-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Life Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1387 e-ISSN: 2163-1395
2012; 2(3): 39-51
doi: 10.5923/j.als.20120203.01
Alpinia Nigra (Family Zingiberaceae): An Anthelmintic Medicinal Plant of North-East India
Bishnupada Roy, Ananta Swargiary, Bikash Ranjan Giri
Department of Zoology, North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong-793 022, Meghalaya, India
Correspondence to: Bishnupada Roy, Department of Zoology, North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong-793 022, Meghalaya, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Traditionally used medicinal plants have been a source of relief in the control of different types of diseases throughout the globe. Economically backward people, who resides in remote areas of developing countries, rely heavily on indigenous way of get rid of parasitic infections using folk medicine. Alpinia nigra is one such medicinal plant, widely used in different parts of North-East India to cure intestinal helminth infection. Essential oils of different species of Alpinia contain flavonoids, terpenoids and kavalactones which have been in used to cure inflammation, hypertension, bacterial and helminth infection. In this review, the crude alcoholic extract of A. nigra that causes destruction and degeneration of surface architecture of tegument, inhibit energy metabolism related enzymes and also enzyme responsible for neuromuscular co-ordination are discussed.
Keywords: Parasitic infection, folk medicine, Alpinia nigra, tegument, energy metabolism, neuromuscular
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Indigenous system of herbal therapy is becoming an increasingly attractive approach to control parasitic infection, particularly in developing countries. Among parasites, helminth and helminthic infections (helminthiasis) remain to be one of the major health problems affecting billions of people all over the world[1,2]. They are the most common infectious agents of human beings that contribute in the wide spread occurrence of undernourishment, anaemia, eosinophilia and pneumonia[3]. They are also responsible for considerable economic losses to the livestock industry of marginal farmers, particularly of developing countries[4-6]. People living in tropical and sub-tropical countries with low per capita income, poor hygienic conditions suffers most because of the presence of favourable conditions for the proliferation of the parasite[7] and, also for the propagation of intermediate hosts that are an essential link in the life cycle of the parasite[8].Over the last few decades the most common method of controlling helminthiasis all over the world include the use of commercial anthelmintic drugs of various types. WHO has listed several essential anthelmintic drugs which are safe to use, available in single dose and of low cost, e.g., mebendazole, albendazole, pyrantel pamoate and levamisole, which are found to be effective against soil-transmitted helminths like Ancylostoma duodenale, Ascarislumbricoides, praziquantel for schistosomes and foodborne trematodes and both ivermectin and diethylcarbamazine (DEC) for curing filariasis[9,10]. However, despite of having developed health care facilities, sophisticated instrumentations and advancement in chemotherapy, there is still lacking of proper and effective tools to deal with helminthic infections. Review of literature revealed that out of 1,556 new chemical entities marketed between 1975 and 2004, only few drugs like albendazole, oxamniquine, praziquantel and ivermectin were developed to treat helminthiasis and found effective[11,12]. Therefore, there is always been a need to find new anthelmintic drugs because current drugs do not control all parasitic infections well. Moreover, high treatment frequency, single-drug regiment or frequent use of the same anthelmintic has led to the development of resistance among helminth population[13,14]. Similarly, its negative, undesired effects as well as limited availability to the rural areas further restricted the effective control of helminthiasis[15-18], causing new threat to human society. Because of this limited availability and in-effectiveness of commercial drugs towards controlling helminthiasis, scientists are now looking for new drugs based on traditional knowledge and traditionally used medicinal plants as an alternative remedies[19-22].Contribution of plants to fight against various diseases dates back several centuries, and has been documented by the ancient Chinese, Indian and North African Civilisations[23-25]. Though the advancement of synthetic medicines, to certain extend, has lifted the health care and livelihood of people, yet the use and importance of plants and its botanicals for the same has never been neglected and a large number of plants are screened for their efficacy against various helminthic infections[26-30]. Several such studies based on traditional medicinal knowledge were done in Indian sub-continent to test the putative anthelminthic activity of different plants. Alpinia nigra is one such plant, shoot of the plant along with a part of rhizome is used by the indigenous tribal people of Tripura, India, as vegetable, whereas aqueous juice of shoot of the plant is consumed to get rid of intestinal helminth infection[31-33].The north-eastern region located between 87º32’E to 97º52’E latitude and 21º34’N to 29º50’N latitude is known for its genetic resources all over the world and is the Biogeographical Gateway to India and finds place in part of two-biodiversity hotspots in India[34]. Use of plant and plant-parts, like leaves, bark, root etc. in order to get rid of various diseases is a kind of common practice to the people of this region, especially the ethnic groups. Out of the estimated 800 species consumed as food plants in India, about 300 species of plants are found in Eastern Himalaya alone[35]. Despite of its biological diversity, the region remains disgracefully data-poor for a wide variety of plant taxa. However, the existing traditional knowledge based on plant and animal resource remains a positive indicator for researcher.
2. Botanical Description of Alpinia nigra (Gaertn.) Burtt
2.1. Taxonomy
- Kingdom: PlantaeOrder: ZingiberalesFamily: ZingiberaceaeSubfamily: AlpinioideaeTribe: AlpinieaeGenus: AlpiniaSpecies: nigra
2.2. Synonyms
- Zingiber nigrum Gaertner, Fruct. Sem. Pl. 1: 35. 1788Alpinia allughas (Retzius) RoscoeHeritieraallughas RetziusLanguas allughas (Retzius) Burkill
2.3. Morphology
- Alpinia nigra belonging to the family Zingiberaceae, is an herbaceous plant, grows well on riverside and can also grow on moist land. The underground stem is rhizome and aerial stem is pseudo-stem which consists of leaf sheath, approximately 3.08 meters in height. Leaves are simple, alternate, oblong, entire and acute at base and apex of the plant with very short petiole and very long leaf sheath with small ligule. The plant has penicle type of inflorescence. The infloret have instant involucre bract and irregular direction. One infloret is composed of four florets. Flower is perfect, irregular symmetry, 3 sepals and 3 lobes, 3 petals and 3 lobes white-green in colour, petals encloses the young flower. Stamen is one, fertile, no spur on anther. The 5 sterile stamens are flat and separated at the apex, call labellum, showy and white-pink, petaloid staminode. Pistil is one, inferior ovary, style is between the anthers. Stigma is over the anthers with three carpels, axile placentation. Fruit is berry having many seeds, pericarp is thin and green when it is young and becomes black and brittle when it gets old. The pollen of A. nigra is monad, inaperture spheroidal, small size, isopolar, radial symmetry and sculpturing is echinate[36].
 | Figure 1. Alpinia nigra, (a) Complete Plant with Flower and (b) Shoot Part Of A. nigra |
2.4. Geographical Distribution
- Alpinia nigra (Gaertn.) Burtt (Zingiberaceae) is distributed primarily in Yunnan and Hainan Province of China, Thailand, Bhutan, Sri Lanka and India[37]. North-east region of India is one of the richest and diverse regions for Zingiberaceaea where 88 different species of plant belonging to 19 genera are reported[38]. A. nigra occurs in marshy slope between low hillocks in different parts of Assam and Tripura, two states of north-east India.
3. Folk Uses
- The genus Alpinia is well known for its immense medicinal value and has been used as a part of the human diet in several parts of the Globe (De Araujo Pinho et al., 2005, Hsu et al., 1987, Jantan et al., 2005)[39-41]. Apart from its different folk medicinal uses like anti-rheumatic oilment, anti-inflammatory, anti-bronchitis, anti-bacterial, antifungal, anti-diabetes, anticancer and as tonicum, the different species are also in use as essential spice and food flavouring product in different parts of Asia[42-55].In Tripura, India, natives consume aqueous juice of shoot of A. nigra to cure intestinal parasitic infection. The plant is also a favourite vegetable diet, however, in some parts it is also used as food flavouring product by the indigenous people of Tripura. Similarly, the aqueous extract of shoot and rhizome of Alpinia nigra (common name “Tora”) has been used in Assam for curing health problems like bone weakness, irregular menstruation, jaundice and gastric ulcers[56].
4. Phytochemicals From Alpinia nigra
- A large number of chemicals have been isolated and studied from the genus Alpinia; however, limited literature is available on A. nigra and its phytochemicals. In China, Qiao et al.[57] studied the seed clusters of A.nigra and isolated two bioactive flavone glycosides, astragalin and kaempferol-3-O-glucuronide from the plant. Out of the two chemicals, kaempferol-3-O-glucuronide was found to be a dominant compound in the seed clusters distributed primarily in the pulp. In addition to this, two major volatile oils, β-Pinene and α-pinene have also been isolated from the fruits and rhizomes, of A. nigra[58].
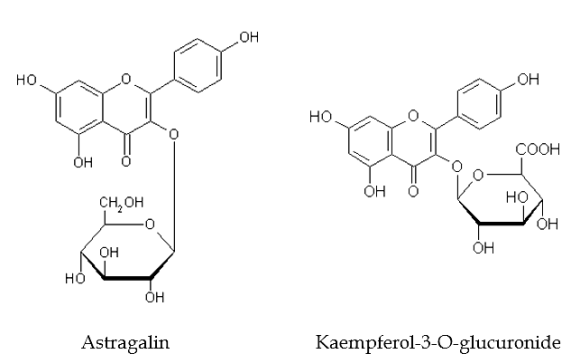 | Figure 2. Two Bioactive Flavone Glycosides From Alpinia nigra Seed Clusters |
5. Anthelmintic Efficacy of Alpinia nigra
5.1. Mortality and Motility Study
- Studies on mortality and motility conducted on intestinal giant fluke, Fasciolopsis buski to see the anthelmintic efficacy of A. nigra crude-extract and reference drug, praziquantel (PZQ) revealed that on exposure to different concentrations of plant extract as well as PZQ, the parasites became immobile, followed by flaccid paralysis and finally death. The effects of different concentrations of plant extract and the drug were shown in Table 1. Flukes maintained in phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) were taken as control. It can be seen from the table 1 that crude extract of A. nigra at its highest dose (20mg/ml) showed more or less similar extent of efficacy when comparedwith PZQ at 2.5mg/ml PBS. Control parasite showed more than 21h of physical activity. A dose dependant efficacy was observed as higher concentration of crude extract leads to paralysis and death at shorter period of time. A similar kind of dose depenent anthelmintic activities were also observed in cestode and nematode parasites when treated with extract of Flemingia vestita, Accacia oxyphylla, Millettia pachycarpa, Potentilla fulgens and Lysimachia ramosa[59-61].
5.2. Histochemical studies
- Trematode have an external body surface covered with an unusual structure termed as tegument. It protects the parasites from the adverse conditions inside the host body and also plays many important functions like evasion of host immune system, absorption of certain nutrients, excretion of metabolites, control of motility and osmotic gradients. Structurally, the tegument consists of cytoplasmic syncytium, basal lamina followed by sub-tegumental cells[62]. The presence of several vital enzymes viz. acid phosphatase (AcPase), alkaline phosphatase (AlkPase), adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase), 5´-nucleotidase (5′- Nu) has been reported in the tegument, and in various organs/tissues of many flat worms[63-66]. All these enzymes which are involved in various metabolic processes are also believed to be involved in absorption and/or digestion in the parasite[67,68]. Investigations on all these key tegumental enzymes and glycolytic enzymes of F. buski revealed to be reduced when treated with A. nigra plant extract and the drug. The alcoholic crude extract of A. nigra and the reference drug (praziquantel) were found to reduce the activities of AcPase, AlkPase and ATPase (Fig. 3-5). In control parasites, the staining intensities of all the enzymes were found to be higher compared to the treated ones. The tegumental layer, subtegumental zone as well as the body musculature was found to be deeply staining. Out of all the tegumental enzymes studied, highest staining intensities were observed in tegumental and sub-tegumental layer. AcPase and AlkPase showed deepest staining compared to the ATPase. The AcPase activity of the somatic musculature and intestine were diminished, while mild visible staining was observed in the tegument and sub-tegument regions of the plant extract-treated fluke (Fig. 3b). Almost all the regions of the praziquantel-treated flukes showed totally diminished staining activity for AcPase (Fig. 3c). Reduction in the activity of AlkPase was also observed in the tegument, sub-tegument, somatic musculature and intestine of the crude plant extract- and praziquantel-treated flukes (Fig. 4). The ATPase activity was also found to be reduced in Alpinia- and praziquantel-treated parasites (Fig. 5) as compared to the controls. In control fluke ATPase activity could be noticed throughout the body, while on exposure to plant extract and drugs, reduction in the staining activity were noticeable. Both in the plant extract and drug treated parasites (Fig. 5b, c), highest reduction in stain intensity has been seen in the dorsal side compared the ventral side of the fluke.
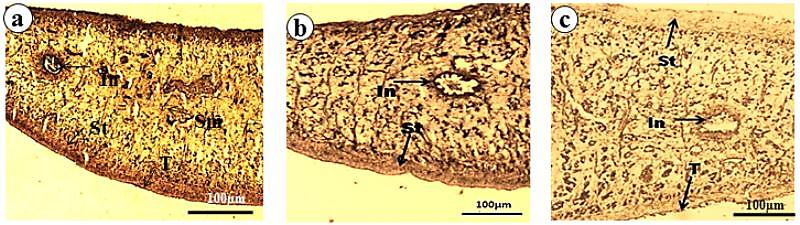 | Figure 3. Acid Phosphatase Activity in F. buski, Photographs of Fresh Frozen Sections. (a) Control, (b) Shoot Extract Of A. nigra Treated Section, (c) Praziquantel Treated Section. [Photographs are adapted from Journal of Parasitic Diseases, 33(1&2), 2009, 48-53, Anthelmintic efficacy of ethanolic shoot extract of Alpinia nigra on tegumental enzymes of Fasciolopsis buski, a giant intestinal parasite, Roy B. and Swargiary A., Fig. no. 1, a, c and e, © Springer, with kind Permission Of Springer Science+Business Media] |
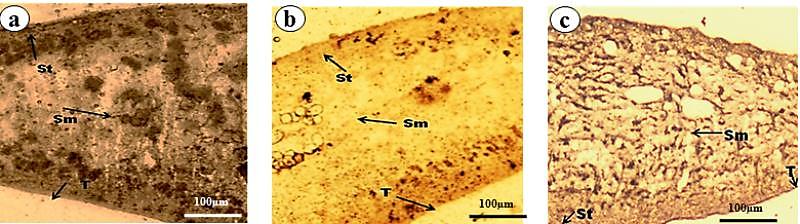 | Figure 4. Alkaline Phosphatase Activity in F. buski, Photographs of Fresh Frozen Sections. (a) Control, (b) Shoot Extract Of A. nigra Treated Section, (c) Praziquantel Treated Section. [Photographs are adapted from Journal of Parasitic Diseases, 33(1&2), 2009, 48-53, Anthelmintic efficacy of ethanolic shoot extract of Alpinia nigra on tegumental enzymes of Fasciolopsis buski, a giant intestinal parasite, Roy B. and Swargiary A., Fig. no. 2, a, c and e, © Springer, with kind Permission Of Springer Science+Business Media] |
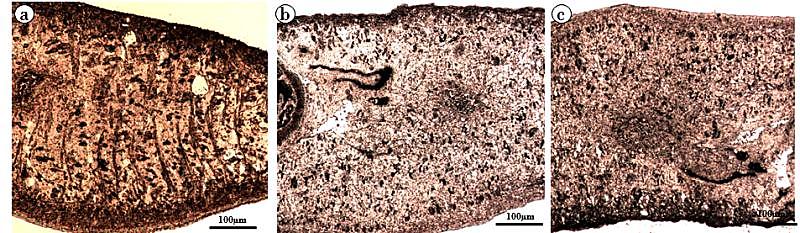 | Figure 5. Adenosine Triphosphatase Activity in F. buski, Photographs of Fresh Frozen Sections. (a) Control, (b) Shoot Extract Of A. nigra Treated Section, (c) Praziquantel Treated Section |
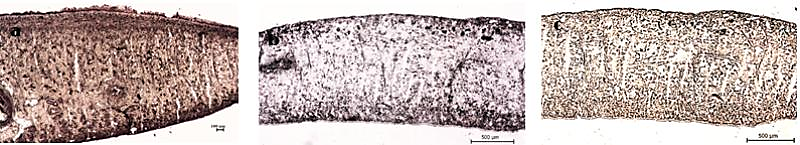 | Figure 6. Malate Dehydrogenase Activity in F. buski, Photographs of Fresh Frozen Sections. (a) Control, (b) A. nigra Treated Section, (c) PZQ Treated Section Of F. buski |
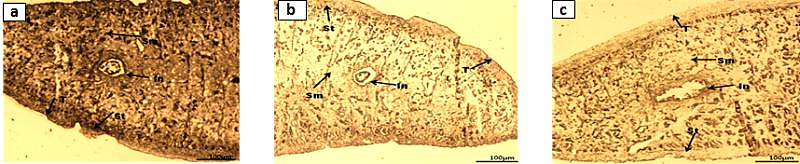 | Figure 8. Acetylcholinesterase Activity in F. buski, Photographs of Fresh Frozen Sections. (a) Control, (b) A. nigra Treated Section, (c) PZQ Treated Section of F. buski |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5.3. Biochemical studies
- On exposure to the crude extract of A. nigra the activities of tegumental enzymes like AcPase, AlkPase, ATPase and AchE were found to be altered significantly in F. buski. All the four enzymes were found to be reduced by 40 to 50% in the parasite treated with shoot-extract of the plant (Table 2). Almost similar percentage of decrease has been recorded in the flukes treated with praziquantel compared to the control one. Biochemical analysis of large number of energy metabolism related enzymes in helminth parasites and their inhibition by different plant extract, active component of plant extract and commercial drugs suggest the extend of their anthelmintic potential[70-73].Glycolysis is the major energy yielding pathway in helminth parasites since the Krebs’ cycle and hexose monophosphate pathways are less functional. The miracidia and cercariae are predominantly aerobic[74]. As they grow into an adult form, the energy production also shifts from aerobic to anaerobic type of metabolism. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), Pyruvate kinase (PK), MDH and LDH are some of the key enzymes in the metabolic pathway of helminth parasites. Since the adult helminth parasites had to survive in a semi-aerobic or anaerobic condition of the host body, they cannot metabolise glucose completely into O2 and H2O. In order to survive such a harsh condition, helminth parasites change their metabolic pathway to a different one. PEPCK, PK, MDH and LDH are among the key enzymes of chemotherapeutic importance. Crude extracts of A. nigra were investigated to test its inhibitory activity against some of the glycolytic enzymes of fluke parasite, F. buski. The enzymatic activities of untreated control parasite showed high enzyme activities. MDH showed highest activity (1.52 µM/min/mg tissue proteins) followed by LDH (0.71 µM/min/mg tissue proteins), PK (0.19 µM/min/mg tissue proteins) and PEPCK (0.12 µM/min/mg tissue proteins) respectively (Table 3). Das et al.[75] studied the glycolytic enzymes of Raillietina echinobothrida and showed almost the similar kind of result with highest activity of MDH in control. Similarly, higher activity of LDH has been seen in the disrupted mitochondria of Hymenolepis microstoma[76]. The relative activities of all the enzymes studied showed more or less similar trend of reduction in the enzyme activity of F. buski following in vitro treatment to the plant extract and reference drug (PZQ). Maximum level of inhibition was observed in the activities of PEPCK, MDH and LDH (Graph 1). The activities of PEPCK and MDH were reduced by almost 31-48% and 26-36% whereas the activities of PK and LDH were reduced to a very less extend. Both A. nigra crude extract-and praziquantel treated F. buski showed less efficacy against pyruvate kinase and LDH enzymes. Similar study was done by Navaneetha and Veerakumari[77] where the Allium sativum bulb-extract was found to reduce the activities of PEPCK and PK in helminth parasite, H. contortus. Banu et al.[78] screened the anthelmintic efficacy of the leaf-and flower-extract of several plants against mMDH and mME of Setaria digitata. All the plant-extracts were found to inhibit the activities of both the enzymes.
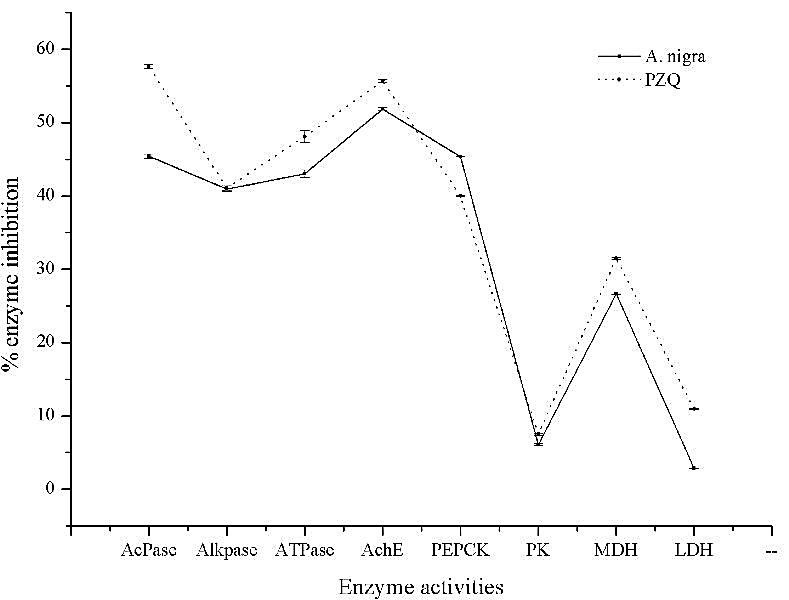 | Graph 1. Showing the % Inhibition of Different Enzyme Activities on Treatment with A. nigra Crude-Extract and PZQ in F. buski |
5.4. Kinetic Study
- Acetylcholine (Ach) is an important cholinergic neurotransmitter in parasitic helminths which is required for proper neuromuscular activity[79]. It is synthesized from choline and acetyl coenzyme-A in presence of choline acetyltransferase. In order to continue the regular sequence of nerve impulse required for normal body mechanism, Ach is to be hydrolysed to choline and acetate with the help of acetylcholinesterase[80]. In parasites acetylcholinesterase has been found to be primarily associated with neuromuscular system and influences the motor activity. In view of the functional significance of AchE in controlling motility of parasites inside the host body, kinetic study was carried out to know the mode of inhibition through different kinetic parameters.
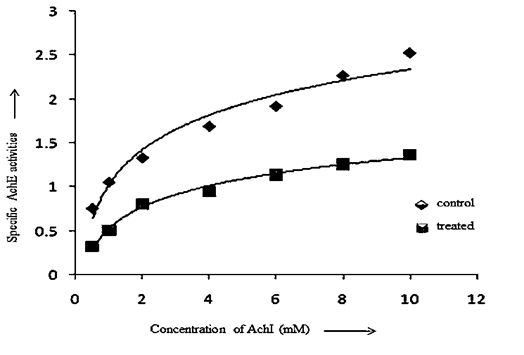 | Graph 2. Specific Activities of Ache in Control and A. nigra Treated F.buski.[Graph was adapted from Medicinal Plants - International Journal of Phytomedicines and Related Industries, 3(2), 2011, 145-150, Kinetics of Acetylcholinesterase inhibition in Fasciolopsis buski and Raillietina echinobothrida by shoot extract of Alpinia nigra, an indigenous medicinal plant, Swargiary A. and Roy B., Figure no. 4, © SMP, with kind permission from SMP] |
|
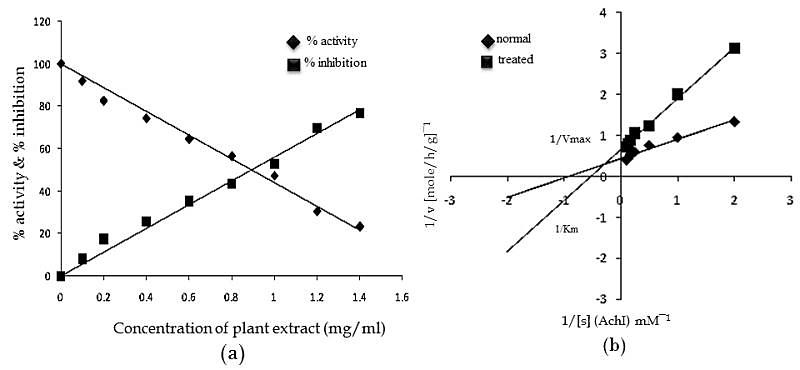 | Graph 3. (a) Showing The % Inhibition of Ache Following Treatment with A. nigra Plant Extract, (b) Lineweaver-Burk Plot Of Ache Inhibition By A. nigra Plant Extract (1 mg/ml) In F. buski.[Graphs were adapted from Medicinal Plants - International Journal of Phytomedicines and Related Industries, 3(2), 2011, 145-150, Kinetics of Acetylcholinesterase inhibition in Fasciolopsis buski and Raillietina echinobothrida by shoot extract of Alpinia nigra, an indigenous medicinal plant, Swargiary A. and Roy B., Figure no. 5 and 6, © SMP, with kind permission from SMP] |
6. Electron Microscopic Studies
- Electron Microscopy has always been an important tool in biological sciences to understand the complex animal life and its functional anatomy.Tegument, being an important organ of helminths for uptake of nutrients, excreation of certain metabolites, control of motility and osmoregulation, it attracts higher attention from scientific community to know and study its structure and function as well. Since, the tegument is one of the tissues most immediately exposed to anthelmintics; it is likely to represent a primary drug target. Any drug-induced disruption to the tegument is likely to have serious consequences for the fluke because it would allow the drug to penetrate to deeper-lying tissues and the damage would be exacerbated by the surfactant action of bile and the immune response.Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) analysis of untreated F. buski revealed normal body contour (Fig. 9). The ventral surface of the parasite contains some scale-like papillae with distinct shape and size arranged in an alternate manner[87].On exposure to crude extract of A. nigra, marked changes in the surface topography of F. buski has been noticed compared to the control one. The treated flukes showed a deformed body with shrunken and wrinkled tegumental surface that showed extensive pit formations and scarring due to sloughing off of the scale-like spines (Fig. 10). The ventral sucker present at the anterior part of the body also deformed to a great extend compared to the untreated flukes (Fig. 10a). It has also been observed that the severity of deformation increased with increasing concentration of plant extract and time of incubation. A similar pattern of alteration has been observed in the surface tegument of the fluke treated with the commercial drug, praziquantel. Destruction of absorptive surface tegument of several helminth parasites of public health importance was observed when treated with phytochemicals from different traditionally used medicinal plants[88-90]. Our recent studies on some of the plants like Millettia pachycarpa, Acacia oxyphylla and Lysimachia ramosa against several helminth parasites showed conspicuous deformity of the surface architecture in all the parasites exposed to the test plant extract and commercial drugs as well. A large number of commercially available anthelmintic drugs like clorsulon, closantel, praziquantel etc. are found to disrupt the external body surface of helminth parasites. McKinstry et al.[91] studied the effect of Nitroxynil (Trodax), a halogenated phenol containing anthelmintic drug on adult Fasciola hepatica. The parasites recovered from rat after 24h, 48h and 72h post-treatment showed extensive swelling and blebbing of the tegument on both surfaces with dorsal anterior region more severely affected than either the posterior dorsal region or entire ventral surface when observed under scanning electron microscope. Similar experiment was conducted by Keiser and Morson[92] in F. hepatica to see the anthelmintic property of two drugs artemether and artesunate. SEM analysis of the flukes incubated in the presence of drugs showed extensive tegumental damage, including sloughing, blebbing and eruptions, particularly in the ventral and dorsal mid-body and tail region of the body. Extensive blebbing of surface layer causing lesions and loss of spines have been observed in F. hepatica after the treatment of deacetylated (amine) metabolite of diamphenethide[93]. Moreover, longer time exposure (24h) to the drug showed maximum damage of the tegument which has been stripped off to expose the basal lamina. A large number of studies have been performed to see the ultrastructural details of several helminth parasites, especially the tegumental regions because of its functional significance. Surface tegument of F. buski is outwardly covered by glycocalyx layer followed by cytoplasmic syncytium. The syncytial zone of the tegument is separated from the muscle layer and the subtegumental cells by a membranous basal lamina. The syncytial layer is connected to the nucleated cell bodies or cytons by cytoplasmic tubes that are lined with microtubules. The cytons are the main cell bodies that contain cellular organalles like mitochondria, Golgi bodies etc. (Fig. 11).
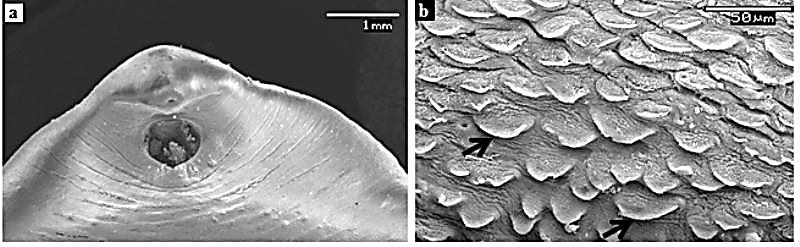 | Figure 9. Surface Topography (SEM) Of F. buski - Control. (a) Anterior Part Of The Parasite With Normal Contour, (b) Tegument Covered With Posteriorly-Directed Scale-Like Papillae Along With Pits At Many Places.[Figure (b) was adapted from Microscopy Research and Technique, 72, 2009, 61–66, Ultrastructural Observations on Fasciolopsis buski and its Alterations Caused by Shoot Extract of Alpinia nigra, Roy et al., Figure no. 1, © 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc] |
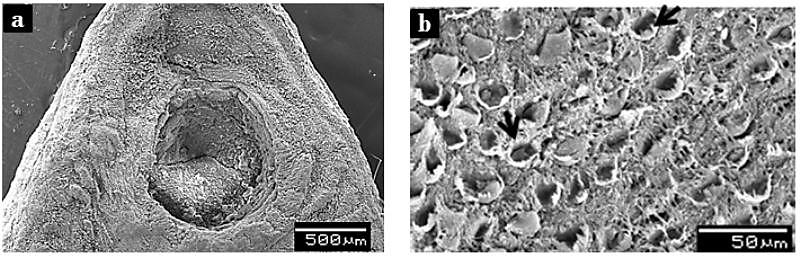 | Figure 10. Surface Topography (SEM) Of F. buski: Alpinia nigra Treated. (a) Anterior Part Of The Parasite Showing Distorted And Wrinkled Ventral Sucker And Its Surrounding Parts, (b) A Portion Of The Ventral Surface Of Body Under Higher Magnification Showing Sloughed Scales (Arrows) And Scars Formation |
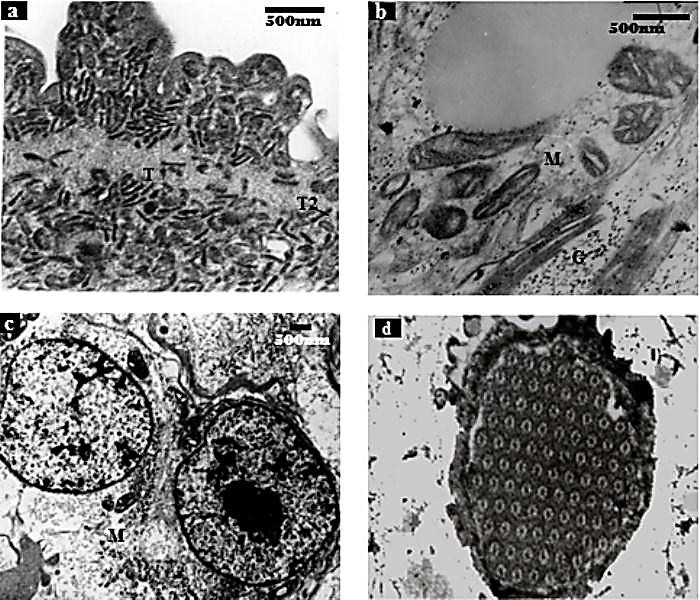 | Figure 11. Transmission Elctron Micrographs Of F. buski - Control. (a) Inveginated Tegument Showing Glycocalyx Layer, Distal Cytoplasm And Electron-Dense With T1 And T2 Tegumental Discs, (b) Photographs Showing Normal Mitochondria And Other Cell Organalles Inside The Cell, (c) Two Tegumental Cytons Lying Beside Each Other, (d) Flame Cells.[Figures (a), (b) and (c) were adapted from Microscopy Research and Technique, 72, 2009, 61–66, Ultrastructural Observations on Fasciolopsis buski and its Alterations Caused by Shoot Extract of Alpinia nigra, Roy et al., Figure no. 4, 5 and 6, © 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc] |
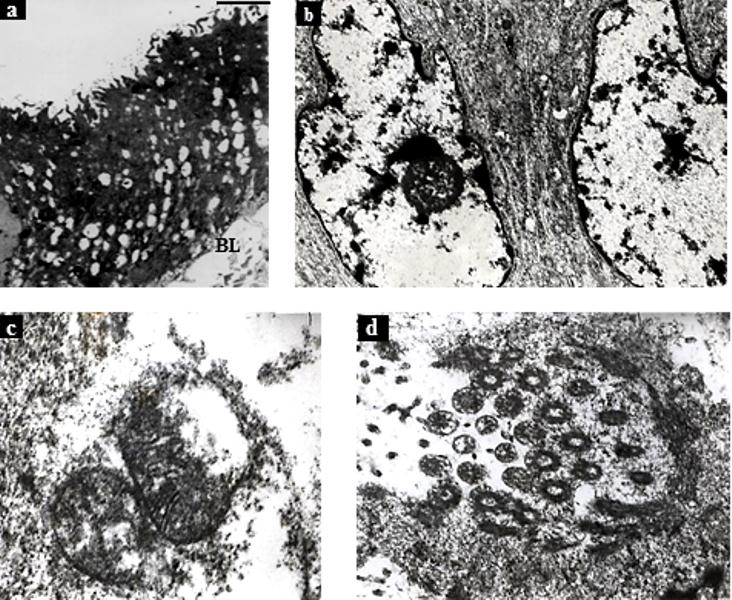 | Figure 12. Transmission Electron Micrographs of F. buski Treated With A. nigra. (a) Shredded Tegument With Intensely Vacuolated Distal Cytoplasm, (b) Abnormal Shape Of Nucleaus With Condensation Of Chromosome Material, (c) Distorted Mitochondria With Disrupted Mitochondrial Membrane And Cristae, (d) Disrupted Flame Cells.[Figure (a) was adapted from Microscopy Research and Technique, 72, 2009, 61–66, Ultrastructural Observations on Fasciolopsis buski and its Alterations Caused by Shoot Extract of Alpinia nigra, Roy et al., Figure no. 12, © 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc] |
7. Conclusions
- Tegumental layers of the flat worms are known to be involved in many vital functions like nutrient uptake, osmoregulation, digestion and protection from the immune attack from host. Considerable structural alteration and changes in enzyme activities, interfaring with the glycolytic pathway and neuromuscular activities are suggestive of an efficient vermicidal activity of A. nigra shoot extract against the trematode parasite. Thus, there is a considerable evidences that the crude extract of the plant have the potential to act as anthelmintic. Further, in vitro and in vivo investigation involving active components of the plant, namely astragalin and kaempferol-3-o-glucuronide is under way to fully assess the anthelmintic potential of the plant and their cytotoxic activity, if any, in the host.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- Infrastructural support from DSA (UGC-SAP) program to the Department of Zoology and UPE-Biosciences program to the School of Life Sciences, North-Eastern Hill University is gratefully acknowledged. Thanks are due to the Head, SAIF, North-Eastern Hill University for providing SEM and TEM facilities.
References
| [1] | WHO, 2002 ‘‘WHO Traditional Medicine Strategy 2002–2005’’. WHO/EDM/TRM/2002.1, pp. 61. |
| [2] | WHO report on neglected tropical diseases 2010: working to overcome the global impact of neglected tropical diseases? ISBN 978 92 4 1564090 (NLM Classification: WC 680). |
| [3] | Bundy, D. A., 1994, Immuno-epidemiology of intestinal helminthic infection. The global burden of intestinal nematode disease, , 88(3), 259-261. |
| [4] | Holden-Dye, L., and Walker, R. J., 2007, Anthelmintic drugs, WormBook, Ed. The C. elegans Research Community. |
| [5] | Singh, T. U., Kumar, D., and Tandon, S. K., 2008, Paralytic effect of alcoholic extract of Allium sativum and Piper longumon liver amphistome, Gigantocotyle explanatum, Indian Journal Pharmacology, 40(2), 64-68. |
| [6] | Ortega, C. D., Ogawa, N. Y., Rocha, M. S., Roberto Blasbalg, M. D., Caiado, A. H. M., Warmbrand, G., and Cerri, G. G., 2010, Helminthic diseases in the abdomen: An epidemiologic and radiologic overview, RadioGraphics, 30(1), 253-267. |
| [7] | Hotez, P. J., Molyneux, D. H., Fenwick, A., Kumaresan, J., Sachs, S. E., Sachs, J. D., and Savioli, L., 2007, Control of neglected tropical diseases, New England Journal of Medicine, 357, 1018-1027. |
| [8] | Roy, B., and Tandon, V., 1992, Seasonal prevalence of some zoonotic trematodes infections in cattle and pigs in the north-east montane zone in India, Veterinary Parasitology, 41(1-2), 69-76. |
| [9] | Albonico, M., Crompton, D. W., and Savioli, L., 1999, Control strategies for human intestinal nematode infections, Advances in Parasitology, 42, 277-341. |
| [10] | Kohler, P., 2001, The biochemical basis of anthelmintic action and resistance, International Journal for Parasitology, 31(4), 336-345. |
| [11] | Chirac, P., and Torreele, E., 2006, Global framework on essential health R&D, Lancet, 367(9522), 1560-1561. |
| [12] | Hotez, P. J., 2008, Forgotten people and forgotten diseases: The neglected tropical diseases and their impact on global health and development, ASM Press, Washington, DC, USA. |
| [13] | Geerts, S., and Gryseels, B., 2000, Drug Resistance in Human Helminths: Current Situation and Lessons from Livestock, Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 13(2), 207-222. |
| [14] | Geerts, S., and Gryseels, B., 2001, Anthelmintic resistance in human helminths: a review, Tropical Medicine and International Health, 6(11), 915-921. |
| [15] | Martin R. J., Robertson, A. P., and Bjorn, H., 1997, Target sites of anthelmintics, Parasitology, 114(4), 111-124. |
| [16] | Satrija, F., Retnani, E. B., Ridwan, Y., and Tiuria, R., 2001, Potential use of herbal anthelmintics as alternative antiparasitic drugs for small holder farms in developing countries. Livestock Community and Environment, Proceedings of the 10th Conference of the Association of Institutions for Tropical Veterinary Medicine, Copenhagen, Denmark, August 2001. |
| [17] | Suleiman, M. M., Mamman, M., Aliu, Y. O., and Ajanusi, J. O., 2005, Anthelmintic activity of the crude methanol extracts of Xylopia aethiopica against Nippostrongylus brasiliensis in rats, Veterinarski Arhiv, 75(6), 487-495. |
| [18] | Waller, P. J., 1997, Anthelmintic resistance, Veterinary Parasitology, 72(3-4), 391-412. |
| [19] | Dasgupta, S., Roy, B., and Tandon, V., 2010, Ultrastructural alterations of the tegument of Raillietina echinobothrida treated with the stem bark of Acacia oxyphylla (Leguminosae), Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 127(2), 568-571. |
| [20] | Mali, R. G., and Mehta A. A., 2008, A review on anthelmintic plants, Natural Product Radiance, 7(5), 466-475. |
| [21] | Roy, B., and Tandon, V., 1996, Effect of root-tuber extract of Flemingia vestita, a leguminous plant, on Artyfechinostomum sufrartyfex and Fasciolopsis buski: a scanning electron microscopy study, Parasitology Research, 82(3), 248-252. |
| [22] | Tandon, V., Yadav, A. K., Roy, B., and Das, B., 2011, Phytochemicals as cure of worm infections in traditional medicine systems. Emerging Trends in Zoology, Narendra Publishing Housee, pp. 1-27. |
| [23] | Roy, B., Lalchhandama, K. and Dutta, B. K., 2007, Anticestodal efficacy of Acacia oxyphylla on Raillietina echinobothrida: a light and electron microscopic study, Pharmacologyonline, 1, 279-287. |
| [24] | Swargiary, A., and Roy, B., 2011, Kinetics of Acetylcholinesterase inhibition in Fasciolopsis buski and Raillietina echinobothrida by shoot extract of Alpinia nigra, an indigenous medicinal plant, Medicinal Plants-International Journal of Phytomedicines and Related Industries, 3(2), 145-150. |
| [25] | Taylor, J. L. S., Rabe, T., McGaw, L. J., Jager, A. K., and Van Staden, J., 2001. Towards the scientific validation of traditional medicinal plants, Plant Growth Regulation, 34(1), 23-37. |
| [26] | Adama, K., Gaston, B. A. M., Tamboura H. H., Amadou, T, and Laya, S., 2009, In vitro anthelmintic effect of two medicinal plants (Anogeissus leiocarpus and Daniellia oliveri) on Haemonchus contortus, an abosomal nematode of sheep in Burkina Faso, African Journal of Biotechnology, 8(18), 4690-4695. |
| [27] | Athanasiadou, S., Githiori, J., and Kyriazakis, I., 2007, Medicinal plants for helminth parasite control: facts and fiction, Animal, 1(9), 1392-1400. |
| [28] | Diehl, M. S., Atindehoub, K. K., Tereb, H., and Betscharta, B., 2004, Prospect for anthelminthic plants in the Ivory Coast using ethnobotanical criteria, Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 95(2-3), 277-284. |
| [29] | Roy, B., Dasgupta, S., and Tandon, V., 2008, Ultrastructural observations on tegumental surface of Raillietina echinobothrida and its alterations caused by root-peel extract of Millettia pachycarpa, Microscopy Research and Technique, 71(11), 810-815. |
| [30] | Roy, B., Swargiary, A., Syiem, D., and Tandon, V., 2010, Potentilla fulgens (Family Rosaceae), a medicinal plant of North-east India: a natural anthelmintic, Journal of Parasitic Diseases, 34(2), 83-88. |
| [31] | Roy, B., Dasgupta, S., and Tandon, V., 2009, Ultrastructural observations on Fasciolopsis buski and its alterations caused by shoot extract of Alpinia nigra, Microscopy Research and Technique, 72(2), 61-66. |
| [32] | Roy, B., and Swargiary, A., 2009, Anthelmintic efficacy of ethanolic shoot extract of Alpinia nigra on tegumental enzymes of Fasciolopsis buski, a giant intestinal parasite, Journal of Parasitic Diseases, 33(1-2), 48-53. |
| [33] | Roy, B., and Tandon, V., 1999, Flukicidal activity of Alpinia nigra (Zingiberaceae) against the trematode, Fasciolopsis buski, in humans, Biomedical Letters, 60(234), 23-29. |
| [34] | Mittermeier, R. A., da Fonseca, G. A. B., Brooks, T., Pilgrim, J. and Rodrigues, A., 2003, Hotspots and Coldspots, American Scientist, 91, 384. |
| [35] | Singh, H. B., and Arora, R. K., 1978, Wild Edible Plants of India, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi. |
| [36] | Delin, W., and Larsen, K., 2000, Zingiberaceae, Flora of China, 24, 322-377. |
| [37] | Wu, D. L., 1981, Flora of China.Vol.16, Fascicle 2. Beijing: Science Press, pp. 67-106. |
| [38] | Prakash, V., and Mehrotra, B. N., 1995, Zingiberaceae of North-East India: diversity and taxonomic status, Food Chemistry, pp. 262-273. |
| [39] | De Araujo Pinho, F. V. S., Coelho-de-Souza, A. N., Morais, S. M., Ferreira Santos, C., and Leal-Cardoso, J. H., 2005, Antinociceptive effects of the essential oil of Alpinia zerumbet on mice. Phytomedicine, 12(6-7): 482-486. |
| [40] | Hsu, S.Y., 1987, Effect of the constituents of Alpinia speciosa rhizome on experimental ulcers, Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi, 86(1), 58-64. |
| [41] | Jantan, I., Rafi, I. A., and Jalil, J., 2005, Platelet activating factor [PAF] receptor-binding antagonist activity of Malaysian medicinal plants, Phytomedicine, 12(1-2), 88-92. |
| [42] | Charles, D. J., Simon, J. E., and Singh, N. K., 1992, The Essential Oil of Alpinia galangal Willd, Journal of Essential Oil Research, 4(1), 81-82. |
| [43] | De Pooter, H. L., Aboutabl, E. A. and El-Shabrawy, A. O., 1995, Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oil of leaf, stem and rhizome of Alpinia specios, Flavour Fragrance Journal, 10(2), 63-67. |
| [44] | Ibrahim, H., Aziz, A. N., Syamsir, D. R., Ali, N. A. M., Mohtar, M., Ali, R. M., and Awang, K., 2009, Essential oils of Alpinia conchigera Griff. and their antimicrobial activities, Food Chemistry, 113(2), 575-577. |
| [45] | Jaju, S., Indurwade, N., Sakarkar, D., Fuloria, N., and Ali, M., 2009, Isolation of galangogalloside from rhizomes of Alpinia galangal, International Journal of Green Pharmacy, 3(2), 144-147. |
| [46] | Janssen, A. M., and Scheffer, J. J., 1985, Acetoxychavicol acetate, an antifungal component of Alpinia galangal, Planta Medica, 51(6), 507-511. |
| [47] | ., ., ., and ., 2005, In vitro enzyme inhibition activities of crude ethanolic extracts derived from medicinal plants of Pakistan, , 19(6), 567-571. |
| [48] | Kubota, K., Nakamura, K., and Kobayashi, A., 1998, Acetoxy-1, 8-cineoles as aroma constituents of Alpinia galangal Willd, Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 46(12), 5244-5247. |
| [49] | Kubota, K., Someya, Y., Yoshida, R., Kobayashi, A., Morita, T., and Koshino, H., 1999, Enantiomeric purity and odor characteristics of 2- and 3-acetoxy-1, 8-cineoles in the rhizomes of Alpinia galangal Willd, Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 47(2), 685-689. |
| [50] | Mallavarapu, G. R., Rao, L. M., Ramesh, S., Dimri, B. P., Rao, B. R. R. and Bhattacharya, A. K., 2002, Composition of the volatile oils of Alpinia galanga rhizomes and leaves from India, Journal of Essential Oil Research, 14, 397-399. |
| [51] | ., ., ., . and ., 2009, An ethnobotanical study of traditional anti-inflammatory plants used by the Lohit community of Arunachal Pradesh, India, ogy, 125(2), 234-245. |
| [52] | Prajapathi, N. D., Purohit, S. S., Arun, K. S., and Kumar, T., 2009, A Handbook of Medicinal Plants: A complete source Book, Agrobios, Jadhpur, India. |
| [53] | Raina, V. K., Srivastava, S. K., and Syamsunder, K. V., 2002, The essential oil of ‘greater galangal’ [Alpinia galangal (L.) Willd] from the lower Himalayan region of India, Flavour Fragrance Journal, 17(5), 358-360. |
| [54] | Sabu, M., 2006, Zingiberaceae and Costaceae of South India, Indian Association for Angiosperm Taxonomy, Calicut University, pp. 68-70. |
| [55] | Sirirugsa, P., 1999, Thai Zingiberaceae: Species diversity and their uses. www.iupac.org/symposia/proceedings/phunket97/sirirugsa, acess in 2005. |
| [56] | , ., ., and ., 2010, Ethnomedical uses of Zingiberaceous plants of Northeast India, ogy, 132(1), 286-296. |
| [57] | Qiao, C. F., Quanbin, H., Jingzheng, S., Zhengtao, W., Luoshan, X., and Hongxi, X., 2007, HPLC determination of two bioactive flavone glycosides and GC-MS analysis of volatile oil constituents in Alpinia nigra, Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines, 2(3), 85-91. |
| [58] | Qiao, C. F., Wang, Z. T., Dong, H., Xu, L. S. and Hao, X. J., 2000, The chemical constituents of Blackfruit Galangal (Alpinia nigra), Chinese Traditional Herbs and Drugs, 31, 404-405. |
| [59] | Challam, M., Roy, B., and Tandon, V., 2010, Effect of Lysimachia ramosa (Primulaceae) on helminth parasites: motility, mortality and scanning electron microscopic observations on surface topography, Veterinary Parasitology, 169(1-2), 214-218. |
| [60] | Lalchhandama, K., Roy, B., and Dutta, B. K., 2009. Anthelmintic activity of Acacia oxyphylla stems bark aginst Ascardia galli. Pharmaceutical Biology, 47(7), 578-583. |
| [61] | Tandon, V., Pal, P., Roy, B., Rao, H. S. P., and Reddy, K. S., 1997, In vitro anthelmintic activity of root-tuber extract of Flemingia vestita, an indigenous plant in Shillong, India, Parasitology Research, 83(5), 492-498. |
| [62] | Mansour, T. E., 2002, Chemotherapeutic Targets in Parasites: Contemporary Strategies, Cambridge University Press, pp. 189-195. |
| [63] | Kar, P. K., and Tandon, V., 2004, Anthelmintic efficacy of genistein, the active principle of Flemingia vestita (Fabaceae): Alterations in the activity of the enzymes associated with the tegumental and gastrodermal interfaces of the trematode, Fasciolopsis buski, Journal of Parasitic Diseases, 28(1), 45-56. |
| [64] | Kwak, K. H., and Kim, C. H., 1996, Characteristics of alkaline and acid phosphatase in Spirometra erinacei, Korean Journal Parasitology, 34(1), 69-77. |
| [65] | Lalchhandama, K., Roy, B., and Dutta, B. K., 2008, Effects of Millettia pachycarpa on the trace metals and tegumental enzymes of Raillietina echinobothrida, Pharmcogonsy Magazine, 4(16), 254-261. |
| [66] | Pal, P., and Tandon, V., 1998, Anthelmintic efficacy of Flemingia vestita (Leguminoceae): Genistein-induced alterations in the activity of tegumental enzymes in the cestodes, Raillietina echinobothrida. Parasitology International, 47(3), 233-243. |
| [67] | Poljakova-Krustena, O., Mizinska-Boevska, Y., and Stojtsova, S., 1983, A cytochemical study of some phosphatases in the tegument of two cestode species, Helminthologia, 16, 64-67. |
| [68] | Roy, T. K., 1982, Histochemical studies on Raillietina (Raillietina) johri (Cestoda: Davaineidae). I. Nonspecifi c and specific phosphatases, Journal of Helminthology, 53(1), 45-49. |
| [69] | ., ., ., ., ., and ., 1973, Acetylcholinesterase secretion by parasitic nematodes. I. Evidence for secretion of the enzyme by a number of species, ogy, 3(5), 589-597. |
| [70] | Agarwal, A., Tekwani, B. L., Shukla, O. P., and Ghatak, S., 1990, Effect of anthelmintics and phenothiazines on adenosine 5'-triphosphatases of filarial parasite Setaria cervi, Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 28(3), 245-248. |
| [71] | Aggarwal, R., Sanyal, S. N., and Khera, S., 1992, Effect of anthelmintics on phosphatases in Ascaridia galli, Acta Vet Hungarica, 40(4), 243-249. |
| [72] | Chopra, A. K., Sharma, M. K., and Upadhyay, V. P., 1991, Effect of ayurvedic anthelmintics on phosphatase activity of Paramphistomum cervi, Indian Journal of Parasitology, 43(1), 65-69. |
| [73] | Vinaud, M. C., Ferreire, C. S., Lino Junior Rde, S., and Bezerra, J. C., 2009, Taenia crassiceps: fatty acid oxidation and alternative energy source in in vitrocysticerci exposed to anthelmintic drugs, Experimental Parasitology, 122(3), 208-211. |
| [74] | Tielens, A. G., Horemans, A. M., Dunnewijk, R.,Van der Meer, P. and Van den Bergh, S. G., 1992, Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 56(1), 49-57. |
| [75] | Das, B., Tandon, V., and Saha, N., 2004, Anthelmintic efficacy of Flemingia vestita (Fabaceae): alteration in the activities of some glycolytic enzymes in the cestode, Raillietina echinobothrida, Parasitology Research, 93(4), 253-261. |
| [76] | Fioravanti, C. F., 1982, Mitochondrial NADH oxidase activity of adult Hymenolepis diminuta (Cestoda), Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 72(4), 591-596. |
| [77] | Navaneetha, L. K., and Veerakumari, L., 2009, Effect of Allium sativum on the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and pyruvate kinase activity of Haemonchus contortus in vitro, Pharmacognosy Magazine, 5(20), 430-432. |
| [78] | ., ., and ., 1992, Mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase and malic enzyme of a filarial worm Setaria digitata: some properties and effects of drugs and herbal extracts, Japanese Journal of Medical Science & Biology, 45(3), 137-150. |
| [79] | Day, T. A., Maule, A.,G., Shaw, C., Halton, D.,W., Moore, S., Bennett, J. L., and Pax, R. A., 1994, Platyhelminth FMRFamide-related peptides (FaRPs) contract Schistosoma mansoni (Trematoda: Digenea) muscle fibres in vitro, Parasitology, 109(4), 455-459. |
| [80] | Voet, D., Voet, J. G., and Pratt, C. W., 2002, Fundamentals of Biochemistry, 2nd edn, John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| [81] | Chance, M. R. A., and Mansour, T. E., 1949, A kymographic study of the action of drugs on the liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica), British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy, 4(1), 7-13. |
| [82] | Chance, M. R. A., and Mansour, T. E., 1953, A contribution to the pharmacology of movement in the liver fluke, British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy, 8(2), 134-138. |
| [83] | Terada, M., Ishii, A. I., Kino, H., and Sano, M., 1982, Studies on chemotherapy of parasitic helminths (VII). Effects of various cholinergic agents on the motility of Angiostrongylus cantonensis, The Japanese Journal of Pharmacology, 32(4), 633-642. |
| [84] | ., and ., 2007, Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by extracts and constituents from Angelica archangelica and Geranium sylvaticum, Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung C, 62(9-10), 689-693. |
| [85] | ., 2002, Inhibitory effect of corynoline isolated from the aerial parts of Corydalis incisa on the Acetylcholinesterase, Archives of Pharmacal Research, 25(6), 817-819. |
| [86] | Mukherjee, P. K., Kumar, V., and Houghton, P. J., 2007, Screening of Indian medicinal plants for acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. earch, (12), 1142-1145. |
| [87] | Roy, B., and Tandon, V., 1993, Morphological and microtopographical strain variations among Fasciolopsis buski originating from different geographical areas, Acta Parasitologica Polonica, 38(2), 72-77. |
| [88] | , H., , J., and , R. C. A., 1983, Proliferation and metastases formation of larval Echinococcus multilocularis. , ), 749-763. |
| [89] | Roy, B., 2001, Stereoscan observation on the surface alteration of Orthocoelium dinniki induced by extract of Spilenthes oleracea L. Revestida Parasitologia, 18, 9-14. |
| [90] | Roy, B., 2003, Anthelmintic activity of Artemesia meritima against Artyfechinostomum sufrartyfex, a zoonotic parasite in North-east India, Revestida Parasitologia, 20, 143-148. |
| [91] | McKinstry, B., Fairweather, I., Brennan, G. P., and Forbes, A. B., 2003, Fasciola hepatica: tegumental surface alterations following treatment in vivo and in vitro with nitroxynil (Trodax), Parasitology Research, 91(3), 251-263. |
| [92] | ., and ., 2008, Fasciola hepatica: tegumental alterations in adult flukes following in vitro and in vivo administration of artesunate and artemether, Experimental Parasitology, 118(2), 228-237. |
| [93] | ., ., and ., 1987, Fasciola hepatica: tegumental surface alterations following treatment in vitro with the deacetylated (amine) metabolite of diamphenethide, Parasitology Research, 73(2), 99-106. |
| [94] | Beugnet, F., Kerboeuf, D., Nicolle, J. C., and Soubieux, D., 1996, Use of free living stages to study the effects of thiabendazole, levamisole, pyrantel and ivermectin on the fine structure of Haemonchus contortus and Heligmosomoides polygyrus, Veterinary Parasitology, 63(1-2), 83-94. |
| [95] | Anderson, H. R., and Fairweather, I., 1995, Fasciola hepatica: Ultrastuctural changes to the tegument of juvenile flukes following incubation in vitro with the deacetylated (Amine) Metabolite of Diamphenethide, International Journal for Parasitology, 25(3), 319-333. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML