-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Life Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1387 e-ISSN: 2163-1395
2011; 1(2): 40-44
doi: 10.5923/j.als.20110102.07
Optical Coherence-domain Imaging of Subcutaneous Human Blood Vessels in vivo
Sergey G. Proskurin
Biomedical Engineering, Tambov State Technical University, Tambov, 392000, Russia
Correspondence to: Sergey G. Proskurin , Biomedical Engineering, Tambov State Technical University, Tambov, 392000, Russia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Experimental methods of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) are applied for two-dimensional mapping of subcutaneous human blood vessels. Structural images of in vivo human finger and human palm macro vessels (0.2-1.0 mm) before and after optical clearing using the modified low power rapid scanning optical delay line are presented. Images are scanned with 12 µm minimum spatial resolution. The described modifications enable to apply low power (0.4-0.5 mW), low noise broadband near infrared light source and to obtain structural images with detection of not only reflected but also multiply scattered coherence-gated photons. The achieved transcutaneous probing depth is about 1.6-1.8 mm.
Keywords: Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), Low Power Rapid Scanning Optical Delay Line, Optical Clearing, Differential Imaging, Blood Vessels Visualization, Coherence Probing Depth (CPD)
Cite this paper: Sergey G. Proskurin , "Optical Coherence-domain Imaging of Subcutaneous Human Blood Vessels in vivo", Advances in Life Sciences, Vol. 1 No. 2, 2011, pp. 40-44. doi: 10.5923/j.als.20110102.07.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)[1] is the new, important and fast developing modality which is based on the principles of scanning low coherence interferometry (LCI) and optical coherence-domain reflectometry[2]. Depth discrimination of multiply scattered light is performed due to application of a broadband light source. It could be a superluminescent diode (SLD), femtosecond pulsed laser or a swept source. Transversal resolution of OCT images is chosen by selecting focusing optics with different numerical apertures in the sample arm. Confocal microscopy principle is utilised in this case when a fibre tip works as a pinhole. Rapid low-coherence devices can be made on the basis of fibre optic Michelson interferometer with the rapid scanning optical delay line (RSOD)[3-7] in the reference arm (RA). By detection the phase shift of the interference fringes of consecutive A-scans it is possible to detect blood flow in capillaries, of about 20 – 70 μm in diameter, in human skin in vivo sing 5 mW broadband source[6]. Simultaneous intensity, birefringence and flow measurements into the depth of about 1.0 - 1.2 mm was demonstrated in the upper part of a large blood vessel and in capillaries of a human finger[7,8]. At the same time very important problem of visualisation of subcutaneous human macro blood vessels, of about 1 mm in diameter, has not been solved till recently[9].Note that further increase of the coherence probing depth (CPD) was investigated using the transitional mode between single backreflection and diffuse wave spectres copy by LCI only. Particle dynamics study of highly scattering media was used utilising singly scattered, multiply scattered and diffuse light detection[10]. The probing depth of the coherence-gated detection of multiply scattered light in this study has reached 1.5 – 2 mm. Scattering properties of the suspension were similar to those of biological tissue.In this paper we describe several modifications of the rapid scanning optical delay (RSOD) to apply a low power (0.5 – 0.2 mW) irradiation of a broadband infrared light source, superluminescent diode in time domain OCT system [9]. These modifications enable to utilise coherence-gated transitional multiply scattered mode to visualise human finger and human palm macro blood vessels with diameter of about 0.2 - 1 mm. Topical application of the optical clearing material[11] have been used to visualise structural signal from the blood, which appears inside the vessel after hand exercise only.
2. Materials and Methods
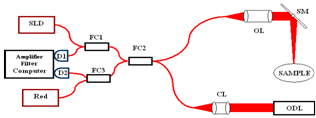
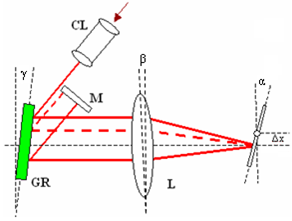
- Figure 1 shows the schematic of the experimental set-up based on the scanning fibre optic Michelson interferometer with two 1x2 and one 2x2 fibre couplers.Light from the sample arm (SA) goes through the system of lenses and is focused on the sample at the distance of about 5 cm from the SA scanning mirror (SM). The transversal resolution becomes respectively low, Ltr=70 μm, to compare with other systems utilising focusing optics with high numerical aperture[6,7]. Confocal parameter in this case is about 3.5 mm. Choice of low numerical aperture of the sample arm optics is a compromise between lateral resolution and the probing depth[10]. Despite the loss of the lateral resolution this approach enables additionally discriminate backscattered and backreflected photons from multiply and diffusely scattered ones.
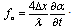 | (1) |
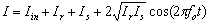 | (2) |
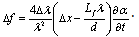 | (3) |
3. Results and Discussion
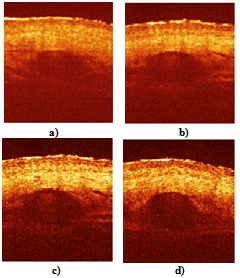
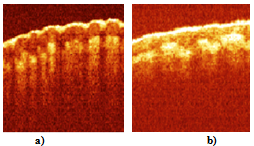
- The described modifications of the time domain OCT system, for the first time, gave the possibility to obtain images of a macro blood vessel (~1 mm in diameter) underneath the native human skin with transcutaneous depth of about 1.5 – 1.6 mm[9]. The images have been taken close to a Y-junction of blood vessels considering possibility of further investigation of blood flow with complex geometry [16-18] in vivo.The described system also gives possibility to use two wavelengths close to 1.3 μm and 1.5 μm simultaneously. Separation of the images could be performed in the processing algorithm, since the two wavelengths will give the two different carriers (1, 3). Figure 3 shows the images of a human finger tip using 1.3 μm SLD (λ=1298 nm, Δλ=52 nm) and 1.5 μm SLD (λ=1482 nm, Δλ=60 nm). Note, the OCT image using 1.5 μm SLD and RSOD was obtained by us for the first time[19].Transcutaneous probing depth of the light at λ = 1.5 μm is approximately twice less to compare with more commonly used for the skin study wavelength 1.3 μm [6]. Therefore we choose standard for this cases 1.3 μm source. All further results are obtained using SLD with λ=1298 nm, Δλ=52 nm.Figure 4 shows two blood vessels of a human subcutaneous Y-junction close to the junction with considerably low resolution but with the increased probing depth up to ~1.5 mm. Refractive index of the tissue, n=1.4, is used in all cases.
 | Figure 3. OCT images of human finger tip in vivo, (a) obtained using SLD with λ=1298 nm, Δλ=52 nm; (b) using SLD with λ=1482 nm, Δλ=60 nm. Size of the images is 2x2 mm2 |
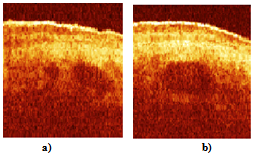 | Figure 4. Subcutaneous macro blood vessels of a human finger in vivo, (a) close to Y-junction; and (b) at the junction. Size of the images is 2x2 mm2 |
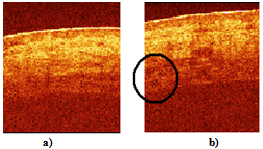 | Figure 6. OCT images of a human palm in vivo, (a) before optical clearing; (b) 15 min after the optical clearing. The circled structures are the blood vessels. Size of the images is 2x2 mm2 |
4. Conclusions
- The modified low power RSOD in the reference arm of the scanning interferometer enables to apply 1.3 μm wavelength simultaneously with 1.5 μm. Application of any other wavelength in between or close to these two is also possible. This enables to make rapid differential and spectral OCT imaging for two or several wavelengths. In addition the modified RSOD is quite small ~ 11x7x5 cm3, what is important from practical point of view. Using this experimental approach for the first time we have demonstrated subcutaneous macro (~0.2 - 1 mm) blood vessels underneath the native human skin by detection of singly and multiply scattered photons. The described set-up enables to increase transcutaneous coherence probing depth up to 1.5 - 1.6 mm and to resolve deeper tissue structures while compromising spatial resolution. Coherent detection of least scattered photons demonstrates transitional coherence-gating mode between single scattered and diffuse photons[20]. Since ballistic photons could be discriminated from the diffuse ones at the depth of about 20 - 25 MFP[10,21] and having in mind the reduced scattering coefficient of biological tissue ~ 1 mm-1, it seems to be reasonable to assume further increase of transcutaneous coherence probing depth to the values of about 2 - 2.5 mm.Doppler OCT technique[6,7] was not applicable in this case due to low phase stability of the consecutive A-scans. In addition, all experiments have been performed when incident light was perpendicular to the surface of the skin. Will it be possible to extract valuable velocity information in such transitional coherence-gated mode to study flows with complex geometry[16-18] in human subcutaneous junction of blood vessels is still a question to solve. Applying optical circulator (Faraday rotator) instead of the first 1x2 fibre splitter it is possible additionally reduce the source power by the factor of two and eliminate the signal reflected back into the source[15].
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This research was supported by The Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) grant GR/ R06816/02.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML