-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Life Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1387 e-ISSN: 2163-1395
2017; 7(3): 31-38
doi:10.5923/j.als.20170703.01

The Comparative Study of 8Hz EMF Effect on Tissue Hydration in Brain Cortex and Subcortex of Rats
Sinerik Ayrapetyan, Armenuhi Heqimyan, Anna Nikoghosyan
UNESCO Chair - Life Sciences International Postgraduate Educational Center, Yerevan, Armenia
Correspondence to: Sinerik Ayrapetyan, UNESCO Chair - Life Sciences International Postgraduate Educational Center, Yerevan, Armenia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Previously we have shown that 8Hz EMF has depressing effect on thermodynamic activity of water, which decreases peroxide formation, and 8Hz EMF-treated aqua solution depresses the growth and development of microbes in aqua medium. Therefore, in order to elucidate the possible mechanism of 8Hz EMF on brain function, in the present work the studies of 8Hz EMF exposure effect on brain tissue hydration, the sensitivity of 8Hz EMF-induced tissue hydration to 10-4M ouabain (Na+/K+ pump inhibition) and 10-9M ouabain (activation of intracellular signaling system) as well as 8Hz EMF exposure effect on the number of Na+/K+ pump units in the membrane of both young and old rats have been performed. The obtained data allow us to suggest that 8Hz EMF exposure has age-dependent modulation effect on brain tissue hydration and this effect is sensitive to Na+/K+ pump activity and intracellular signaling system. It has been shown that, in spite of the fact that the number of expressed Na+/K+ pump units in cell membrane of subcortex is significantly less expressed than in cortex cells, the sensitivity of signaling system controlling cell hydration to 8Hz EMF in subcortex cells is more pronounced than in cortex ones.
Keywords: 8Hz EMF, Tissue Hydration, Brain, Na+/K+ Pump, Na+/Ca2+ Exchange
Cite this paper: Sinerik Ayrapetyan, Armenuhi Heqimyan, Anna Nikoghosyan, The Comparative Study of 8Hz EMF Effect on Tissue Hydration in Brain Cortex and Subcortex of Rats, Advances in Life Sciences, Vol. 7 No. 3, 2017, pp. 31-38. doi: 10.5923/j.als.20170703.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- There is a great number of scientific studies demonstrating that ELF EMF has strong modulation effect on brain function [1-4]. However, the cellular and molecular mechanism of ELF EMF effect on brain has not been fully elucidated yet. It is known that cell hydration is a fundamental parameter determining its metabolic activity, which is realized through hydration-induced changes of intracellular macromolecules’ activity by folding-unfolding mechanism [5] and through surface-dependent changes of the number of functionally active membrane proteins, having enzymes [6], receptors [7] and ionic channels-forming properties [8]. As physicochemical properties of water are sensitive to EMF [9-11] and cell membrane is highly permeable for water [12, 13], water molecules take the role of a primary messenger for EMF signal transduction from cell bathing medium into cell metabolism. Therefore, the metabolically controlled cell hydration is suggested as a biomarker for estimation of EMF effect on cells and organisms [14]. It is known that Na+/K+-ATPase (working molecules of Na+/K+ pump) has three catalytic isoforms (α1, α2, α3) in neuronal and muscle membranes [15]. These isoforms have different affinities to cardiac glycoside-ouabain and functional activities: α1 (with low affinity) and α2 (with middle affinity) isoforms are involved in transportation of Na+ and K+ through membrane, while α3 (with high affinity) isn’t directly involved in transporting Na+ and K+ and has only intracellular signaling function [15, 16]. Previously it has been shown that among these three families of receptors, α3 isoform is a target for EMF effect: magnetic field has activation effect on cGMP-dependent Na+/Ca2+ exchange in forward (F) mode leading to the increase of membrane receptors’ affinity to ouabain, while extremely high frequency of EMF has activation effect on cAMP-dependent Na+/Ca2+ exchange in reverse (R) mode leading to the decrease of membrane receptors’ affinity to ouabain [17]. Our previous study of the effects of extremely low frequencies (less than 10Hz) of EMF (ELF EMF) on physicochemical properties and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) formation in water and water solution has elucidated that 8Hz frequency window strongly depresses water molecules dissociation and H2O2 formation in PS [18, 19]. It has also been shown that 8Hz EMF has pronounced inhibitory effect on bacterial growth rate and development [20]. Thus, the aim of the present work was to perform a study of 8Hz EMF exposure effect on brain tissue (cortex and subcortex) hydration of rats in order to elucidate the cellular mechanism of 8Hz EMF effect on rats’ brain function. For this purpose, the effects of 8Hz EMF on brain tissue hydration, the sensitivity of 8 Hz EMF-induced tissue hydration to 10-4M ouabain (Na+/K+ pump inhibition) and 10-9M ouabain (activation of intracellular signaling system) as well as 8Hz EMF effect on ouabain binding with cell membrane in both young and old rats have been studied.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
- All procedures performed on animals were carried out following the protocols approved by Animal Care and Use Committee of Life Sciences International Postgraduate Educational Centre (LSIPEC, Yerevan, Armenia). Experiments were performed on 30 young (6 weeks old) and 30 old (18 months old) Wistar albino rats. They were regularly examined, kept under control of the veterinarians in LSIPEC and reserved in a specific pathogen-free animal room under optimum conditions of 12 h light/dark cycles, at temperature of 22 ± 2°C, with a relative humidity of 50% and were fed ad libitum on a standard lab chow and water.
2.2. Chemicals
- Tyrode’s PS containing (in mM) 137 NaCl, 5.4 KCl, 1.8 CaCl2, 1.05 MgCl2, 5 C6H12O6, 11.9 NaHCO3, and 0.42 NaH2PO4 and adjusted to pH 7.4 with NaOH was used. All chemicals were obtained from “Medisar” Industrial Chemical Importation Company (Yerevan, Armenia). [3H]-ouabain with specific activity (25.34 Ci/mM) and non-radioactive ouabain (PerkinElmer, Massachusetts, USA) at 10-9M and 10-4M concentrations dissolved in PS were used for tissue incubation.
2.3. Source of EMF Radiation
- The background of magnetic field in the area of experimental setup in the laboratory, due to the 60Hz electricity system, was less than 0.001mT. The holder of the exposure tube and the coil holder were placed on two neighboring tables to exclude the vibration during the exposure. The room temperature was 23oC. The exposure set up is presented in Figure 1.
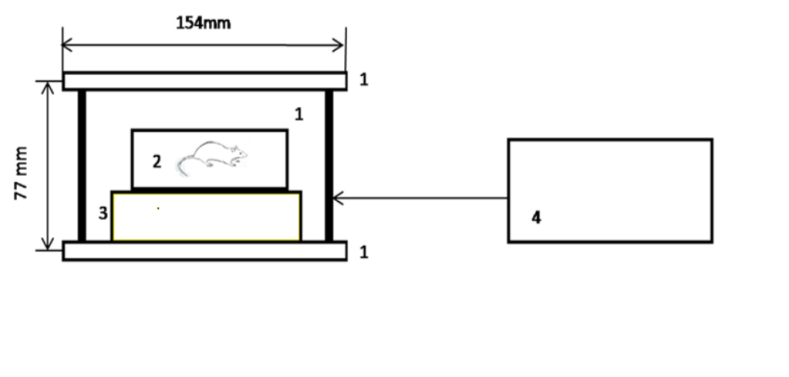 | Figure 1. The exposure set up: 1-Helmholtz coil (D=154mm, H=77mm), 2-plexiglas box (134mm x 105mm x 55mm), 3-wooden table, 4- 8Hz generator having output amplifier connected to coil |
2.4. Tissue Preparation
- It is well known that anesthetics with different chemical and pharmacological profiles significantly affect metabolic processes, which play an important role in regulation of cell volume [21, 22]. Therefore, in the present experiments animals were sharply immobilized by freezing method (dipping their noses into liquid nitrogen for 3-5 sec) and decapitated [23]. After such a procedure the full absence of somatic reflexes on extra stimuli was recorded. Experiments were performed on 30 young and 30 old animals. From each group 15 young and 15 old animals were considered as sham animals, while 15 young and 15 old animals were exposed with 8 Hz. 9 cortex samples and 9 subcortex samples were dissected from each animal. The obtained 135 samples from 15 sham animals were divided into 3 groups. 45 samples were incubated in PS, 45 samples – in PS containing 10-4M [3H]-ouabain and 45 samples – in PS containing 10-9M [3H]-ouabain. Thus, each column on the figures presents the mean value of the data from 45 samples. The same procedure has been performed on 15 animals exposed with 8 Hz. The protocol of experiments was the same for both young and old animals. Brain was gently taken out from its cavity and then cortex and subcortex tissues were isolated into 9 samples from each animal, weighing from 50 to 70 mg. For each experimental group five animals were chosen. All data were received from three independent experiments.
2.5. Definition of Water Content of Brain Tissues
- Water content of brain cortex and subcortex tissues was determined by traditional “tissue drying” method [23]. After measuring the wet weight (w.w.) of brain tissue samples it was dried in oven (Factory of Medical Equipment, Odessa, Ukraine) for 24h at 105°C for determination of dry weight (d. w.). The quantity of water in 1g of d.w. tissue was counted by the following equation: (w.w.–d.w./d.w). For investigation of water content variations and ouabain effects, each animal group was divided into 2 subgroups: in the first (sham) subgroup there were animals without any radiation, in the second animals the animals were radiated by 8Hz EMF.From each experimental group the samples were divided into three parts (15 in each). The first group of samples was incubated in PS, the second – in PS containing 10-9M ouabain and the third – in PS containing 10-4M ouabain.
2.6. Counting of [3H]-Ouabain Receptors in Membrane
- Brain cortex and subcortex samples were incubated in 10 ml of 10-9M and 10-4M [3H]-ouabain solutions for 30min. Then they were washed three times, each wash was about 5 min in duration in normal PS (ouabain-free) for removing [3H]-ouabain from tissue. After determination of wet and dry weights of samples, they were homogenized in 50 µl of 68% HNO3 solution. Then 2ml of Bray’s scintillation fluid was added and chemoluminescence of samples was quantified with 1450-MicroBeta liquid scintillation counter (Wallac, Turku, Finland). The number of [3H]-ouabain molecules’ binding with cell membranes was defined per mg of dry weight of samples.
2.7. Statistic Analysis
- Microsoft Excel and Sigma-Plot (Version 8.02A, NY, USA) were used for data analyses. Significance in comparison with the sham group was calculated with Student’s t-test with the following symbols (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001).
3. Results
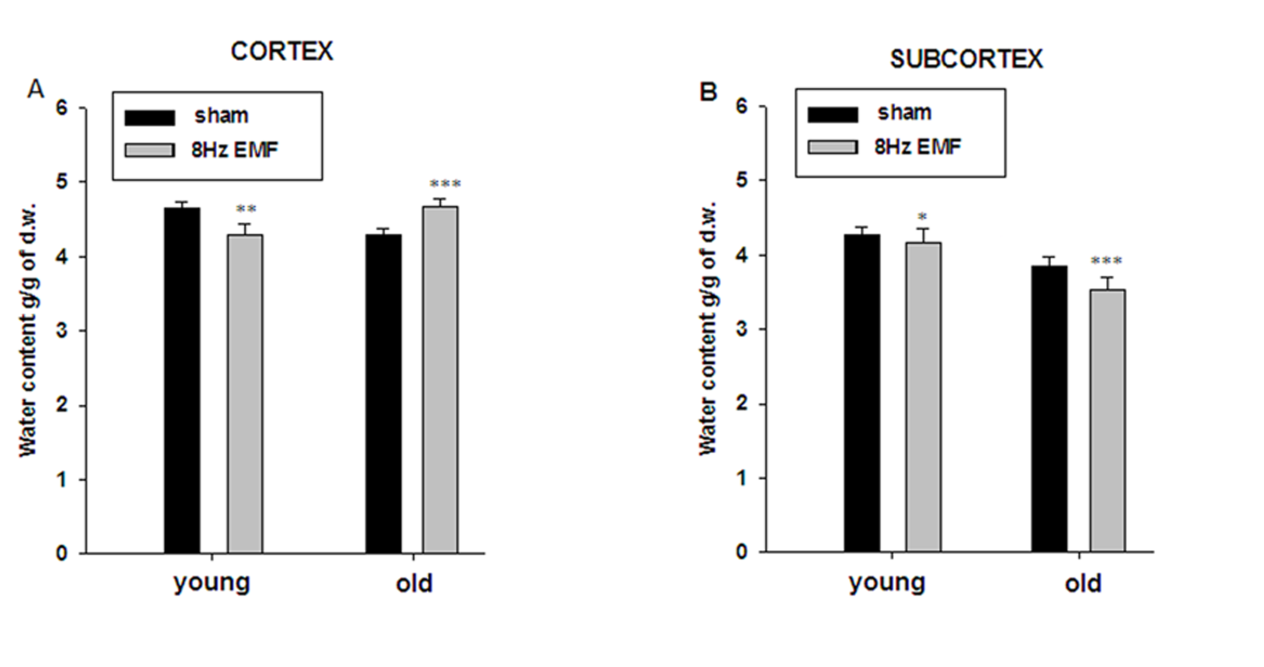
- It is known that there is an age-dependent impairment of brain cell metabolism, which is accompanied by cell dehydration and increase of intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i), having a crucial role in determination of magnetic sensitivity of cells [24]. Therefore, the experiments were performed on young and old animals in order to elucidate the metabolic-dependent character of 8Hz EMF effect on brain tissue hydration and ouabain binding with cell membrane.As it can be seen in Figure 2, 8Hz EMF exposure leads to tissue dehydration in cortex and subcortex of young animals. However, in old animals the same exposure causes hydration in cortex and dehydration in subcortex tissue.
4. Discussion
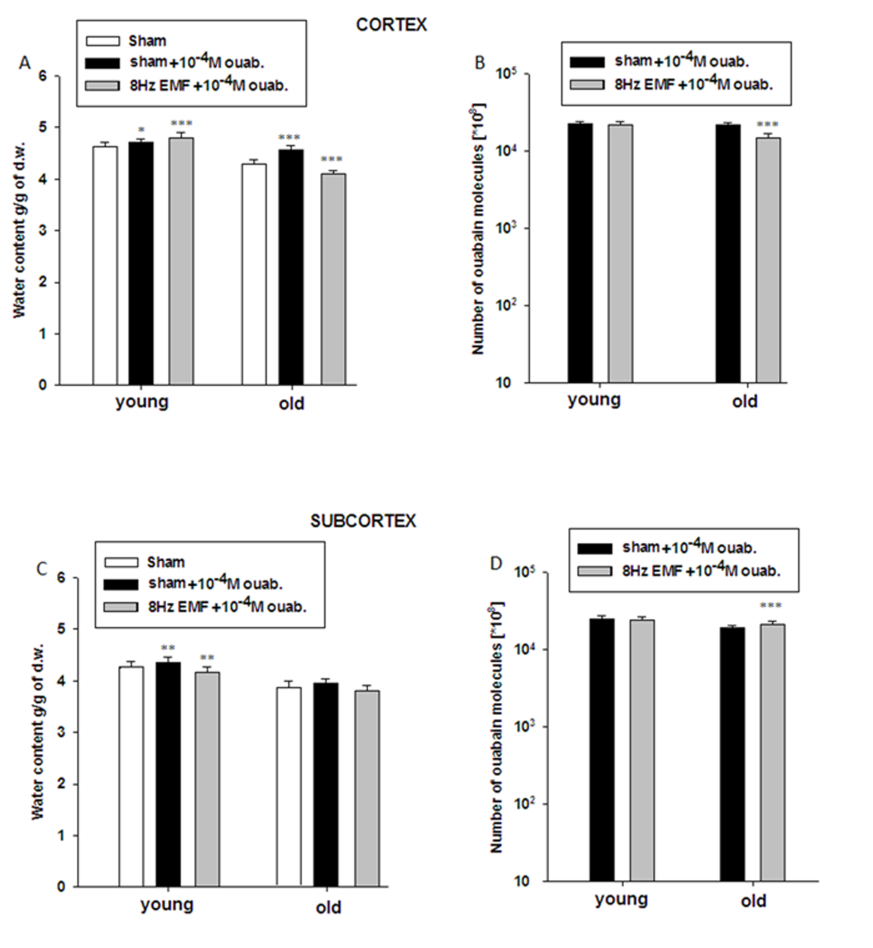
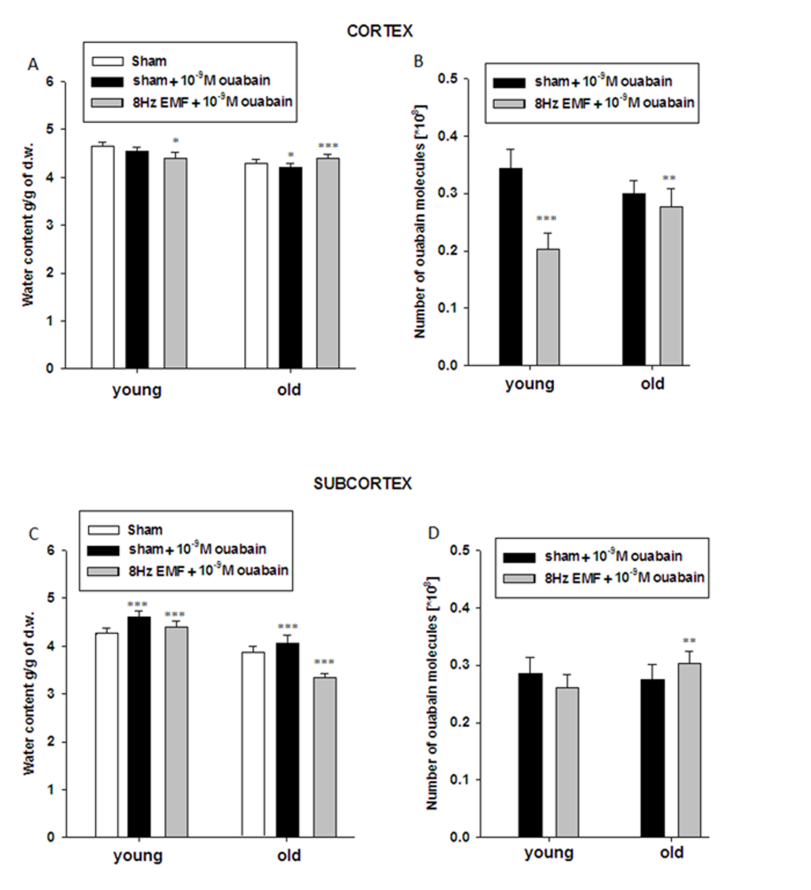
- The data presented in Figure 2A and Figure 2B indicate that brain tissue hydration is sensitive to the impact of 8Hz EMF and 8Hz EMF-induced brain tissue hydration has age-dependent, i.e. metabolic-dependent character. Moreover, the obtained data indicate that in old animals 8Hz EMF brings to hydration in cortex tissue and dehydration in subcortex tissue. It is known that age-dependent dehydration of brain tissue is due to Na+/K+ pump dysfunction leading to the increase of [Ca2+]i, which in its turn brings to phosphorylation-induced contraction of myosin-like protein in cytoskeleton and fibrilization of cytoplasm [29]. By our previous study it has been shown that static and pulsing magnetic fields activate cGMP-dependent F Na+/Ca2+ exchange pushing out Ca2+ from the cell [17]. As Na+/Ca2+ exchange functions in stoichiometry of 3Na+:1Ca2+ [25], it was predicted that F Na+/Ca2+ exchange should have hydration effect on cells. However, as it is presented in Figure 2, 8Hz EMF has dehydration effect in cortex and subcortex tissues of young rats, while the same exposure brings to subcortex tissue dehydration and cortex tissue hydration in old rats (Figure 2A, B). It is known that [Ca2+]i is a strong inhibitor for Na+/K+ pump [30] and F Na+/Ca2+ exchange-induced decrease of [Ca2+]i reactivates electrogenic Na+/K+ pump having dehydration effect on cells [31]. Therefore, 8Hz EMF-induced dehydration in brain tissues of young animals having low [Ca2+]i can be explained by reactivation of Na+/K+ pump, while 8Hz EMF-induced hydration in cortex tissues of old animals can be due to high [Ca2+]i-induced dysfunction of Na+/K+ pump [32], which F Na+/Ca2+ exchange is not able to reactivate. Therefore, in old animals 8Hz EMF-induced cortex tissue hydration can be considered as a result of direct effect of F Na+/Ca2+ exchange, while 8Hz EMF-induced dehydration in subcortex tissues of old animals can probably be explained by high capacity of cGMP-dependent F Na+/Ca2+ exchange (leading to the decrease of [Ca2+]i and reactivation of Na+/K+ pump activity) in subcortex tissues compared with cortex ones. The obtained data on the effects of 10-4M ouabain (Na+/K+ pump inactivation) on brain tissue hydration indicate that in sham animals 10-4M ouabain-induced hydration has age-dependent increasing and decreasing characters in cortex and subcortex tissues, respectively (Fig. 3A,C). These data show that in subcortex tissues age-dependent dysfunction of Na+/K+ pump is more pronounced than in cortex tissues. The fact that in cortex tissues of old animals Na+/K+ inactivation causes more increase of tissue hydration than in young animals can be explained by high [Ca2+]i in old animals, which is more increased by applying 10-4M ouabain leading to activation of “Ca2+ - calmodulin - NO syntase - cGMP” metabolic chain bringing to stimulation of F Na+/Ca2+ exchange having hydration effect on cells. The absence of 10-4M ouabain-induced hydration in subcortex tissue of old animals (Fig. 3A,C) can probably be explained by less expressiveness of the aforementioned metabolic chain in subcortex tissues. This suggestion cannot be final and needs more detailed investigation. The data showing, that 10-4M ouabain-induced hydration in cortex tissues of young animals exposed with 8Hz EMF is more pronounced than in cortex tissues of sham animals and this hydration effect in 8Hz EMF-exposed animals is not accompanied by the increase of the number of pump units (ouabain receptors) in membrane, support the above mentioned suggestion that 8Hz EMF activates Na+/K+ pump through stimulation of cGMP-dependent F Na+/Ca2+ exchange (decreasing [Ca2+]i) which results in increasing Na+/K+ pump sensitivity to its inhibitor - ouabain. Previously it has been shown that Na+/K+ pump inactivation-induced hydration is due to both Na+ uptake and cAMP-dependent R Na+/Ca2+ exchange-induced activation of intracellular oxidative processes leading to the release of endogenous water molecules [26]. As [Ca2+]i is high in brain cells of old animals leading to the depression of oxidative processes in cell and endogenous water release, in the brain tissues of old animals the ouabain-induced activation of cAMP-dependent R Na+/Ca2+ exchange has only direct dehydration effect on cell. This suggestion is supported by the data that cell dehydration is accompanied by the decrease of Na+/K+ pump units in membrane of cortex tissues of old animals (Fig. 3B). In subcortex tissues of 8Hz EMF-exposed young animals 10-4M ouabain-induced dehydration could be explained by the absence or weakening of cAMP-dependent R Na+/Ca2+ exchange-induced activation of intracellular oxidative process. This suggestion is confirmed by the data that 8Hz EMF-induced cell hydration in subcortex is less pronounced that in cortex (Fig. 2). In subcortex of 8Hz EMF-exposed old animals the ouabain non-significantly decreases tissue hydration, which is accompanied by the increase of number of ouabain bindings with membrane. This can be interpreted by the decrease of [Ca2+]i, which increases the affinity of ouabain receptors [26]. These data support the above mentioned suggestion that 8Hz EMF-induced dehydration in subcortex tissues of sham animals is due to activation of cGMP-dependent F Na+/Ca2+ exchange leading to reactivation of Na+/K+ pump (Fig. 2). Thus, based on the facts that a) in sham condition 10-4M ouabain has hydration effect on cortex and subcortex tissues of both young and old animals b) in cortex tissues of 8Hz EMF-exposed animals 10-4M ouabain brings to hydration in young animals and dehydration in old animals, c) in subcortex tissues of 8Hz EMF-exposed animals 10-4M ouabain has dehydration effect in young animals and the effect is absent in old animals, we suggest that Na+/K+ pump is not a direct target for 8Hz EMF and it has age-dependent, i.e. [Ca2+]i- dependent character.The data presented in Figure 4 show that the number of ouabain receptors counted by [3H]-10-9M ouabain is much higher in cortex than in subcortex tissue (Fig. 4B,D). The fact that in sham animals 10-9M ouabain has no significant effect on hydration of cortex samples, while in subcortex it has strong activation effect on them indicates that in spite of the fact that the activity of Na+/K+ pump is less expressed in subcortex than in cortex tissues, oxidative processes (activated by cAMP) leading to the increase of endogenous water release are more active in subcortex than in cortex tissues (Fig. 4). These data predict that subcortex is more sensitive to the factors (which have modulation effect on metabolism) than cortex. The data presented in Figure 4 indicate that in cortex and subcortex tissues of 8Hz EMF-exposed young animals 10-9M ouabain has dehydration effect, which is accompanied by the decrease of ouabain binding sides in membrane, while in old animals 10-9M ouabain has activation effect on cell hydration in cortex and dehydration in subcortex tissues. Such hydration effect of 10-9M ouabain on cortex tissue is accompanied by the decrease of the number of ouaban bindings with cell membrane (receptors’ affinity), which is due to elevation of [Ca2+]i, as a result of activation of cAMP-dependent R Na+/Ca2+ exchange. The data that subcortex tissue dehydration in old animals is accompanied by the increase of ouabain binding clearly indicate that membrane receptors’ affinity to ouabain is increased. This can be explained by the activation of cGMP-dependent F Na+/Ca2+ exchange leading to decrease of [Ca2+]i [26].
5. Conclusions
- Thus, from the obtained data it can be concluded that cortex and subcortex tissue hydration of sham animals is sensitive to 8Hz EMF exposure and this sensitivity has metabolic and age-dependent character. In subcortex tissues Na+/K+ pump units are less expressed than in cortex ones and Na+/K+ pump does not have a significant role in controlling cell hydration and [Ca2+]i.. Therefore, in subcortex tissues cGMP/cAMP-dependent Na+/Ca2+ exchange controlling intracellular oxidative phosphorylation processes and endogenous release of water molecules in cytoplasm has a major role in regulation of cell hydration and [Ca2+]i. This suggestion is supported by the obtained data of the present work indicating that hydration of subcortex tissue has more pronounced age-dependent decreasing character compared with the hydration of cortex tissue. Thus, on the basis of previous and present data we suggest that 8Hz EMF effect on brain tissue hydration is realized through activation of cGMP-dependent F Na+/Ca2+ exchange, which determines high sensitivity of subcortex tissue hydration to 8Hz EMF exposure.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This work was supported by Armenian Governmental Grants, European Office of Aerospace Research and Development Research Grant Project No#A -803P and European Office of Aerospace Research and Development Research Grant Project No #1592P. We express our gratitude to Ani Gyurjinyan from UNESCO Chair in Life Sciences for editing the article.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML