-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Applied Mathematics
p-ISSN: 2163-1409 e-ISSN: 2163-1425
2016; 6(2): 36-39
doi:10.5923/j.am.20160602.03

Applied Problems of Markov Processes
Roza Shakenova , Alua Shakenova
Kazach National Research Technical University Named after K. I. Satpaev, Almaty, Kazakhstan
Correspondence to: Roza Shakenova , Kazach National Research Technical University Named after K. I. Satpaev, Almaty, Kazakhstan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In this paper authors proposed that the human-being’s state of health can be described as the function of three main factors: economics, ecology and politics of government. We obtained three models of the state of health from the worst to the best using Markov processes. We hope that our theoretical models can be applied in practice.
Keywords: Limiting probability, Probability of state, Markov Processes
Cite this paper: Roza Shakenova , Alua Shakenova , Applied Problems of Markov Processes, Applied Mathematics, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2016, pp. 36-39. doi: 10.5923/j.am.20160602.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
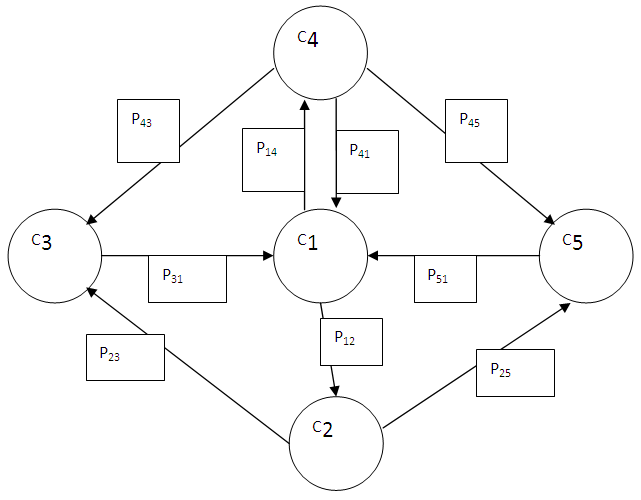
- Markov chains can be used in the description of different economical, ecological problems. The main problem is to find final (limit) probabilities of different states of a certain system. We may use graphs for the system with discrete states. The vertices of graph correspond to the states of the system on the picture #1. The arrows between graphs show the possibility of system’s transfer from one state to another. The final states of human-beings’ health are very important in medicine. Therefore, this paper considers the problem of determining final probabilities of human-being’s state of health. Let’s recall basic definitions. Law of the random variable distribution is every relationship between the possible values of a random variable and their probabilities. The table below shows the law of distribution of a discrete random variable.
 The set of different states of one physical system with discrete states, where random process occurs, is finite or countable.
The set of different states of one physical system with discrete states, where random process occurs, is finite or countable. | (1) |
 to another state
to another state 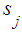 directly or through other states [2], [3]. Usually the graph of states describes the states visually, where the vertices of graph correspond to the states. If the probability of each state in the future for every time
directly or through other states [2], [3]. Usually the graph of states describes the states visually, where the vertices of graph correspond to the states. If the probability of each state in the future for every time 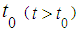 of the system
of the system 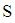 with discrete states,,
with discrete states,, 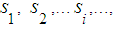 depends on the state in the present
depends on the state in the present 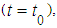 and does not depend on its behavior in the past
and does not depend on its behavior in the past 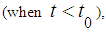 then the random process is Markov process. Let’s consider conditional probability of transferring of system S on the kth step in the state
then the random process is Markov process. Let’s consider conditional probability of transferring of system S on the kth step in the state 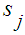 , if it is known that it was in the state
, if it is known that it was in the state  on the (k-1)th step. Denote this probability by:
on the (k-1)th step. Denote this probability by: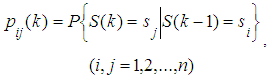 | (2) |
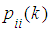 is the probability that the system remains in the state
is the probability that the system remains in the state 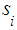 on kth step. Probabilities
on kth step. Probabilities 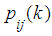 are transition probabilities of Markov chain on the kth step. Transition probabilities can be written in the form of square table (matrix) of size n. This is Stochastic matrix; the sum of all probabilities of one row is equal to
are transition probabilities of Markov chain on the kth step. Transition probabilities can be written in the form of square table (matrix) of size n. This is Stochastic matrix; the sum of all probabilities of one row is equal to 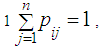 because the system can be in one of mutually exclusive states.
because the system can be in one of mutually exclusive states.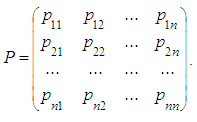 | (3) |
 with their sum equal to one.Markov chain is called uniform, if transition probabilities do not depend on the step’s number (3).Let’s consider only uniform Markov chains to simplify life.
with their sum equal to one.Markov chain is called uniform, if transition probabilities do not depend on the step’s number (3).Let’s consider only uniform Markov chains to simplify life.2. The Formula for Total Probability
- Let the event
 can occur together with only one of following events
can occur together with only one of following events 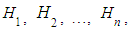 which form the full group of pair wise mutually exclusive events, i.e.
which form the full group of pair wise mutually exclusive events, i.e. 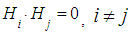 and
and 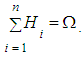 Then the probability of
Then the probability of  can be calculated using the formula of total probability.
can be calculated using the formula of total probability.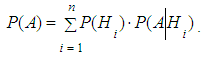 | (4) |
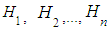 are called hypotheses, and the values
are called hypotheses, and the values 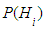 - probabilities of hypotheses.Make hypothesis such that the system was in the state
- probabilities of hypotheses.Make hypothesis such that the system was in the state 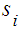 at initial time with (k=0). The probability of this hypothesis is known and equal to
at initial time with (k=0). The probability of this hypothesis is known and equal to 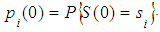 Assuming that this hypothesis takes place, the conditional probability of System
Assuming that this hypothesis takes place, the conditional probability of System 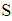 being in the state
being in the state 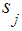 on the first step is equal to transition probability
on the first step is equal to transition probability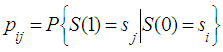 Applying formula for total probability we obtain the following:
Applying formula for total probability we obtain the following: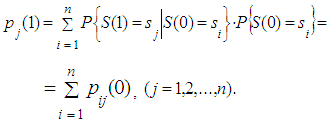 | (5) |
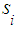 on the first step, The probability of this hypothesis is known and equal to
on the first step, The probability of this hypothesis is known and equal to 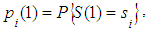
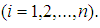 Given this hypothesis, the conditional probability of the system being in the state
Given this hypothesis, the conditional probability of the system being in the state 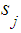 on the second step is equal to
on the second step is equal to 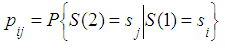 Using the formula for total probability we obtain:
Using the formula for total probability we obtain: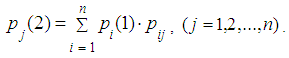 Applying this method several times we obtain recurrent formula:
Applying this method several times we obtain recurrent formula: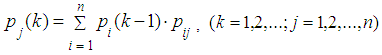 | (6) |
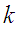 the stationary mode sets up, at which the system continues to wander over states, but the probabilities of these states do not depend on the number of step. These probabilities are denoted final (limit) probabilities of Markov chains. The equations for such probabilities can be written using mnemonic rule: Given stationary mode, total probability flux of the system remains constant: the flow into the state s is equal to the flow out of the state s.
the stationary mode sets up, at which the system continues to wander over states, but the probabilities of these states do not depend on the number of step. These probabilities are denoted final (limit) probabilities of Markov chains. The equations for such probabilities can be written using mnemonic rule: Given stationary mode, total probability flux of the system remains constant: the flow into the state s is equal to the flow out of the state s.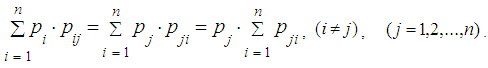 | (7) |
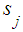 . Add normalization condition
. Add normalization condition 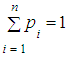 to these n equations.
to these n equations. 3. Markov Chains. The state of Health
- Let the System
 be human-being from certain ecological, economic sphere. It can be in the following states:
be human-being from certain ecological, economic sphere. It can be in the following states: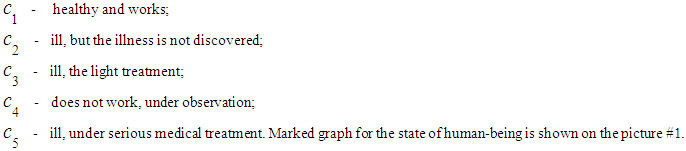 The problem: To construct the equation and find the final probabilities of human-being’s state of health. Solution: Let’s consider
The problem: To construct the equation and find the final probabilities of human-being’s state of health. Solution: Let’s consider 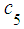 on the graph. Two arrows are directed into this state; consequently, there are two terms for addition on the left side (7) for
on the graph. Two arrows are directed into this state; consequently, there are two terms for addition on the left side (7) for  (state
(state 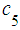 ). One arrow is directed out of this state, subsequently, there is only one term on the right side (7) for
). One arrow is directed out of this state, subsequently, there is only one term on the right side (7) for 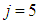 (state
(state 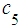 ). Hence, using balance condition (7), we obtain the first equation:
). Hence, using balance condition (7), we obtain the first equation: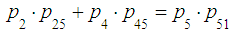 | (8) |
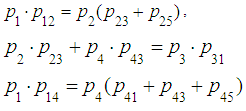 ,The fifth equation is the normalization condition:
,The fifth equation is the normalization condition: We rewrite the system of equations in the following way:
We rewrite the system of equations in the following way: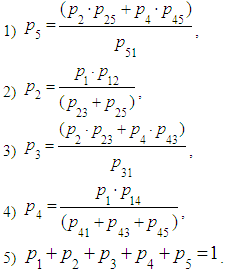 Let’s solve the system of equations. From 2) we find:
Let’s solve the system of equations. From 2) we find: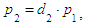 where
where 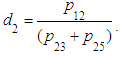 From 4) we find:
From 4) we find: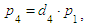 where
where 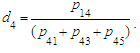 From 3) find:
From 3) find: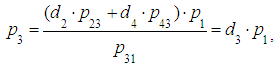 where
where 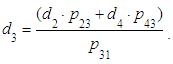 From 1)find:
From 1)find: 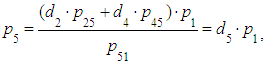 where
where 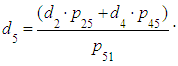 Giving corresponding values of probabilities:
Giving corresponding values of probabilities: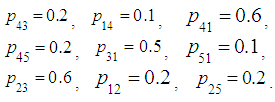 Calculating the following values:
Calculating the following values: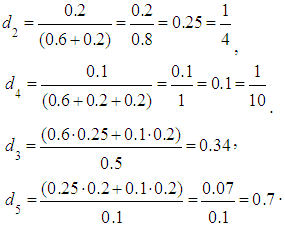 ,According to the equality5) we have:
,According to the equality5) we have: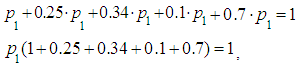
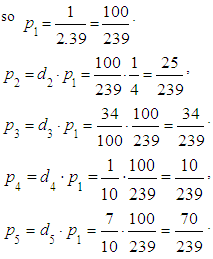 Normalization condition
Normalization condition 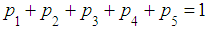
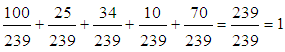 works. We did not need the probabilities
works. We did not need the probabilities 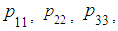
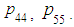
4. Conclusions
- In summary, we have found final probabilities of human-being’s state of health, considering the system C- a human-being from a certain ecological, economical sphere. Looking at initial stages of disease in medicine it is possible to make prognosis about the final probabilities of sick human-being’s state of health. Doctors together with researchers could invent such project for human-being’s health recovery.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML