-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Life Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1387 e-ISSN: 2163-1395
2012; 2(1): 20-27
doi: 10.5923/j.als.20120201.03
Occurrence of Sclerotinia Foliage Blight Disease of Cucumber and Pepper Plants under Protected Cultivation System in Egypt I. Chemical and Biological Control Measures in Vitro
M. M. Abdel-Kader , Nehal S. El-Mougy , E. I Embaby , S. M. Lashin
Plant Pathol. Dept., National Research Centre, Giza, Egypt
Correspondence to: Nehal S. El-Mougy , Plant Pathol. Dept., National Research Centre, Giza, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
During the winter season 2011, a sever Sclerotinia blight disease symptoms were observed on cucumber and Pepper plants grown in the Protected Cultivation Station, Ministry of Agriculture located at Tookh province, Qalubiya governorate, Egypt. Surveyed plastic houses at the previous location revealed that the recorded Sclerotinia blight disease incidence was 2.8 and 3.3% for cucumber and pepper plants, respectively. The isolated causal pathogens for cucumber and pepper foliage blights were identified as Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary and S. minor Jagger, respectively. This is thought to be the first report of these fungi to cause foliage blights on cucumber and pepper in Egypt. As control measures antagonistic agents and fungicides against the growth both pathogenic fungi under in vitro conditions were evaluated. The obtained results showed complete growth inhibition was recorded for both S. sclerotiorum and S. minor at 100ppm of Topsin-M and Ridomil Gold, while Rizolex-T gave the same effect at 200ppm. The fungicide, Previcure had inhibitor effect on the mycelia growth of both fungi only at the high concentration 800ppm. Moreover, the antagonistic fungi (Trichoderma spp.) showed superior inhibitory effect against the growth of pathogenic fungi compared with bacterial isolates (B. subtilis & P. florescence). No significant differences between the tested antagonistic microorganisms and commercial biocides were observed.
Keywords: Antagonistic Agents, Cucumber, Foliage Blight Disease, Fungicides, Pepper, Pseudomonas Fluorescens, Sclerotinia Sclerotiorum, S. Minor, T. Harzianum, T. Viride
Cite this paper: M. M. Abdel-Kader , Nehal S. El-Mougy , E. I Embaby , S. M. Lashin , "Occurrence of Sclerotinia Foliage Blight Disease of Cucumber and Pepper Plants under Protected Cultivation System in Egypt I. Chemical and Biological Control Measures in Vitro", Advances in Life Sciences, Vol. 2 No. 1, 2012, pp. 20-27. doi: 10.5923/j.als.20120201.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Cucumber and pepper crops are cultivated throughout the world as important vegetables or a food source. In Egypt, most vegetable crops except potato are cultivated in the plastic-house conditions during the winter season. The plastic-house conditions are favorable for occurrence of fungal diseases on the crops due to the high humidity. Especially, Sclerotinia rot is apt to readily occur under cool and moist conditions[1,2]. Severe outbreaks of stem or fruit rot symptoms with sclerotial formation were observed during a disease survey of vegetable crops in the Protected Cultivation Station, Ministry of Agriculture located at Tookh province, Qalubiya governorate, Egypt during the cool season 2011. The disease was recorded as Sclerotinia stem rot, Sclerotinia fruit rot, fruit and stem rot, fruit rot, stem blight and rot, white mold or pink joint depending on the species of the infected crops[3]. It has been reported that Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary and S. minor Jagger cause Sclerotinia rot in a variety of plants[1,3-5]. Some mycological and pathological characteristics of S. sclerotiorum and S. minor causing Sclerotinia rot of vegetable crops were also reported[6]. As control measures, chemical fungicides are successfully reported to control Sclerotinia spp.In this regards, it was reported that among the fungicides tested, the most effective fungicides in inhibiting the sclerotial germination were Ridomil gold, Benlate, Tecto-60 and Topsin-M[7]. Also, In vitro test, Rizolex-T and Topsin-M at 200 ppm was completely inhibited the growth of R. solani and F. oxysporum, respectively[8], meanwhile among the fungicides tested, Ridomil MZ 72 WP (metalaxyl 8%+ mancozeb 64% WP) was found to give the best protection against Sclerotinia root rot incidence in both common and Tartary buckwheat (by 50 and 56% protection of root rot incidence over the control, respectively) and thereby increased the plant stand[9]. Few studies have been conducted on the detailed characteristics of the disease occurrence and the pathogenicity of the causal Sclerotinia species on different crops. Therefore, this study was conducted to reveal trends of the disease occurrence on cucumber and pepper crops in Egypt, the pathological aspects of the causal Sclerotinia spp. as well as the efficacy of some biological and chemical measures for controlling Sclerotinia spp. under laboratory conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Disease Survey
- The most reported areas for high production of vegetables under protected cultivation system in Egypt were subjected to survey the infected plants with Sclerotina foliage blight. The surveyed plants were Cucumber, Pepper, Tomato and Cantaloupe. The percentage diseases incidence was recorded at different commercial greenhouses distributed in five governorates, i.e. Giza, Cairo, Kalubia, Ismaelia and Behiera. The average percentages of plant infections were calculated as the number of infected plants in relative to the total number of examined plants.
2.2. Isolation Trails
- Plant samples showing Sclerotinia foliage blight symptoms were collected and subjected to isolation trails. Sclerotinia spp. were isolated from the lesions appeared on diseased plants. Lesion pieces (2-3 cm2) cut from the diseased plant parts were placed on 2% water agar (WA) after surface-sterilizing with 1% sodium hypochlorite solution for 1 minute. The plates were incubated for 1~2 days at 22oC. The fungi grown from the lesion pieces were transferred to potato dextrose agar (PDA) slants and cultured for identification. Identification for the isolated fungi were carried out according to[19,20].
2.3. Pathogenicity Test
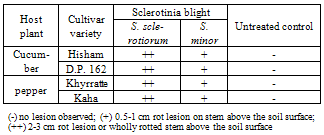
- Pathogenic ability of S. sclerotiorum and S. minor to induce foliage blight infection of cucumber and sweet pepper seedlings was tested under greenhouse conditions. Two cultivars each of Cucumber (D.P 162 & Hisham) and sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Khyrratte & Kaha were used for pathogenicity test. Transplants (5 weeks-old) were sown in plastic pots (25 cm in diameter) filled with sterile soil containing loamy soil artificially infested individually (at the rate of 5% w:w) with the inoculum of each tested isolate which previously grown for two weeks on sand barley medium (1:1, w:w and 40% water). Then, the pots were placed in a dew chamber with 100% relative humidity at 22oC for 48 hr and then moved into the greenhouse. Three pots each containing five transplants were used as replicates for each tested isolate as well as control. Disease incidence was rated based on the degree of rot symptoms induced 30 days after transplanting as the following scale:(-) no lesion observed; (+) 0.5-1 cm rot lesion on stem above the soil surface; (++) 2-3 cm rot lesion or wholly rotted stem above the soil surface.
2.4. Laboratory Control Measures
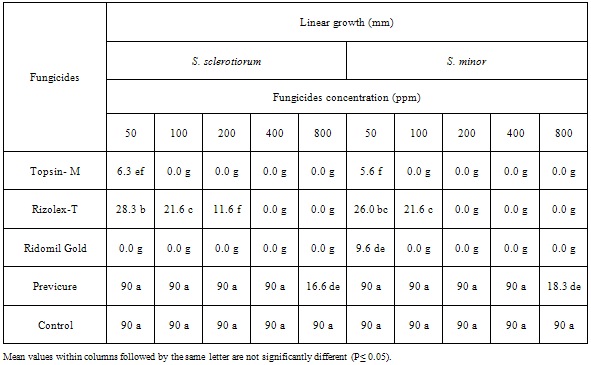
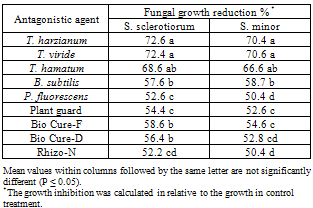
- I: Sensitivity test against fungicidesThe inhibitory effect of four fungicides against the S. sclerotiorum and S. minor fungal growth was evaluated under in vitro conditions. The fungicides, Ridomil (a.i. 2,6 dimethyl phenyl-metalaxy acetylamoni-propionic acid methyl ester 47%), Topsin- M (a.i. Thiophanate-Methyl 70%), Rizolex-T (a.i. Tolclofos-methyl 50%) and previcure (a.i. Propamocarb hydrochloride 72.2%) were tested. Eight concentrations of each fungicide, i.e. 50,100,200,400 and 800ppm based on the active ingredient were prepared in PDA medium poured in Petri-dishes. Control treatment was fungicide-free medium. Petri-dishes were inoculated with 5mm disc of 10-day-old tested fungal cultures. Three replicates were used for each particular treatment as well as control. All previous plates were incubated at 25+10C for 7 days then examined. Average linear growth was measured and percentage of growth reduction was calculated in relative to that grown in control treatment.II: Sensitivity test against antagonistic microorganismsThe inhibitory effect of the isolated fungal and bacterial antagonistic agents against the linear growth of S. sclerotiorum and S. minor fungi was evaluated using the modified dual culture technique[19]. The antagonistic microorganisms, i.e. Trichoderma harzianum, T. viride, T. hamatum, Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas fluorescens, were obtained from the Plant Pathology Department of the National Research Centre, Giza, Egypt. These microorganisms were isolated from the rhizosphere of various healthy and root rot infected leguminous crops, grown in the Delta and Middle Egypt regions, and proved their high pathogenic or antagonistic ability during previous work at the same department. Fungal and bacterial cultures were maintained on potato dextrose agar (PDA) and nutrient agar slant media at 5±1℃ as stock cultures until use. All isolates were refreshed by growing at the optimum growth conditions at the beginning of the present tests. In vitro antagonistic studies of biocontrol microorganisms and pathogenic fungi were performed on PDA medium in 9-cm-diameter Petri dishes. The commercial biocides products, e.g. Plant guard, Biocure-F, Biocure- D, Rhizo-N were also tested against pathogenic fungi as a reference to the present tested antagonistic microorganisms. The control treatment was inoculated with a culture disk of either a pathogenic or antagonistic culture alone at the same conditions. All inoculated Petri dishes were incubated at 28±1℃ for five days, then the antagonistic effect was measured. This test was repeated five times and the growth inhibition was calculated as the percentage reduction in colony growth diameter of pathogenic fungi in the presence of antagonistic microorganism in relative to their growth in control treatment. Statistical analysisAll experiments were set up in a complete randomized design. One-way ANOVA was used to analyze differences between inhibitor effect and linear growth of pathogenic fungi in vitro. A general linear model option of the analysis system SAS[21 was used to perform the ANOVA. Duncan’s multiple range test at P < 0.05 level was used for means separation [22].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Disease survey
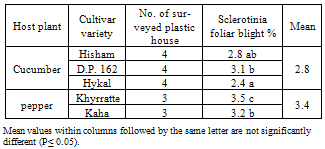
- Sclerotinia foliage blight occurred in cucumber and pepper plants grown under protected cultivation system at Tookh location at Kalubia governorate, Egypt (Table 1). Occurrence of the disease was observed in 18 out of 28 surveyed plastic houses during the growing winter season, 2011. The mean of disease severely occurred as high as 3.4% in pepper and as low as 2.8% in cucumber plants.
|
 | Figure 1. Typical symptoms of natural infection with Sclerotinia foliage blight disease of cucumber (a) and pepper (b) plants grown under protected cultivation system |
3.2. Pathogenicity Test
- Isolation from the collected cucumber and pepper samples showing foliage blight symptoms resulted in two species of the fungus Sclerotinia. The identified fugal species were S. sclerotiorum and S. minor. Pathogenicity test for these fungi revealed that they are able to induce foliage blight symptoms of either cucumber and pepper plants (Table 2). Data also show that there was no significant difference between the two fungi either for host or their cultivars tested. Data also showed that S. sclerotiorum was more aggressive for inducing the disease infection than S. minor for both host plants and consequently their cultivar varieties. The soil-borne plant pathogens Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and S. minor cause severe economic losses of many vegetable and ornamental crops around the world. Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and S. minor have been reported to be the pathogen of Sclerotinia rot of various crops[1,3,25]. In general, sclerotia of Sclerotinia spp. can survive in nature for many years [30] and play the important role as an inoculum source of the disease occurrence[2]. It has not yet been studied on the sclerotial density and viability of the two Sclerotinia spp. in the field of vegetable crops. There have been reports on differences in virulence of S. sclerotiorum isolates to individual plants and in susceptibility of some plants to the isolates[6,31]. It has been also reported that there are differences in susceptibility of cultivars or lines of some crops to the pathogen[32,33]. However, the present study showed that there was no significant difference in virulence of S. sclerotiorum isolates to cucumber and pepper crops, as reported by previous workers in other crops[34,35].On the other hand, S. minor was relatively less virulent on the two tested host plants cultivars than on another one, suggesting that there might be some differences in susceptibility of these cultivars to S. minor.
|
3.3. Laboratory Control Measures
- I: Sensitivity test against fungicidesThe major value of any chemical compound as a disease control agent ultimately depends on the mode of action of the molecule at the physiological level on one or more components of the life cycle of the pathogen. Eruptive germination of sclerotia followed by mycelial growth occurs when S. minor and S. sclerotiorum initiate disease infection to plants. Suppression of these activities should reduce the capacity of these pathogens to cause disease in the field. Laboratory test of the fungicidal effect against S. sclerotiorum and S. minor is a simple approach for understanding a small sector of chemical system on Sclerotinia foliage blight disease of cucumber and pepper plants caused by these pathogenic fungi. Data in Table (3) and figure (2) reveal that the reduction in the growth of both tested fungi was correlated to the increasing concentrations of either Rizolex-T, Topsin-M and Ridomil Gold in medium. Data also indicate that the two tested fungi varied in their sensitivity against the fungicides used. Complete growth inhibition was recorded for both S. sclerotiorum and S. minor at 100ppm of Topsin-M and Ridomil Gold, while the same effect was recorded at 400ppm and 200ppm of Rizolex-T for both species of Sclerotinia, respectively. The growth of S. minor showed more positive response to Rizolex-T, Topsin-M and Ridomil Gold concentrations, than the growth of S. sclerotiorum. In this concern, significant decrease in mycelial growth and sclerotial production, of the fungus of S. sclerotiorum, with higher concentration of fungicide was recorded [7]. Mycelial growth was most sensitive to Benlate, Ridomil gold, Tecto-60 and Topsin-M at both the concentrations of 100 and 200ppm. Similar results concerning the inhibitor effect of Rizolex-T and Topsin-M at different concentrations against soilborne fungi, R. solani and F. oxysporum were also [36, 37, 38]. Furthermore, Rizolex-T could control root rot of cowpea caused by R. solani and F. solani when used as seed dressing or soil drench in solarized soil [39]. Also, lupine seeds dressing with recommended dose of Rizolex-T resulted in significant reduction in root rot incidence caused by R. solani, S. rolfsii and F. solani [40].
|
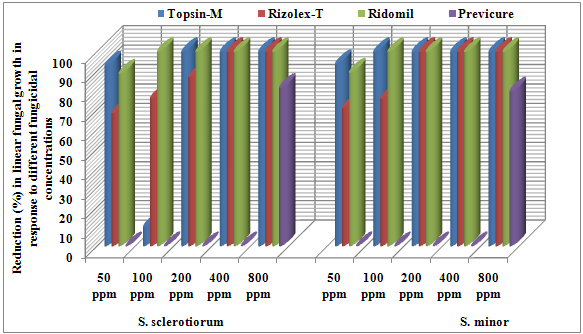 | Figure 2. Reduction in linear fungal growth of S. sclerotiorum and S. minor in response to different concentrations of fungicides in vitro |
|
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This work was supported financially by the Science and Technology Development Fund (STDF), Egypt, Grant No. 1059.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML