Dorrah Azis, Agus Sutrisno, Desfan Hafifullah, Subian Saidi
Department of Mathematics, University of Lampung, Lampung, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Agus Sutrisno, Department of Mathematics, University of Lampung, Lampung, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
Generally, the order of integral and derivative are connected with the real numbers, such as the first, second, third and more order of integral and derivative. This study aims to develop a theory of an integral or derivative which has order in a 5th order function and exponential function by using Riemann and Liouville method. The result of this study showed that the fractional derivative of order 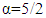 in the 5th Order Function using Riemann-Liouville Method is the same as the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa. In addition the fractional derivative of the exponential function using the Riemann-Liouville Method is equal to in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function.
in the 5th Order Function using Riemann-Liouville Method is the same as the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa. In addition the fractional derivative of the exponential function using the Riemann-Liouville Method is equal to in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function.
Keywords:
Fractional Integral, Fractional Derivative, 5th Order Function, Exponential Function, Riemann-Liouville Method
Cite this paper: Dorrah Azis, Agus Sutrisno, Desfan Hafifullah, Subian Saidi, The Use of Fractional Integral and Fractional Derivative α=5/2 in the 5th Order Function and Exponential Function Using the Riemann-Liouville Method, Applied Mathematics, Vol. 11 No. 2, 2021, pp. 23-27. doi: 10.5923/j.am.20211102.03.
1. Introduction
Calculus is a branch of mathematics that studies the concept of calculating limits, changes in functions, derivatives, integrals and infinite series. In calculus, a function can undergo integrals and derivatives either once, twice, and so on with natural number orders. Then a question arises related to the order of fractions, for example, how are the integral and intermediate derivatives of the function, so that a material development is born, namely fractional calculus. Fractional calculus appeared almost simultaneously with classical calculus set. This is because in theory the fractional calculus is the basis for the expansion of the gamma and beta functions. On September 30, 1695, fractional calculus was first introduced in the writings of Leibniz who at that time sent a letter to L'hopital about how a derivative of a function that has a fraction order [DS]. The fractional calculus provides the answer to the question whether the operation of derivatives of integers of order 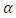 and
and 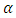 is not an integer? Many mathematicians participated in his contributions such as Abel, Riemann, Liouville, Euler, Laplace, Lacroix, Fourier. In 1819, Lacroix became the first mathematician to write a paper on the definition of fractional derivatives, he started from the function
is not an integer? Many mathematicians participated in his contributions such as Abel, Riemann, Liouville, Euler, Laplace, Lacroix, Fourier. In 1819, Lacroix became the first mathematician to write a paper on the definition of fractional derivatives, he started from the function 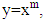 where
where 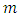 is a positive integer.The functions used in fractional derivatives are factorial functions using the gamma and beta function approaches, expressed in the Legendre symbol
is a positive integer.The functions used in fractional derivatives are factorial functions using the gamma and beta function approaches, expressed in the Legendre symbol 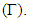 Not only for power functions, fractional calculus can also be developed in other functions such as trigonometry, Laplace, exponential, and exponential algebra with various working methods. The working method in fractional calculus has versions including Riemann-Liouville, Grundwald-Letnikov, M. Caputo (1967), Oldham and Spanier (1974), K.S. Miller and B. Ross (1993), Kolwankar and Gangal (1993). The method that is often used in fractional calculus is the Riemann-Liouville and Caputo method. Based on the above background and problems, the author will examine more deeply about fractional integrals and fractional derivatives using the Riemann-Liouville method with the order
Not only for power functions, fractional calculus can also be developed in other functions such as trigonometry, Laplace, exponential, and exponential algebra with various working methods. The working method in fractional calculus has versions including Riemann-Liouville, Grundwald-Letnikov, M. Caputo (1967), Oldham and Spanier (1974), K.S. Miller and B. Ross (1993), Kolwankar and Gangal (1993). The method that is often used in fractional calculus is the Riemann-Liouville and Caputo method. Based on the above background and problems, the author will examine more deeply about fractional integrals and fractional derivatives using the Riemann-Liouville method with the order 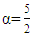 on the 5th power and exponential function.
on the 5th power and exponential function.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Polynomial Methods
According to [CS], polynomial functions are functions that have many terms in the independent variable. The form of the polynomial function equation is as follows: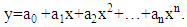 | (1) |
2.2. Exponential Functions
According to [JM], exponential function is a function with the independent variable being the power of a constant, inverse 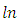 is an exponential function and is represented by
is an exponential function and is represented by 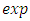 with the following definition:
with the following definition: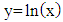 | (2) |
with inverse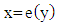 | (3) |
2.3. Fractional Integral
Definition 2.3According to [HR], based on its work, the fractional integral has various methods, such as Riemann, Liouville, Riemann-Liouville, Caputo and others. Fractional integrals are defined as follows: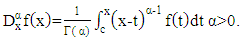 | (4) |
if 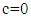 in Equation (4), then the Riemann-Liouville fractional integral is obtained which is defined as:
in Equation (4), then the Riemann-Liouville fractional integral is obtained which is defined as: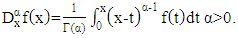 | (5) |
According to [BN], for 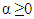 and
and 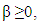 fractional integral has the following properties:
fractional integral has the following properties: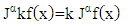 | (6) |
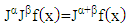 | (7) |
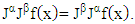 | (8) |
2.4. Fractional Derivative
Definition 2.4According to [KM], the Riemann-Liouville fractional derivative is defined as: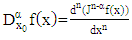 | (9) |
or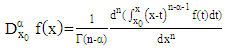 | (10) |
with 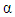 of any order,
of any order, 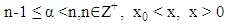 and
and 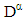 operator of the fractional derivative of order
operator of the fractional derivative of order 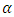 . The properties of the fractional derivative by [JG] is:
. The properties of the fractional derivative by [JG] is: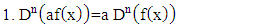 | (11) |
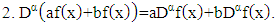 | (12) |
The method used in this research is carried out by primary literature studies, namely developing theories that have been worked on by previous researchers, literature study, namely studying text books in the Mathematics Department library and the University of Lampung library, journals and internet access that support the research process.The procedure in the Riemann-Liouville method is:1. The form of the equation for the powers of five and the exponential.2. Choose 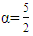 for the respective order integrals and derivatives.3. Formulate fractional integrals and fractional derivatives in the quadrangle and exponential equation.4. Perform operations for each term in the equation.5. After obtaining the results of the integral and its derivatives substitute it to the initial equation form.6. Replace the value in each of the equation variables with the number one (option).
for the respective order integrals and derivatives.3. Formulate fractional integrals and fractional derivatives in the quadrangle and exponential equation.4. Perform operations for each term in the equation.5. After obtaining the results of the integral and its derivatives substitute it to the initial equation form.6. Replace the value in each of the equation variables with the number one (option).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Fractional IntegralForm of 5th Order Function α Order
Fractional integral order 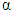 from the polynomial function according to Riemann-Liouville can be stated as the multiplication form of gamma function and polynomial function. The general fractional integral form
from the polynomial function according to Riemann-Liouville can be stated as the multiplication form of gamma function and polynomial function. The general fractional integral form 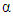 order with the polynomial function
order with the polynomial function 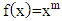 for
for 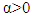 and
and 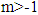 is:
is: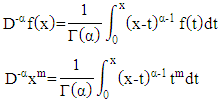 For example:
For example: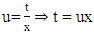 then
then 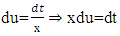 when
when 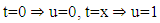 So, the general form of fractional integral
So, the general form of fractional integral 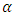 order from the polynomial function
order from the polynomial function 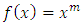 is:
is: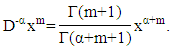 So that the fractional integral with
So that the fractional integral with 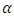 order from the polynomial function which form is
order from the polynomial function which form is 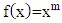 can be stated as a multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function which is stated in the Theorem 3.1.Theorem 3.1Fractional integral with
can be stated as a multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function which is stated in the Theorem 3.1.Theorem 3.1Fractional integral with 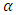 order from the polynomial function form of
order from the polynomial function form of 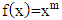 is
is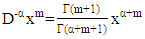 | (13) |
for 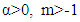 and
and 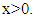
3.2. General Fractional Integral Form of Exponential Function α Order
Fractional integral 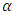 orderfrom the exponential function according to Riemann-Liouville can be stated as a multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function. The general form of fractional integral
orderfrom the exponential function according to Riemann-Liouville can be stated as a multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function. The general form of fractional integral 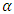 order with the exponential function
order with the exponential function 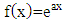 as follows:
as follows: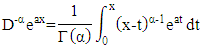 For example:
For example: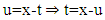 then
then 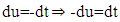 when
when 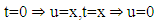 then the general form of fractional integral
then the general form of fractional integral 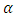 order with
order with 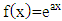 is
is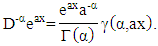 So that the fractional integral
So that the fractional integral 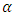 orderfrom the exponential function which form is
orderfrom the exponential function which form is 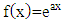 can be stated as a multiplication form of an incomplete gamma function with the exponential function which can be stated in the theorem 3.2.Theorem 3.2Fractional integral
can be stated as a multiplication form of an incomplete gamma function with the exponential function which can be stated in the theorem 3.2.Theorem 3.2Fractional integral 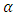 orderfrom the exponential function form
orderfrom the exponential function form 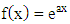 is
is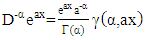 | (14) |
for 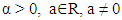 and
and 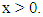 Fractional derivative function can be define using the definition of function integration, assuming
Fractional derivative function can be define using the definition of function integration, assuming 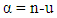 with
with 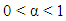 and
and 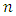 is the smallest integer which is bigger than
is the smallest integer which is bigger than 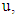 so that the derivative function with
so that the derivative function with 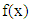 can be stated as:
can be stated as: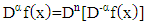 | (15) |
with 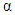 is any order,
is any order, 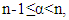 and
and 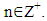 Therefore, will be analyzed the general form of fractional derivative 5th order function and exponentialfunctionwith
Therefore, will be analyzed the general form of fractional derivative 5th order function and exponentialfunctionwith 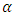 order.
order.
3.3. General Fractional Derivative Form of 5th Order Function α Order
Assume that to find the fractional derivative 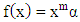 order with
order with 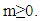 Based on equation (15) and Theorem 3.1, assumed that
Based on equation (15) and Theorem 3.1, assumed that 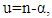 with
with 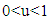 and
and 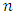 is the smallest integer larger than
is the smallest integer larger than 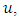 it means that
it means that 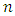 is the multiple order from that derivative. So that the definition will be:
is the multiple order from that derivative. So that the definition will be: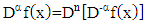 Choose
Choose 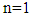 and
and 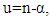 then
then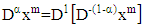 By substituting equation (13) we get
By substituting equation (13) we get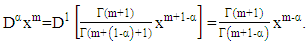 | (16) |
In equation (16), can be seen that the general form of fractional derivative is eligible for 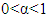 or this can be meant that the derivative is defined for the first one that matches with the boundary of the
or this can be meant that the derivative is defined for the first one that matches with the boundary of the 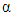 order. This is also applies for the other
order. This is also applies for the other 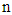 , if we choose
, if we choose 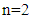 then the boundary of the fractional derivative will be changed to
then the boundary of the fractional derivative will be changed to 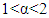 which means that the value of this derivative will be the same with the result of the fractional integral two times or vice versa. So that the fractional integral with
which means that the value of this derivative will be the same with the result of the fractional integral two times or vice versa. So that the fractional integral with 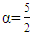 order from the polynomial function which form is
order from the polynomial function which form is 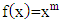 can be made by choosing
can be made by choosing 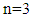 so that
so that 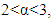 then
then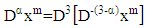 By substituting equation (13) we get
By substituting equation (13) we get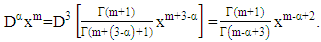 | (17) |
So that the fractional derivative 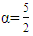 order can be defined as the third form of derivative which means that the value of this derivative will be the same with the fractional integer three times or vice versa, then the fractional derivative can be stated as the form of multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function which is explained in the theorem 3.3.Theorem 3.3Fractional derivative
order can be defined as the third form of derivative which means that the value of this derivative will be the same with the fractional integer three times or vice versa, then the fractional derivative can be stated as the form of multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function which is explained in the theorem 3.3.Theorem 3.3Fractional derivative 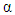 order from the polynomial function form of
order from the polynomial function form of 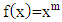 is
is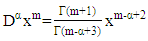 | (18) |
for 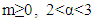 and
and 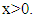
3.4. General Fractional Derivative Form of Exponential Function α Order
Based on Theorem 3.2, the fractional derivative of order 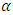 with
with 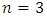 of the exponential function of the form
of the exponential function of the form 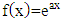 is
is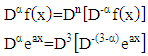 by substituting equation (14), we obtained
by substituting equation (14), we obtained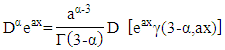 based on the specific value equation for the incomplete derivative of the gamma function i.e.
based on the specific value equation for the incomplete derivative of the gamma function i.e.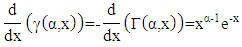 then
then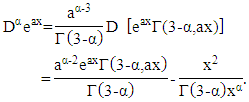 So that the fractional derivative of order
So that the fractional derivative of order 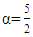 can be interpreted as containing in the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa, then the fractional derivative of the exponential function can be expressed in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function described in the following theorem:Theorem 3.4Fractional derivative
can be interpreted as containing in the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa, then the fractional derivative of the exponential function can be expressed in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function described in the following theorem:Theorem 3.4Fractional derivative 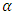 order from the exponential function form of
order from the exponential function form of 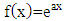 is
is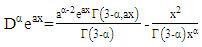 | (19) |
for 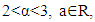 and
and 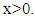
3.5. Integral Fractional of 5th Order Function and Exponential 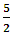 Order
Order
Looking for the derivative of the function 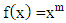 which is a 5th order function with
which is a 5th order function with 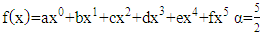 order as follows:
order as follows: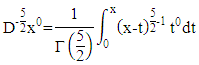 for example:
for example: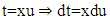
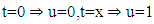 then
then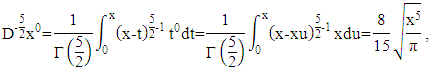 in the same way, the fractional integral of each term is obtained by
in the same way, the fractional integral of each term is obtained by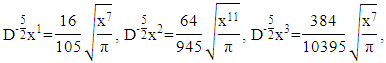
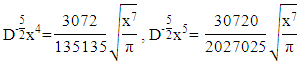 Choose
Choose 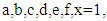 then we get
then we get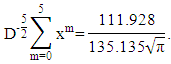 Next, looking for the fractional integral with the order
Next, looking for the fractional integral with the order 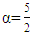 from the exponential function
from the exponential function 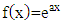 as follows:
as follows: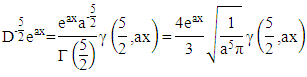 Choose any
Choose any 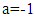 for obtain
for obtain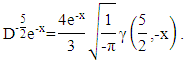
3.6. Derivative Fractional 5th Order Function and Exponential 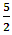 Order
Order
Looking for the derivative of the function 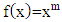 which is a 5th order function with
which is a 5th order function with 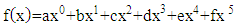 orde
orde 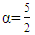 as follows:
as follows: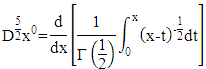 for example:
for example: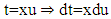 and
and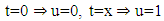 then
then In the same way, you get the fractional derivative of each term
In the same way, you get the fractional derivative of each term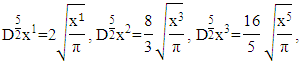
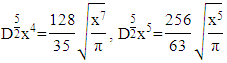 Choose
Choose 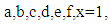 then
then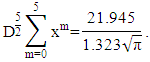 Next, looking for the fractional derivative with the order
Next, looking for the fractional derivative with the order 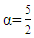 from the exponential function
from the exponential function 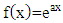 as follows:
as follows: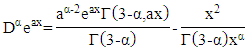 Thus
Thus 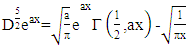 Choose any
Choose any 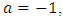 we get
we get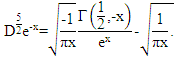
4. Conclusions
We can conclude that the fractional derivative of order 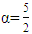 in the 5th Order Function using Riemann-Liouville Method is the same as the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa. In addition the fractional derivative of the exponential function using the Riemann-Liouville Method is equal to in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function.
in the 5th Order Function using Riemann-Liouville Method is the same as the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa. In addition the fractional derivative of the exponential function using the Riemann-Liouville Method is equal to in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function.
References
| [1] | Badruzzaman, F.H., Nahar, J., dan Johansyah, M.D. 2017 [BN]. Analisis Turunan dan Integral Fraksional Fungsi Pangkat Tigadan Fungsi Eksponensial. Jurnal Matematika. 16(2): 1-9. |
| [2] | Conte, S.D. 1980 [CS]. Dasar-Dasar Analisis Numerik Suatu Pendekatan Algoritma. Edisi ketiga. Erlangga, Jakarta. |
| [3] | Das, S. 2008 [DS]. Functional Fractional Calculus for System Identification and Controls. Springer, London. |
| [4] | Herrmann, R. 2011 [HR]. Fractional Calculus an Introduction for Physicists. World Scientific, New Jersey. |
| [5] | Jameson, G.J.O. 2017 [JG] The Incomplete Gamma Function. Gazette Article. 100(2006): 298-306. |
| [6] | Johansyah, M.D., Badruzzaman, F.H., danNahar, J. 2017 [JM] Kajian Dasar Integral danTurunan Fraksional. IRONS. 16(2): 204 209. |
| [7] | Kilbas, A.A., and Marichev, O.I. Samko, S.G., 2006 [KM]. Theory and Aplications Fractional Differential Equation. Elsevier, Amsterdam. |



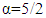 in the 5th Order Function using Riemann-Liouville Method is the same as the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa. In addition the fractional derivative of the exponential function using the Riemann-Liouville Method is equal to in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function.
in the 5th Order Function using Riemann-Liouville Method is the same as the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa. In addition the fractional derivative of the exponential function using the Riemann-Liouville Method is equal to in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function.
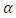 and
and 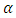 is not an integer? Many mathematicians participated in his contributions such as Abel, Riemann, Liouville, Euler, Laplace, Lacroix, Fourier. In 1819, Lacroix became the first mathematician to write a paper on the definition of fractional derivatives, he started from the function
is not an integer? Many mathematicians participated in his contributions such as Abel, Riemann, Liouville, Euler, Laplace, Lacroix, Fourier. In 1819, Lacroix became the first mathematician to write a paper on the definition of fractional derivatives, he started from the function 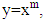 where
where 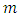 is a positive integer.The functions used in fractional derivatives are factorial functions using the gamma and beta function approaches, expressed in the Legendre symbol
is a positive integer.The functions used in fractional derivatives are factorial functions using the gamma and beta function approaches, expressed in the Legendre symbol 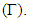 Not only for power functions, fractional calculus can also be developed in other functions such as trigonometry, Laplace, exponential, and exponential algebra with various working methods. The working method in fractional calculus has versions including Riemann-Liouville, Grundwald-Letnikov, M. Caputo (1967), Oldham and Spanier (1974), K.S. Miller and B. Ross (1993), Kolwankar and Gangal (1993). The method that is often used in fractional calculus is the Riemann-Liouville and Caputo method. Based on the above background and problems, the author will examine more deeply about fractional integrals and fractional derivatives using the Riemann-Liouville method with the order
Not only for power functions, fractional calculus can also be developed in other functions such as trigonometry, Laplace, exponential, and exponential algebra with various working methods. The working method in fractional calculus has versions including Riemann-Liouville, Grundwald-Letnikov, M. Caputo (1967), Oldham and Spanier (1974), K.S. Miller and B. Ross (1993), Kolwankar and Gangal (1993). The method that is often used in fractional calculus is the Riemann-Liouville and Caputo method. Based on the above background and problems, the author will examine more deeply about fractional integrals and fractional derivatives using the Riemann-Liouville method with the order 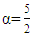 on the 5th power and exponential function.
on the 5th power and exponential function.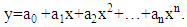
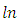 is an exponential function and is represented by
is an exponential function and is represented by 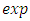 with the following definition:
with the following definition: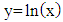
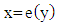
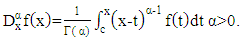
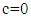 in Equation (4), then the Riemann-Liouville fractional integral is obtained which is defined as:
in Equation (4), then the Riemann-Liouville fractional integral is obtained which is defined as: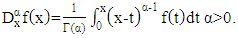
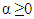 and
and 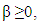 fractional integral has the following properties:
fractional integral has the following properties: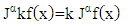
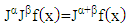
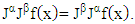
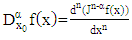
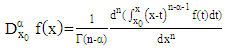
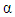 of any order,
of any order, 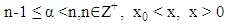 and
and 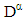 operator of the fractional derivative of order
operator of the fractional derivative of order 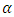 . The properties of the fractional derivative by [JG] is:
. The properties of the fractional derivative by [JG] is: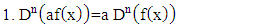
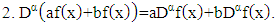
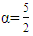 for the respective order integrals and derivatives.3. Formulate fractional integrals and fractional derivatives in the quadrangle and exponential equation.4. Perform operations for each term in the equation.5. After obtaining the results of the integral and its derivatives substitute it to the initial equation form.6. Replace the value in each of the equation variables with the number one (option).
for the respective order integrals and derivatives.3. Formulate fractional integrals and fractional derivatives in the quadrangle and exponential equation.4. Perform operations for each term in the equation.5. After obtaining the results of the integral and its derivatives substitute it to the initial equation form.6. Replace the value in each of the equation variables with the number one (option).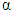 from the polynomial function according to Riemann-Liouville can be stated as the multiplication form of gamma function and polynomial function. The general fractional integral form
from the polynomial function according to Riemann-Liouville can be stated as the multiplication form of gamma function and polynomial function. The general fractional integral form 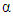 order with the polynomial function
order with the polynomial function 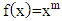 for
for 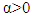 and
and 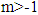 is:
is: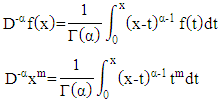 For example:
For example: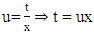 then
then 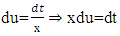 when
when 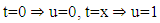 So, the general form of fractional integral
So, the general form of fractional integral 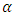 order from the polynomial function
order from the polynomial function 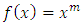 is:
is: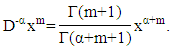 So that the fractional integral with
So that the fractional integral with 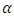 order from the polynomial function which form is
order from the polynomial function which form is 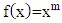 can be stated as a multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function which is stated in the Theorem 3.1.Theorem 3.1Fractional integral with
can be stated as a multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function which is stated in the Theorem 3.1.Theorem 3.1Fractional integral with 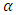 order from the polynomial function form of
order from the polynomial function form of 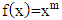 is
is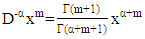
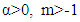 and
and 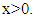
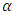 orderfrom the exponential function according to Riemann-Liouville can be stated as a multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function. The general form of fractional integral
orderfrom the exponential function according to Riemann-Liouville can be stated as a multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function. The general form of fractional integral 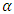 order with the exponential function
order with the exponential function 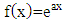 as follows:
as follows: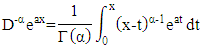 For example:
For example: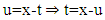 then
then 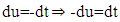 when
when 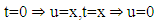 then the general form of fractional integral
then the general form of fractional integral 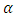 order with
order with 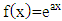 is
is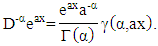 So that the fractional integral
So that the fractional integral 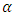 orderfrom the exponential function which form is
orderfrom the exponential function which form is 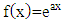 can be stated as a multiplication form of an incomplete gamma function with the exponential function which can be stated in the theorem 3.2.Theorem 3.2Fractional integral
can be stated as a multiplication form of an incomplete gamma function with the exponential function which can be stated in the theorem 3.2.Theorem 3.2Fractional integral 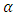 orderfrom the exponential function form
orderfrom the exponential function form 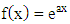 is
is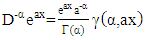
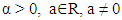 and
and 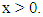 Fractional derivative function can be define using the definition of function integration, assuming
Fractional derivative function can be define using the definition of function integration, assuming 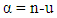 with
with 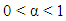 and
and 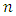 is the smallest integer which is bigger than
is the smallest integer which is bigger than 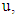 so that the derivative function with
so that the derivative function with 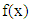 can be stated as:
can be stated as: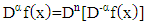
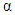 is any order,
is any order, 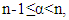 and
and 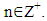 Therefore, will be analyzed the general form of fractional derivative 5th order function and exponentialfunctionwith
Therefore, will be analyzed the general form of fractional derivative 5th order function and exponentialfunctionwith 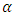 order.
order.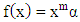 order with
order with 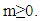 Based on equation (15) and Theorem 3.1, assumed that
Based on equation (15) and Theorem 3.1, assumed that 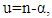 with
with 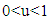 and
and 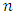 is the smallest integer larger than
is the smallest integer larger than 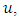 it means that
it means that 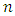 is the multiple order from that derivative. So that the definition will be:
is the multiple order from that derivative. So that the definition will be: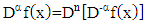 Choose
Choose 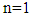 and
and 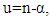 then
then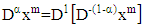 By substituting equation (13) we get
By substituting equation (13) we get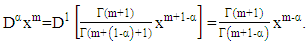
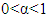 or this can be meant that the derivative is defined for the first one that matches with the boundary of the
or this can be meant that the derivative is defined for the first one that matches with the boundary of the 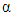 order. This is also applies for the other
order. This is also applies for the other 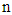 , if we choose
, if we choose 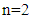 then the boundary of the fractional derivative will be changed to
then the boundary of the fractional derivative will be changed to 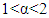 which means that the value of this derivative will be the same with the result of the fractional integral two times or vice versa. So that the fractional integral with
which means that the value of this derivative will be the same with the result of the fractional integral two times or vice versa. So that the fractional integral with 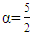 order from the polynomial function which form is
order from the polynomial function which form is 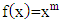 can be made by choosing
can be made by choosing 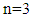 so that
so that 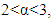 then
then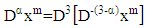 By substituting equation (13) we get
By substituting equation (13) we get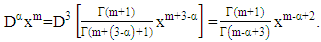
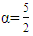 order can be defined as the third form of derivative which means that the value of this derivative will be the same with the fractional integer three times or vice versa, then the fractional derivative can be stated as the form of multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function which is explained in the theorem 3.3.Theorem 3.3Fractional derivative
order can be defined as the third form of derivative which means that the value of this derivative will be the same with the fractional integer three times or vice versa, then the fractional derivative can be stated as the form of multiplication of gamma function and polynomial function which is explained in the theorem 3.3.Theorem 3.3Fractional derivative 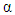 order from the polynomial function form of
order from the polynomial function form of 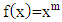 is
is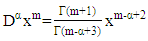
 and
and 
 with
with 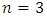 of the exponential function of the form
of the exponential function of the form 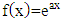 is
is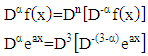 by substituting equation (14), we obtained
by substituting equation (14), we obtained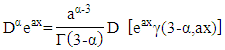 based on the specific value equation for the incomplete derivative of the gamma function i.e.
based on the specific value equation for the incomplete derivative of the gamma function i.e.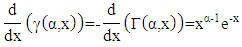 then
then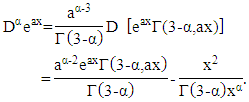 So that the fractional derivative of order
So that the fractional derivative of order 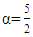 can be interpreted as containing in the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa, then the fractional derivative of the exponential function can be expressed in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function described in the following theorem:Theorem 3.4Fractional derivative
can be interpreted as containing in the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa, then the fractional derivative of the exponential function can be expressed in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function described in the following theorem:Theorem 3.4Fractional derivative 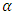 order from the exponential function form of
order from the exponential function form of 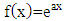 is
is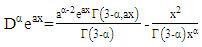
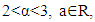 and
and 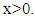
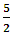 Order
Order 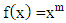 which is a 5th order function with
which is a 5th order function with 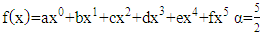 order as follows:
order as follows: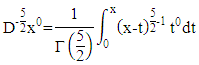 for example:
for example: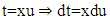
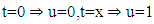 then
then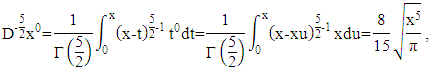 in the same way, the fractional integral of each term is obtained by
in the same way, the fractional integral of each term is obtained by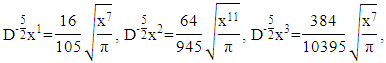
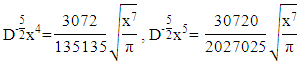 Choose
Choose  then we get
then we get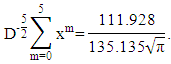 Next, looking for the fractional integral with the order
Next, looking for the fractional integral with the order  from the exponential function
from the exponential function 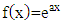 as follows:
as follows: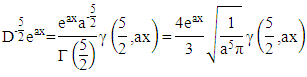 Choose any
Choose any 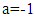 for obtain
for obtain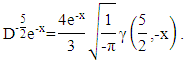
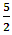 Order
Order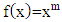 which is a 5th order function with
which is a 5th order function with 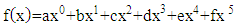 orde
orde 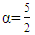 as follows:
as follows: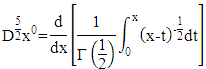 for example:
for example: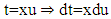 and
and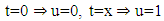 then
then In the same way, you get the fractional derivative of each term
In the same way, you get the fractional derivative of each term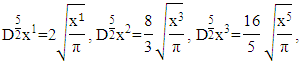
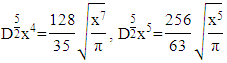 Choose
Choose 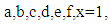 then
then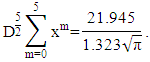 Next, looking for the fractional derivative with the order
Next, looking for the fractional derivative with the order 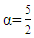 from the exponential function
from the exponential function 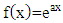 as follows:
as follows: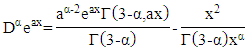 Thus
Thus 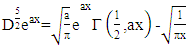 Choose any
Choose any 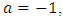 we get
we get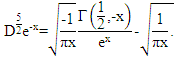
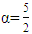 in the 5th Order Function using Riemann-Liouville Method is the same as the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa. In addition the fractional derivative of the exponential function using the Riemann-Liouville Method is equal to in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function.
in the 5th Order Function using Riemann-Liouville Method is the same as the form of a third derivative, which means that the value of this derivative will be the same as the result of three times the fractional integral or vice versa. In addition the fractional derivative of the exponential function using the Riemann-Liouville Method is equal to in the form of multiplication of the incomplete gamma function upper limit with exponential function.  Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML