-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Architecture Research
p-ISSN: 2168-507X e-ISSN: 2168-5088
2015; 5(3): 89-96
doi:10.5923/j.arch.20150503.01
Chinese Architects’ Awareness of, and Attitudes towards, Low-Carbon Architectural Design
Xia Bing , Chen Yi
College of Architecture and Urban Planning, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
Correspondence to: Xia Bing , College of Architecture and Urban Planning, Tongji University, Shanghai, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Environmental issues have drawn increasing attention in China, and consequently low-carbon architectural design has become more in demand. By analyzing the results of a questionnaire survey, this paper aims to investigate Chinese architects’ perception of low-carbon design, their current design practices as well as their expectations of future developments. From September to November in 2014, 168 Chinese architects participated in an online survey for this study. The findings suggest that although the awareness of low-carbon issue is relatively strong, Chinese architects confront many barriers in practice by the lack of design methods appropriate for local circumstances of architectural practice. The paper concludes that crucial for improving the status of low-carbon design in China is to integrate existing technologies with design methods.
Keywords: Low-carbon architectural design, Design methods, Chinese architects, Questionnaire survey
Cite this paper: Xia Bing , Chen Yi , Chinese Architects’ Awareness of, and Attitudes towards, Low-Carbon Architectural Design, Architecture Research, Vol. 5 No. 3, 2015, pp. 89-96. doi: 10.5923/j.arch.20150503.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Environmental problems are an important issue around the world. In 2009, the Chinese State Council committed to reduce 40 to 45% of carbon emissions per unit of GDP by 2020 (compared with 2005) [1]. According to the carbon emissions prediction curve [2] as shown in Figure 1, it can be easily noted that the task and pressure for China's carbon emissions reduction are still enormous. Between 2008 and 2050, the proportion of China's urban population will rise from 46.4% 75%. This means there are still 400 million people who will migrate into cities from rural areas [3]. In the construction sector, every year about two billion square meters of new buildings are completed; this figure accounts for nearly half of the world’s new construction [4]. It will consume about 40% of global cement and steel production [5]. The final energy consumption of the construction industry accounts for 27.5% of the country’s total energy consumption, and will gradually increase to around 40% [6]. These realities make the reduction of carbon emissions more difficult. Since 2002, with every 1 percent increase in the proportion of urban population, carbon emissions have risen by 414 million tons (correlation coefficient of 0.995) [7]. The reducing carbon emissions in the building industry is of great importance in achieving the national carbon reduction goal; in this, the architect plays a key role and assumes major obligations. In view of this, it is necessary to carry out investigations on the design practices of Chinese architects to understand the current status of China's low-carbon building design. Results of the data and statistical analysis in this survey will serve as groundwork and guidance for the future low-carbon design research and provide strategies for reducing carbon emissions. After the relevant literature reviews, this paper reports on an investigation using an online questionnaire that dealt with three aspects: low-carbon consciousness, the current design situation, and the expectations and vision of architects.
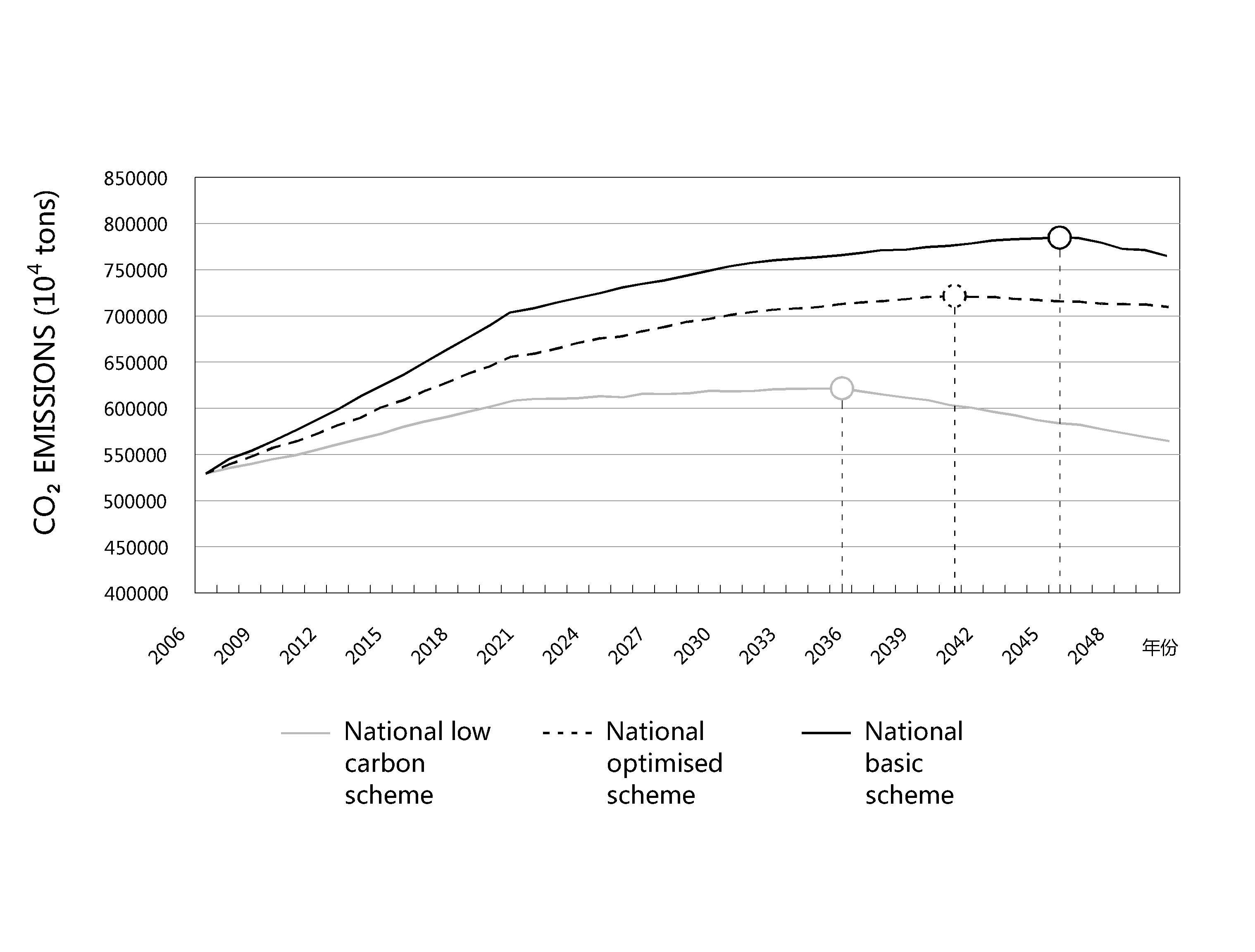 | Figure 1. China’s carbon emissions prediction curve |
2. Previous Research
2.1. General Condition and Trend of Low-carbon Building in China
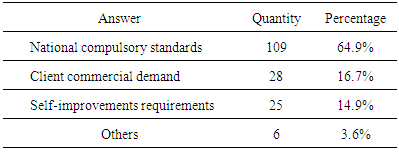
- In China, the time is ripe for promoting large-scale construction of low-carbon building. First, low-carbon and energy-efficient buildings are entering a period of rapid development. According to the 12th National Five-Year Plan, the total of new green building area will reach 8.0×108 m2. By the end of 12th Five-Year Plan, more than 20 percent of new urban buildings will meet green building standards and 20 percent of cities will have begun to plan and/or build various types of eco-city. Second, a social consensus on the development of low-carbon building has come into being, with flourishing and diverse education and outreach activities advocating low-carbon life. Third, China has established a three-level system of standards and management systems: master plan (e.g. Five-Year Plan), indicator requirements (e.g. Green Building Evaluation Standard and Public Building Energy Efficiency Design Standards), and implementation guidance (e.g. China Ecological Residential Technology Assessment Manual and Green Olympic Construction Implementation Guide). Fourth and finally, the solar PV, LED, and other green technology industries are steadily developing, strongly supporting the development of low-carbon buildings [8] [9] [10]. On the negative side, there are three main obstacles to the development of low-carbon buildings: 1) Various climates and building energy-use types in different regions have led to discrepancies in the degree of acceptance of low-carbon buildings, e.g. there are more areas of hot summers and cold winters than areas of severely cold winters where heating must be provides [10]. 2) Some implementations and adoptions of green low-carbon technologies are not satisfied, e.g. there is underutilization of solar water heating systems and adjustable external shading. At the same time, some low-carbon building equipment is not running as designed because of design defects such as shading of solar panels [11]. 3) For the architect, traditional design processes, the lack of multi-disciplinary cooperation methods, and insufficient knowledge constrain the achievement of low-carbon building design [12].
2.2. Current Condition Analysis on Architects’ Design
- Architects play an important role in the development of low-carbon buildings, so many scholars have conducted research related to architectural design practices and methods. As a survey on Australian architects reflects, although most architects consider low-carbon technologies to be important criteria for judging the success of contemporary architecture, they often are not expressed in virtual design practices. Reasons for this include architects being unfamiliar with the basic principles and methods for low-carbon building design. Other factors include the design process, economics, aesthetics, etc., which often overwhelm the importance of low-carbon goals, hence low-carbon is not deemed as the dominant factor of shaping design concepts [13] [14] [15]. A survey also showed that the main drivers of low-carbon buildings are regulations, clients, and the desire to improve the design competency of architects themselves.Another study on the integration of solar architecture design revealed that architects, when facing new technologies, currently lack innovative design methods in the concept stage [17].
3. Research Methods
3.1. Layout of Questionnaire
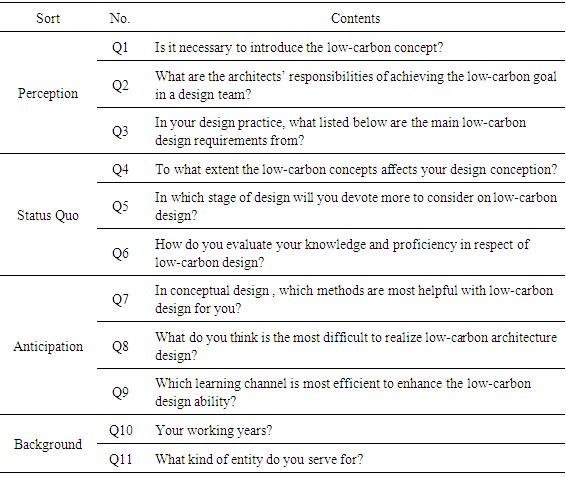
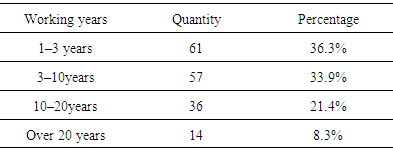
- Based on the literature noted, we based our research on three aspects: lower design perception, the status quo of low-carbon design, and lower design expectations. We hope through these three aspects of investigation to acquire a better understanding of the status of China's low-carbon building design.The questionnaire consisted of 11 closed-end questions, divided into four groups (Table 1). Questions 1–3 mainly addressed the first aspect. Questions 4–6 were designed to measure the status of low-carbon design to address the second aspect. Questions 7–9 responded to third aspect. Two background questions (10 and 11) took the architects’ professional experience and the types of units they serve as variables to enable further analysis of the data obtained.
|
3.2. Distribution and Sampling
- The survey was distributed online and completed surveys were collected. Specific steps were: create an electronic questionnaire on a professional survey web page (www.wenjuan.com), send architects the address of web page by email, after receiving a confirmation. These architects were randomly selected from a list of recent participants in ongoing education at the College of Architecture and Urban Planning, Tongji University. Between September and November 2014, a total of 168 Chinese architects responded to our questionnaire, most of whom come from the major cities of China and various municipalities, including Shanghai, Nanjing, Hangzhou, Beijing, Wuhan, Guangzhou, Kunming, Lanzhou, etc.Two factors could have affected the outcome of the investigation. First, the respondents were from China's major cities, which may affect the nationwide representativeness of the conclusions. The level of metropolitan architects’ education and professional capacity are generally higher than that those of medium and small cities. Second, architects who have little interest in this issue may not have replied. This self-selection bias may have introduced some discrepancy between the statistical data and the actual situation.
3.3. Data Collection and Analysis Methods
- The questionnaire web page had easy access to data processing and data analysis tools. After each interviewee completed all the questions, the answers were automatically rendered into a data chart. Cross-table analysis was used here to determine distribution and correlation, taking the answers of every two questions as variables.
4. Analysis
- As shown in Table 2, of the 168 architects surveyed, most were young architects of around 10 working years, in which 61 (36.3%) has 1–3 years of work experience, 57 (33.9%) 3–10 years; among those with more than 10 years of experience, from 10 to 20 years are 36 (21.4%), more than 20 years accounting to 14 (8.3%).
|
|
4.1. Consciousness of Low-carbon Design
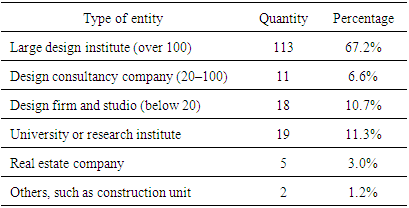
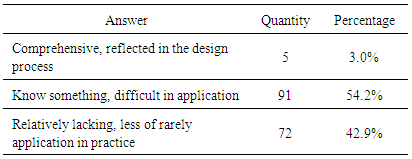
- The survey data showed that Chinese architects have a strong sense of responsibility for low-carbon design. More than 90 percent of the architects believed that the introduction of low-carbon ideas is necessary. On the contrary, only about 5 percent think it unnecessary, and about 4 percent gave a noncommittal answer. (Table 4)
|
|
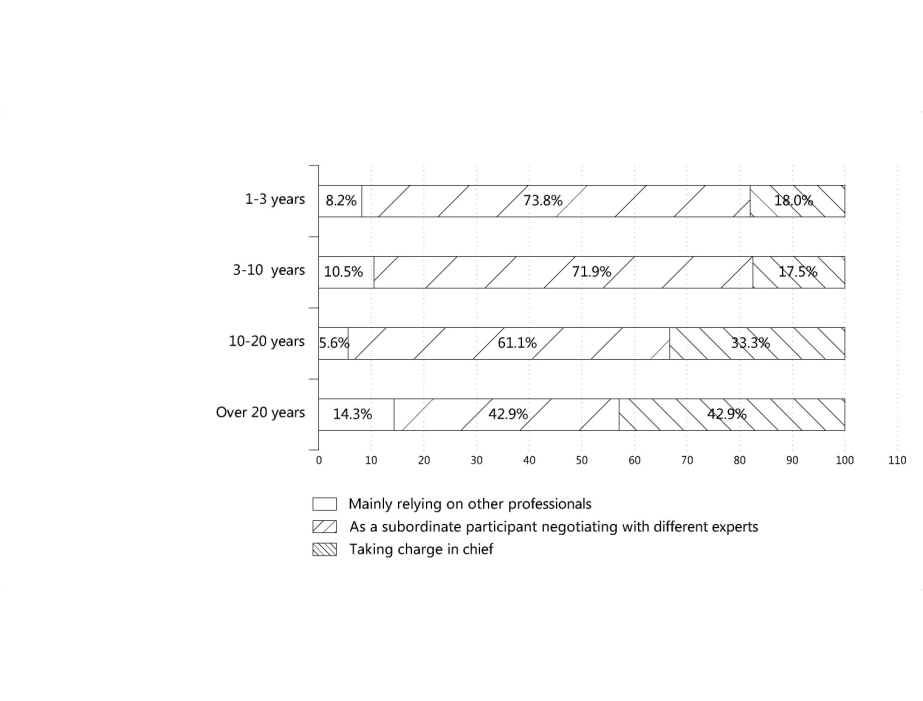 | Figure 2. Cross-tabular analysis between Q2 and working years |
|
4.2. Status Quo of Low-carbon Design
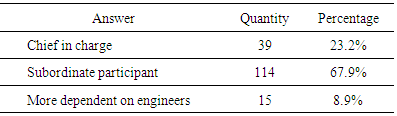
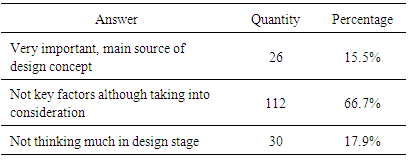
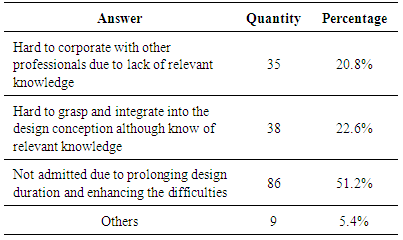
- In the concept design, two-thirds of the architects took low-carbon issues into consideration, but not as the determining factor; only 26 respondents (15.5%), deemed low-carbon design as the primary design factor and viewed it as a starting point of design creation. The number who said they do not consider low-carbon at all was 30 (17.9%) (Table 7). As apparently implied in Figure 3, architects’ involvement and regard has a direct relationship to their consciousness of the role in the low-carbon design, but only 10 interviewees thought that architects should take the main responsibility for low-carbon design and implement it in concept.
|
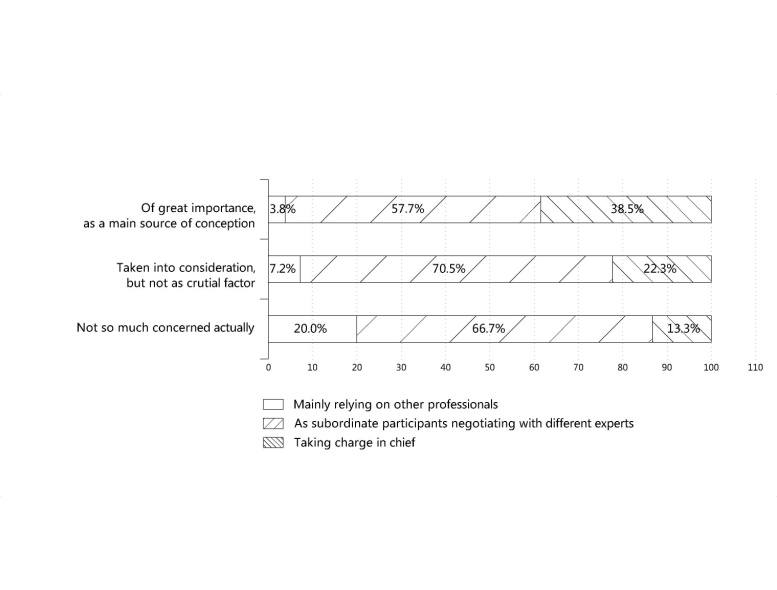 | Figure 3. Cross-tabular analysis of Q2 and Q4 |
|
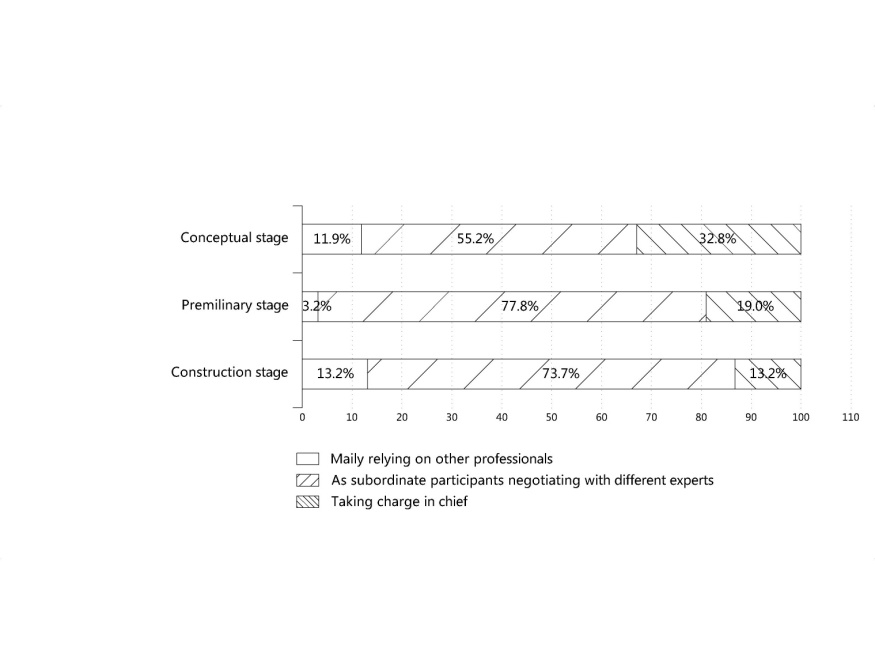 | Figure 4. Cross-tabular analysis of Q2 and Q5 |
|
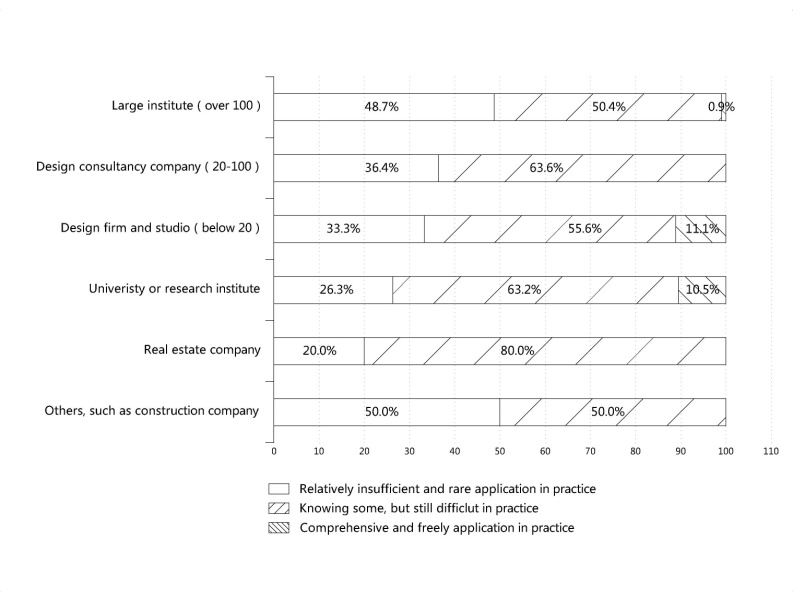 | Figure 5. Cross-tabular analysis of Q6 and Q11 |
4.3. Anticipation of Low-carbon Design
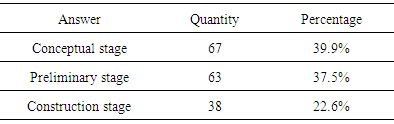
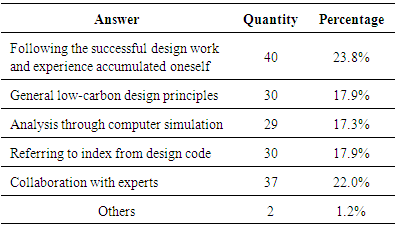
- The third part was to comprehend the architects’ expectations for low-carbon design from the perspectives of design tools and methods, design difficulties, and design education.Table 10 shows that each of the five listed design methods and tools has practically the same popularity. Reference to successful design cases (23.8%) and collaboration with energy experts (22.0%) were slightly more popular than the remaining three: reference to index (17.9%), BIM software (17.3%), and following general design principles (17.9%). This reflects that the analogy approach (case reasoning) describes most architects’ thinking characteristics, which have a greater value in use. It is also noticeable that various design tools and methods were used in various design stages instead of only one. Even within a stage, various methods were used to compare, analyze, and confirm with each other.
|
|
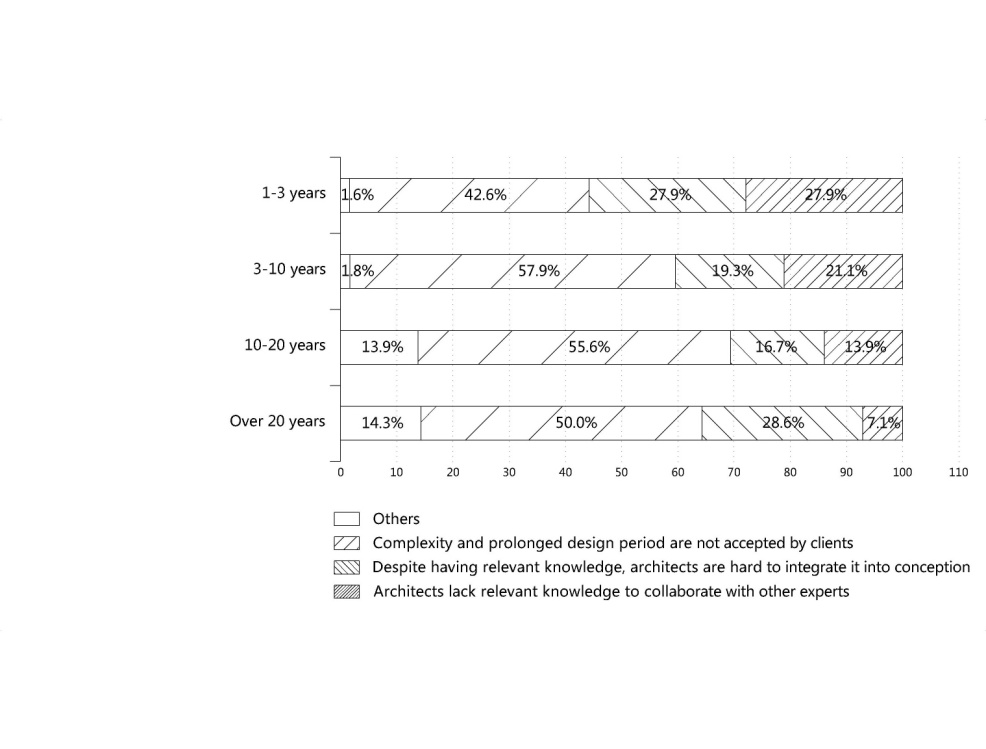 | Figure 6. Cross-tabular analysis of Q8 and working years |
|
5. Conclusions
- The following conclusions can be drawn from the above analysis:1) The development trend of China's low-carbon buildings has been good, and is advancing to a higher, better degree.2) Even though Chinese architects have a strong awareness of design for low-carbon energy (even stronger than their colleagues in developed counties [14] [20] [21]), in the design practice, especially the concept design stage, they still encounter many obstacles, mainly due to the lack of good design methods that are suitable for working architects. This is also a common problem for architects worldwide who practice low-carbon architectural design [16] [17] [20].3) The key to improving the situation of low-carbon design in China relates to combining innovative design methods with existing techniques and to find the appropriate ways to apply those methods and techniques.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Sincere thanks to the architects who participated in our survey, and to the NSFC (National Natural and Science Foundation of China) who funded this research, project approval No. 51278338.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML