-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Life Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1387 e-ISSN: 2163-1395
2014; 4(6): 253-259
doi:10.5923/j.als.20140406.01
Rhizosphere Microflora and Physico-Chemical Nature of Selected Garden Soil
Olajide Adedayo Ajayi
Department of Microbiology, Adekunle Ajasin University, Akungba-Akoko, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Olajide Adedayo Ajayi, Department of Microbiology, Adekunle Ajasin University, Akungba-Akoko, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
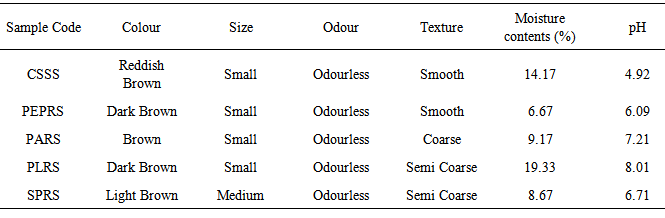
The samples used for this study were obtained from different rhizosphere garden soil sources. This include sweet potato rhizosphere soil (SPRS), plantain rhizosphere soil (PLRS), pineapple rhizosphere soil (PARS), pepper rhizosphere soil (PEPRS) and the control soil sample source (CSSS). The bacterial population determined by a pour plate technique showed a range of 4 x10-5 cfu/mL in control soil sample source (CSSS), to 29 x10-5 cfu/mL in sweet potato rhizosphere soil (SPRS). The bacterial isolates include Aerobacter spp., Bacillus cereus, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus spp., Escherichia spp., Lactobacillus spp., Micrococcus spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas spp., Rhizobium spp., Staphylococcus spp., while the fungi isolates were Aspergillus, Fusarium, Candida, Epidermophyton, Geotrichum, Verticillum, Trichophyton, Tubercularia, Beauveria, Cladosporium, Chaetomium, Botryotrichum and Rhizopus. Bacillus spp. constituting 53.34% and Pseudomonas spp. constituting 13.33% of the total isolates are the most dominant microorganism in soil sources studied. The moisture content for the samples range from 6.67% in PEPRS to 19.33% in PLRS. Some physiological studies show the range of pH from pH 4.92 in CSSS to pH 8.01 in PLRS sample sources. The soil pH values obtained in this study were near neutral ranges, which favour microbial growth. Various species of fungi were encountered in soil sources including the harmful ones. Hence, fungicides can be applied occasionally on these soils to reduce the fungi load in these areas when necessary.Data obtained in this study is valuable to monitor and protect the environment including agriculture products for sustainable economic development.
Keywords: Garden soil, Microflora, Physico-chemical, Rhizosphere
Cite this paper: Olajide Adedayo Ajayi, Rhizosphere Microflora and Physico-Chemical Nature of Selected Garden Soil, Advances in Life Sciences, Vol. 4 No. 6, 2014, pp. 253-259. doi: 10.5923/j.als.20140406.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Soil plays vital role in many life processes especially for plant survival and related human activities. It comprises mixture of ingredients such as minerals, air, water, organic materials in the form of solids, gases and liquids and various forms of organisms including decaying remains of once-living things [1, 2]. Soil inhabits various species of microorganisms in nature. One estimate put the number at over a million species per gram of soil, although a later study suggests a maximum of just over 50,000 species per gram of soil [3, 4]. The total number of organisms and species can vary widely according to soil type, location, and depth [5]. Micro-organisms including fungi and bacteria, have an effective chemical exchanges between roots and soil and act as a reserve of nutrients. Humans impact soil formation by removing vegetation cover with erosion as the result [6]. The rhizosphere soil sources are the narrow region of soil that is directly influenced by root secretion and associated soil [7].Soil formation, or pedogenesis, is the combined effect of physical, chemical, biological and anthropogenic processes on soil parent materials. Soil genesis involves processes that result from additions, losses, transformations and translocations of material that compose the soil. Soil life cycle can be influenced by at least five classic soil forming factors that are dynamically intertwined in shaping the way soil is developed. This includes parent material, regional climate, topography, biotic potential and the passage of time [8]. Soil is made up of different structures. Part of this are finely ground rock particles, grouped according to the size as sand, silt and clay. Each size plays significantly different role whereby the largest soil particles, sand, determine aeration and drainage characteristics, while the tiniest, that is the sub-microscopic clay particles are chemically active. They binding with water and plant nutrients thus significantly improves nutrient cycling. The ratio of these sizes determines soil type: clay, loam, clay-loam, silt-loam, and so on. In addition to the mineral composition of soil, humus (organic materials) also plays a crucial role in soil characteristics and fertility for plant life. Soil may be mixed with larger aggregate, such as pebbles or gravel. Not all types of soil are permeable, such as pure clay [9]. In related development, in 1975, the U.S. Department of agriculture created a taxonomic scheme that grouped all soils into 12 major groups known as orders [10].Organisms living in the soil create a community called the “edaphon” and they constitutes about 1-10% of the dry mass of the soil organic matter. The soil biota includes, Mega fauna-size which varies in size from 20 cm upward e.g. moles, rabbits, rodents; Macro fauna- size ranges between 2-200 mm e.g. woodlice, earthworm, beetles, centipedes, slugs, snails, ants and harvestman; Mesofauna- size ranges between 100 micrometer-2mm e.g. tardigrade, mites and springtails; Microfauna and Microflora-size are between 1-100 micrometer e.g. yeast, bacteria (commonly actinobacteria) fungi, protozoa, roundworms and rotifers as described by Tropical Soil Biology Fertility and International Center for tropical Agriculture, TSBF-CIAT [11]. Of these, bacteria and fungi play key roles in maintaining a healthy soil. They act as decomposers that breakdown organic material to produce detritus and other breakdown products [12, 11]. A gram of garden soil can contain around one million fungi such as yeast and molds [13]. Many fungi help in diseases control. For example, nematode-trapping fungi that parasitize diseases causing nematode and fungi that feed on insects may be useful as bio control agent. To date, several mycopesticides have been developed and used in several countries including the United Kingdom and the United States [14]. Many fungi just like bacteria can be cultivated by standard laboratory techniques. Common genera include Absidia, Alternaria, Aspergillus, Chaetomium, Fusarium, Mucor, Penicillium and Moterella. These are the fungi that are commonly isolated from the soil dilution techniques [15].Mycorrhiza which is a symbiotic relationship between fungi and plants roots is another major living group considered in soil biological activities. Land management practices affect the formation of mycorrhizal fungi in soil which decline fallowed fields or in those planted crops that do not form mycorrhizae. Some inoculums of mycorrhizal fungi are commercially available and can be added to the soil at the planting time [16]. Generally, edaphology, the science of plant nutrition and plant growth and pedology, the science of soil formation or soil genesis” are of importance in determining the nature of soil and microbial activities [17]. This study is embarked upon to establish some facts on rhizosphere microbial ecology of selected garden soil sources in the tropics and plant nutrition. This will enhance sustainable food production and biosafety resources. Similarly, dominant microbial species of novel scientific interest and some of their ecological attributes in the rhizosphere community niche were determined during the study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Sources
- The samples used for this study were obtained from different rhizosphere garden soil sources in Akungba-Akoko community, Nigeria. This include sweet potato rhizosphere soil (SPRS), plantain rhizosphere soil (PLRS), pineapple rhizosphere soil (PARS), Pepper rhizosphere soil (PEPRS) and the control soil sample source (CSSS). The soil samples were collected using a sterile spoon for removal of the sub-surface soil into sterile sample bottles which were then transferred to the laboratory for analysis. The samples were preserved at 4℃ in refrigerator to slow down biological activities and reduce chemical reactions in nature.
2.2. Inoculums Preparation and Microbiological Analysis of Soil Samples
- The stock cultures for this study were prepared by weighing 1g of the soil samples into test tubes containing 10ml of sterile distilled water and shaken properly for homogeneity. A pour plate technique was used to estimate the soil microbial population. Serial dilution preparations of 10-1 to 10-10 were done for the soil samples. Appropriate diluents were plated for microbial enumeration. Sterile molten nutrient agar (NA) and eosin methylene blue agar (EMB) was used for bacteria while, potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium was used for fungi cultivation. The plates were allowed to solidify, inverted and incubated at 37℃ for 24 hours for bacteria and 25℃ for 5 days for fungi [18]. Total microbial counts were estimated for the sample sources.
2.3. Identification and Preservation of Bacterial Isolates
- Bacterial species isolated were characterized and identified by standard microbiological techniques [18, 19]. This include the Gram stain reaction, some cultural and biochemical characteristics of the isolates based on their fermentations of sugars such as fructose, glucose, maltose, sucrose, arabinose and other related carbon sources and media. Pure culture of isolates from sample sources were prepared on nutrient agar slants in McCartney bottles and kept in the refrigerator at 4℃ to preserve them and to serve as stock culture for subsequent tests during identification.
2.3.1. Identification of Fungi
- Each fungal colony was picked from the plates containing massive growth of organisms with sterile inoculating needle and stabbed on sterile plates were prepared containing potato dextrose agar using an aseptic technique. After inoculation, the prepared plates containing each colony were incubated invertedly at 25℃ for 5 days for further identification purposes.
2.3.2. Lactophenol Staining
- A small portion of the mycelium was removed from the fungal culture and teased in the drop of lactophenol cotton blue stain earlier introduced on a clean microscopic slide. The organisms were teased very well and covered with a cover slip, then examined with the aid of a light microscope under objective x40 [20]. The compendium of fungi was used for the identification of fungal isolates [20].
2.3.3. Physiochemical Analysis
- Some physicochemical parameters of the sample sources, such as colour, size, odour, and texture were physically determined amongst other parameters such as moisture contents, pH values, metals and mineral elements composition as described below.
2.3.4. Moisture Contents Determination
- Clean petri-dish used for this study was dried in an oven at 80℃ for about 30 minutes. It was then cooled and weighed (W1). A known weight of the prepared sample sources was placed into the petri-dish, the weight was also noted (W2) and kept in an oven maintained at 105℃ for about 3hrs. The petri-dish with the sample was then removed at hourly intervals for the purpose of getting a constant weight. It was cooled and weighed until a constant weight (W3) was obtained. The loss in weight during drying is equal to the moisture content of the sample as calculated below:5g of the soil sample sources of PARS, SPRS, PLRS, PEPRS and CSSS were used for the experiments:
 pH: The pH of each soil sample was measured by using pH meter (HANNAH PK 05) in the laboratory. The meter was standardized with buffer at pH 4.7 and 9 before use. The pH 7 was equally determined. The sensitive bulb was then immersed into the sample to get appropriate reading for this study.
pH: The pH of each soil sample was measured by using pH meter (HANNAH PK 05) in the laboratory. The meter was standardized with buffer at pH 4.7 and 9 before use. The pH 7 was equally determined. The sensitive bulb was then immersed into the sample to get appropriate reading for this study.2.3.5. Determination of Metals and Mineral Elements
- Some metals and mineral elements determined for the sample sources were Iron (Fe), Zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), potassium (K), Sodium (Na) and lead (Pb). Modified EDTA extraction method used to quantify lead (Pb), Zinc (Zn) and related metalsDilute, Ethylene-diamine-tetra-acetic acid, EDTA has been a preferred extractant for soils long before some other known methods. Different concentrations of EDTA (0.01 to 0.1M) have been used in combination with buffered pH values of 4.6 to 9.0, although pH 7 appears to be favourable [21]. Different soil extractant ratios and extraction times have been used. Clayton and Tiller [21] used a 7-d extraction with 0.1M EDTA at pH 6.0 for classification of soils with respect to the degree of contamination with Cd, Pb and Zn. Any other short term extraction period can however be adapted for routine analysis. Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu) and Manganese (Mn) analysis.Iron (Fe) constitutes a major aesthetic problem and not physiological because its high concentration may stain laundry and fixtures. Copper (Cu) can constitute astringent taste and discoloration to water sources. Similarly, it can cause corrosion of pipe, fittings and utensils – through which it flow or has contact with. While, Manganese (Mn) is also highly toxic to humans and stains fixtures. Its laundry – Total laundry value, TLV is 0.05 Mg/I [22].Standard Preparations of the SamplesMehlich-3 extracts also helps in determination of Cu, Mn and Fe constituents of the samples and taking the final reading on Atomic Adsorption Spectrophotometer, AAS as described below:1. MIXED STOCK SOLUTION: To a 250ml volumetric flask, add 50.00ml of 1000ppm Mn, 50.00 ml 1000 ppm Fe, and 1.00 ml of 1000pm Cu. Dilute to the mark with Mehlich-3 extractant. This solution contains 200 ppm Mn and Fe and 4.00 ppm Cu. 2. STANDARDS: Provision was made for 7, 50-ml centrifuge tubes, into which 50ml of Mehlich-3 extractant was added. 1.25, 2.50, 3.75, 5.00, 7.50 and 10.00 ml of liquid was removed from the 5 respective tubes. The same amount of the mixed stock solution was added. These samples contain 0, 5.00, 10.00, 15.00, 20.00, 30.00 and 40.00ppm Fe and Mn and 0, 0.100, 0.200, 0.300, 0.400, 0.400, 0.600, and 0.800 ppm Cu.3. Standards was read and sample extracts was undiluted on the AAS.4. Calculations: Concentration of sample from a standard curve (ppm) was determined using the following calculations:
 Note: The standards are scaled to provide the following approximate maximum sample contents in ppm: Fe and Mn, 100; and Cu, 5. Higher contents will require dilution.Mehlich-3 extractionThe process of melich-3 extraction is stated bellows:1. Mehlich-3 extraction solution: In a 500ml polythene bottle, add ≈250ml water, dissolve 69.45g NH4F and 36.75 EDTA, and make to 500ml. To a 10 liter jug, add about 8 liters of water and 200g NH4NO3. Add 40ml of the EDTA/NH4F solution, 115 ml acetic acid, and 8.2 ml of 70% nitric acid. Dilute to 10 liters. The pH should be 2.5 ± 0.1 by adjustment with the acid.2. Using a 3.0ml scoop, weigh 3.0ml scoop, weigh 3.0 ml of soil in a 50ml centrifuge tube, and record weight to the nearest 0.0g. NOTE: All centrifuge tubes and caps should be acid washed before use, and stored in protective plastic to prevent contamination. This method is very sensitive to Zn contamination.3. Add 30ml of Mehlich-3 extractant to a batch of 24 samples. Cap and shake for 5 minutes. Let stand for 10 minutes, then centrifuge.4. Repeat step 3 until all samples have been centrifuged. Be sure to stagger samples appropriately so that samples sit exactly 10 minutes between shaking and centrifugation.Reagent 0.05M EDTA (PH7); dissolve 93.05g of EDTA (di-sodium salt) in approximately 4L of distilled and deionised water (DO). Adjust to pH 7.0 with 7M NH4OH, and make up to 5L with diluents water.Procedure 1. Weigh 5g of air-dried (<2mm) soil into a 125 Erlenmeyer flask and add 25ml of 0.05M EDTA solution.2. Shake for 1h at a speed of 120 cycles min-13. The samples were filtered through a Whatman No. 42 filter paper after shaking and analyze for metals by atomic spectroscopicThe Ca and Mg content of the samples was determined using extraction method. The resultant reading was taken on the Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAS).These were done by preparing some stock solutions and follow the sequence below:1. MIXED STOCK SOLUTION – In a 1000ppm volumetric flask, add 8.00ml of 1000ppm of Ca and 1.60 ml of 1000pm Mg, Add 5.00ml of Mehlich-3 extractant. Dilute to 100ml with 1000ppm La or Sr solution (below). This solution contains 80ppm Ca, and 16 ppm Mg.2. STRONTIUM, 1000PPM: Dilute 6.08g of SrCl2 6H2O to 2 litres in a volumetric flask. Alternatively, make 1000ppm La solution by diluting 5.35g of LaCl3.7H2O to 2 litres.3. STANDARD PREPARATION: into 5 50-ml centrifuge tubes, add 38ml of 1000ppm Sr (or La) and 2.00ml of Mehlich-3 extraction solution, and mix well. Then remove from the respective tubes O, 2.00, 4.00, 6.00, and 8.00, 12.0, and 16.0ppm. Ca; O, 0.800, 1.60, 2.40 and 3.20ppm.Mg.4. SAMPLE PREPARATION: Add 0.500ml of sample to a glass vial. Dilute with 9.50 of 1000 ppm Sr (or La).5. Read standards and samples on the AAS. The burner head should be rotated for Mg.6. Calculations: Determine concentration of sample from a standard curve (ppm). The following calculation applies: Water sample/soil concentration (cmol (+).kg-1) == ppm x 30Eq.wt x Sample wtWhere the equivalent weights (Eq.wts) are as follows Ca = 20.04
Note: The standards are scaled to provide the following approximate maximum sample contents in ppm: Fe and Mn, 100; and Cu, 5. Higher contents will require dilution.Mehlich-3 extractionThe process of melich-3 extraction is stated bellows:1. Mehlich-3 extraction solution: In a 500ml polythene bottle, add ≈250ml water, dissolve 69.45g NH4F and 36.75 EDTA, and make to 500ml. To a 10 liter jug, add about 8 liters of water and 200g NH4NO3. Add 40ml of the EDTA/NH4F solution, 115 ml acetic acid, and 8.2 ml of 70% nitric acid. Dilute to 10 liters. The pH should be 2.5 ± 0.1 by adjustment with the acid.2. Using a 3.0ml scoop, weigh 3.0ml scoop, weigh 3.0 ml of soil in a 50ml centrifuge tube, and record weight to the nearest 0.0g. NOTE: All centrifuge tubes and caps should be acid washed before use, and stored in protective plastic to prevent contamination. This method is very sensitive to Zn contamination.3. Add 30ml of Mehlich-3 extractant to a batch of 24 samples. Cap and shake for 5 minutes. Let stand for 10 minutes, then centrifuge.4. Repeat step 3 until all samples have been centrifuged. Be sure to stagger samples appropriately so that samples sit exactly 10 minutes between shaking and centrifugation.Reagent 0.05M EDTA (PH7); dissolve 93.05g of EDTA (di-sodium salt) in approximately 4L of distilled and deionised water (DO). Adjust to pH 7.0 with 7M NH4OH, and make up to 5L with diluents water.Procedure 1. Weigh 5g of air-dried (<2mm) soil into a 125 Erlenmeyer flask and add 25ml of 0.05M EDTA solution.2. Shake for 1h at a speed of 120 cycles min-13. The samples were filtered through a Whatman No. 42 filter paper after shaking and analyze for metals by atomic spectroscopicThe Ca and Mg content of the samples was determined using extraction method. The resultant reading was taken on the Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAS).These were done by preparing some stock solutions and follow the sequence below:1. MIXED STOCK SOLUTION – In a 1000ppm volumetric flask, add 8.00ml of 1000ppm of Ca and 1.60 ml of 1000pm Mg, Add 5.00ml of Mehlich-3 extractant. Dilute to 100ml with 1000ppm La or Sr solution (below). This solution contains 80ppm Ca, and 16 ppm Mg.2. STRONTIUM, 1000PPM: Dilute 6.08g of SrCl2 6H2O to 2 litres in a volumetric flask. Alternatively, make 1000ppm La solution by diluting 5.35g of LaCl3.7H2O to 2 litres.3. STANDARD PREPARATION: into 5 50-ml centrifuge tubes, add 38ml of 1000ppm Sr (or La) and 2.00ml of Mehlich-3 extraction solution, and mix well. Then remove from the respective tubes O, 2.00, 4.00, 6.00, and 8.00, 12.0, and 16.0ppm. Ca; O, 0.800, 1.60, 2.40 and 3.20ppm.Mg.4. SAMPLE PREPARATION: Add 0.500ml of sample to a glass vial. Dilute with 9.50 of 1000 ppm Sr (or La).5. Read standards and samples on the AAS. The burner head should be rotated for Mg.6. Calculations: Determine concentration of sample from a standard curve (ppm). The following calculation applies: Water sample/soil concentration (cmol (+).kg-1) == ppm x 30Eq.wt x Sample wtWhere the equivalent weights (Eq.wts) are as follows Ca = 20.04 Mg = 12.16Note: The standards are scaled to provide the following approximate maximum soil. The following approximate maximum soil contents, in cmol (+).kg-1: Ca, 8 and Mg 2.6. Higher contents will require dilution.
Mg = 12.16Note: The standards are scaled to provide the following approximate maximum soil. The following approximate maximum soil contents, in cmol (+).kg-1: Ca, 8 and Mg 2.6. Higher contents will require dilution.3. Results
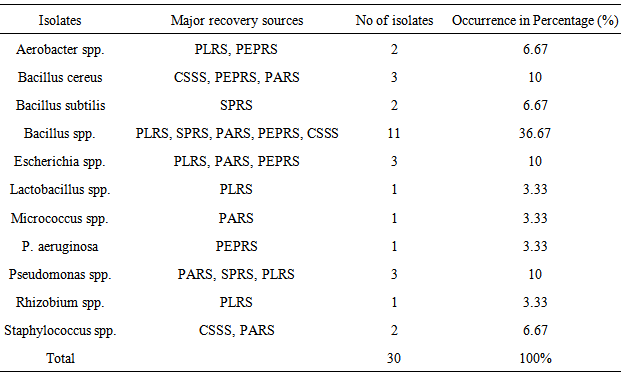
- Sample obtained from rhizosphere soil sources for the purpose of this study were determined for some microbiological and physico-chemical parameters. Total of 30 bacterial species and 25 fungal isolates were obtained during the study. The thirty (30) isolates recovered during the study were identified by standard microbiological methods. Biochemical characteristics test showed that all the isolates were able to ferment glucose, maltose, and sucrose with subsequent production of acids except Pseudomonas spp. This organisms were categorized into eight (8) genera out of which twenty (20) were Gram Positive; while ten (10) were Gram-negative bacteria. The Gram-Positive species under this context were Bacillus subtilis, Bacilluscereus, Bacillus spp, Micrococcus spp., Staphylococcus spp and Lactobacillus spp. Gram-negative isolates include Aerobacter spp, Escherichia spp, Lactobacillus spp, Pseudomonasaeruginosa and Pseudomonas spp. The bacillus spp were the predominant organism constituting 53.34% of the total isolates, while the least genera were Lactobacillus spp., Micrococcus spp. and Rhizobium spp. having 1% each of the total isolates (Table 1).
|
|
|
|
4. Discussions
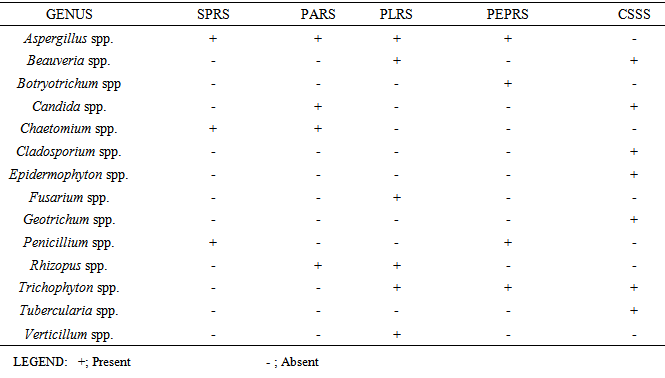
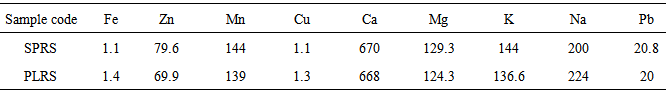
- Various types of microorganism were isolated from the different rhizosphere garden soil samples collected from a tropical region, Akungba-Akoko community, Nigeria. This contains many bacteria that feed sloughed-off plant cells stem rhizodeposition and the protein and sugars released by roots, such as Aerobacter spp., Bacillus spp., Bacillus cereus, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia spp., Lactobacillus spp., Micrococcus spp., Pseudomonas spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Rhizobium spp., Staphylococcus spp. Others are fungi species such as Aspergillus, Beauveria, Botryotrichum, Candida, Chaetomium, Cladosporium, Epidermophyton, Fusarium, Geotrichum, Penicillium, Rhizopus, Trichophyton, Tubercularia and Verticillum. These organisms are either obligate aerobes or facultative anaerobes and because of their uniqueness, unpredictable nature, biosynthetic capabilities, their functions and how they affect the soil quality, they could be differentiated into beneficial and harmful groups as reported by Dahlgren and Driscoll [23].Bacillus spp constituting 53.34% and Pseudomonas spp. constituting 13.33% of the total isolates are the most dominant microorganism in soil sources studied. Autochthonous bacterial population is uniform and constant in soil, since their nutrition is derived from native soil organic matter (eg. Arthrobacter and Nocardia whereas Zymogenous bacterial population in soil is low, as they require an external source of energy, eg. Pseudomonas and Bacillus and this increases gradually when a specific substrate is added to the soil. To this category belong the cellulose decomposers, nitrogen utilizing bacteria and ammonifiers [24]. The presence of Bacillus spp, Pseudomonas spp, Aerobacter spp and some enteric organisms from soil sources is consistent with previous reports [24] where similar group of organisms were obtained from such environment. Escherichia spp and some other enteric microorganism obtained from all the soil samples could also be associated with some environmental contaminants in the fact that domestic animals roam free and their droppings contain these organisms [25]. The highest occurrence of Bacillus spp might be due to their ability to form spores and produce hydrolytic enzymes.The main habitat of endospore forming Bacillus organisms is the soil. Bacillus subtilis is a model organism for studying endospore formation in bacteria. Bacillus subtilis supports plant growth and act as biofungicides or antibacterial agents for benefiting agricultural crops. Bacillus subtilis also reduces mild steel corrosion [26]. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the predominant inhabitant of environment that contains high dissolved oxygen and this clearly makes it the most abundant organism on earth [27]. These bacteria are capable of degrading several remains of plant in the soil [1]. The bacterial isolates obtained in this study shows diversified phenotypic characteristics. In this regard, it is quite obvious that the control sample soil (CSSS) and other sources, SPRS, PARS, PEPRS are composed of Gram positive and Gram negative organisms, while, PLRS soil comprises of only Gram positive organisms. In the fungal group Aspergillus spp is one of the organisms recovered. An immunocompromised individual exposed to high doses of fungi spores such as Aspergillus spp, can come down with respiratory problems e.g. asthma. Dahlgren and Driscoll [23] showed that some genera of fungi causes diseases of hair, skin, and the nail e.g. Trichophyton spp and Epidermophyton spp which were also isolated in this study. The nature of isolates obtained in this study also correlates with the report of Thorn [15] which showed common genera of fungi such as Chaetomium, Fusarium, Penicillium, Aspergillus, Mucor and Alternaria isolated in the soil. According to Dighton et al. [28], the development of fungi is especially favoured by the soil having an acidic reaction and where an aerobic condition is likely to be present near the surface since they exist both in mycelia and spore stages. The benefits derived from these fungi include active decomposition of cellulose and lignin of plant tissues and formation of water stable aggregates according to Dighton et al. [28] Yeasts were not isolated much in this study in corroboration with report of Dighton et al. [28] that yeasts are generally not found in large number except in soils of vineyards and orchards.Table 3 shows some physico-chemical parameters of the soil sample sources including the colour which range from red to dark brown and the size which were observed as small, smooth to medium semi coarse texture respectively among other values. The moisture content were 6.67% in pepper rhizosphere soil sample (PEPRS) to a high of 19.33% in plantain rhizosphere soil sources (PLRS). The pH range from pH 4.92 in control soil sample source (CSSS) to pH 8.01 in plantain rhizosphere soil sample (Table 3a). The soil pH values obtained in this study were near neutral ranges, which favour microbial growth. Among the mineral elements considered for this purpose which were Fe, Zn, Mn, Cu, Ca, Mg, K, Na, and Pb. The Fe, Cu, Ca and Pb for the rhizosphere sources determined are in close range of composition (Table 3b). This is in corroboration with the study of Chapin [29] who showed the nature of crop responses to nutrient stress and compares these responses to those of species that have evolved under more natural conditions, particularly in low-nutrient environments. The effect of various mineral elements in soil on plant nutrition and growth is generally considered under this context.This study shows that there are both beneficial and harmful groups of fungi present in the soil. Similarly, some forms of bacterial species encountered apart from coliforms which signify contamination may be indicative of some crop microflora in the planting zone. Some precautionary measures should be taken to protect our environment and assess the applicability of fertilizer based on the microbial population or soil structure of the sampled site. Nevertheless, modern technology (nuclei acid probes) to obtain such detailed overview of microbial diversity can be intensified in extension of this investigation in future. Fungicides can be applied occasionally on this soil sources especially when there are lots of people inhabiting the areas to reduce the fungi load for epidemiological reasons. According to Inderjit et al. [30] root pathogenic fungi such as Verticillum causes major economic losses in agriculture, so care should be taken to monitor soil sources where these group of organisms are encountered in order to protect our agricultural systems. Hence, the data obtained in this study can serve as a guide to monitor and protect human health including the agriculture products for sustainable economic development.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Thanks to my junior science colleagues that assisted in the sample collection and Prof. O.P.G. Nmorsi, Ambrose Alli University, Nigeria, for his encouragement in making further research developments.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML