-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Life Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1387 e-ISSN: 2163-1395
2014; 4(3): 151-155
doi:10.5923/j.als.20140403.10
Consumer Buying Behaviour; A Factor of Compulsive Buying Prejudiced by Windowsill Placement
Irfan Hameed, Yasir Ali Soomro
PhD Scholar & Assistant Professor, Iqra University, Pakistan
Correspondence to: Irfan Hameed, PhD Scholar & Assistant Professor, Iqra University, Pakistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This empirical research investigates the impact of windowsill placement on the compulsive buying behavior of consumers on three different types of products i.e., convenience products, shopping products, and specialty products. Positive effect of windowsill placement on all three types of product categories has been hypothesized. The categorical regression (Optimal scaling) was used to test the hypotheses. The data was collected via self administered questionnaire from Pakistan through systematic random sampling, and the sample consisted of 500 respondents. The results of data analysis supported only the 1st hypothesis which highlighted that placement of products in shopping centers has an impact of unplanned buying of consumers for convenience products. While rest of the two hypotheses regarding shopping and convenience products were not supported by the data. This research is helpful for those companies which believe in classical conditioning. This is perhaps one of the first study in non-western (Pakistani) context.
Keywords: Windowsill placement, Compulsive buying, Convenience products, Shopping products, Specialty products
Cite this paper: Irfan Hameed, Yasir Ali Soomro, Consumer Buying Behaviour; A Factor of Compulsive Buying Prejudiced by Windowsill Placement, Advances in Life Sciences, Vol. 4 No. 3, 2014, pp. 151-155. doi: 10.5923/j.als.20140403.10.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- This study is an insight into the compulsive buying pattern of individuals on the basis of maneuvers used by marketers. The relationship between windowsill placement and the demand of customers have been studied with respect to different consumer product categories. Windowsill placement has been used as independent variable and types of consumer products have been used as dependent variables namely convenience products, shopping products, and specialty products. Unsought products have not been used for research purpose because of its very nature. Operational definitions of the variables have been given below under the heading of theoretical background.
2. Theoratical Backround
2.1. Consumer Products
- Consumer products are products and services bought by final consumers for personal consumption. Marketers usually classify these products and services further based on how consumers go about buying them. Consumer products include convenience products, shopping products, specialty products, and unsought products (Kotler, Armstrong, 2012).
2.2. Windowsill Placement
- Windowsill placement refers to the placement of the product in the shopping center also known as shelf placement. In this study word windowsill placement denotes favorable position in the shopping center like placing it just behind the cashier, at eye level, or at the entrance of the store. All eye-movement studies of advertising or catalog displays show that visual area strongly increases attention (Janiszewski, 1998; Lohse, 1997). Several shopper surveys (Inman, Winer, & Ferraro, 2009) and field experiments (Chevalier, 1975; Curhan, 1974; Inman & McAlister, 1993; Wilkinson, Mason, & Paksoy, 1982) have shown that large increases in shelf space increase brand sales even when the price and location of the products remain unchanged (Campo & Gijsbrechts, 2005). There is a broad consensus on the following aspects of how people visually process scenes (Henderson & Hollingworth, 1999; Pieters & Wedel, 2007; Rayner, 1998; Wedel & Pieters, 2008).
2.3. Compulsive Buying Behavior
- When individuals buy compulsively, they purchase excessive quantities of products that they don’t need and cannot afford (Roberts & Roberts, 2012). It is conceptualized as a response to deal with unpleasant life experiences, inner deficiencies or negative feelings (Faber & O'Guinn, 1992; O'Guinn & Faber, 1989). This feeling makes consumers purchase products to help alleviate negative feelings of stress, disappointment, frustration or lack of self esteem (Scherhorn, 1990). Pricing strategy obviously effect buying behavior to a great extent (Hameed, Soomro, Hameed, 2012).Convenience Goods: Commonly available, generally affordable, often prone to rapid consumption and re-buy, in which case these are referred to as Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG’s) like toothpaste, soups etc.Shopping Goods: A category of consumer goods that are purchased after the buyer has spent some time and effort comparing the price, quality, style and other attributes of the product in several stores Types of Consumer Products. Shopping goods include buying a Nike shirt or Adidas shirt.Specialty Goods: A category of consumer goods for which the consumers have a strong brand preference and are willing to spend substantial time, effort and money for acquiring the desired brand for example Buying Rolex watch, BMW car etc.
2.4. Hypotheses Construction
- Three hypothesized statements have been made to check the relationship between dependent and independent variable (s). Firstly the relationship of shelf placement on sales of convenience products, secondly the relationship of shelf placement on sales of shopping products, thirdly the relationship of shelf placement on sales of specialty products. The impact of placement has been studied with the help of the statistical test by using Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS). The test used is categorical regression (Optimal scaling) to interpret the findings that whether placement of products in shopping centers has an impact of unplanned buying of consumers or not. If yes then it is on which types of products.H1: There is a positive impact of windowsill placement in supermarkets on compulsive buying behavior of consumers for convenience products.Convenience products = α + β (Windowsill placement) + ξH2: There is a positive impact of windowsill placement in supermarkets on compulsive buying behavior of consumers for shopping products.Shopping goods = α + β (Windowsill placement) + ξH3: There is a positive impact of windowsill placement in supermarkets on compulsive buying behavior of consumers for specialty products.Specialty goods = α + β (Windowsill placement) + ξ
3. Research Methods
3.1. Participants and Design
- Data has been collected from the public of the most crowded city of the Pakistan (i.e. Karachi). Probability based sampling technique (i.e. systematic random sampling technique) has been used for selecting the sample out of the entire population. Every fifth person in the market was asked to fill a questionnaire so everybody had equal chance of being part of the research sample. Authors were not sure of the gender and age of the respondents so that’s why had sample respondents from various ages, background, income level, which made the research finding to be more generalized. Sampling friction have been calculated with the help of this formulaSampling friction = sample size / populationOn average almost one thousand individuals visit each superstore in evening and the target was to select one hundred respondents from each store, Sampling friction = 1000 (200 respondents from each store * 5 stores in total) / 5000 (1000 individuals in each store * 5 stores)=> 1000 / 5000 => 1/5 (every fifth respondent was asked to be part of the sample)Hence every tenth respondent have been targeted for the purpose of data collection. A sample size of five hundred respondents has been used for the research purpose. Hundred respondents were selected from every supermarket altogether five supermarkets were targeted.
3.2. Measures
- Self-administered closed ended questionnaires have been used for the purpose of data collection. All questionnaires were standardized and each questionnaire was having sixteen questions in total which were succeeding likert scale having 5 choices and they were coded in this phenomenon. 1 for strongly disagree, 2 for Disagree, 3 for Neutral, 4 for Agree, 5 for strongly agree.
4. Results & Discussion
4.1. Findings and Interpretation of the Results
- H1: There is a positive impact of windowsill placement in supermarkets on compulsive buying behavior of consumers for convenience products.
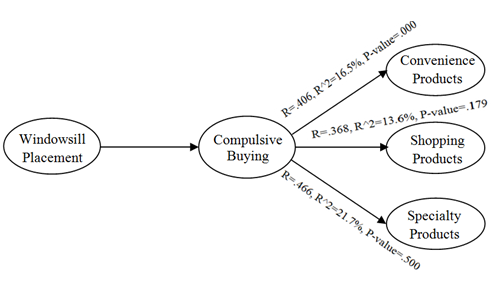
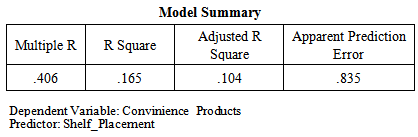 Correlation Coefficient (R) is 0.406 which shows that the relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for convenience products is moderate. Moreover value of Correlation Coefficient (R) is above 0 hence the relationship between the variables is direct. Coefficient of Determination (R^2) is 0.165 which shows that the 16.5% model is being explained by the windowsill placement and remaining 83.5% is being explained by unknown variables (which are not taken in to account for the purpose of this research).
Correlation Coefficient (R) is 0.406 which shows that the relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for convenience products is moderate. Moreover value of Correlation Coefficient (R) is above 0 hence the relationship between the variables is direct. Coefficient of Determination (R^2) is 0.165 which shows that the 16.5% model is being explained by the windowsill placement and remaining 83.5% is being explained by unknown variables (which are not taken in to account for the purpose of this research).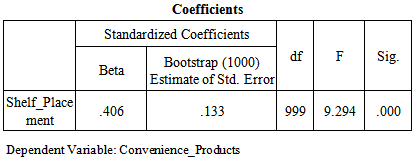 The significance value is 0.000 which is less than 0.05 so this shows that there is significant impact of windowsill placement in supermarkets on compulsive buying behavior of consumers for convenience products. F value is also greater than 3.83 (i-e 9.294) which also shows model is significant.Degree of freedom (DF) is associated with the sources of variance. The total variance has N-1 degrees of freedom. The Regression degrees of freedom correspond to the number of coefficients estimated minus 1. As our model is SLR so regression DF doesn’t make sense but DF total is 999 (1000-1). More over on the basis of p-value null hypothesis that there is no relationship has been rejected and alternate/research hypothesis has been accepted. As far as that there is positive relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for convenience products has been accepted on the basis of Beta value that is .406 in the above coefficient table which is positive showing the relationship is positive. Bootstrap confidence intervals provide a way of quantifying the uncertainties in the inferences that can be drawn from a sample of data. The idea is to use a simulation, based on the actual data, to estimate the likely extent of sampling error. To really have stable estimates, we have used 1000 replications. H2: There is a positive impact of windowsill placement in supermarkets on compulsive buying behavior of consumers for shopping products.
The significance value is 0.000 which is less than 0.05 so this shows that there is significant impact of windowsill placement in supermarkets on compulsive buying behavior of consumers for convenience products. F value is also greater than 3.83 (i-e 9.294) which also shows model is significant.Degree of freedom (DF) is associated with the sources of variance. The total variance has N-1 degrees of freedom. The Regression degrees of freedom correspond to the number of coefficients estimated minus 1. As our model is SLR so regression DF doesn’t make sense but DF total is 999 (1000-1). More over on the basis of p-value null hypothesis that there is no relationship has been rejected and alternate/research hypothesis has been accepted. As far as that there is positive relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for convenience products has been accepted on the basis of Beta value that is .406 in the above coefficient table which is positive showing the relationship is positive. Bootstrap confidence intervals provide a way of quantifying the uncertainties in the inferences that can be drawn from a sample of data. The idea is to use a simulation, based on the actual data, to estimate the likely extent of sampling error. To really have stable estimates, we have used 1000 replications. H2: There is a positive impact of windowsill placement in supermarkets on compulsive buying behavior of consumers for shopping products.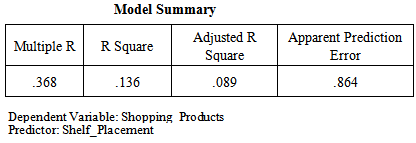 Correlation Coefficient (R) is 0.368 which shows that the relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for shopping products is weak. Moreover value of Correlation Coefficient (R) is above 0 hence the relationship between the variables is direct. Coefficient of Determination (R^2) is 0.136 which shows that the 13.6% model is being explained by the windowsill placement and remaining 86.4% is being explained by unknown variables (which are not taken in to account for the purpose of this research.
Correlation Coefficient (R) is 0.368 which shows that the relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for shopping products is weak. Moreover value of Correlation Coefficient (R) is above 0 hence the relationship between the variables is direct. Coefficient of Determination (R^2) is 0.136 which shows that the 13.6% model is being explained by the windowsill placement and remaining 86.4% is being explained by unknown variables (which are not taken in to account for the purpose of this research.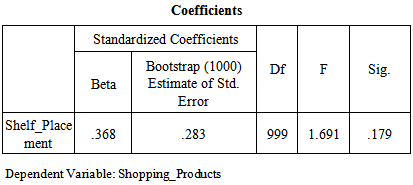 The significance value is 0.179 which is greater than 0.05, So on the basis of p-value null hypothesis that there is no relationship has been accepted and alternate/research hypothesis that there is positive relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for shopping products has been rejected.F value is also less than 3.83 (i-e 1.691) which also shows model is insignificant. Degree of freedom (DF) is associated with the sources of variance. The total variance has N-1 degrees of freedom. The Regression degrees of freedom correspond to the number of coefficients estimated minus 1. As our model is SLR so regression DF doesn’t make sense but DF total is 999 (1000-1). More over on the basis of p-value null hypothesis that there is no relationship has been rejected and alternate/research hypothesis has been accepted. As far as that there is positive relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for shopping products has been rejected has there is no impact but relationship as per the beta value is + .368. Bootstrap confidence intervals provide a way of quantifying the uncertainties in the inferences that can be drawn from a sample of data. The idea is to use a simulation, based on the actual data, to estimate the likely extent of sampling error. To really have stable estimates, we have used 1000 replications. H3: There is a positive impact of windowsill placement in supermarkets on compulsive buying behavior of consumers for specialty products.
The significance value is 0.179 which is greater than 0.05, So on the basis of p-value null hypothesis that there is no relationship has been accepted and alternate/research hypothesis that there is positive relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for shopping products has been rejected.F value is also less than 3.83 (i-e 1.691) which also shows model is insignificant. Degree of freedom (DF) is associated with the sources of variance. The total variance has N-1 degrees of freedom. The Regression degrees of freedom correspond to the number of coefficients estimated minus 1. As our model is SLR so regression DF doesn’t make sense but DF total is 999 (1000-1). More over on the basis of p-value null hypothesis that there is no relationship has been rejected and alternate/research hypothesis has been accepted. As far as that there is positive relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for shopping products has been rejected has there is no impact but relationship as per the beta value is + .368. Bootstrap confidence intervals provide a way of quantifying the uncertainties in the inferences that can be drawn from a sample of data. The idea is to use a simulation, based on the actual data, to estimate the likely extent of sampling error. To really have stable estimates, we have used 1000 replications. H3: There is a positive impact of windowsill placement in supermarkets on compulsive buying behavior of consumers for specialty products.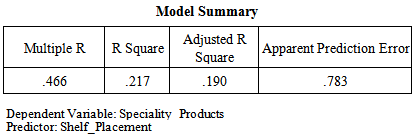 Correlation Coefficient (R) is 0.466 which shows that the relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for specialty products is moderate. Moreover value of Correlation Coefficient (R) is above 0 hence the relationship between the variables is direct. Coefficient of Determination (R^2) is 0.217which shows that the 21.7% model is being explained by the windowsill placement and remaining 78.3% is being explained by unknown variables (which are not taken in to account for the purpose of this research.
Correlation Coefficient (R) is 0.466 which shows that the relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for specialty products is moderate. Moreover value of Correlation Coefficient (R) is above 0 hence the relationship between the variables is direct. Coefficient of Determination (R^2) is 0.217which shows that the 21.7% model is being explained by the windowsill placement and remaining 78.3% is being explained by unknown variables (which are not taken in to account for the purpose of this research.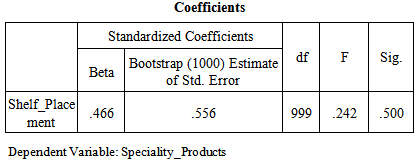 The significance value is 0.500 which is greater than 0.05 so on the basis of p-value null hypothesis that there is no relationship has been accepted and alternate hypothesis that there is positive relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for specialty products has been rejected.F value is also less than 3.83 (i-e 2.42) which also shows model is insignificant. Degree of freedom (DF) is associated with the sources of variance. The total variance has N-1 degrees of freedom. The Regression degrees of freedom correspond to the number of coefficients estimated minus 1. As our model is SLR so regression DF doesn’t make sense but DF total is 999 (1000-1). More over on the basis of p-value null hypothesis that there is no relationship has been rejected and alternate/research hypothesis has been accepted. As far as that there is positive relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for specialty products has been rejected has there is no impact but relationship as per the beta value is + .466. Bootstrap confidence intervals provide a way of quantifying the uncertainties in the inferences that can be drawn from a sample of data. The idea is to use a simulation, based on the actual data, to estimate the likely extent of sampling error. To really have stable estimates, we have used 1000 replications.
The significance value is 0.500 which is greater than 0.05 so on the basis of p-value null hypothesis that there is no relationship has been accepted and alternate hypothesis that there is positive relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for specialty products has been rejected.F value is also less than 3.83 (i-e 2.42) which also shows model is insignificant. Degree of freedom (DF) is associated with the sources of variance. The total variance has N-1 degrees of freedom. The Regression degrees of freedom correspond to the number of coefficients estimated minus 1. As our model is SLR so regression DF doesn’t make sense but DF total is 999 (1000-1). More over on the basis of p-value null hypothesis that there is no relationship has been rejected and alternate/research hypothesis has been accepted. As far as that there is positive relationship between windowsill placement in supermarkets and compulsive buying behavior of consumers for specialty products has been rejected has there is no impact but relationship as per the beta value is + .466. Bootstrap confidence intervals provide a way of quantifying the uncertainties in the inferences that can be drawn from a sample of data. The idea is to use a simulation, based on the actual data, to estimate the likely extent of sampling error. To really have stable estimates, we have used 1000 replications. 5. Conclusions, Implications and Future Research Directions
5.1. Conclusions
- There is a positive relationship between convenience products and the independent variable which is windowsill placement. Whereas there is no relationship of windowsill placement of shopping, as well as specialty products in supermarkets. It was proved that people prefer buying specialty products such as, electronics from their original stores. The points I came across through this research were how the manufacturers advertise their product (whether it be by windowsill placement or by salesperson or TV commercials). Customers should know what they want to and do not want to buy. Customers should be aware of the strategic techniques of the manufacturers.
5.2. Implications and Future Research Directions
- In order to attract more consumers to buy their products, manufacturers must put in a lot of effort to make their product eye catching by windowsill placement. Stores should be well maintained. Racks should be checked to time and the products where people make decision without much thinking they should be placed at the front. Frequent promotions can be offered in order to enhance awareness about the products. This research can further be carried in other countries. This research has been done by taking in to account a city of Pakistan. Furthermore it can be done on unsought products. In which ways we can enhance the sales of unsought products because of their very nature.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML