in the Universe appear to depend on which method is used to weigh them. The new work was presented at a specialist discussion meeting on ‘Scaling Relations of Galaxy Clusters’ organised by the Astrophysics Research Institute (ARI) at Liverpool John Moores University and supported by the Royal Astronomical Society.Clusters of galaxies are the largest gravitationally bound objects in the Universe containing thousands of galaxies like the Milky Way and their weight is an important probe of their dark matter content and evolution through cosmic time. Measurements used to weigh these systems carried out in three different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: X-ray, optical and millimetre wavelengths, give rise to significantly different results.Eduardo Rozo, from the University of Chicago, explained that any two of the measurements can be made to fit easily enough but that always leaves the estimate using the third technique out of line. Dubbed the ‘Axis of Evil’, it is as if the Universe is being difficult by keeping back one or two pieces of the jigsaw and so deliberately preventing us from calibrating our weighing scales properly.More than 40 of the leading cluster astronomers from UK, Europe and the US attended the meeting to discuss the early results from the Planck satellite, currently scanning the heavens at millimetre wavelengths, looking for the smallest signals from clusters of galaxies and the cosmic background radiation in order to understand the birth of the Universe. The Planck measurements were compared with optical images of clusters from the Sloan Digitised Sky Survey and new X-ray observations from the XMM-Newton satellite.ARI astronomers are taking a leading role in this research through participation in the X-ray cluster work and observations of the constituent galaxies using the largest ground-based optical telescopes.One possible resolution to the ‘Axis of Evil’ problem discussed at the meeting is a new population of clusters which is optically bright but also X-ray faint. Dr Jim Bartlett (Univ. Paris), who is one of the astronomers who presented the Planck results, argued that the prospect of a new cluster population which responds differently was a ‘frightening prospect’ because it overturns age old ideas about the gravitational physics being the same from cluster to cluster.Chris Collins, LJMU Professor of Cosmology, who organized the meeting said: ‘I saw this meeting as an opportunity to bring together experts who study clusters at only one wavelength and don’t always talk to their colleagues working at other wavelengths. The results presented are unexpected and all three communities (optical, X-ray and millimetre) will need to work together in the future to figure out what is going on.’Cosmic spin - news from New Scientist, October 2011This information can be downloaded from ‘www. Andyross.net/spin.htm’. The universe might be spinning. Michael Longo at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor thinks so. At the heart of the story is conservation of parity: the universe does not tell left from right. In 2007, Longo was mining the databases of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) to collect images of about a million galaxies across the northern sky. He was looking for spiral galaxies whose swirling arms were clearly visible, showing what direction the galaxies are spinning in.By 2010, Longo and his team had a sample of 15,158 clearly rotating spiral galaxies, the farthest 1.2 billion light years away. In most sectors of the northern sky, equal numbers of galaxies were rotating to the right, or clockwise, and to the left, anticlockwise. But along one direction, at about 10 degrees to our own galaxy’s spin axis, there were more left-handed spirals than right-handed ones. Longo looked at the southern sky, which is not covered by the SDSS. Stretching off as far as the telescope could see, along the same axis in the southern sky, he saw an excess of right-handed spirals. It was the opposite view of the same effect. Longo says that if the asymmetry is real, the universe has a net angular momentum and was born in a spin.Experiments in the sixties showed that CP symmetry, parity (P) and charge (C) conservation together, is broken in nature. In 1967, Soviet physicist Andrei Sakharov showed that CP violation in the early universe could explain the predominance of matter over antimatter in the universe.In 2004, Alexander, then at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Centre in Menlo Park, California, and colleagues showed that if gravity violated parity in the first instants after the big bang, that would have produced asymmetric gravitational waves, causing inflation to produce more matter than antimatter.The cosmic microwave background has a uniform temperature of some 2.7 K, but look closely and you see warmer and colder spots. On the very largest scales, some of the spots seem to line up in a direction dubbed the “axis of evil”. The axis along which galaxies seem to be rotating with the same handedness is roughly the axis of evil.Longo suggests that an initially spinning universe brought on a parity-violating asymmetry in gravity that allowed matter to prevail over antimatter. And that process left the axis of evil in the cosmic background radiation and the inconspicuous alignment of galaxies that he spotted.The Universe: The new Axis of Evil - news from “The Independent”, 01 February 2006Ever since 1965, when two researchers at Bell Telephone Labs in New Jersey stumbled on it by accident, astronomers have known that the Universe is alive with the dim “afterglow” of the big bang fireball. Now, something unexpected has cropped up in that afterglow - a feature dubbed “the axis of evil”. Some think it is being caused by the gravity of a tremendous concentration of 100,000 galaxies in our cosmic backyard. Others say it is telling us there is something wrong with our big bang picture of the Universe.The axis of evil is the biggest surprise thrown up by NASA’s Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP). Launched on 30 June 2001, it has, from its vantage point 150 million kilometres beyond the Earth on the extension of the line joining our planet to the Sun, been taking the temperature of big bang afterglow, known as the “cosmic background radiation”. Understanding exactly what WMAP has found requires a little diversion into the technicalities of the background radiation.It is coming from every direction in the sky and its average temperature is minus 270 C. Of key importance are subtle variations in temperature from place to place - “hot spots” that are ever-so-slightly warmer than average, and “cold spots” that are ever-so-slightly cooler. These arise because the matter in the fireball of the big bang was slightly lumpy. (One lump became your home - the Milky Way.)The hot spots and cold spots in the big bang afterglow come in all sizes. For instance, there are big blotches that stretch across much of the sky and, superimposed on these, smaller goose pimples.To make sense of it all, astronomers like to break up their “temperature map” of the sky into manageable chunks they call “multi poles”. The simplest is the “dipole” - merely one huge hot spot and one huge cold spot. It has nothing to do with the big bang. Rather, it is caused by the motion of the Milky Way, which is flying through space at about a million kilometres per hour. This makes the afterglow of the big bang appear hotter in the direction the Milky Way is flying and colder in the opposite direction.The second simplest chunk of the cosmic background radiation is the “quadrupole”. This is like the dipole, but is made up of two hot regions and two cold regions. Next comes the “octu pole”, which is comprised of three hot regions and three cold regions. The simplest multi pole chunks of the big bang radiation correspond to the biggest blotches, the more complex to the smallest freckles.If the standard big bang picture of the Universe is correct, the blotches and freckles should be scattered randomly about the sky. “The big surprise is they are not,” says Chris Vale of the University of California at Berkeley. “The quadrupole and octu pole blotches are aligned with each other - along the axis of evil.”Nobody knows why. Could it be that all our preconceived notions about the big bang are wrong, or is it something less challenging? Vale leans towards the latter. He notes that the dipole direction is at right angles to the direction of the axis of evil. Recall that the dipole direction has nothing to do with the big bang, whereas the axis direction does, so their positions should not be related. “The fact that they are hints at an unexpected connection,” says Vale.According to Vale, if there is a giant concentration of mass in the local universe, its tremendous gravity could be distorting the cosmic background. The phenomenon is known as “gravitational lensing”. It could cause the big hot spot of the dipole to “spill over” into the smaller hot spots. “The dipole hot spot is several hundred times hotter than the quadrupole,” says Vale. “So it is not necessary for much to spill over to explain the axis of evil.” Vale claims the best candidate for the local mass concentration is the “Shapley Supercluster” in our cosmic backyard, which contains 100,000 galaxies. It is not visible to the naked eye, despite covering at least 1,000 times the apparent size of the full Moon. Other astronomers think Vale could be on to something. “Vale’s model generates a good match of what we see,” says WMAP scientist Gary Hinshaw of the Goddard Space Flight Centre in Greenbelt, Maryland. “It’s remarkable.”However, some physicists wonder whether the axis of evil requires a rethink of our ideas about the Universe. They include Joao Magueijo at Imperial College in London, who coined the term “the axis of evil”. According to Magueijo, there may be something seriously wrong with our big bang models. Big bang models come out of Einstein’s theory of gravity. The only way theorists can apply the hideously complicated theory to the Universe is to make two simplifying assumptions. One is that the Universe is roughly the same in all places, and the other is that it is roughly the same in all directions.But if the Universe is the same in all directions, as the big bang models require, that means that the hot spots and cold spots in the afterglow of the big bang should be randomly splattered about the sky - the big temperature splotches and the small temperature goose pimples should have no preferred direction. The fact that they are aligned along the axis of evil leads Magueijo to suggest that may be the assumptions behind the big bang models are wrong. In other words, the Universe is not the same in all places or directions, but has a special direction.According to Magueijo, there are a number of ways the Universe could have a special direction. One is if we live in a “slab universe”. This is a Universe in which space is infinite in two directions but in the other is only about 20 billion light years across - the diameter of the observable universe. Another possibility is that we live in torus-shaped universe, like a giant ring doughnut. Yet another is that Universe is spinning. But how could such a weird state of affairs have arisen? “That’s the big question,” Magueijo says.So perplexing is the axis of evil that Hinshaw and WMAP’s principal investigator, Chuck Bennett, have obtained a grant for a five-year examination of the WMAP data. They hope to explore the possibilities that the WMAP instrument was in error, or that something else went wrong. “There’s no question there’s stuff that looks unusual,” says Bennett. We will have to wait and see whether the study reveals the axis of evil to be a cosmic mirage, or shows the big bang model to be in serious trouble.‘Axis of evil’ a cause for cosmic concern - News from New Scientist, 11-Apr-2007Some believe it is just a figment of overactive imaginations. But evidence is growing that the so-called “axis of evil”- a pattern apparently imprinted on the radiation left behind by the big bang – may be real, posing a threat to standard cosmology. According to the standard model, the universe is isotropic, or much the same everywhere. The first sign that this might not be the case came in 2005, when Kate Land and João Magueijo of Imperial College London noticed a curious pattern in the map of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) created by NASA’s WMAP satellite. It seemed to show that some hot and cold spots in the CMB are not distributed randomly, as expected, but are aligned along what Magueijo dubbed the axis of evil.Some astronomers have suggested straightforward explanations for the axis, such as problems with WMAP’s instruments or distortions caused by a nearby super cluster (New Scientist, 22 October 2005, p 19). Others doubt the pattern’s very existence. “There” still a fair bit of controversy about whether there “even something there that needs to be explained,” says WMAP scientist Gary Hinshaw of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Centre in Greenbelt, Maryland.Now, two independent studies seem to confirm that it does exist. Damien Hutkeepers of the University of Liège in Belgium analysed the polarisation of light from 355 quasars and found that as the quasars get near the axis, the polarisation becomes more ordered than expected. Taken together, the polarisation angles from the quasars seem to corkscrew around the axis. “This is really promising,” says Hinshaw. “Cosmologists should sit up and take notice.”Cosmologist Carlo Contaldi of Imperial College London is intrigued, but thinks more quasars should be analysed before drawing conclusions. “There is a danger that once people know about the axis of evil, they start seeing evil in all sorts of sets of data,” he says. The quasar finding has support from another study, however. Michael Longo of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor analysed 1660 spiral galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey and found that the axes of rotation of most galaxies appear to line up with the axis of evil (www.arxiv.org/astro-ph/0703325). According to Longo, the probability of this happening by chance is less than 0.4 per cent. “This suggests the axis is real, and not simply an error in the WMAP data,” he says. Land, now at the University of Oxford, thinks Longo must rule out other reasons for why the spirals are aligned the way they are. For instance, neighbouring galaxies could have formed from the same rotating dust cloud, giving them similar orientations, she says. “But if he is correct, then this is really exciting, not only as independent confirmation of the axis, but because it’ll help us understand what may have created it”, she says.One way to create the axis was presented by Contaldi at a conference on outstanding questions in cosmology at Imperial College last month. The universe is thought to be isotropic because the early universe went through a period of exponential expansion known as inflation, smoothing out any unevenness.Contaldi modified inflation to allow the universe to expand more in one direction. “Provided inflation stops at a relatively early point, this would leave traces of the early[unevenness] in the form of the axis of evil,” he says. Longo favours a more radical theory proposed by Leonardo Campanelli of the University of Ferrara, Italy, which suggests that magnetic fields stretched across the universe could be responsible (New Scientist, 2 September 2006, p 28). “A magnetic field would naturally orient the spiral galaxies,” says Longo.Regardless of the reasons, one thing is clear: the axis of evil won’t be written off any time soon. “Interest keeps growing as people find more weirdly connected observations that can’t all be put down to coincidence,” says Land. “And hey, everybody loves a conspiracy.”
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML