-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Life Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1387 e-ISSN: 2163-1395
2016; 6(2): 31-38
doi:10.5923/j.als.20160602.01

Promoting Role of Bacillus Subtilis BS87 on the Growth and Content of Some Natural Products in the Medicinal Plants Anoectochilus Roxburghii and A. Formosanus
Nada Mohammed Reda Refish1, 2, Alkooranee Jawadayn Talib1, 3, Gu Jian-Wei1, Chunhua Fu1, Longjiang Yu1
1Institute of Resource Biology and Biotechnology, Department of Biotechnology, College of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
2Department of Biology, College of Educational, University of Kufa, Najaf, Iraq
3Plant Protection, College of Agriculture, University of Basrah, Basrah, Iraq
Correspondence to: Nada Mohammed Reda Refish, Institute of Resource Biology and Biotechnology, Department of Biotechnology, College of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Anoectochilus genus is an epiphytic Orchid used as a traditional Chinese folk medicine for the treatment of many diseases. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) such as Bacillussubtilis play an important role in promoting medicinal orchids growth. This study aimed to investigate the promoting role of B.subtilis BS87 on the biomass and contents of some natural products in A.roxburghii and A.formosanus such as flavonoids, steroids and essential oils, in A.roxburghii and A.formosanus treated for 90 days with B.subtilis BS87, the flavonoid contents reached 1.208% and 1.424%, respectively, whereas the steroid content in both species was closely values approximately. The essential oil content was 0.11% was 0.21%, respectively, which was significantly different to levels in control plants in pot culture. After 90 days of symbiotic cultivation, increased shoot height, fresh weight and leaf number were observed in treatedA.roxburghii and A.formosanus plants compared with control plants. In addition, qRT-PCR showed that the expression levels of seven plant growth-related genes, namely AR017, AR019, AR020, AR023, AR037, AR044, and AR047 were in-creased in both A.roxburghiiand Aformosanus plants treated with B.subtilisBS8790 days post-inculcation compared with control plants.
Keywords: Anoectochilus formosanus, Anoectochilus roxburghii, Bacillus subtilis BS87, Essential oils, Flavonoids, Steroids, Natural products, Anoectochilus
Cite this paper: Nada Mohammed Reda Refish, Alkooranee Jawadayn Talib, Gu Jian-Wei, Chunhua Fu, Longjiang Yu, Promoting Role of Bacillus Subtilis BS87 on the Growth and Content of Some Natural Products in the Medicinal Plants Anoectochilus Roxburghii and A. Formosanus, Advances in Life Sciences, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2016, pp. 31-38. doi: 10.5923/j.als.20160602.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Anoectochilus is a genus of about 40 orchids (family Orchidaceae) in the tropical zone areas of Asia and Australia. The genus includes 20 species; two varieties have been found in southwestern and southern China [1]. The Asian plants A. formosanus and A. roxburghii are distributed throughout China, Taiwan, and Japan, which used for the treatment of many diseases including fever, pleurodynia, lung, snake bite, liver disease, hypertension, and malnourishment in children [2-4]. Moreover, A. formosanus is used to treat many diseases such as chest and abdominal pain, nephritis, impotence, spleend as an anti-inflammatory agent [5, 6], and is used to possess antioxidant activity and in the treatment of cancer [7, 8], liver disease [9], hepato toxicity [10], and diabetes [11]. It also increase sendurance capacity [12]. The highly potent medicinal activity of A. formosanus and A. roxburghii are due to their secondary metabolites, such as kinsenosides, flavonoids, steroids, and essential oils; the first kinsenosides were isolated from A. koshunensis [13]. Another study assessed the essential oil from A. roxburghii and its effect on inhibiting hyperplasia of a human cell lung cancer cell line [14]. There are many organisms that are vital constituents of soil and affect different biotic activities of the soil ecosystem in terms of nutrient turnaround and the potential for crop production [15, 16]. Bacteria of diverse genera have been identified as plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), such as Bacillus sp. The effect of PGPR on plant growth directly or indirectly leads to the promotion of plant growth, either by supplying the plant with a compound that is synthesized by the bacterium (for example plant hormones and plant growth regulators), facilitating the absorption of certain nutrients from the environment, protecting plants from pathogens, improving soil structure, bio remediating contaminated soils by sequestering toxic heavy metal species, and meeting xenobiotic components and the indirectly way as induced resistance in plants [17-19]. In earlier studies, growth genes have been shown to be involved in the growth of various plants after treatment with Bacillus sp.; B. subtilis OKB105 was found to affect the transcription of 176 genes involved in metabolism, the transport of nutrients, stress responses, chemotaxis, sporulation, teichuronic acid biosynthesis, and motility in rice seedlings [20]. Another study showed that rice proteins involved in plant growth were induced after exposure to B. cereus NMSL88 [21]. Several genes of A. roxburghii are differentially expressed during symbiosis with the mycorrhizal fungus Epulorhiza sp. (AR-18) compared with non-treated plants, where seedlings treated with the fungus for 35 days showed an average growth increase of 10.3% compared with non-treated seedlings [22]. The present study aimed to identify the optimum tissue culture medium and identify the plant growth-promoting activity of B. subtilis BS87 on A. roxburghii and A.formosanus. We investigated the promoting role of B. subtilis BS87 on the biomass and flavonoid, steroid and essential oil contents of A. roxburghii and A. formosanus in greenhouse experiments. These findings will help elucidate the effect of B. subtilis BS87 on the production of secondary metabolites in orchid plants.
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Bacillus Subtilis BS87 Bacteria on A. Roxburghii and A. Formosanus Vegetative Growth
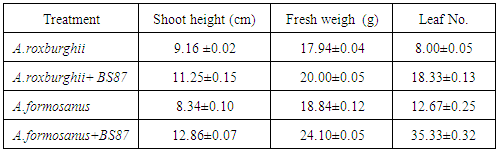
- All A. roxburghii and A. formosanus plants inoculated or control were harvested three months after cultivation to determine the influence of Bacillus subtilis BS87 on the growth of A. roxburghii and A. formosanus plants. The results show that Bacillus subtilis BS87 significantly affected the growth of micropropagated A. roxburghii and A. formosanus plants in vitro plants in pots, as the BS87 plants appeared to be more vigorous than the controls plants (Figure 1). The shoot height (cm), fresh weigh (g) and leaf number of BS87-colonized A. roxburghii plants were 11.25, 20.00 and 18.33, respectively; these values were 9.16, 17.94 and 8.00 in control plants (Table 1). The shoot height (cm), fresh weigh (g) and leaf number of BS87-colonized A.formosanus plants were 12.86, 24.10 and 35.33, respectively; these values were 8.34, 18.84 and 12.67 in control plants (Table 1).
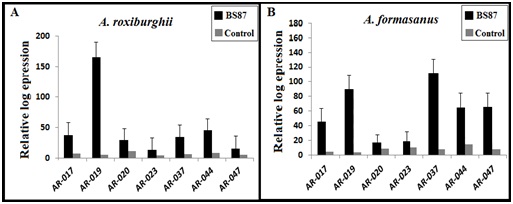 | Figure 2. Expression of growth-related genes after treatment with B. subtilis BS87 or with water as a control treatment in 90-day-old Anoectochilus roxburghii and A. formosanus plants |
|
2.2. Bacillus Subtilis BS87-Induced Gene Expression
- Increased growth in plant is associated with the expression of growth marker genes. To determine whether BS87 acts as an inducer of growth in A. roxburghii and A. formosanus under greenhouse conditions, we used the genes AR-017, AR-019, AR-020, AR-023, AR-037, AR-044, and AR-047 as markers for the growth plants in this experiment. The expression of these selected genes was assessed 90 days after inoculation using quantitative real time-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) (Figure 2). The expression of these genes increased in A. roxburghii (Figure 3 A) and A. formosanus plants (Figure 2 B) after 90 days of treatment with 10 ml of B. subtilis BS87 compared with control plants. The expression of AR-019 increased with a peak in A. roxburghii plants (Figure 2, A) and the expression of AR-037 increased with a peak in A. formosanus plants (Figure 2, B) treated with B. subtilis BS87 (Figure 2, A and B). The expression of AR-020, AR-037, AR-044, and AR-047 were increased in A. formosanus compared with A. roxburghii plants at 90 days post inoculation with B. subtilis BS87, whereas the expression of AR-017 and AR-044 were increased in A. roxburghii compared with A. formosanus plants (Figure 2, A and B).Total RNA was extracted and first-strand cDNA was synthesized for expression analysis. Expression of the genes AR-017, AR-019, AR-020, AR-023, AR-037, AR-044 and AR-047 was monitored by qRT-PCR. Each experiment was repeated at least three times.
2.3. Effects of Bacillus subtilis BS87 Bacteria on Flavonoids, Steroids and Essential Oil Compounds in A. Roxburghii and A. Formosanus
- In this experiment, we studied the content of flavonoids, steroids and essential oil compounds in A. roxburghii and A. formosanus 90 days post-inoculation with BS87 bacteria compared with control. The results showed that the flavonoid content reached 0.850 and 1.208% in A. roxburghii control plants and treated with Bacillus subtilis BS87, respectively, while levels reached 1.050 and 1.424%, respectively, in A. formosanus. The contents of steroid compounds differed significantly between control plants and treated plants, i.e.0.007 and 0.008%, respectively, in A.roxburghii and 0.005 and 0.013%, respectively, in A. formosanus. The content of essential oil compounds differed significantly between control plants and treated plants with Bacillus subtilise 87, i.e.0.11 and 0.30%, respectively, in A. roxburghii and 0.18 and 0.21%, respectively, in A. formosanus (figure 3). And there is a common material in the installation each oil essential for A.roxburghii and A. formonosanus with and without treated Bacillus subtilis which were Hexadecane, Hexadecanoic acid and Methyl ester ( Figure 3).F1, T1- the contents of products for Anoectochilus roxburghii and Anoectochilus formosanus respectively in greenhouse experiments after 90 days control plants.F2, T2-the contents of products for Anoectochilus roxburghii and Anoectochilus formosanus respectively in greenhouse experiments after 90 days treated with bacteria.
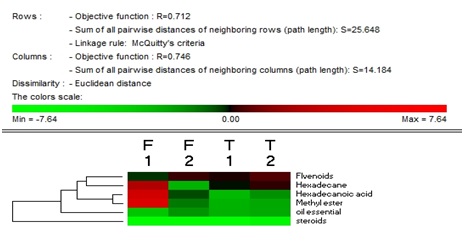 | Figure 3. Effects of B. subtilis BS87 BS87 bacteria on flavonoids, steroids and essential oil compounds in A. roxburghii and A. formosanus |
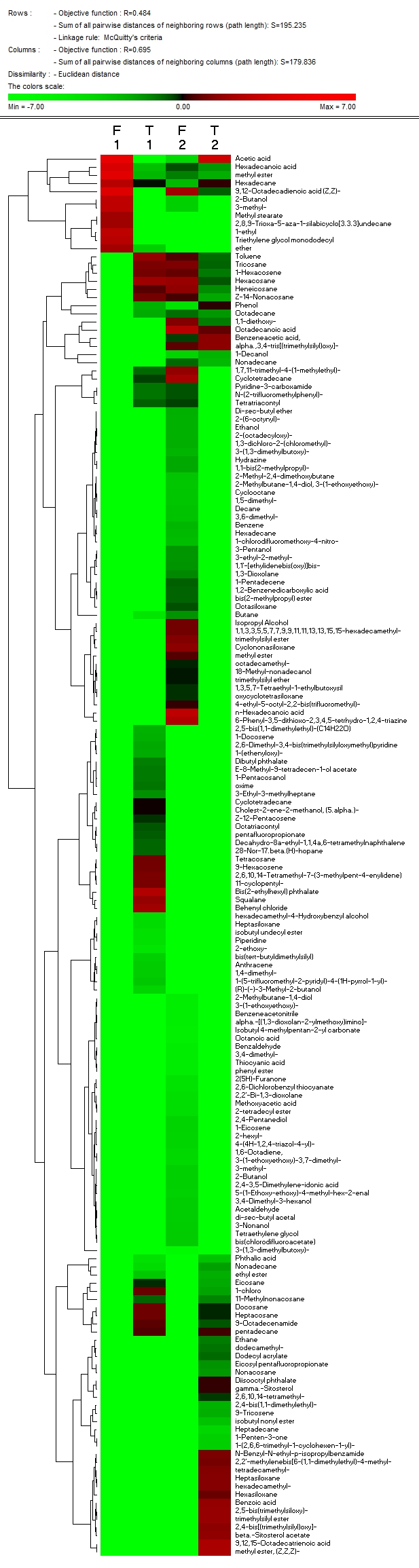 | Figure 4. Essential oils contents for Anoectochilus roxburghii and Anoectochilus formosanus in greenhouse experiments after 90 days, treated with and control plants |
3. Discussion
- This genus is included A. formosanus, A. roxburghii, and A. koshunensis, which are generally used in the treatment of some diseases [1, 23]. Anoectochilus species have a unique mycorrhizal relationship and complex interactions with fungal groups such as Rhizoctonia, Agaricales, and Ascomycetes.These interactions have been related to host plant growth, yield, fitness, and stress responses [24-27]. Has been observed in A. formosanus Hayata. Bacillus subtilis BS87 has not been tested in practice on medicinal plants. However, as a PGPR, it can lead to increased growth and induced resistance in plants. Therefore, we analyzed the effect of this bacteria in A. roxburghii and A. formosanus under greenhouse conditions. We observed that B. subtilis BS87 induced the expression of the plant growth-related genes AR-017, AR-019, AR-020, AR-023, AR-037, AR-044, and AR-047 compared with control plants. It was also noted that the bacteria stimulated plant growth, indicated by the wet weight and plant height as compared with non-treatment plants, thus demonstrating the broad range of activity of Bacillus. subtilis BS87. These results are consistent with several studies that showed the ability of Bacillus. subtilis to stimulate the growth of different plants. Bacillus. subtilis has been widely studied for the improvement of plant growth under both natural and controlled conditions [28], and strains of Bacillus. subtilis have been shown to promote tomato and corn plant growth and induce At4g36110, At2g46370, and At1g69490 gene expression in Arabidopsis [29]. Therefore, we hypothesized that the increase in A. roxburghii and A. formosanus biomass may have been due to the influence of BS87 on photosynthesis and enzyme activity in the host plants. Here, we assessed the expression of candidate growth genes in A. roxburghii and A. formosanus leaves collected from plants treated or not with Bacillus. subtilis BS87 by qRT-PCR. We used GAPDH primer as the housekeeping gene to ensure the validity of expression analysis in this experiment. We found a significant increase in the expression of all growth genes in A. roxburghii and A. formosanus treated with Bacillus. subtilis BS87 compared with control plants. Such increases in gene expression occurred in response to BS87, thereby suggesting that host plants quickly respond to elicitors of growth such as Bacillus. subtilis BS87. In previous studies, five genes, i.e. AR-DD017, AR-DD019, AR-DD037, AR-DD044, and AR-DD047, including genes encoding a hypothetical protein and a uracil phosphor ribosyl transferase, were up-regulated in A. roxburghii (60 days old) treated with the mycorrhizal Epulorhiza sp. fungus (AR-18), assessed by differential display reverse transcription (DDRT)-PCR DDRT-PCR. Seedlings grown with Epulorhiza sp. AR-18 for 35 d showed an average growth increase of 10.3% compared with non-treated seedlings [22]. These results are consistent with our results regarding the expression of genes associated with the growth in A. roxburghii and A. formosanus. The results of the present study show that A. roxburghii and A. formosanus treated with Bacillus. subtilis BS87 gave the best results in terms of increased contents of flavonoids, steroids and essential oil compounds compared to plants control after 90 days of inoculation. Recent research has demonstrated that the essential oils of A. roxburghii are biologically active and may function as antioxidants as well as anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor agents [30-32]. Anoectochilus was analyzed and two species in this genus were compared. The results showed that, using an HPLC rapid test of flavonoid aglycones, two kinds of flavonoid aglycones from A. formosanus could be detected simultaneously [3].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant and Bacterial Materials
- A. roxburghii, A. formosanus and B.subtilis BS87 used in this study were stored in our research laboratory. A. roxburghii and A. formosanus explants were grown on improved MS medium [33], supplemented with 3% (w/v) sucrose, and 0.75% (w/v) agar, at pH 5.8. Explants were grown in flasks with a 12h light/12h dark photoperiod at (24±1)°C. B. subtilis BS87 was grown in conical flasks (300 ml) containing 150 ml of B. subtilis at 48 h on a rotary shaker (150 rpm) at (28± 2°C). The density of the suspension was set at 2×107 colony forming units (cfu)/ml [34]. Pure cultures of bacteria were maintained on respective agar slants and stored at 4°C for further use.
4.2. Plant Inoculation
- Experiments were designed under greenhouse conditions using the micropropagation of A. roxburghii and A. formosanus. After 90 days of micropropagation in vitro, aseptic plants were grown in a greenhouse in 8 cm × 8 cm × 9 cm plastic pots containing 1 kg of a peat moss/humus soil mixture at a ratio of 1:1 that had been inoculated with B. subtilis BS87 (2×107cfu) at a dose of 10 ml/pot, then mixed with the upper soil surface in each pot. Other A. roxburghii and A. formosanus plants were planted separately in sterile soils not treated with bacteria as the control treatment. Plants were grown at 20-25°C with a 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle and 62.5% humidity. Irrigation was applied by drenching twice a week. Each group consisted of five pots with three to four in vitro micropropagated plants per pot.
|
4.3. Gene Expression Assay
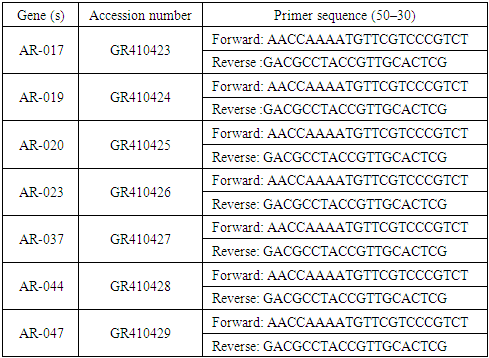
- Total RNA was isolated from 1 g of stem and leaf tissues from A. roxburghii and A. formosanus treated or control plants. subtilis at 90 days post inoculation. RNA was isolated using the RNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen 74904). After treatment with DNase I (New England M0303S) at 37°C for 30 min, 5 µl of RNA was used for first-strand cDNA synthesis using Super Script II reverse transcriptase, following the instructions of the manufacturer (In vitrogen 18064-014). All cDNA samples were stored at −20°C until used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis. qRT-PCR was performed using an Applied Biosystems machine and Step One Software v2.3 (USA). The specific primers used for qRT-PCR are listed in Table 1. The PCR reaction was performed using 1 µl of cDNA as the template in a total reaction volume of 20 µl in 0.5 ml PCR tube using iTaqTM SYBR® Green Super-mix with ROX (California, USA). Then, 0.3 µl of each primer and double-distilled H2O were made up to a total volume of 8.4 µl and mixed in a 96-cell plate. The GAPDH primer was used as the control for the experiment (Table 2).
4.4. Extraction and Sample Preparation for A.Roxburghii and A. Formosanus
- 4.4.1. Measurement of Intracellular and Extracellular Total Flavonoid Contents for A.roxburghii and A. formosanus After 90 days of growth in the greenhouse, 15 plants from each treatment group were harvested. Whole plant powder was prepared, and 0.1-1g was added to 4ml of cold 70 ethanol. The homogenate was centrifuged at 12,000 g for 5min at 4°C and the supernatant was used to measure the intracellular contents. The determination of the flavonoid content followed the methods of Jia and Eberhardt with modifications. The supernatant was diluted five-fold with 70% ethanol (1ml of supernatant in 4ml of 70% ethanol). Take rutin solution at the concentrations of 0.2,0.4,0.6,0.8 and 1.0 mg /L, and placed in a tube with 0.3ml of 5% NaNO2 and1ml of 70% ethanol; the contents were mixed and set aside for 6 min, then 0.3 ml of 4% Al(NO3)3 was added and the tube was set aside again for 6 min. Next, 2ml of 4% NaOH was added and measured at 510 nm after 10 min. 4.4.2. Measurement of Intracellular and Extracellular Total Steroid Contents for A. roxburghii and A. formosanusTo measure the steroid content, 0.2g of fresh plant materials was placed in a 100ml blue cap bottle, then 75 ml of n-hexane was added and magnetically stirred for 10 min. This was followed by 30min of ultrasonic extraction, then the supernatant was poured into two 50ml centrifuge tubes and allowed to stand. Next, 20ml of n-hexane was added to the residue and magnetically stirred for 5 min. The supernatant was transferred to a centrifuge tube, and centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was transferred to around bottom flask and concentrated to dryness at 40°C by rotary evaporation. The evaporation residue was dissolved in 25 ml of ethanol and 5ml KOH solution (500 g/L), refluxed for 30 min in a boiling water bath, then cooled to room temperature with running water immediately after the reaction. The saponification solution was transferred to a 200ml separator funnel (Teflon stopcock), then the round bottom flask was washed with 10ml of deionized water and combine the lotion into the separator funnel, then extracted three times with 50, 50 and 30 ml of petroleumether (the boiling point is 30-60°C). The organic phase was combined in a 200ml separator funnel, the 30ml of deionized water was added and the solution was mixed for 2 min. The lower aqueous layer was washed with de ionized water repeatedly until a neutral pH was achieved. Then, 3-5g of an hydrous sodium sulfate was added to the extract and mixed for 2 min, then the extract was placed in a 100ml round bottom flask and concentrated to dryness by rotary evaporation. The unsaponifiable matter was then dissolved with glacial acetic acid and diluted to 5ml, and used as the sample solution. The absorbance was measured at289 nm4.4.3. Extraction of the Essential OilAt least10g of field culture plant material was washed with water to remove any debris, then cut into pieces. The sample was placed in a round flask and water was added to cover the sample. The bottles were placed in a reflux device, and the essential oil was distilled at 100°C (samples were heated with an electric jacket by setting the temperature to 200°C). Next, 5 ml of ether solute was placed in the receiving tube when steam was seen in the condensation tube. The ether and oil were collected in a new flask after 30 min. Another 5 ml of ether solute was placed in the receiving tube and collected after 20 min. This step was repeated many times in a period of 5 h. In the meantime, an NaCl solution was prepared (108g in 300 ml of distilled water). The volume of the water layer and the ether layer were equalized, and the NaCl solution was added to the collected solution (ether and oil) and shaken for 2min, then allowed to stand for several minutes until layer separation occurred. The upper layer was transferred to a new flask using a separator funnel. The chromatographic column was then prepared using sodium anhydrous sulfate. The collected solution was dried and the outflow liquid was collected in a 100 ml round distilling flask (if the volume was more than 50 ml, a 150 ml round distilling flask was used) and evaporated using a rotary evaporator. When the volume decreased to 25 ml, the solution was transferred to a previously weighed flask and evaporation was continued. The weight of the flask was measured again after evaporation.
5. Conclusions
- It is necessary to find ways to protect, increase the growth, and enhance the yields of medicinal products from the Anoectochilus genus. We have found the application of Bacillus subtilis BS87 increased medicinal plant growth (A. roxburghii and A. formosanus), considering parameters such as shoot height, fresh weight and leaf number, and increased the yield of flavonoids, steroids and essential oil compounds. Then comparative between essential oil compounds after treated with Bacteria and with control plants. The results showed that the flavonoid content reached 0.850 and 1.208% in A. roxburghii control plants and treated with Bacillus subtilis BS87, respectively, while levels reached 1.050 and 1.424%, respectively, in A. formosanus. The contents of steroid compounds differed significantly between control plants and treated plants, i.e.0.007 and 0.008%, respectively, in A.roxburghii and 0.005 and 0.013%, respectively, in A. formosanus. The content of essential oil compounds differed significantly between control plants and treated plants with Bacillus subtilis 87, i.e.0.11 and 0.30%, respectively, in A. roxburghii and 0.18 and 0.21%, respectively, in A. formosanus.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This study was supported by the National ’11th five –year plan, to support Science and Technology Project of China 92008BAI63B04).Thanks to Analytical and Testing Canter, Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML