-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Life Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1387 e-ISSN: 2163-1395
2014; 4(1): 1-11
doi:10.5923/j.als.20140401.01
Field Application of λ-cyhalothrin 2.5 EC on Maize Cobs for the Management of Sitophilus zeamais (Motschulsky) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) Infestation in the Field and Store
Zakka U1, Lale N. E. S1, Umeozor O. C2
1University of Port Harcourt, Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Crop and Soil Science, Port Harcourt, Nigeria
2University of Port Harcourt, College of Natural and Applied Sciences, Faculty of Biological Science, Department of Animal and Environmental Biology, Port Harcourt, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Zakka U, University of Port Harcourt, Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Crop and Soil Science, Port Harcourt, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Maize is a major staple cereal crop in West Africa serving as one of the sources of energy for humans and feed for livestock. The crop is highly susceptible to depredation in storage by maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais (Motschulsky) but commences infestation in the field. The combinations of varietal resistance, time of harvest at commencement of yellowing of cobs, at advanced yellowing and at complete drying, and field application of λ-cyhalothrin 2.5 EC at different doses (300ml/ha, 600ml/ha and 800ml/ha) for efficient protection of maize against Sitophilus zeamais infestation in storage was evaluated in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria for two seasons. Three local maize cultivars (Akparike, Bende and Ogbia muno) and four hybrid maize (ACR.97 TZL COMP.1-W, TZL COMP.4C2, ADV.NCRE-STR and BG 97 TZE COMP.3XL) were used. The three factors were investigated in a Randomized Complete Block Design arranged in a split plot with cultivars as the main factors, chemical application rates as the sub plot factor and harvest time as the sub-sub plot factor. The study was carried out at the Faculty of Agriculture, University of Port Harcourt, Nigeria located in the Niger Delta Region. There were significant differences (P ≥ 0.05) in mean number of teneral adults among harvest times in all the treatments; more maize weevils emerged in maize cultivars harvested late with a range of 13.19 observed in maize treated with λ-cyhalothrin 2.5 EC at 800ml/ha (TRT 3) to 22.81 in maize treated with λ-cyhalothrin 2.5 EC at 300ml/ha (TRT 1). Mean grain weight decreased with increase in time of harvest of the cobs. On average, the number of teneral adults that emerged from each maize variety treated with different doses of insecticide and harvested at different times increased as harvesting time increased but decreased with increase in concentration of insecticide. Overall, the susceptibility index increased with delay in harvest time and decreasing dosage of insecticide. Combining early harvest, application of λ-cyhalothrin and resistant variety could be an appropriate tactic to effectively manage S. zeamais infestationin the storage in the Niger Delta agro-ecological zone.
Keywords: λ-cyhalothrin 2.5 EC, Varietal Resistance, SitophilusZeamais,Harvest time Hybrid and Teneral Adult
Cite this paper: Zakka U, Lale N. E. S, Umeozor O. C, Field Application of λ-cyhalothrin 2.5 EC on Maize Cobs for the Management of Sitophilus zeamais (Motschulsky) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) Infestation in the Field and Store, Advances in Life Sciences, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 1-11. doi: 10.5923/j.als.20140401.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Maize is one of the most important cereal crops grown on about 3.8 million ha in West Africa and Nigeria produces about 1.5 million metric tons annually from approximately 2 million ha of land[1]. It is well known for its food, feed value and as raw materials for many industrial products for breweries and pharmaceutical companies[2] and holds considerable promise as a weapon against poverty and food crises in the West African sub-region[3]. The major constraint to utilization of maize in the tropics and subtropics is the attack by maize weevil (Sitophilus zeamais)[4]. S. zeamais belongs to the family Curculionidae in the order Coleoptera and is a principal post-harvest pest and infestation commences in the field as soon as maize cobs begin to turn yellow[5]. Adult weevils and larvae feed on undamaged grains and frequently cause severe powdering, rendering the product unfit for human consumption[6]. The annual losses of grains due to weevils are estimated at an average of 25 to 40 % after 6 months of storage[7, 8] and depending on the crop variety, it can reach 50 %[9]. Enobakhare and Law-Ogbomo[10] and Lale and Kartay[11] have shown from their studies that some cultivars of maize were relatively resistant to S. zeamais attack. In addition, harvest time modification has also been shown to be an effective strategy for reducing field-infestation of crop produce by field-to-store insect pests[12]. In Africa harvested maize is usually left in the field for further drying and this undue delay in harvesting increases infestation rate by pests[13]. Semple et al.[14] concurred that maize more than any other cereal, is prone to field infestation by field-to-store pests and it is heavily attacked when standing in the field at the early stage of ripening by S. zeamais which may complete one or even two life cycles before harvest. Protection of stored produce by judicious application of insecticides in conjunction with the use of improved warehouse sanitation and other physical methods, host–plant resistance and biological methods invariably remain a vital factor in reducing losses during storage[15]. In this study therefore, the combination of varietal resistance with application of λ-cyhalothrin 2.5 EC directly on maize cobs with time of harvest was assessed as a possible strategy for the management of S. zeamais infestation in storage.
2. Materials and Methods
- The experiment was conducted at the Teaching and Research Farm of the Faculty of Agriculture, University of Port Harcourt located at latitude 4.54oN and longitude 6.55oE with an elevation of approximately 20 m above sea level. Mean annual rainfall is variable and ranges from 2000 mm to 2680 mm. Annually, the mean monthly maximum temperature ranges from 28℃ to 33℃ while the mean monthly minimum temperature ranges from 20℃ to 23℃.
2.1. Experimental Procedures
- Seven maize cultivars comprising four hybrids (ACR.97 TZL COMP.1-W, TZL COMP.4C2, ADV.NCRE-STR and BG 97 TZE COMP.3XL) developed by the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture, Ibadan, Nigeria obtained from their germplasm and three local cultivars (Akparike, Bende and Ogbia muno) obtained from the open markets in Elibrada Emuoha, Rivers State, Nigeria were sown on 17 October in 2008 and 2009 cropping seasons and sprayed with λ-cyhalothrin 2.5 EC at three levels of 300ml/ha (TRT 1), 600ml/ha(TRT 2) and 800ml/ha(TRT 3) and harvested at different times with the cultivars as the main factors, chemical application rates as the sub plot factor and harvest time as the sub-sub plot factor[16]. Each plot measured 3 m by 6.6 m. The experiment was laid out in a strip plot design in which the treatments were replicated three times. Each plot was sown with double 10 rows of each maize variety at a depth of 2-3 cm by placing 3-4 seeds/hole and the plants were thinned after 2 weeks to two plants per stand. Spacing between rows and plants were 0.75 and 0.3 m, respectively, and distance between treatments and replicates was 1.5 m. Fertilizer was applied 3 weeks after planting (WAP) and 6 WAP to give 60 kgN (119 g N/plot) and 60 kgP2O5 ha-1 (119 gP2O5/plot) as recommended for the area in two splits[17]. The fields were kept weed-free by hand weeding.
2.2. Harvest Time
- Mature cobs were harvested at three different stages[at the commencement of yellowing (Harvest 1; HVT1), at advanced yellowing (Harvest 2; HVT2) and at complete drying (Harvest 3; HVT3)] to evaluate the effectiveness of the combination of the various techniques in mitigating the introduction of S. zeamais into the store. The cobs were left to dry for 35 days under an open shade with each harvest time kept in a cluster and kept one meter apart in order to minimize cross infestation. After drying, each cob was shelled by hand and the grains collected on a piece of white cloth.
2.3. Number of Teneral S. Zeamais Adults
- Twenty grammes were weighed from each lot using a sensitive Mettler balance (Model A & D FX-6000), placed in a 1-L Kilner jars and left undisturbed under laboratory conditions (25-30℃ and 70-90% r.h)[18]. Record of the number of adults that emerged was taken daily by emptying the content of each jar carefully onto a white paper and adult insects counted and removed to determine their daily emergence pattern. The content of each jar was carefully placed back into the jar and the jar kept in its original position.
2.4. Moisture Content Determination
- The percent moisture content was calculated as weight of moisture/weight of wet sample x 100[19].
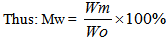 Where Wm=water weight in grain at MwWo= total grain weight at MwSince Wo=Wm+WdWhere: Wd=dry matter weight at Mw moisture content
Where Wm=water weight in grain at MwWo= total grain weight at MwSince Wo=Wm+WdWhere: Wd=dry matter weight at Mw moisture content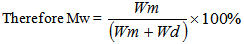
2.5. Grain Weight Loss
- Grain weight loss was determined as described by[20]:
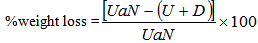 Where U= weight of undamaged fraction (the seeds in the sample that were not damaged) in a sampleN=total number of grains in a sampleUa=average weight of one undamaged kernel (kernels without weevil emergence hole)D= weight of damaged fraction in a sampleThis was confirmed by the modified gravimetric method of[21] by counting damaged grains and weighing the final samples using the formula:
Where U= weight of undamaged fraction (the seeds in the sample that were not damaged) in a sampleN=total number of grains in a sampleUa=average weight of one undamaged kernel (kernels without weevil emergence hole)D= weight of damaged fraction in a sampleThis was confirmed by the modified gravimetric method of[21] by counting damaged grains and weighing the final samples using the formula: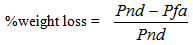 Where: Pnd = weight of non damaged kernelsPfa = final weight of sample
Where: Pnd = weight of non damaged kernelsPfa = final weight of sample2.6. Susceptibility Index
- Susceptibility index of[22] was determined for each maize variety or cultivar.
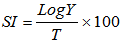 Where: SI= Susceptibility indexLog Y= log number of F1 emerged adultsT=Mean developmental periods (days)
Where: SI= Susceptibility indexLog Y= log number of F1 emerged adultsT=Mean developmental periods (days)2.7. Statistical Analysis
- Data collected were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) using the Statistical software package SAS 2000 version and according to the procedures reported by[23].
3. Results
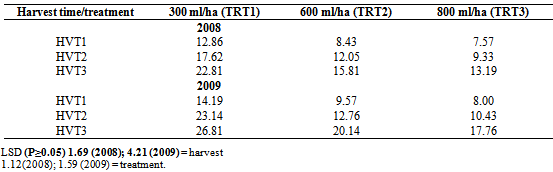
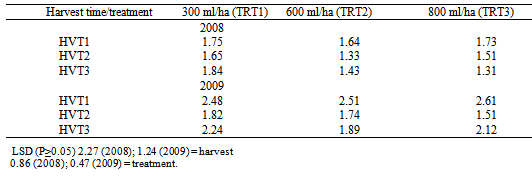
- Table 1 shows the adult progeny (F1) of S. zeamais that emerged in the different maize seeds treated in the field at different doses of λ-cyhalothrin 2.5 EC and harvested at different times. There were significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) in the mean number of teneral adults that emerged in both years among harvest times in all the treatments. More weevils emerged in maize cultivars harvested latest (HVT 3; where the cobs were allowed to dry completely on the field) with a range of 13.19 observed in TRT 3 to 22.81 in TRT 1. The least number of maize weevils were recorded in maize variety harvested early (HVT 1 where the maize cobs were harvested at the point where they just turned yellow) with a range of 7.57 observed in TRT 3 to 12.86 in the maize cultivars in the field treated with λ-cyhalothrin 2.5 EC at 300ml/ha (TRT 1). Progeny number with respect to dose of chemical applied was in the following order 300 ml/ha (TRT 1) > 600 ml/ha (TRT 2) > 800 ml/ha (TRT 3).
|
|
|
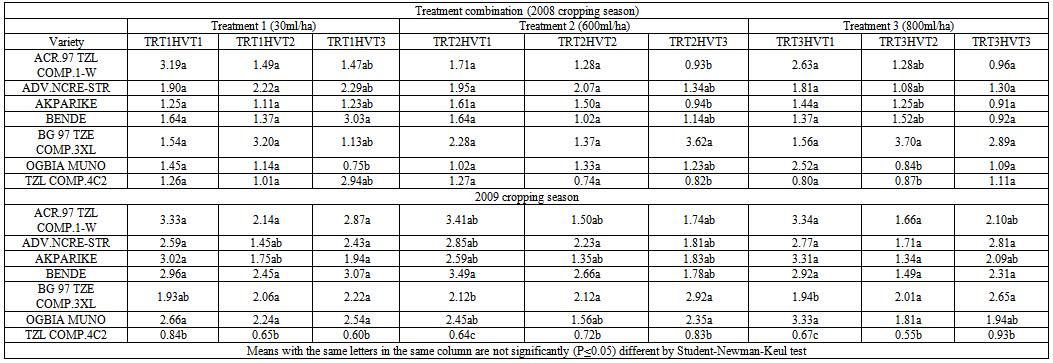 | Table 6. Mean weight loss (%) of maize grains due to S. zeamais infestation in different varieties under different harvest time and doses of Attacke 2.5 EC (λ-cyhalothrin 2.5 EC) applied on maize cobs as a management technique |
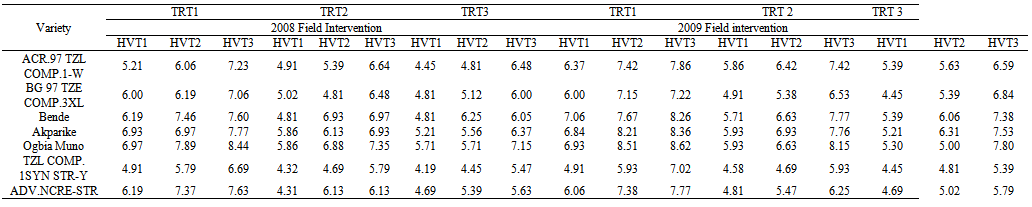 | Table 7. Index of susceptibility of different maize varieties to S. zeamais infestation under different field treatment and Store intervention techniques |
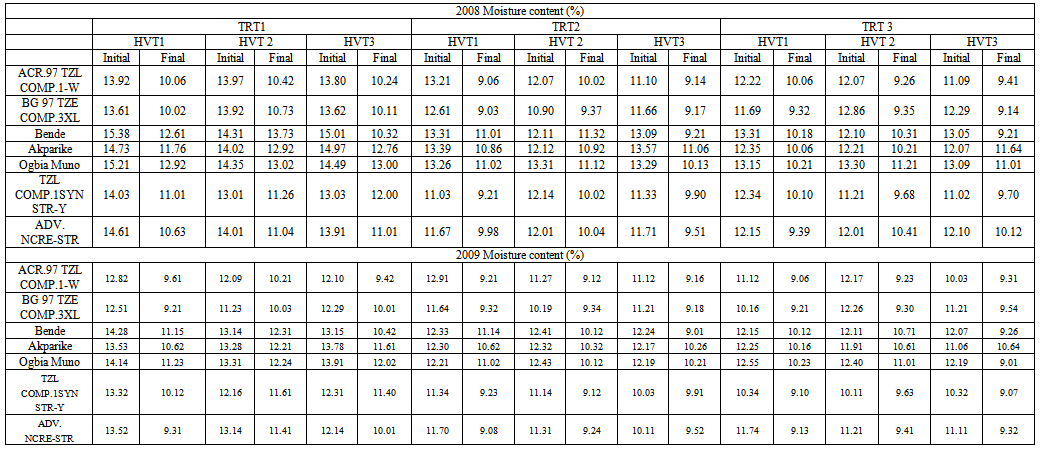 | Table 8. Grain moisture content according to treatment combinations showing initial and final values for 2008 and 2009 cropping seasons |
4. Discussion
4.1. Harvest Time as a Suitable Tool in Curbing the Introduction of S. Zeamais to Store and a Practical Management Technique in Maize Production
- The length of time that maize and other cereals are left in the field before harvest plays a great role in determining the insect pest load especially in the case of field-to-store pests. The result that late harvest of maize, where the cobs were allowed to dry completely in the field (HVT 3), supported higher number of adult weevils confirms the work of[12] on Callosobruchus maculatus in cowpea who reported that cowpea seeds harvested very late supported more storage bruchids than cowpeas harvested early. It is evident from the result that late harvesting of maize would only increase the number of both teneral adults and/or immature stages that will further develop and reproduce in store. This assertion concurs with the findings of[24] that the higher the initial infestation at harvest the higher the subsequent infestation in the store and that the presence of adult maize weevil on stored ears after 30 days of storage is an indication that the maize weevils had mated and reproduced in the field on the ears before harvest. Early harvest might, therefore, offer the maize an opportunity to escape invasion and colonization by the weevils in the field as[25] stated in his work that early harvest of maize would probably reduce damage and losses attributed to insect pests. Staggered harvesting of maize as indicated in study will encourage an escape from weevil infestation as suggested by[26] for cowpea harvest as a mitigating measure against bruchids in Nigeria. However, harvesting as soon as the maize attains physiological maturity would mean repeated harvest and increased labour costs, but these would most probably be offset by the increased value of sound maize saved from infestation by weevils. This agrees with[27] who observed a steady increase of 33 % in maize production for a period of about 5 years in Brazil due to adoption of good harvest practices.
4.2. Field Application of Insecticide as a Strategy for Mitigating S. Zeamais Infestation and Ensuring Healthy Maize Grains in Store
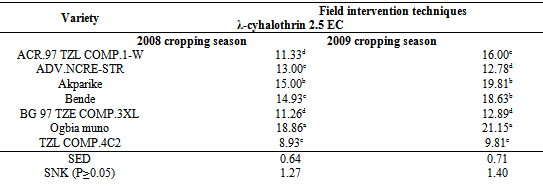
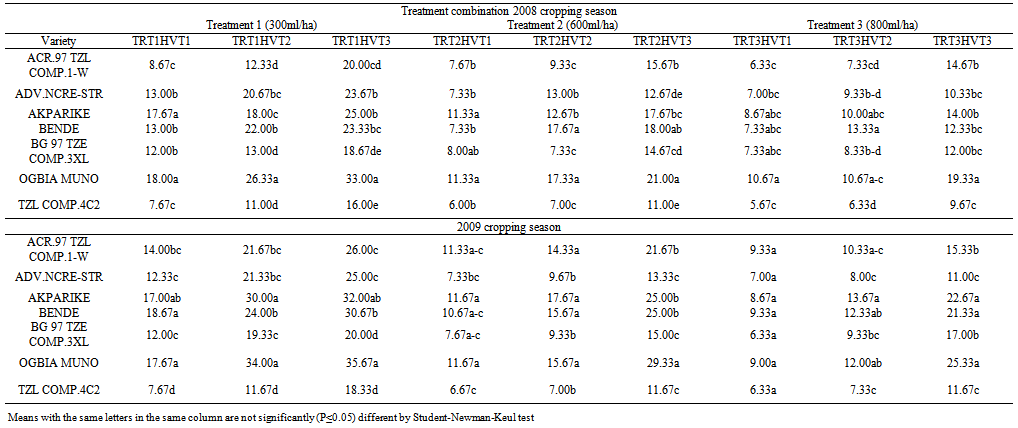
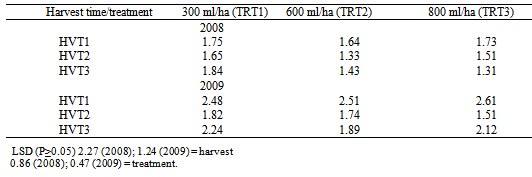
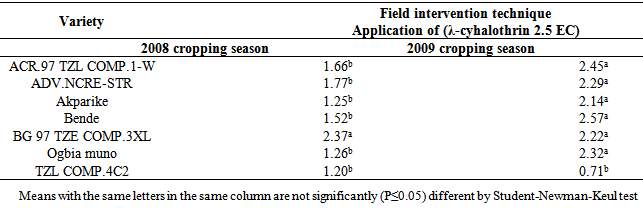
- The direct application of insecticide to the maize cobs in the field at an appropriate dosage served as an appropriate means of breaking the cycle of S. zeamais from building up in the store and also reduces the unnecessary injection of chemicals into farm produce such as maize. This finding concurs with[28,29] who reported that pre-harvest sprays of neem seed products and pirimiphos-methyl with harvest time modification of cowpea resulted in a significant reduction of bruchids in store. Bosque-Perez and Buddenhagen[30] reported that maize weevil is a serious field-to-store pest of maize in the tropics; the insect infests the ripening cob of maize before harvest and multiplies further during storage[31] and infestation builds up in store, a function of the number of eggs laid and developing stages initiated in the field[32]. Controlling the build-up of weevil number through application of chemical directly on the maize cobs or by modifying the harvest time to enhance escape and the use of resistant variety as reported in this study can significantly reduce the pest load to be encountered in the store. Similar observations were made by[33] by pre-harvest application of some synthetic insecticides in reducing field infestation of maize by Sitotroga cerealella (Olivier) and S. oryzae (L.); Ajayi and Lale[34] reported on pre-oviposition application of spice oils in stored bambaranut seeds against C. maculatus and[28] reported on pre-harvest application of spice oils and insecticides on cowpea and/or bambaranuts against bruchid infestation.The result of the study in both years indicating TZLComp.4C2, ACR97TZL Comp.1-W and to some extent ADV.NCRE-STR as resistant varieties over the local varieties commonly cultivated in the study area suggests that these improved varieties possess some degrees of resistance as they supported fewer adult weevils in all the treatment combinations. The reasons for the poor performance of S. zeamais on these varieties could be attributed partly to what[35] reported as the presence of the secondary metabolites in them which were probably lacking in the local cultivars which improve defense against microbial attack and herbivore predation. Such metabolites have chronic effect rather than acute toxicity on insects. Therefore, the insects may attempt to breed on the field but will fail to maximize the substrates and will consequently affect the overall progeny development. Other possible reasons may be high kernel hardness and other seed coat characteristics exhibited by the improved varieties as deduced by Adesuyi[36] who reported that the presence of toxic alkaloids or amino acids in some products affects their susceptibility to pest infestation. Certain seed coat characteristics discourage oviposition and inhibit digestive enzyme. Throne et al.[37] in their work on resistance of tripsacorn to S. zeamais and Oryzaephilus surinamensis found out that whole tripsacorn kernels were immune to attack by maize weevils and suggested that such immunity may have been conferred by the hardness of the fruitcase which discouraged the weevils from laying eggs; immunity was also partly due to possible repellent chemicals in the fruitcase. The result of the study also showed lack of consistency among the varieties with respect to all the parameters tested except for TZLComp.4C2. This lack of reproducibility in results was also reported by[16] that millet varieties identified to be resistant did not show this response for all parameters and[38] reported some degree of variation and inconsistency in levels of infestation by Coniesta ignefusalis in millet and sorghum grown under natural field conditions. Researchers have attributed such variations partly to the differences in maturity periods as well as to differences in stem and plant characteristics of the different millet cultivars studied and also by[39,16]. The high weevil numbers recorded in some of the hybrids- Bg 97 TZE Comp.3XL, ACR 97 TZL Comp.1-W and ADV.NCR-STR relative to number of weevils recorded in the local maize cultivars which suffered virtually the same levels of damage in some treatments may reduce the readiness of local farmers to adopt these new cultivars of maize in their cropping system. However, the levels of susceptibility observed in the local cultivars commonly cultivated in the study area imply that farmers must control grain weevils both in the field and in the store to guarantee good maize storage in this agroecology. Lale and Makoshi[40] opined that use of resistant variety for the management of storage pests in tropical agriculture has advantages: it is easy to use, economical, safe and effective.The absence of a specific trend in response to concentrations of insecticide used in the field in relation to grain weight loss could mean that the loss in moisture content of the grains might have played a significant role. This was the case when harvest was made at the onset of maturity the grains had higher moisture content, and the implication therefore, is that moisture levels need to be reduced before grains are stored otherwise it will encourage weevil activity. As reported by[12] weight loss in the cowpea was largely due to moisture loss and to the feeding activity of the bruchids. Caneppele et al.[41] also reported a positive correlation between percentage moisture content and the number of insects and weight loss. Puzzi[42] suggested that the increase in moisture with increase infestation may be due to the galleries that expose the endosperm allowing moisture absorption by hygroscopic carbohydrates. It is a known fact that low moisture level is the key to safe storage of farm produce and biological activity occurs only when it is present at a certain critical level; the elevation of moisture content and temperature of the grain mass is generally a result of the metabolic activity of insects[42]. High moisture content increases activities of biotic agents, thus increasing loss in storage[19]. Although early harvest encourages retention of high moisture content of the grains, early harvest is still a reasonable proposition because infestation levels are low at this point[43,8]. The ability of maize grains to support large weevil population and yet suffer insignificant weight loss could therefore be used in judging its quality of resistance or otherwise[44]. Olubayo and Port[12] recorded an average of 17.1% moisture content on cowpea harvested early, 13.7% for seeds harvested at the recommended time, 13.5% for late harvested cowpea seeds and 13.2 % for the seeds harvested very late. The high SI value obtained in the study however concurs with the result of[45] who obtained 14 on susceptible varieties and[46] who in a similar study recorded an index of 11.1 on a most susceptible cultivar and an index of 7.9 as the lowest. Ashamo[44] recorded a suitability index of less than 5 which he attributed to the fact that the cultivars used were improved and all of them showed relative resistance to S. zeamais infestation with the lowest value being 3.23. Siwale et al.[47] gave some explanation as to why he obtained a lower value (0.77) as partly due to the resistant variety used and partly due to moisture content which was not the case in this study where susceptible cultivars were equally used in order to determine the effectiveness of the mitigating measure being tested. Ashamo[44] reported that a relatively lower SI index could partly be attributed to the grain hardness which is an estimate of the percentage of corneous endosperm in the grain and that it is most likely to be the most important factor in governing its susceptibility to insect attack[47]. Leuschner et al.[48] also observed a distribution of larger numbers of S. oryzae progenies among genotypes of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum L.) that had higher proportion of soft endosperm.
5. Conclusions
- The study has shown that the local cultivars of maize supported higher populations of S. zeamais progeny than the improved varieties invested with thicker testae and harder kernels. Akparike, a local susceptible cultivar, had a thick testa, indicating that physical properties alone do not account for the observed resistance in the improved varieties.The results have also shown that the length of time the maize is left on the field after physiological maturity plays significantly influences the intensity of infestation of field-to-store pests: maize harvested late when the cobs were completely dry supported the highest number of weevils and suffered greater grain weight loss.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would like to thank AAU for funding the work, IITA Ibadan, Nigeria for providing the improved varieties used in the studies and the comments by two anonymous reviewers towards improving the quality of this paper are acknowledged.
References
| [1] | IITA 1981. Annual report of International Institute of Tropical Agriculture, Ibadan, Pp53-55. |
| [2] | Iken, JE and Amusa, NA 2004. Maize research and production in Nigeria. African Journal of Biotechnology 3 (6)302-307. |
| [3] | Bergvinson, DJ 2000. Storage pest resistance in maize. Maize Research Highlights 1999-2000 Caneppele, MAB, Caneppele, C., Lazzari, FA and Lazzari, SMN 2003. Correlation between the infestation level of Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky, 1885 (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and the quality factors of stored corn, Zea mays L. (Poaceae). Revista Brasileira de Entomolgia 17(4) 625-630. |
| [4] | Akob, CA and Ewete, FK 2007. The efficacy of ashes of four locally used plant materials against Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Cameroon. International Journal of Tropical Insect Science 27:21-26. |
| [5] | Haines, CP 1991. Insects and Arachnids of tropical stored products: their biology and identification, NRI, Chatham, Kent (UK). |
| [6] | Ofuya, TI, Idoko, JE and Akintewe, LA 2008. Ability of Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) from four locations in Nigeria to infest and damage three varieties of maize, Zea mays L. Nigerian Journal of Entomology, 25:34-39. |
| [7] | Bell, A. and Posamentier, H 1998. Les pertes dues aux insects sur les stocks paysans de cereals en Côte d’Ivoire. Cereals en region chaude AUPELF-UREF, Eds John Libbey Eurotext, Paris 47-56 (Translated version). |
| [8] | Gerald, N 2008. Maize weevils. In Tongjura, JDC, Amuga, GA and Mafuyai, HB 2010. Laboratory assessment of the susceptibility of some varieties of Zea mays infested with Sitophilus zeamais, Motsc. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Jos, Plateau State, Nigeria. Science World Journal 5(2) 55-57. |
| [9] | Helbig, J 1995. The ecology of Prostephanus truncatus in Togo with particular emphasis on interaction with the predator Teretriosoma nigrescens. Deutsche Geselshaft techniche Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Eschborn, Germany. 111. |
| [10] | Enobakhare, DA and Law-Ogbomo, KE 2002. Reduction of post harvest loss caused by Sitophilus zeamais (Motsch) in three varieties of maize treated with plant products. Post Harvest Science 1:1-6. |
| [11] | Lale, NES and Kartay, MO 2006. Role of physical characteristics of the seeds in the resistance of local cultivars of maize to Sitophilus zeamais infestation in storage. Tropical Science 45:112-114. |
| [12] | Olubayo, FM and Port, GR 1997. The efficacy of harvest time modification and intercropping as methods of reducing the field infestation of cowpea by storage bruchids in Kenya. Journal of Stored Product Research 33:271-276. |
| [13] | Katinila, N, Verkuijl, H, Mwangi, W, Anandajayasekeram, P and Moshi, AJ 1998. Adoption of Maize Production Technologies in Southern Tanzania. Mexico, D.F.: International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), the United Republic of Tanzania, and the Southern Africa Centre for Cooperation in Agricultural Research (SACCAR). |
| [14] | Semple, RL, Hicks, PA, Lozare, JV and Castermans, A. (Editors) (May, 1992). Proceedings and selected papers from the Regional Training Course on Integrated Pest Management Strategies in Grain Storage Systems, conducted by the National Post-harvest Institute for Research and Extension (NAPHIRE). Department of Agriculture, June 6-18, Philippines. A REGNET (RAS/86/189) Publication in Collaboration with NAPHIRE. |
| [15] | Obeng-Ofori, D 2008. Major stored product arthropod pests In: Cornelius, EW and Obeng-Ofori, D (Editors) Post harvest Science and Technology. Teaching and Learning Innovation Fund (TALIF) Smartline Publishers Accra, Ghana, 504Pp |
| [16] | Sastawa, BM, Lale, NES and Ajayi, O 2002. Evaluating host plant resistant and sowing date modification for the management of the stem borer, Coniesta ignefusalis Hampson and the head miner Heliocheilus albipuctella de Joannis infesting pearl millet in the Nigerian sudan savvana. Journal of plant Diseases and Protection 109 (5) 530-542. |
| [17] | ICAR 2006. Handbook of Agriculture 5th edition. Sharma, R. P. (Editor. English Editorial unit) Kuldeep Sharma, In charge, Director of Information and Publications of Agriculture, Indian Council of Agricultural Research Krishi Anusandhan Bhavan, New Delhi. |
| [18] | Zakka, U 2005. Development of Dermestes maculatus (De Geer, 1776) Coleoptera: Dermestidae on different fish substrates. Mpil. Thesis in Entomology University of Ghana. Pp128. |
| [19] | Obeng-Ofori, D and Boateng, BA 2008. Global population growth, crop losses and post harvest technology. In: Cornelius, E.W and Obeng-Ofori, D. (Editors) Post harvest Science and Technology. Teaching and Learning Innovation Fund (TALIF) Smartline Publishers Accra, Ghana, 504Pp. |
| [20] | Lale, NES 2002. Stored product entomology and acarology in Tropical Africa (First Edition) Mole Publications (Nigeria) Ltd, Maiduguri 204pp. |
| [21] | Compton, JAF, Flovo, A, Ofosu, A and Agbo, B 1998. The modified count and weight method and improved procedure for assessing weight loss in stored maize cobs. Journal of Stored Product Research 34(4)277-285. |
| [22] | Dobie, P 1974. The laboratory assessment of the inherent susceptibility of maize varieties to post-harvest infestation by Sitophilus zeamais Mot. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Journal of Stored Products Research. 10:183-192. |
| [23] | Gomez, KA and Gomez AA 1983. Statistical procedures for Agricultural Research. 2nd Edition. An International Rice Rsearch Institute book. A Wiley-Interscience Publications, New York. 680Pp. |
| [24] | Demissie, G, Tefera, T and Tadesse, A 2008. Importance of husk covering on field infestation by Sitophilus zeamais Motsch (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) at Bako, Western Ethiopia. African Journal of Biotechnology 7(20) 3777-3782. |
| [25] | Mejia, D 2003. Maize Overall Losses. Post-Harvest Operation, Agro industry and Infrastructure, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Regional Office for the Near East, Cairo, Egypt. |
| [26] | Caswell, GH 1970. The storage of cowpea in the Northern States of Nigeria. Proceedings of Agricultural Society of Nigeria 5:4-6. |
| [27] | CONAB-Companhia National de Abastecimento 2002. In Caneppele, MAB, Caneppele, C, Lazzari, FA and Lazzari, SMN 2003. Correlation between the infestation level of Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky, 1885 (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and the quality factors of stored corn, Zea mays L. (Poaceae). Revista Brasileira de Entomolgia 17(4) 625-630. |
| [28] | Kabeh, JD and Lale, NES 2004. Effect of Pre-harvest Sprays of neem (Azadrichta indica A. Juss) seed products and pirimiphos-methyl and harvest time modification on infestation of cowpeas by storage bruchids in the field and store in Maiduguri, Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Entomology 21:104-116. |
| [29] | Lale, NES and Kabeh, JD 2004. Pre-harvest spray of neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) seed products and pirimiohos-methyl as a method of reducing field infestation of cowpeas by storage bruchids in the Nigeria Sudan savvana. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology 6, 987-993. |
| [30] | Bosque-Perez, NA and Buddenhagen, IW 1992. The development of host plant resistance to pests: outlook for the tropics. In: Demissie, G, Tefera, T and Tadesse, A. 2008. Importance of husk covering on field infestation by Sitophilus zeamais Motsch (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) at Bako, Western Ethiopia. African Journal of Biotechnology 7(20) 3777-3782. |
| [31] | Giles, PH 1969. Observation in Kenya on flight activity of stored products insects particularly Sitophilus zeamais Motsch. Journal of Stored Product Research. 4, 317-329. |
| [32] | Dick, KM and Credland, PF 1984. Egg production and development of three strains of Callosobruchus maculatus (Fab.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) Journal of Stored product Research, 20:221-227. |
| [33] | Sharma, RK 1995. Pre-harvest spray for the control of Sitotroga cereallela (Olivier) and Sitophilus oryzae (Linn) in stored maize. Indian Journal of Entomology 57:157-158. |
| [34] | Ajayi, FO and Lale, NES 2001. Seed coat texture, host species and time of application affect the efficiency of essential oils applied for the control of Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in stored pulses. International Journal of Pest Management 47(3)161-166. |
| [35] | McMullen, MD, Frey, M and Degenhardt, J 2009. Genetics and Biochemistry of insects resistance in maize. In: Bennetzen, J.L. and Hake, S.C. (Eds.) Handbook of maize: its biology, Springer Science + Business Media LLC 2009. |
| [36] | Adesuyi, SA 1977. Relative resistance of some varieties of maize to attack by Sitophilus zeamais (Mots.) A Report of Nigerian Stored Product Research Institute 1976/1977 Technical Report 8:79-82. |
| [37] | Throne, JE, Baker, JE, Messina, FJ, Kramar, KJ, Howard, JA 2002. Varietal resistance. In: Subramanyam, Bh., Hagstrum, D.W. (Eds.) Alternatives to pesticides in Stored-Product IPM. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell, MA 165-192pp. |
| [38] | Ajayi, O 1990. Possibilities of integrated control of millet stem borer, Acigona ignefusalis Hampson (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in Nigeria. Insect Science Application, 2:109-117. |
| [39] | Youm, O and Gilstrap, FE 1994. Habitat selection, crop damage and oviposition preference by Coniesta (=Haimbachia) ignefusalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). International Journal of Pest Management. 40: 231-236. |
| [40] | Lale, NES and Makoshi, SM 2000. Role of chemical characteristics of the seed coat in the resistance of selected cowpea varieties to Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in Nigeria. International Journal of Pest Management, 46(2) 97-102. |
| [41] | Caneppele, MAB, Caneppele, C, Lazzari, FA and Lazzari, SMN 2003. Correlation between the infestation level of Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky, 1885 (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and the quality factors of stored corn, Zea mays L. (Poaceae). Revista Brasileira de Entomolgia 17(4) 625-630. |
| [42] | Puzzi, D 1986. Abestecimento e Armazenamento de graos. In Caneppele, MAB, Caneppele, C, Lazzari, FA and Lazzari, SMN 2003. Correlation between the infestation level of Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky, 1885 (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and the quality factors of stored corn, Zea mays L. (Poaceae). Revista Brasileira de Entomolgia 17(4) 625-630. |
| [43] | Pingali, PL and Pandey, S 2001. 1999-2000 World maize Facts and Trends. Meeting World Maize Needs: Technology opportunities and priorities for the public sector. CIMMYT, Mexico City. |
| [44] | Ashamo, MO 2001. Varietal resistance of maize to the maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais Motsch. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Journal of Plant Disease and Protection 108: 314-319. |
| [45] | Arnason, JT, Baum, B, Gale, J, Lambert, JDH, Bergvinson, D, Philogene, BJR, Serratos, JA, Mihm, J, Jewel, DC 1994. Variation in resistance of Mexican landraces of maize to maize weevils Sitophilus zeamais, in relation to taxonomic and biochemical parameters. Euphytica 74, 227-236. |
| [46] | Morah, SC and Mbata, GN 1982. Assessment of the relative susceptibility of som maize varieties to post-harvest infestation by the maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais Motsch. A Rep. Nigerian Stored Product Research Institute 1982 Technical Report 5, 63-68. |
| [47] | Siwale, J, Mbata, K, Microbert, J and Lungu, D 2009. Comparative resistance of improved maize genotypes and landraces to maize weevil. African Crop Science Journal 17(1)1-16. |
| [48] | Leuschner, K, Monyo, ES, Chinhema, E, Tembo, E, and Martin, D 2000. Pearl millet grain size and hardness in relation to resistance to Sitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). African Crop Science Journal. 8:77-84. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML