-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Architecture Research
p-ISSN: 2168-507X e-ISSN: 2168-5088
2019; 9(3): 74-81
doi:10.5923/j.arch.20190903.03

Nature-Based Framework for Sustainable Architectural Design - Biomimetic Design and Biophilic Design
Abeer Makram
Department of Architecture, Delta University for Science and Technology, Gamasa, Egypt
Correspondence to: Abeer Makram , Department of Architecture, Delta University for Science and Technology, Gamasa, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Sustainable architectural design is the design of the age. It is based on the solution of environmental, social and economic problems of architectural design for providing resources and improving the quality of life for mankind. Sustainable solutions of architectural design result mainly from the principle of sustainability which is derived from natural systems and what they offer to humans. The main objective of this paper is to highlight the natural strategies of solving the problems of sustainable architectural design as an integrated approach for the knowledge of the secrets of sustainability. These strategies of sustainable architectural design derived from nature and interacting with it. The first strategy is inspired from nature by implementing the Biomimetic design which mimics the performance of nature and provides clean technologies. The second strategy is integrated into nature by using Biophilic design and its role in achieving human well-being and improving their performance. This research follows the deductive approach that analyzes the design strategies and methods taken from nature to contribute to the development of a comprehensive nature-based framework for sustainable architectural design to benefit the designers, innovators and decision makers that nature is the main source for achieving sustainability in architectural design.Keywords Sustainable architectural design, Natural strategies, Biomimetic Design, Biophilic Design, Nature-based framework
Keywords:
Cite this paper: Abeer Makram , Nature-Based Framework for Sustainable Architectural Design - Biomimetic Design and Biophilic Design, Architecture Research, Vol. 9 No. 3, 2019, pp. 74-81. doi: 10.5923/j.arch.20190903.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Sustainable architectural design is a set of rules and principles that are stronger than strict laws. It gives a great conception of the whole-building as an approach to design, construction, maintenance and operations. It is a vast and complex concept. The concept of sustainability reflects the quality of life and allows people to live in a healthy environment while improving social, environmental and economic conditions. [1] This concept is formed from the idea of sustainability, sustainable development and the framework for sustainable design based on the sustainable triple bottom line principles which are the conservation of resources, cost efficiency and design for the human. Each principle has strategies and methods throughout the life cycle of construction projects.Since nature is based on the principle of sustainability, the accuracy of the human will never match the beauty, simplicity or directness of nature; where there is nothing missing or is not necessary as it is the optimal design. Thus, the copying or imitation of the phenomena of nature or mechanisms of survival and environmental efficiency in manufacturing processes [2] act as the sustainability concept in the architectural design, which is called the biomimic design. The human instinctively tends to nature and so do all the other organisms. Therefore, the integration of design with nature is called biophilic design that has physiological benefits focused on human health and well-being and improve their performance. Thus, the application of biophia and biomimicry concepts in design, construction and maintenance of buildings achieves the principles of sustainability in the project.
2. Sustainability as Learning from Natural
- Sustainability is the endurance and derivative of the Latin term sustinere. It describes how biological systems remain diverse and always productive. It improves human life and well-being and thus natural world preserve the natural resources over a long time. [3]. Sustainable design is a part of the sustainability movement. It is the philosophical basis for changing the definition of how building design, construction and operation becomes more environmentally responsible and responsive to people. [4]The philosophy of learning from nature published in a book called Biomimicry by the biologist Janine Benyus in 1996. Biomimicry has taken the term from the Greek word “Bio-mimesis” meaning life and imitation. It described this science in three main aspects:- The Inspiration from nature as a model. - The Measurement from nature as judgment- The Mentor from nature as a valuation.Benyus describes that all natural innovations have nine common things:1. Nature is based on sunlight.2. Nature only uses the energy it needs.3. In nature, the shape matches the function.4. Nature recycles everything.5. Nature is based on participation.6. Nature is full of diversity.7. Nature requires local experience.8. Nature does not have excesses or excessiveness.9. Nature taps the power of limits. [4]Thus, learning from nature provides us with the methods that must be implemented in daily design solutions through Biomimetic design to create sustainable societies as nature does. [5] In order to achieve comprehensive sustainability, these societies must be provided with restorative environments. In the literature of environmental psychology, the potential therapeutic benefits and positive effects on human health and wellbeing by exposure to nature environments were studied by Stephen Kellert and Elizabeth Calabrese in document “The Practice of Biophilic Design”. It focuses on nature positive experience in the built environment to reach restorative environments that act as a basis for Biophilic design. [6]
3. Nature-based Sustainable Architecture Design Framework
- Sustainability requires a holistic approach to conceptualize all issues, understand principles and deal with them. Nature is an auxiliary device for thinking rationally and applying the principles of design in a visual, easy to understand and easily accessible method. Thus, nature as a source of holistic creativity acts as a mentor helping to understand the principles of sustainable design. [7] To achieve sustainability in architectural design by natural design two strategies are used:■ First, nature-inspired design strategies based on the principle of learning from nature.■ Second, nature into the built-environment strategies which integrate nature into the built environment. This research is concerned with the development of a conceptual framework consisting of three levels of principles, strategies and methods, all of which are compatible with two objectives:■ Creating an integrated environmental awareness inspired from nature using Biomimetic design ■ Application of methods of improvement, health and well-being of human engaged with nature using Biophilic design.There are three principles in sustainable architecture ■ Resource efficiency - Reduction and preservation of the natural resources■ Life Cycle Design - Methodology for the impact of the building process on the environment.■ Humane Design - Human interaction with the natural world. [8]The most important part of the principles of sustainability existed in nature through the biomimetic principles [4] which is a principle based on the direct learning from nature. Thus, the primary principles of Economy of Resources and Life Cycle Design have strategy inspired by nature. Moreover, the most important principle to enhance human health and wellbeing is the principle of human design which existed in Biophilic design principles and its strategy to apply the Positive experience of nature in the built environment. [7]
3.1. Nature-Inspired Design Strategy
- This strategy focuses on eco-efficiency which is based on the use of the least resources, waste and pollution. It consists of some aspects that have a common characteristic of learning from the nature which use nature design principles to develop sustainable solutions. This strategy is based mainly on the principle of "Learning from nature "and looking at nature as a model of sustainability. [9]Biomimicry uses principles that exist in nature as a basis for human-based design, which shows how important it is to learn from the natural world. [10]. The approach of biomimicry as a design process is divided into two parts: First: determining the human needs or design problem. Second: searching for ways to solve this problem by organisms or ecosystems. The Biomimetic design which mutates the creative nature designs has managed to produce design technology which developed new materials and products.
3.1.1. Aspects Based on the Principle of Resource Efficiency
- These aspects are derived from simulating living organisms to access different design methods to conserve resources (energy, water and materials). These methods may simulate nature in terms of form, material, construction, process and function. First, (Table 1) illustrates the reduction of energy consumption by ventilation and natural lighting methods and keeping comfortable temperature levels by way of insulation methods and using natural forms to interact with the surrounding environment [11]. Second, it illustrates preserving materials by using localized materials, environment friendly forms, and long lasting materials which simulates natural materials in terms of being more durable, require less maintenance and deal with the surrounding environment. Third, it shows how water conservation is carried out by simulating nature methods of manufacturing surfaces, harvesting, collecting water, or designing water collecting devices.
 | Table 1. Natural methods to conserve resources |
3.1.2. Aspects based on the Principle of Life Cycle Design
- These aspects mimic natural systems with a completely closed loop of waste management. It is done over the life of the building to achieve the optimum consumption of resources and site where the resources move to zero waste ways. It is the use of resources for the largest possible period so that they can be recovered and refurbished to dispose of waste. It consists of two aspects and some optimization methods. (Table. 2.)First: The Optimum Consumption of Resources: The large number of organisms form an industrial network that mimics the systems of nature and produces a large amount of useful outputs as inputs where the resources move to zero waste ways. Second: Resource Management: It is the prevention of environmental pollution through application of surfaces to prevent pollution, anti-bacterial, anti-fogging and anti-corrosion, reducing CO2 emissions, preventing harmful emissions by simulating plants, insects and birds.
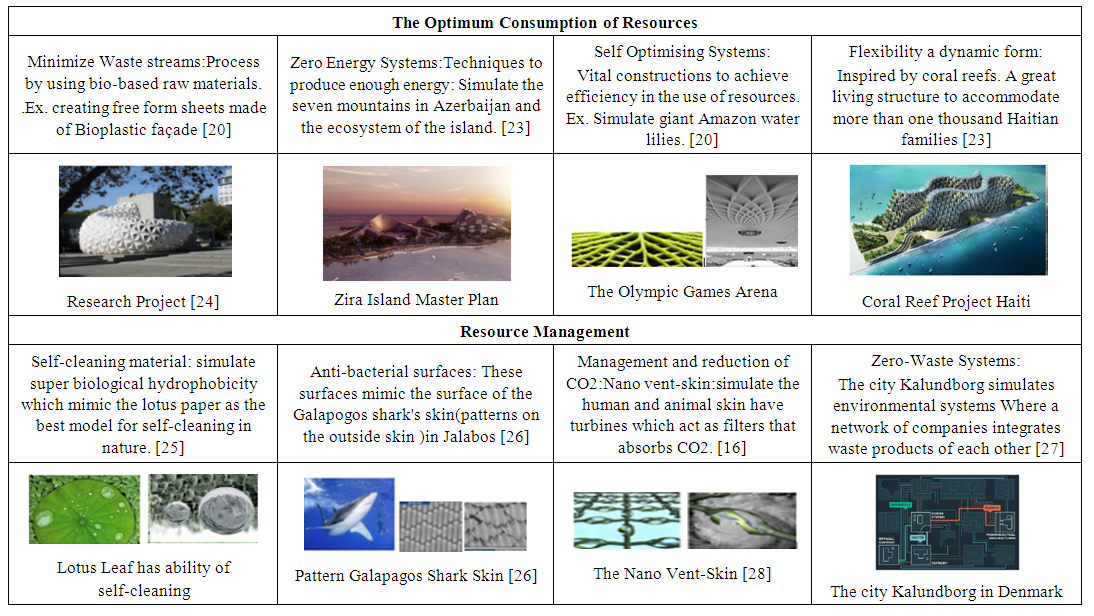 | Table 2. Natural systems to Resource and Waste performance methods (optimization Methods) |
3.2. Nature into the Built-Environment Strategy
- Human beings have a biological attractiveness to the natural environment, which helps to achieve well-being which is the Hypothesis of Biophila. Therefore, the buildings and living spaces of biophilic design include the basic elements from natural ventilation and natural lighting to natural shapes, products and landscapes and all that makes people feel that they are in a natural environment. [29] The relationship between man and nature is divided into three categories: Nature in the Space, Natural Analogues, and Nature of the Space that are reflected in the biophilic design features through 14 patterns. These patterns are used as a tool to improve well-being in the built environment. [30] (Table 3) shows their different types.
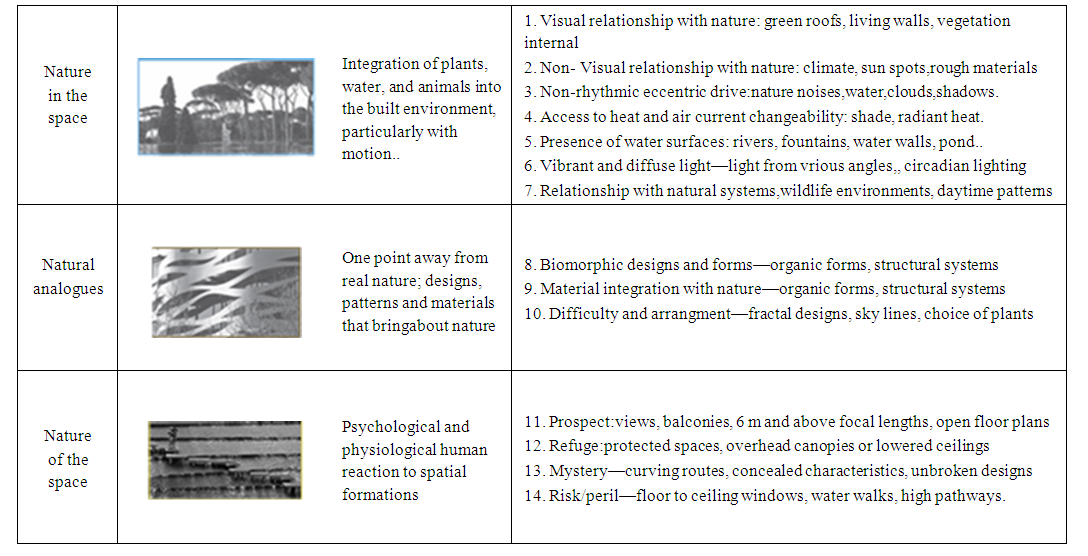 | Table 3. Patterns of biophilic design. [30] [31] |
3.2.1. Natural Environmental Protection
- The elements of the biophilic design; green areas, trees, green roofs, green walls…etc, have an important role in preserving the environment by energy saving, water conservation and filtration, Phytroremediation, Carbon Reduction and Biodiversity / Environmental Biodiversity (Table 4) show natural environment protection methods.
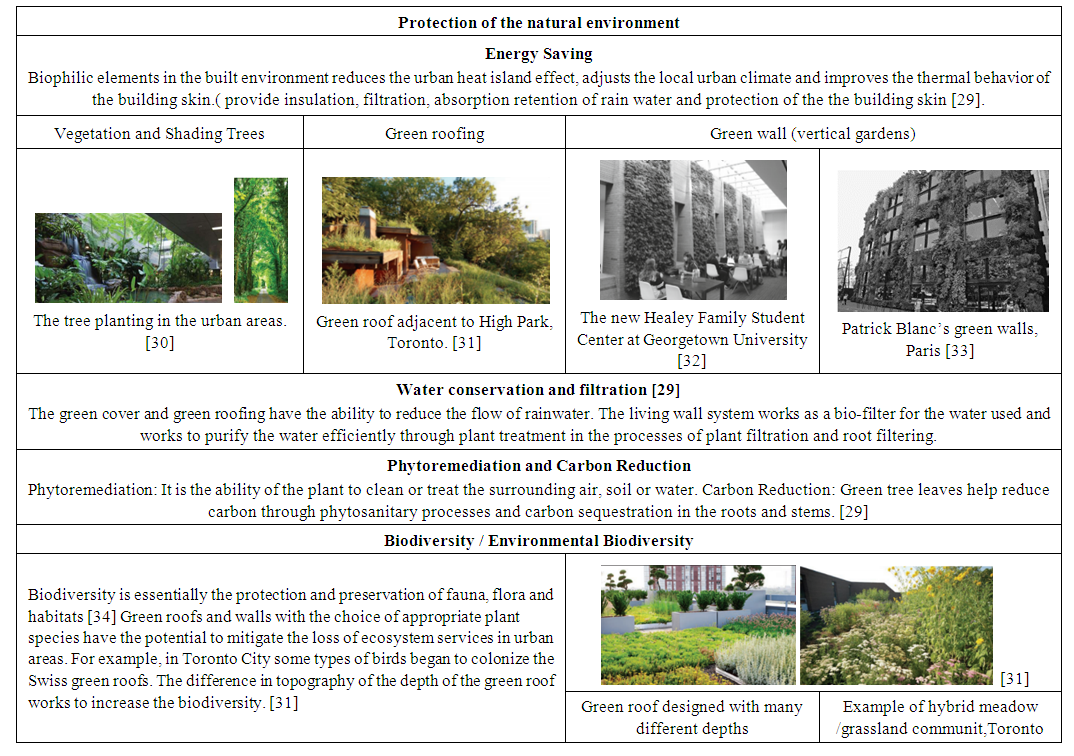 | Table 4. Natural Environmental Protection methods |
3.2.2. Natural Design for Human Wellbeing
- Biophilic helps to clarify how individuals interact with their environment through the link of health to nature in the built environment. Generally, there are 3 responses to health in biophila; cognitive, psychological and physiological. These responses which are reflected by nature on the human are important to the designer and planner. The theories of the relationships state that the landscape is a priority because it has an impact on the development of humanity, as its innate quality reflects the survival of humanity over time. [35] The Biophilic design achieves comfort for the inhabitants of buildings in addition to restorative and Well-Being methods by providing its elements of natural ventilation and natural lighting and the connection to the natural environment through openings and surfaces that allow the supply of fresh air and allow communication with the outside, achieving the psychological and biological comfort of man. There are different responses to man during the three categories of his relationship by nature; support of reduces stress, enhance cognitive performance in addition to better the emotion and mood. As such the previous energy saving methods of vegetated facades, shading, green roofing and others achieve thermal, visual and acoustic comfort, the provision of daylight, natural air and presence the indoor plants, and good landscape are all elements that achieve high quality internal environment. [29]
3.2.3. Integrating Nature into Urban Design and Planning
- All the elements of Biophilic are used at the level of regions, cites, neighborhoods, and building [35] to reach the natural, easily accessible, close daily contact and for all the people to achieve a peaceful and happy life. (Table 5) shows the different levels of the elements of Biophilic Urban Design across Scales. The types of natural elements in each part vary depending on the scale of attention. Urban nature has been used as a key strategy for building viability and flexibility in urban design and development. For example, the use of urban nature in Berlin (Germany), Toronto (Canada) and Chicago) USA) has turned each city towards the strategy of “Biophilic Urbanism”. It works to integrate nature in urban areas to provide people with regular experiences and useful nature. [38]
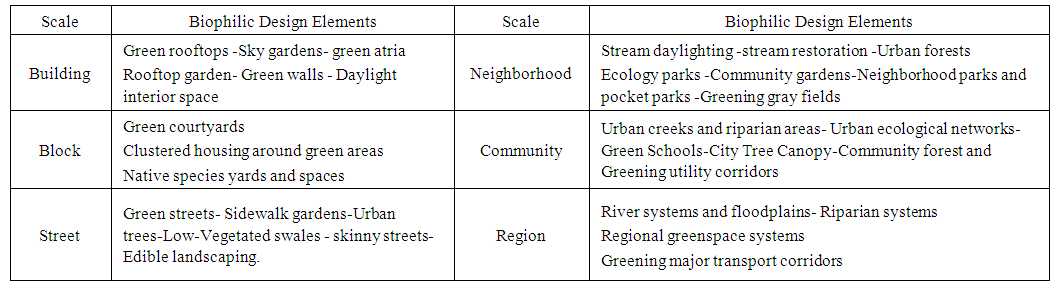 | Table 5. Biophilic Urban Design Elements across Scales [35] |
4. Results and Conclusions
- Sustainability is a principle of life and is derived from nature. Consequently, the principles of sustainable architectural design require strategies that have a common characteristic, which is the link to nature. Hence the research proposes a framework (Fig. 1) that links these principles with two strategies,the first is based on the principle of learning from nature to develop sustainable solutions by looking at nature as a model. This strategy is based on biomimic design. However, the second strategy is based on the principle of integrating nature in buildings and living spaces to make the people feel themselves in a natural environment. This strategy are based on the biophilic design. Hence, these strategies are implemented by a set of methods based on nature to form this framework. The proposed framework is an approach to architects,designers, innovators and decision makers to the comprehensive use of nature to achieve the sustainable principles in architectural projects and emphase that nature is the main source for achieving sustainability in architectural design.
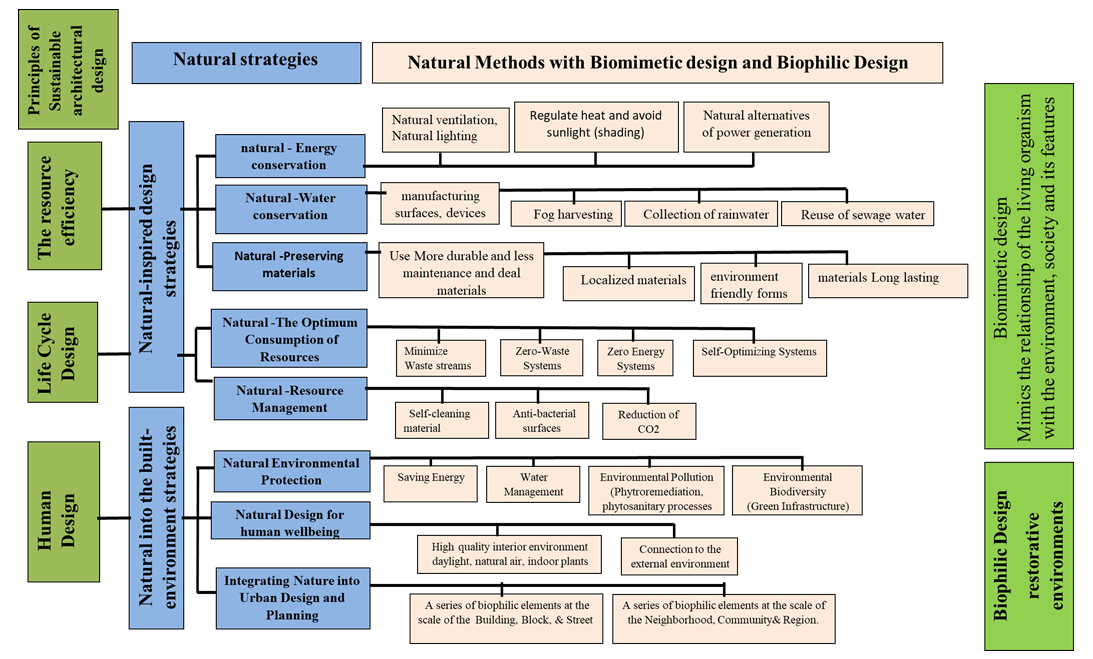 | Figure 1. Conceptual nature-based framework for sustainable architectural design |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML