-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Life Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1387 e-ISSN: 2163-1395
2015; 5(2): 27-38
doi:10.5923/j.als.20150502.01
Prediction of Phenolic Compounds and Formulated Glyphosate Toxicity in Binary Mixtures Using Rhizobium Species Dehydrogenase Activity
C. O. Nweke1, J. C. Orji1, N. C. Ahumibe2
1Department of Microbiology, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria
2Department of Biotechnology, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria
Correspondence to: C. O. Nweke, Department of Microbiology, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The toxicities of binary mixtures of formulated glyphosate and phenols (2,4-dichlorophenol, 4-chlorophenol or phenol) were assessed on the basis of inhibition of INT-dehydrogenase activity in Rhizobium species. The binary mixtures were studied along fixed ratio rays. The effective doses (IC50s) were estimated using monotonic logistic and hormesis dose-response models. The joint action of the mixtures on test organism predicted with concentration addition (CA) and independent action (IA) models showed varying degrees of accuracy when compared with the experimentally-determined values. The overestimation, underestimation and accurate prediction of the mixture toxicities indicate possible synergistic, antagonistic and additive action of the mixtures. The model deviation ratios (MDR) between predicted and experimentally observed effect concentrations for most mixtures lie between 0.5 and 2.0. Thus, the joint action of the mixtures were considered additive.
Keywords: Concentration addition model, Independent action model, Roundup®, Phenols, Mixture toxicity
Cite this paper: C. O. Nweke, J. C. Orji, N. C. Ahumibe, Prediction of Phenolic Compounds and Formulated Glyphosate Toxicity in Binary Mixtures Using Rhizobium Species Dehydrogenase Activity, Advances in Life Sciences, Vol. 5 No. 2, 2015, pp. 27-38. doi: 10.5923/j.als.20150502.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Glyphosate [N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine], a post-emergence herbicide that inhibits the photosynthetic processes in plants is one of the most commonly used herbicide in agriculture. Glyphosate is the active ingredient in Roundup®, a popular herbicide formulation containing isopropylamine (IPA) salt of glyphosate (36% glyphosate) and a surfactant, polyoxyethyleneamine (POEA). In order to improve herbicide action, glyphosate is often used in combination with other herbicides including 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) [1-3].In soils, these herbicides are liable to biodegradation by microorganisms and other biological factors. Glyphosate is moderately persistent in soil with half-life ranging from 2 to 197 days [4-7]. The amine salts and esters of 2,4-D with half-life ranging from 1 to 14 days are not persistent under most environmental conditions [8]. In the environment, 2,4-D is degraded to 2,4-dichlorophenol [9] which can further be degraded to 4-chlorophenol and phenol [10-12].The phenolic intermediates of 2,4-D biodegradation and glyphosate could interact in the environment where mixture of the herbicides were applied. It is therefore necessary to evaluate the toxic effects of the interaction of glyphosate with 2,4-dichlorophenol, 4-chlorophenol and phenol. There is paucity of information about joint toxicity of glyphosate and phenolic compounds. Nweke et al. [13] evaluated the joint action of binary mixtures of Roundup® and these phenolic intermediates of 2,4-D biodegradation against dehydrogenase activity in Rhizobium species isolated from the root nodule of a leguminous plant. In the work, Brain and Cousens [14] hormesis model as reparameterized by Schabenberger et al. [15] (Eq. 1) was used to predict the effective doses of the individual chemicals and their binary mixtures. Isobolographic analysis, Toxic Unit (TU) and Toxic Index (TI) models were used to evaluate the joint action of the mixtures against the dehydrogenase activity of the test organism.
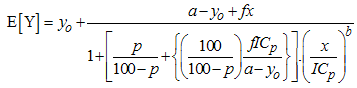 | (1) |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Organism
- Rhizobium species was isolated from the root nodules of Vigna unguiculata and prepared for toxicity assay as described by Nweke et al. [13].
2.2. Binary Mixture Ratios
- The binary mixtures of 2,4-DCP, 4-CP and phenol with glyphosate (as active ingredient in formulated glyphosate pesticide, Roundup®) were studied along fixed ratio rays as described by Nweke et al. [13]. The bioassays were aimed at determining the toxicity of each of the three phenolic compounds mentioned above in binary mixture with glyphosate as a function of the following weight to weight ratios: p (%) = 100, 80, 60, 50, 20, and 0 of phenolic compound and 100-p (%) of glyphosate, corresponding to phenolic compound: glyphosate ratios of: 100:0 %, 80:20%, 60:40 %, 50:50 %, 20:80 % and 0:100 % respectively.
2.3. Dehydrogenase Activity Assay
- Assay of dehydrogenase activity inhibition in suspended cells of Rhizobium species exposed to varying concentrations of the phenolic compounds and glyphosate as individual chemicals and mixtures was done as described by Nweke et al. [13]. The assay was based on inhibition of iodonitrotetrazolium formazan (INTF) production by the bacterial cells in response to the test chemicals. The INTF was extracted with amyl alcohol and the absorbance of the extract determined in a spectrophotometer.
2.4. Data Analysis
- The dehydrogenase activities at varying concentrations of the individual component and binary mixtures of glyphosate with 2,4-dichlorophenol, 4-chlorophenol or phenol were calculated relative to the control as shown in Eq. 2 to normalize data to percent inhibition scale. The relative responses were generated as mean and their standard deviations from triplicate determinations.
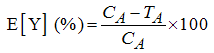 | (2) |
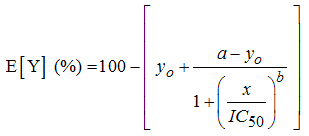 | (3) |
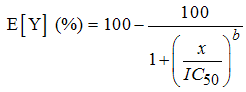 | (4) |
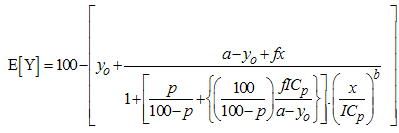 | (5) |
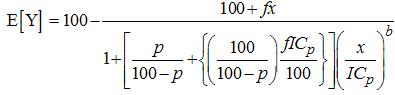 | (6) |
2.5. Prediction of Mixture Toxicities
2.5.1. Concentration Addition Model
- The concept of concentration addition is based on the assumption that the components of a given mixture act similarly. If the effect of the mixture is additive (concentration addition), the effective concentration of the mixture (ICx(mix)) can be predicted from the equation:
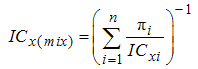 | (7) |
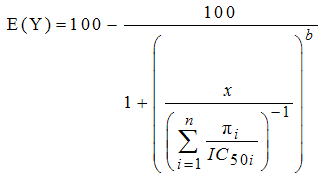 | (8) |
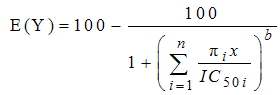 | (9) |
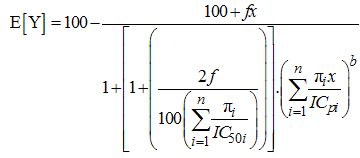 | (10) |
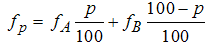 | (11) |
2.5.2. Independent Action (Response Addition) Model
- The concept of independent action or response addition is based on the assumption that the components of a given mixture act dissimilarly. The mathematical expression is as follows:
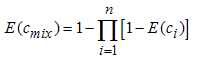 | (12) |
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity of Single Chemicals
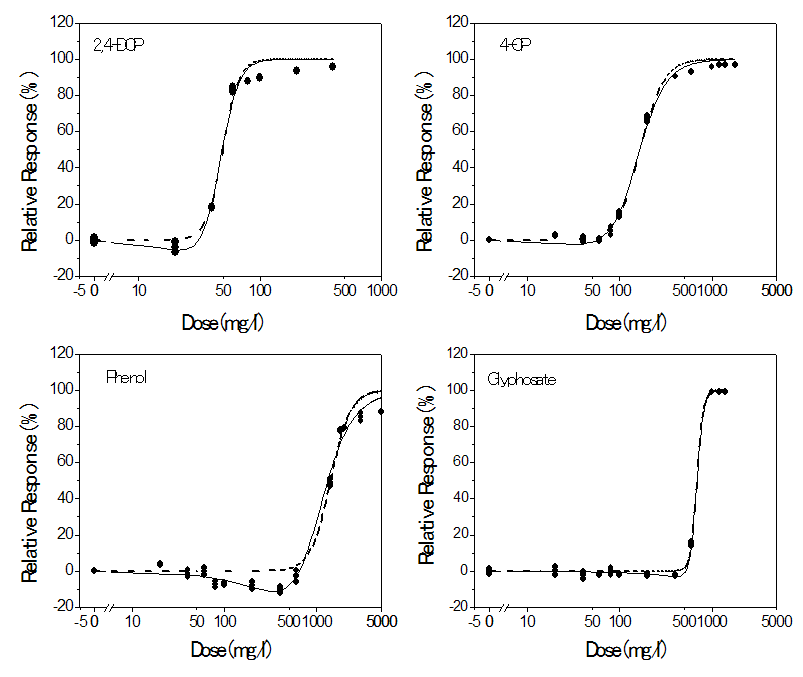
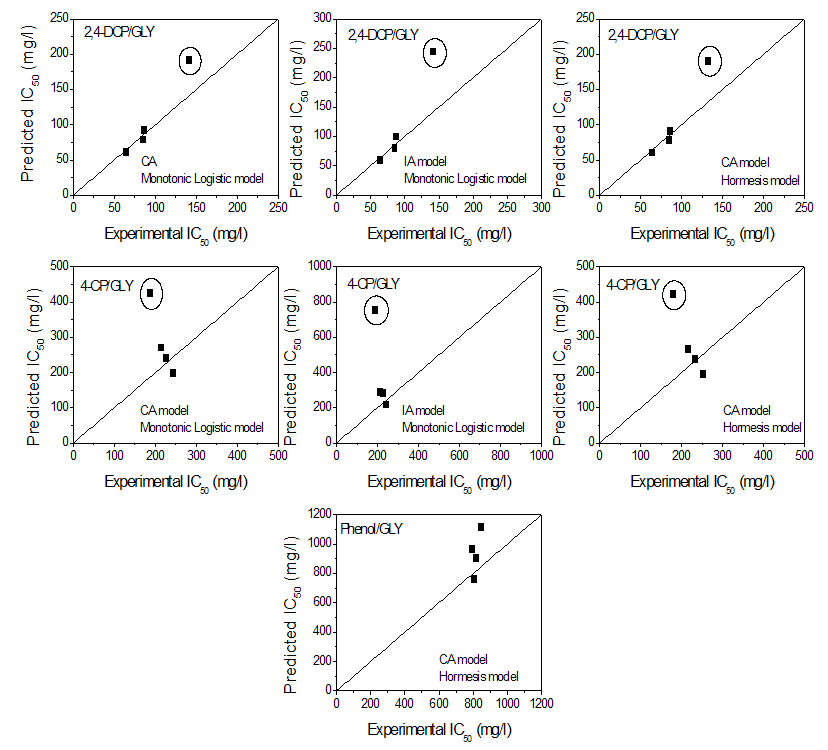
- The inhibition of dehydrogenase activity in Rhizobium species by glyphosate, 2,4-dichlorophenol, 4-chlorophenol and phenol as single compound as well as the fit of the logistic and hormesis models are shown in Figure 1. All the compounds presented biphasic dose response curves characterized by stimulation of dehydrogenase activity at low doses and inhibition at high doses. However, 4-chlorophenol and glyphosate presented marginal hormetic effects at concentrations ranging from 20 to 60 mg/l and 20 to 400 mg/l respectively. Relatively, 2,4-DCP and phenol were found to have a more significant stimulatory effect on the dehydrogenase activity in Rhizobium species with stimulation peak value been 6.9% and 10.3% respectively. At concentrations above the stimulatory levels, glyphosate and phenolic compounds increasingly inhibited dehydrogenase activity as the concentration increased, reaching saturation at values below 100%. The maximum inhibition of dehydrogenase activity ranged from 88.37% for phenol to 99.14% for formulated glyphosate. The IC50s of the individual compounds varied significantly (p < 0.05).The decreasing order of toxicity was 2,4-DCP > 4-CP > glyphosate > phenol.
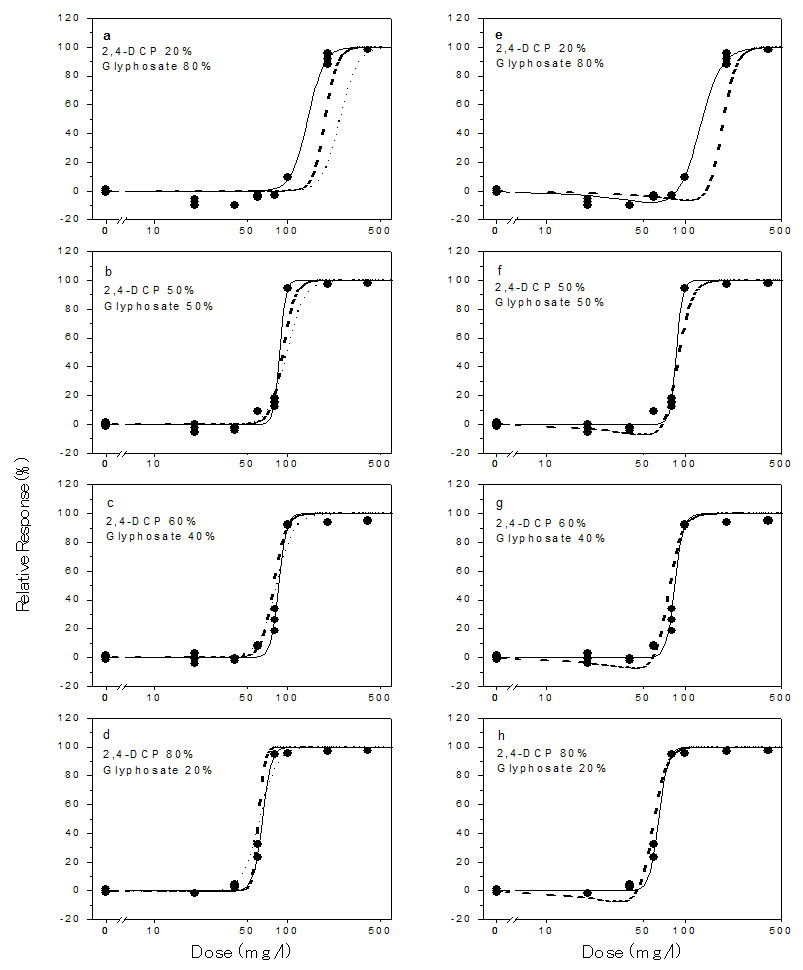
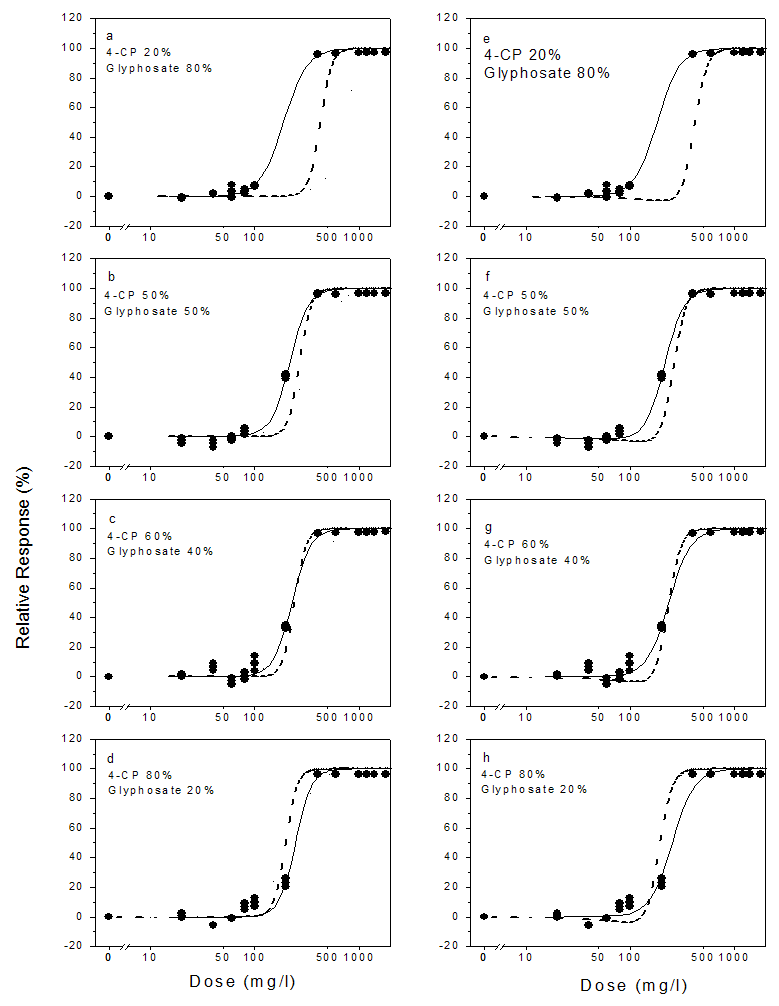
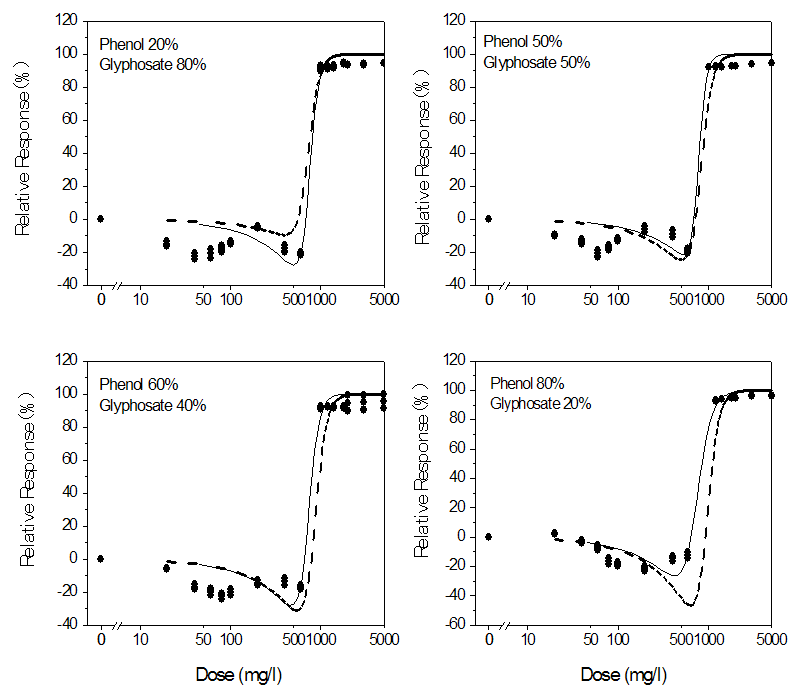
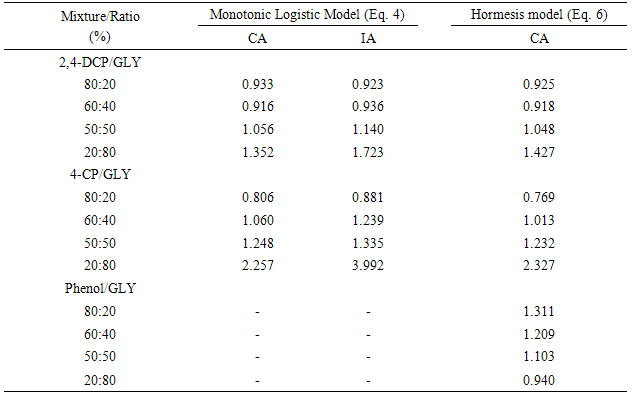
3.2. Toxicity of Binary Mixtures of Chemicals
- The dose response plots, the model fits for the chemical mixtures and the toxicities of the mixtures predicted from the CA and IA models are shown in Figures 2 – 4. The binary mixtures of phenolic compounds with glyphosate as with the individual compounds were found to be stimulatory to the dehydrogenase activity at low doses and inhibitory at high doses. This stimulatory effect was higher with phenol and glyphosate mixtures. The peak stimulation values were 24.02%, 22.7%, 24.4% and 23.2% for mixtures containing 20%, 50%, 60% and 80% phenol respectively (Fig. 4). As with the individual compounds, the mixtures showed saturation of inhibitory effect. The maximum inhibition of dehydrogenase activity ranged from 94.40% to 99.77% in the mixtures. The experimental data were adequately described by the logistic and hormesis models.
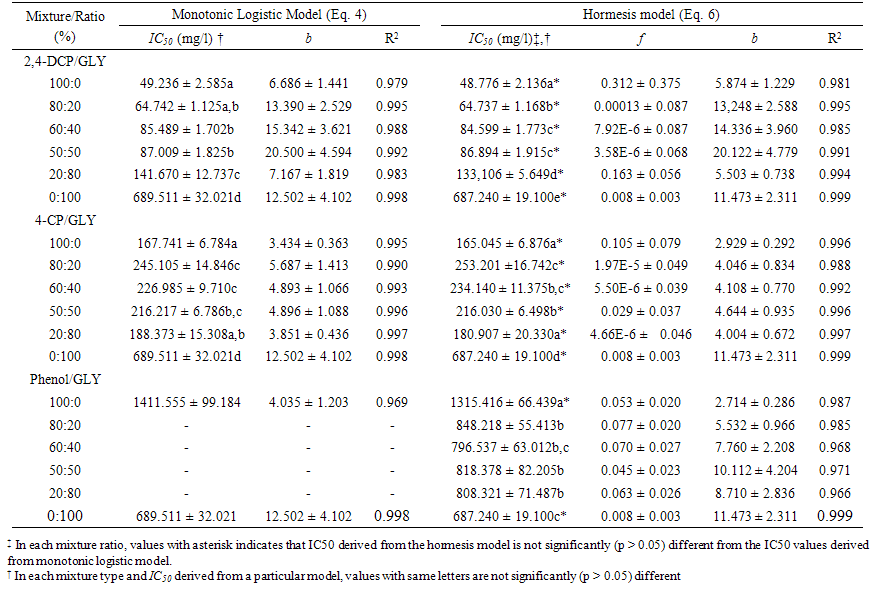 | Table 1. Parameters of the dose-response functions for the individual chemicals and mixtures |
|
4. Discussion
- The monotonic and hormesis models gave good descriptions of the experimental data with R2 values ranging from 0.966 to 0.999 and greater than 0.99 in most cases. The effects of using monotonic logistic model to determine the toxicity of hormetic mixtures were marginal. Changes in IC50 values of the mixtures were insignificant when monotonic logistic model was used instead of hormesis model. This indicates, as was observed by Calabrese [20], that above the toxic threshold, the shape of the dose-response curve is similar for monotonic and hormesis model. Similar observation was made by Belz et al. [17] on the growth of Lactuca sativa and Lemna minor exposed to binary mixtures of herbicides. Hormesis in microorganisms have been reported to be associated with microbial exposure to phenols and glyphosate for a number of microbial responses. This phenomenon has been widely reported among bioluminescent bacteria [21-23]. Activities of dehydrogenase enzymes in bacterial cells have also been reported to be stimulated by phenols at low doses [24-26]. Above the hormetic doses, hormetic substances become toxic. This was also observed with the phenolic compounds and formulated glyphosate used in this study. At high concentrations, the phenols inhibited the dehydrogenase activity of the Rhizobium species in a manner proportional to their octanol-water partition coefficient. Similarly, the formulated glyphosate exerted toxic effects on the activity of dehydrogenases in the test organism. These substances are known to be toxic to microorganisms. Phenols for instance are known membrane-damaging substances [27-29]. Glyphosate is reportedly toxic to microorganisms [30, 31]. In Roundup®, its toxicity may further be increased by the surfactant component, polyoxyethyleneamine [30]. In mixtures, these substances could interact to modulate the toxicity of each other. The presence of glyphosate modulated the toxicity of the phenolic compounds. This modulation was more prominent with 20% 2,4-DCP/80% glyphosate and 20% 4-CP/80% glyphosate mixtures. According to our previous analyses, synergistic, additive and antagonistic actions depending on the relative ratios of the individual components were possible [13]. The isobolographic analysis indicated that 20% 2,4-DCP/80% glyphosate and 20% 4-CP/80% glyphosate mixtures were synergistic [13]. This observed deviation from additivity was supported in the present study by the predictions of CA models based on the monotonic logistic model and the hormesis model. These variations in the predictions of the CA model could be attributed to synergistic and antagonistic effects of some mixtures [32-34], as were suggested by the isobolographic analysis of the mixtures [13]. The model deviation ratios (MDR) between predicted and experimentally observed effect concentrations lie between 0.5 and 2.0, suggesting that the deviations are marginal and within the expected inter-laboratory/inter-experiment deviation for most species [18, 19]. These ratios and their effects corroborated the results of the previous study done with isobolographic analysis of the experimental data [13].The size of hormetic effects were either overestimated or underestimated by the CA model, which might be related to non-linear relationship of the size of hormesis with the mixture ratio. This observation could be attributed to marginal hormetic responses in the mixtures. Size of hormesis was suggested to change linearly with mixture ratio if there are no interactions between the chemicals showing large and reproducible hormesis [17].The results indicated that the toxicities of the mixtures could be predicted by CA and IA models. These models were intended for the prediction of toxicity of chemical mixture on the basis of dose-response curve of the individual components in the mixture. While the CA model assumes that the mixture components have similar mode of action, IA model assumes that the components have dissimilar mode of action. Although the phenolic compounds and the glyphosate or its adjuvant, POEA may have different modes of action against bacteria, significant difference did not exist between the predicted values of mixture toxicity on the basis of CA and IA for most mixtures of glyphosate with 2,4-DCP or 4-CP. Similar insignificant differences between mixture toxicity predicted on the basis of CA and IA for phenolic compounds with similar and dissimilar action mechanisms was reported by Huang et al. [32]. Likewise, in a similar study, Barata et al [35] reported accurate prediction of mixture toxicity of dissimilarly acting chemicals by the CA and IA models. In addition, virtually identical toxicities predicted from CA and IA model for mixtures of similarly-acting phenylurea derivatives were reported [36]. This showed that both concepts, concentration addition and independent action, may serve as valuable tools for predicting toxicity of chemical mixtures [37].
5. Conclusions
- The toxicities of the binary mixtures of formulated glyphosate and phenols (2,4-DCP, 4-CP and phenol) were analyzed using concentration addition (CA) and independent action (IA) models. The CA and IA models predicted the toxicity of the mixtures with variable degree of accuracy in relation to experimental values, indicating possibility of synergistic, additive and antagonistic actions depending on the relative ratios of the individual components. However, most model deviation ratios (MDR) between predicted and experimentally observed effect concentrations lie between 0.5 and 2.0. These values are within the expected inter-laboratory/inter-experiment deviation for most species. We therefore concluded that the joint action of the mixtures on Rhizobium species dehydrogenase activity were additive. This information constitutes an essential contribution towards assessing the environmental risk of glyphosate and some intermediates of 2,4-D degradation. Biodegradation processes and the prevailing environmental conditions that determine the residual amounts of these herbicides and their metabolic intermediates in the environment may constitute important factors affecting toxicity of these chemicals. This study needs to be extended to microbial communities of soil or aquatic ecosystems, since microbes exist as a consortium rather than pure cultures in natural environments.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML