-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Architecture Research
p-ISSN: 2168-507X e-ISSN: 2168-5088
2017; 7(3): 69-83
doi:10.5923/j.arch.20170703.02

Strategies for the Enhancement of Users’ Interactions in Al Mirqab Al Jadeed Street in Doha, State of Qatar
Mahmoud H. Al Saeed1, Raffaello Furlan2
1Architect, AAU (Jordan), Pursuing a Master’s in Urban Planning and Design, Qatar University, State of Qatar
2College of Engineering, Department of Architecture and Urban Planning, Qatar University, State of Qatar
Correspondence to: Raffaello Furlan, College of Engineering, Department of Architecture and Urban Planning, Qatar University, State of Qatar.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Al Mirqab Al Jadeed Street, with its unique mix of land use and geographical location, has become one of the most densely populated streets in Doha City, the capital of Qatar. Over the past few years, many establishments and transitional developments, such as various services, commercial malls, and the like, have altered Al Mirqab Al Jadeed’s urban characteristics. Moreover, this rapid development has overtaken urban spaces, leaving no place for green areas or proper urban furniture—and thus resulting in human social decay. This shortage of green areas has discouraged and diminished the quality of outdoor activity (whether in terms of walkability or social interaction) in the street, thereby affecting the quality of living, human health, social fabric, and surrounding neighborhoods. This research study investigates existing urban components (soft and hard) as well as green areas (pocket gardens, shading elements, footpaths, etc.) in the streets, considering their influence on human behavior from a social and environmental point of view. In doing so, it engages with issues of social sustainability and urban design in the context of local neighborhoods. A literature review was conducted of topics having to do with sustainable development (social sustainability) and principles of urban design, exploring the body of knowledge about sustainable development. Accordingly, site observation and analysis, together with in-depth interviews, have been adopted as the main research methods, so to highlight the street urban fabric while simultaneously enhancing quality of life and social interactions in Al Mirqab Al Jadeed Street. The findings of this study elucidate the connection between social sustainability and urban design standards, shedding light on the effect of built forms on user behavior and thereby contributing to the body of knowledge about socially sustainable development and urban design. In doing so, they support the application of theoretical knowledge on a practical level and in real-world scenarios.
Keywords: Al Mirqab Al Jadeed Street, Social sustainability, Urban design, Social interactions, Urban fabric, Doha, Qatar
Cite this paper: Mahmoud H. Al Saeed, Raffaello Furlan, Strategies for the Enhancement of Users’ Interactions in Al Mirqab Al Jadeed Street in Doha, State of Qatar, Architecture Research, Vol. 7 No. 3, 2017, pp. 69-83. doi: 10.5923/j.arch.20170703.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The GCC countries have been growing rapidly over a very short period: The discovery of “black gold” has led to explosive urban growth. The state of Qatar is in many ways no different from other GCC countries in having adopted its own economic strategies that aim to adapt to and indeed encourage rapid urban growth. In the 21st century, Qatar entered an era of modern urbanization, driven by the promise of greater oil production. (Fromherz, 2012; Jaidah & Bourennane, 2010; Jodidio & Halbe, 2015; Qatar, 2008; Salama & Wiedmann, 2013) This growth has also had negative effects, such as neglect of the natural environment as well as of well-being and quality of life within the built environment of Doha. (Furlan & Almohannadi, 2016; Furlan, Muneerudeen, & Khani, 2016; Furlan & Sipe, 2017; Furlan & Wadi, 2017; Furlan, Zaina, & Zaina, 2016) Al Mirqab Al Jadeed Street (MJ Street) is one of the major streets of the Al Mirqab district (Figure 1). The street was designed in the late 1980s to create a neighborhood for growing commercial and residential activities. In the period 2005–2017, several services and commercial establishments were also founded, such as the Doha Souq Mall and the Al Doha Clinic Hospital. The well-known Al Mirqab Shopping Mall is found along this spacious street, as are many other establishments. Various land uses can be seen giving rise to a rapidly expanding range of activities (residential, commercial, mixed-use, governmental services). The street fronts 12 housing units and 75 commercial establishments. (Authority, 2010) Almost 2,000 people live in the settlement, (statistics, 2015) of whom 61% are male and 39% female. Fully 60% of the total population is made up of employees, including both visiting workers and permanent residents.
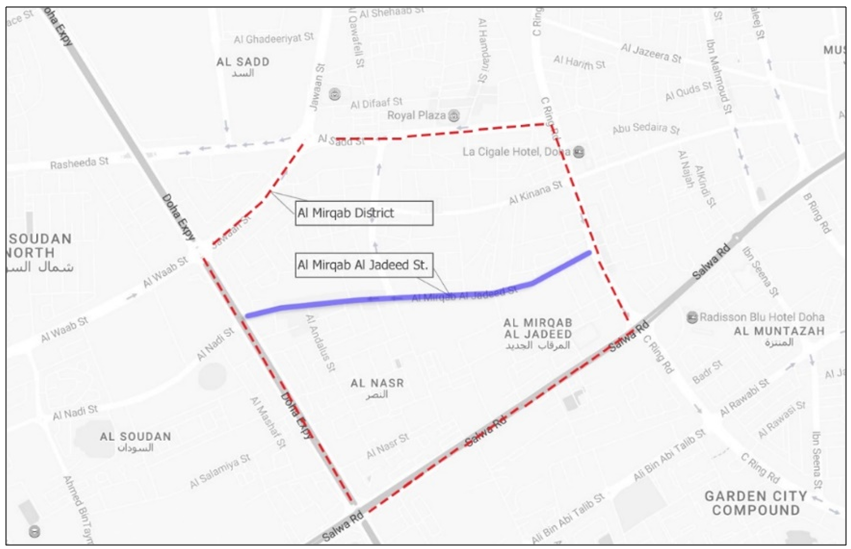 | Figure 1. Al Mirqab Al Jadeed Street within the Al Mirqab district limits (Source: Author, 2017) |
2. Background
- Social SustainabilityCities are geographical settlements inhabited by a group of people that fulfill the needs of their users either physically or psychologically even as the size of the settlement grows with its population (Stevenson, 2013). Today, 54% of the world’s population lives in urbanized areas (United Nations, 2016), This continuous population growth in urbanized areas has prompted concerns about cities’ ability to achieve self-sufficiency without abandoning user satisfaction or quality of life.Humans’ gregariousness gives rise to cities. At first in tribal and communal contexts, humans’ mutual support allowed the accumulation of surplus and the attendant formation of hierarchical societies that in turn supported consolidation into villages, towns, and eventually cities. (Brown & Dixon, 2014) Indeed, cities are places where emotions and sociological aspects are balanced. (Landry, 2006, p. 11)The definition of social sustainability is a point of contention among scholars, some of whom argue that it indicates the zone created by the intersection of economic growth, social development, and environmental protection:(First model: Intersected circles- the Venn model) Venn diagram suggests that there are potential positive-sum “win–win” calculations in the overlaps including areas outside that need periodization. If each of the circles is associated with the intersects of particular stakeholders/actors at whatever level of intervention, then the areas of overlap represent potential spheres of cooperation or partnership. (Meadowcroft, 1999)According to the Rio Declaration (1992), sustainable development is all about balancing and sustaining three-dimensional issues in all their interconnectedness so as to achieve a sort of process prioritization (Figure 2). (Manzi, Lucas, Jones, & Allen, 2010)
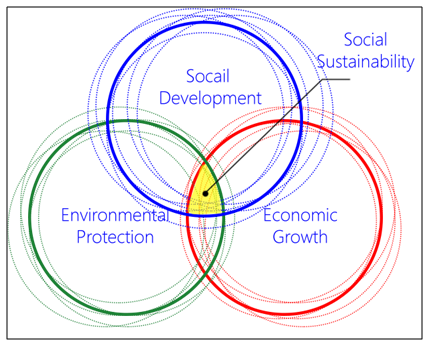 | Figure 2. A Venn diagram explains the circles of social sustainability (Source: O’Ridan, 1998) |
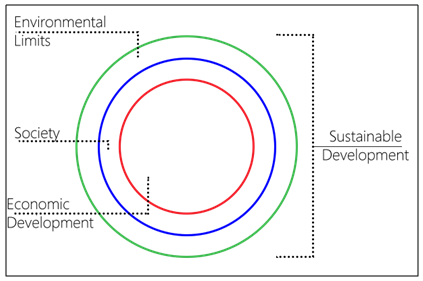 | Figure 3. Russian doll model of overlapping circles (Source: O’Ridan, 1998) |
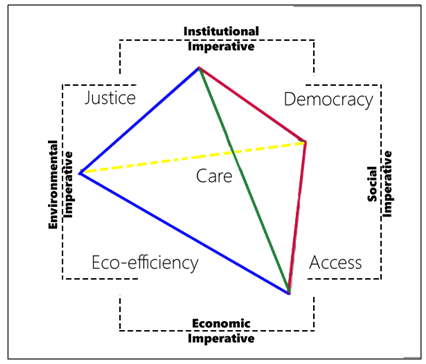 | Figure 4. The Jarvis model (Source: O’Ridan, 1998) |
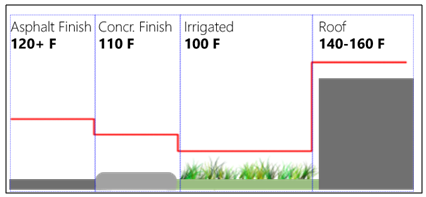 | Figure 5. Temperature differences for different surface materials |
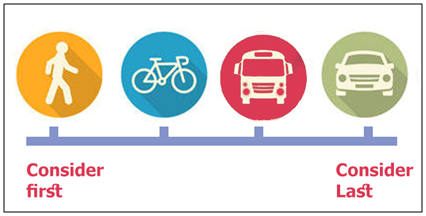 | Figure 6. Transportation prioritization chart explaining the Priority of each type of transportation (Source: NACTO, 2016) |
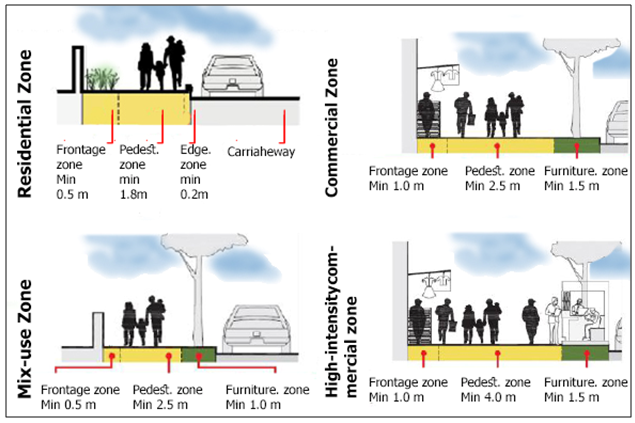 | Figure 7. Pedestrian walkway dimensions (Source: NACTO, 2016) |
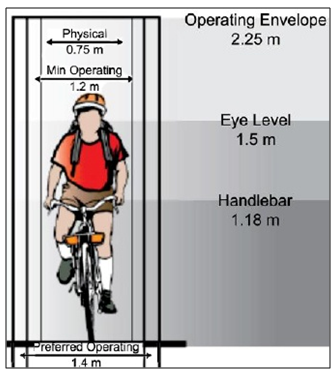 | Figure 8. Cycle tracks dimension (Source: NACTO, 2016) |
3. Methodology
- According to Schindler and Cooper (2011); Ghauri and Gronhaug (2005); Dawson (2002) that research is a scientific and systematic search for relevant information on a specific topic. In other words of Schindler and Cooper (2011) that research is “a process through which a researcher will make plans and strategies in order to answer the research questions and achieve objectives of the research”. This research paper examines the relationships between the physical and nonphysical aspects of built form, investigating their influence on the inhabitants of a location, for that purpose the authors uses quantitative methods to assess the data collected from various sources related to the chosen research subject and point of interest, the type of collected data focuses on numbers and statistics which has been collected by the authors as a primary source of data nevertheless government annual statistics used as secondary type of data. In order to collect such data a period of four months (January-April, 2017) was dedicated for that purpose.Al Mirqab Al Jadeed Street was chosen as the research area for its major role in the local economy. Its location makes it one of the mostly densely populated, and thus most desirable, streets for multipurpose use. In sum, this research employs three kinds of data collection and analysis (Figure 9).
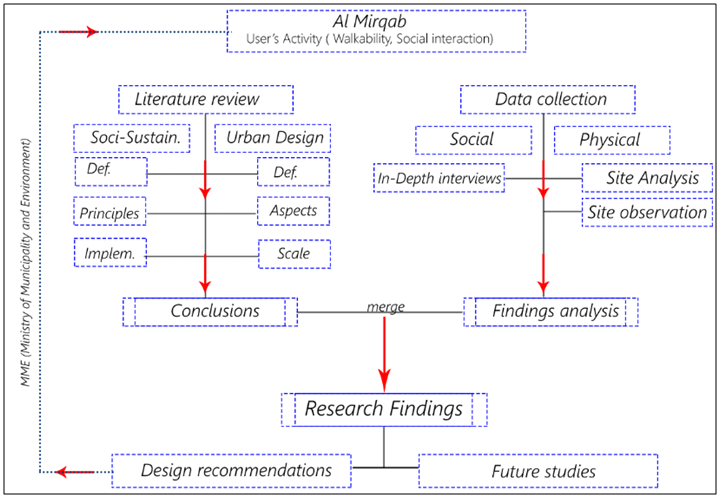 | Figure 9. Overall process chart (Source: Authors, 2017) |
4. Findings
- This section relates to the research findings by revisiting the researched points of interest and answering the questions that arose, as well as by examining the hypotheses through an analysis of the collected data. It also reflects on the literature and suggests a scope for further research into the subject under investigation. Site analysisThe Study AreaThe street encompasses 77 establishments accommodated by approximately 155.5 acres of land on a stretch, 1.75 km long. MJ Street includes major establishments such as Doha Souq Mall, Al Mirqab Mall, the Doha Clinic Hospital, 25 service agencies, and more than 20 restaurants. MJ Street divides Al Mirqab district into the Al Naser and Al Mirqab Al Jadeed sub-districts, connecting C Ring Road with the Doha Expressway (Figure 10).
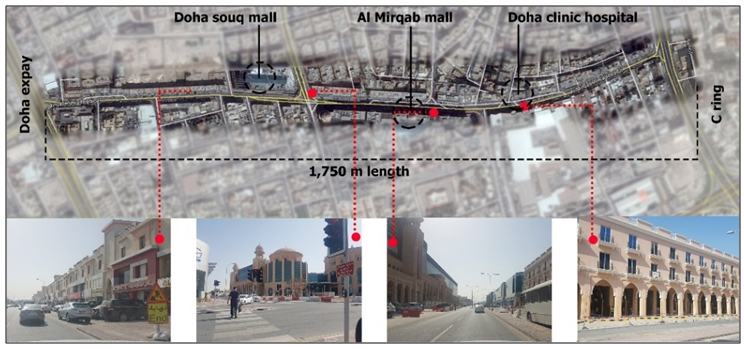 | Figure 10. MJ Street geographical parameters and location (Source: Author, 2017) |
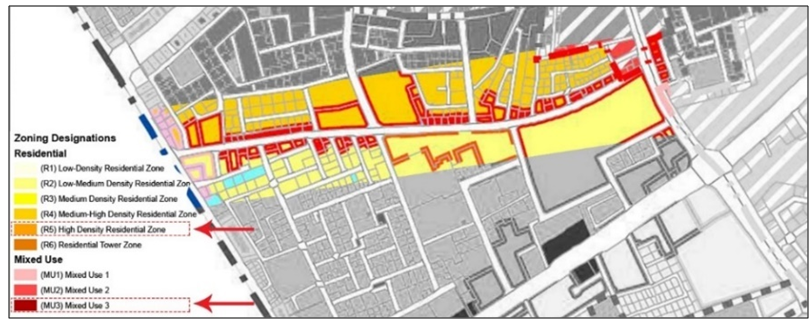 | Figure 11. Land use classification along MJ Street (Source: MME, 2015) |
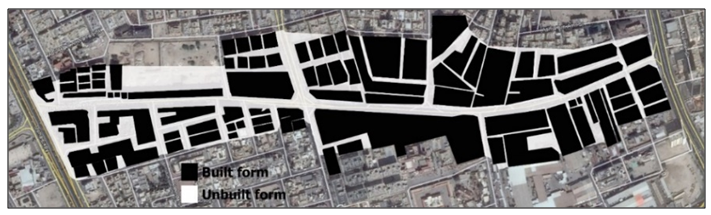 | Figure 12. Built form density solid and void ratio (Source: Author, 2017) |
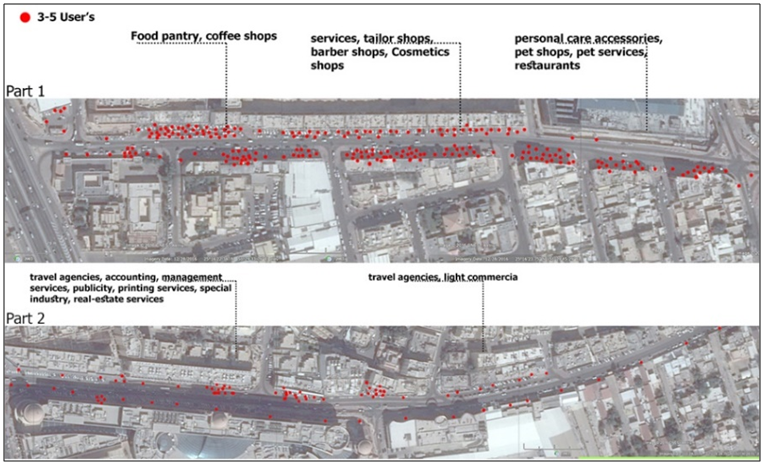 | Figure 13. Pedestrian density across MJ Street (Source: Author, 2017) |
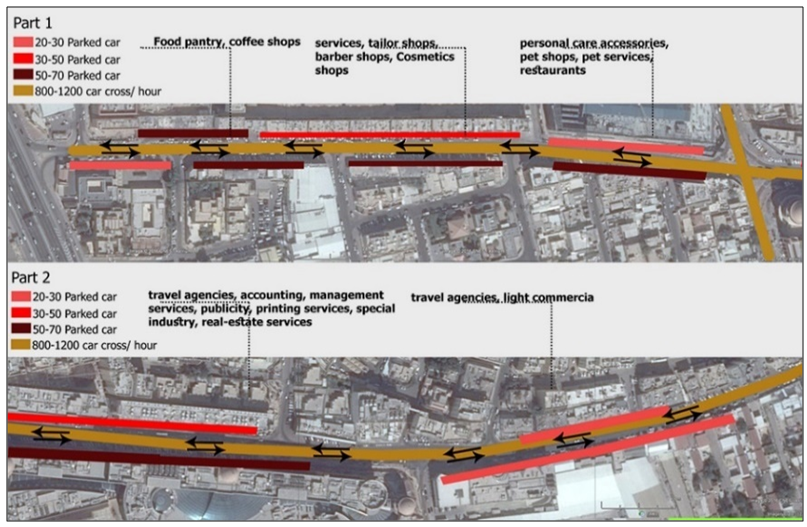 | Figure 14. Vehicular density and movement directions across MJ Street (Source: Author, 2017) |
 | Figure 15. Vehicular encroachment on pedestrian paths (Source: Author, 2017) |
 | Figure 16. Monitoring the availability of both hardscape and softscape (Source: Author, 2017) |
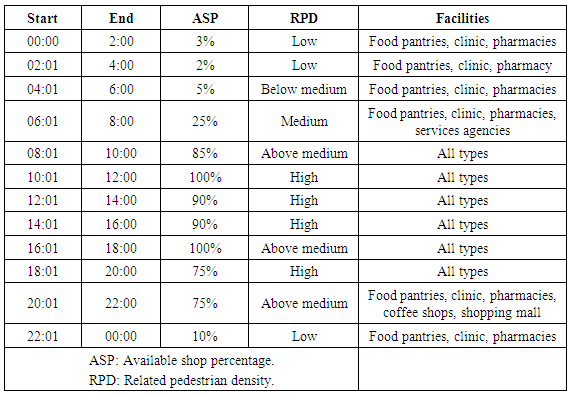 | Figure 17. Daily operating hours (Source: Author, 2017) |
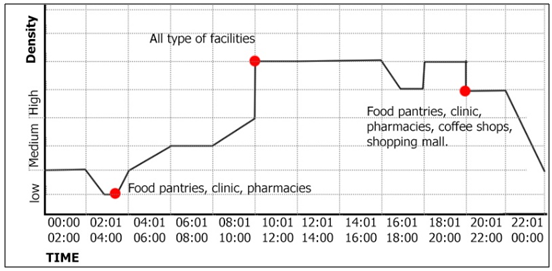 | Figure 18. The daily life cycle of the street (Source: Author, 2017) |
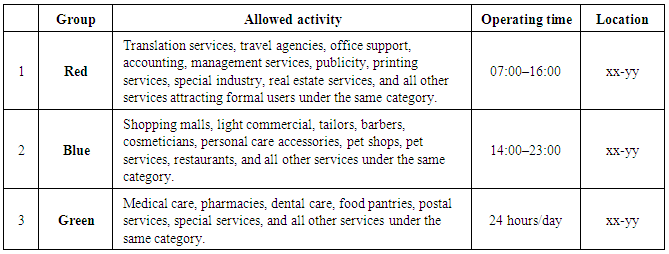 | Figure 19. Group categorization (Source: Author, 2017) |
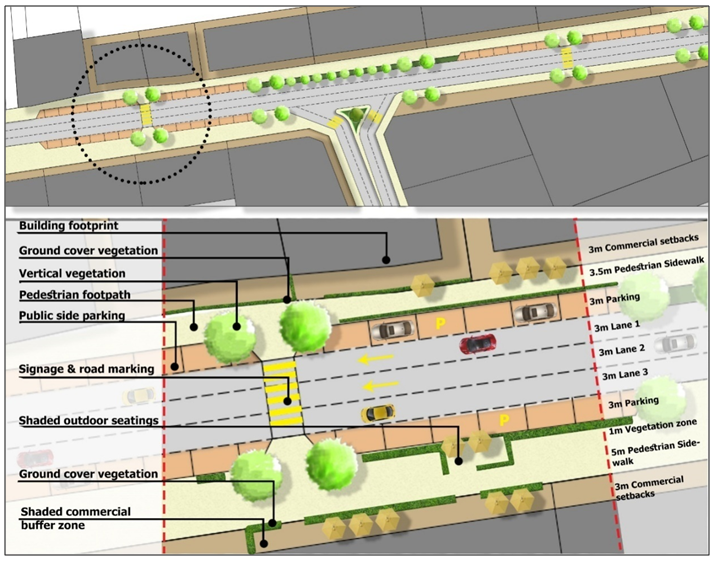 | Figure 20. Proposed circulation on MJ Street (Source: Author, 2017) |
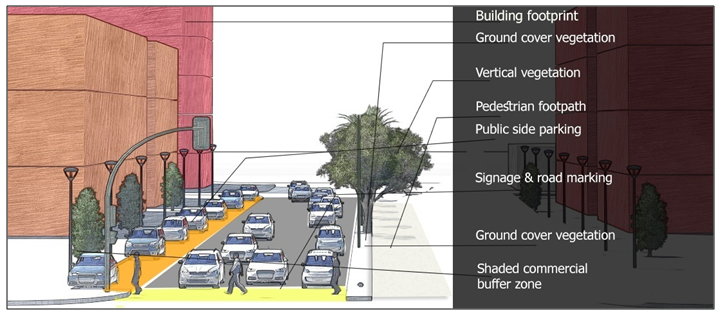 | Figure 21. Perspective drawing demonstrating proposed strategies for MJ Street (Source: Author, 2017) |
5. Conclusions and Discussion
- This section summarizes the discussions, which have been generated mainly from the literature, site analysis, and data analysis, as well as proposed strategies for addressing the research problems. These decisions are layered, beginning with current issues and continuing to affect the role of government—always linked to the proposed methods of treatment of MJ-street.The social characteristics of MJ Street have placed it in a complicated situation in which interactions between inhabitants and built forms occur at the lowest level, with limited consideration for the availability of ways of enhancing the street as well as inhabitants’ quality of living. Accordingly, the social sustainability of the street should be explored, enhanced, and raised with the aid of the main pillars of social sustainability: environment, economic, and social development. Such integrated strategies comport with the thrust of the Qatar National Vision (QNV) for 2030 by placing the responsibility for accomplishing this on governmental institutions. Institutional bodies, following governmental agendas, should address changes in long-term alignment, carried out at all levels—both physical and institutional. In particular, a proper agenda will emphasize the role of the street in the state’s plans while also considering components of proper urban design and relevant environmental standards. Because urban design seeks to develop functional and sustainable settlements according to measurements that go beyond merely contemporary issues, responsible design strategies for MJ Street should consider the characteristics of the street, including its commercial and residential activity, prioritizing the human scale and paying attention to pedestrian needs and behaviours. Such design standards should also consider the environmental aspects of enhancing residential activities and must include pathway design, city furniture, and green areas as elements increasing the quality of life for street inhabitants and visitors. Informing the development and enhancement of the quality of the street and residences alike, data obtained through site analysis, observation, and in-depth interviews —both social and physical—highlight three systematic recommendations. First, considering the social pattern of commercial activity, the authors propose a method for reducing the influence of such activity on users. Second, they consider issues of accessibility and vehicular congestion in the street. Third, they consider environmental aspects such as vegetation and inhabitant health.
6. Contribution to Knowledge
- Because issues of social sustainability and urban design have failed to attract suitable levels of attention from local scholars, gaps have arisen in the research. Accordingly, this paper investigates the relationship between social sustainability and urban design standards in the state of Qatar with an eye to translating theoretical knowledge into applicable principles of urban planning. In doing so, it will help close the gaps in knowledge related to Qatar and GCC countries.
7. Implications for Practice and Advancement of Research
- This paper could be further expanded to urban planning, urban design, social development, and environmental engineering. Urban design and social development chiefly focus on the relationship between built and unbuilt forms with an eye to creating healthy, sustainable communities for current and future generations.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- Mahmoud H. Al Saeed has 5 years’ experience working as an architect and as a green building specialist, with 3 years served in the gulf region and 2 in Jordan. He has a LEED GA certificate, a CGP certificate, and an UPDA certificate for practice as an architect and has been a member of GORD (the Gulf Organization of Research and Development — QA1669 001858) since 2014. Dr. Raffaello Furlan holds Bachelors and Masters Degrees from IUAV University in Venice (Italy), and a PhD in Architecture from Griffith University in Brisbane (Australia). He has held visiting and permanent positions in Australia (University of Queensland and Griffith University in Brisbane), UAE (Canadian University of Dubai) and Qatar (Qatar University). He has been teaching Art History, History of Architecture, Project Management, Urban Design, Architecture Design and Interior Design. His areas of interest include Vernacular Architecture, Architecture and Urban Sociology, Project management, Art History. Member of the Board of Architects in Italy and Australia, he has 20 years professional experience, split between design management, project management and supervision roles, with some highly respected companies, 6 years of which were in Italy, 10 years in Australia, and 4 years in Middle East. He is an assistant professor in the Department of Architecture and Urban Planning (DAUP) at Qatar University. This research study was developed as an assignment as part of the core course Research and Statistical Analysis in Planning (MUPD601, Spring 2017) taught by Dr. Raffaello Furlan at Qatar University, College of Engineering, Department of Architecture and Urban Planning (DAUP), for the Master’s in Urban Planning and Design (MUPD) program.The authors would like to acknowledge the support of Qatar University in creating an environment that encourages scientific research. Also, they express their gratitude to the government of Qatar, namely to the Ministry of Municipality and Environment (MME), for providing relevant visual data and cardinal documents to aid the purpose of this research study. Finally, the authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their comments, which have improved the quality of this paper. The authors are solely responsible for the statements made herein.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML