-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Algorithms Research
p-ISSN: 2324-9978 e-ISSN: 2324-996X
2023; 6(1): 1-8
doi:10.5923/j.algorithms.20230601.01
Received: May 1, 2023; Accepted: Jun. 3, 2023; Published: Jun. 14, 2023

Use of Markov Chain Model for In-Patient Bed Assignment
Balagopal Ramdurai
Senior Member- IEEE, Researcher & Product Innovator, Chennai, India
Correspondence to: Balagopal Ramdurai, Senior Member- IEEE, Researcher & Product Innovator, Chennai, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Bed allocation in a hospital refers to the process of assigning available beds to admitted patients who require hospitalization. It involves determining the appropriate type of bed and the most suitable ward or unit for the patient based on their medical condition, treatment requirements, and available resources. The process of bed allocation is typically managed by hospital administrators, nurses, and physicians who work together to ensure that patients receive the appropriate level of care and support during their stay in the hospital. Bed allocation is an important aspect of hospital management as it helps to optimize the use of resources, minimize wait times for patients, and ensure that patients receive timely and appropriate care. The proposed model incorporates historical patient data and real-time information to estimate the probabilities of transitioning between different states. By analyzing this probabilistic information, hospitals can make informed decisions regarding bed allocation, ensuring that patients are admitted to the most appropriate beds based on their medical needs and the availability of resources. Through simulation experiments and data analysis, the effectiveness of the Markov chain model is evaluated in terms of bed occupancy rates, patient wait times, and overall resource utilization. The results demonstrate that the proposed model offers significant improvements over traditional bed allocation methods, resulting in reduced patient wait times, optimized bed occupancy, and better overall management of hospital resources. A study published in the Journal of Healthcare Engineering looked at the impact of bed allocation on patient flow in a hospital. The study found that an optimized bed allocation system could improve patient flow and reduce wait times, leading to better patient outcomes.
Keywords: Hospital management, Patient flow, Bed Availability, Resource Allocation, Optimization, Wait times, Ward allocation
Cite this paper: Balagopal Ramdurai, Use of Markov Chain Model for In-Patient Bed Assignment, Algorithms Research , Vol. 6 No. 1, 2023, pp. 1-8. doi: 10.5923/j.algorithms.20230601.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Healthcare is moving towards a patient-centric approach, where the patient experience is given a lot of importance. Digital health technologies are playing an important role in enhancing the patient experience. Patients can access healthcare services and information through various digital platforms, such as telemedicine, online portals, and mobile apps. This article is to outline how digital technologies and use of Artificial intelligence can optimize the bed allocation there by increasing overall patient satisfaction and outcome.How does one define patient experience- “The patient experience describes an individual's experience of illness/injury and how healthcare treats them. Increasing focus on patient experience is part of a move towards patient-centred care” & to simplify “it begins with the front door and ends with the billing/payment clerk”. Therefore its imperative for health care providers to consider every touch points at every step of the care.According to (McCarthy, McGee, & O'Boyle and PricewaterhouseCoopers) Studies show that up to 65% of patient’s rate waiting times in clinics as unsatisfactory and 34% of patients said they would change their habits based on their experience. Five Key factors determining Patient Experience-As per the survey conducted across over 230 healthcare provider, top 5 things patients say to improve patient experience 1. 50% shorter wait-time2. 49% on advance knowledge of treatment costs3. 47% on not feeling rushed during appointments 4. 44% Providers with treating specific illness5. 41% easy to schedule appointments As healthcare organizations continue to focus on driving positive patient experiences, it’s changing the way chief information officers are looking at their jobs.And CIOs are starting to recognize that.A 2018 survey from Impact Advisors and the Scottsdale Institute found that 80 percent of CIOs rank digital health and the patient experience as top healthcare priorities. And while much of that may include patient-facing tools such as wearable sensors or care management apps, CIOs are also putting a lot of weight on provider-facing data and processes that help them do their jobs better.And this is pushing more healthcare organizations to implement cutting edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
2. What is Bed Allocation?
- Bed allocation refers to the process of assigning available hospital beds to patients who require hospitalization. It involves determining the appropriate type of bed and the most suitable ward or unit for the patient based on their medical condition, treatment requirements, and available resources.Bed allocation is typically managed by hospital administrators, nurses, and physicians who work together to ensure that patients receive the appropriate level of care and support during their stay in the hospital. Bed allocation is an important aspect of hospital management as it helps to optimize the use of resources, minimize wait times for patients, and ensure that patients receive timely and appropriate care.The distribution of hospital beds can be used as an indicator to assess the distribution of health services. This study aimed to determine and prioritize indicators of hospital bed allocation in Iran. In the first phase of the study, scoping review to identify criteria affecting hospital bed allocation was used. [1]Bed allocation is an important aspect of hospital management as it ensures that patients receive timely and appropriate care based on their medical condition and treatment requirements. Here are some of the key reasons why bed allocation is important:1. Efficient Use of Resources: Bed allocation helps to ensure that hospital resources, such as beds and staff, are used efficiently. By allocating beds based on patient need, hospital administrators can ensure that patients receive the appropriate level of care while minimizing the number of empty beds.2. Timely Access to Care: Bed allocation helps to ensure that patients receive timely access to care. By assigning patients to the appropriate ward or unit, hospital administrators can ensure that patients receive the appropriate level of care and treatment as quickly as possible.3. Improved Patient Outcomes: Proper bed allocation can help to improve patient outcomes. By ensuring that patients are assigned to the appropriate ward or unit, healthcare providers can provide the necessary care and support to improve patient health and well-being.4. Reduced Wait Times: Bed allocation can help to reduce wait times for patients. By efficiently allocating beds based on patient need, hospital administrators can minimize the amount of time that patients spend waiting for a bed or for treatment.5. Increased Patient Satisfaction: Proper bed allocation can also lead to increased patient satisfaction. By ensuring that patients receive timely access to care and are assigned to the appropriate ward or unit, patients are more likely to be satisfied with their hospital experience.Optimal utilisation of hospital beds is very important. Identifying vacant beds (bed availability) for new/emergency patients is a very time consuming task for administrators. Non-availability of hospital beds can shed a negative light on the image of the hospital. [2]
3. Key Factors
- There are several key factors that can affect bed allocation in hospitals. These include:1. Patient Medical Condition: The patient's medical condition is the primary factor that affects bed allocation. Patients with more serious or complex medical conditions may require specialized care and facilities that are not available in all hospital wards.2. Treatment Requirements: The type and intensity of treatment required by the patient also affects bed allocation. Patients requiring surgery, intensive care, or other specialized treatments may require a specific type of bed or ward that is equipped to provide the necessary care.3. Bed Availability: The availability of beds in the hospital is another key factor that affects bed allocation. If there are limited beds available, hospital administrators may need to prioritize patients based on the severity of their medical condition.4. Staffing Levels: The availability of nursing staff and other healthcare professionals can also affect bed allocation. If there are not enough staff available to provide the required level of care, patients may need to be allocated to a different ward or unit.5. Hospital Capacity: The overall capacity of the hospital can also affect bed allocation. If the hospital is at or near capacity, it may be more difficult to allocate beds to patients based on their medical condition and treatment requirements.6. Patient Preferences: In some cases, patient preferences may also be taken into account when allocating beds. For example, patients may prefer to be in a private room or to be located closer to family members.Overall, the key factors affecting bed allocation in hospitals are related to the patient's medical condition, treatment requirements, and available resources such as beds, staff, and hospital capacity.Due to changing patient loads and demand patterns over time, assigning bed complements for various medical services in a hospital is a recurring problem facing the administrators. For a large public health care delivery system, the article presents an approach for periodically reallocating beds to services to minimize the expected overflows. [3]
4. Application of Artificial Intelligence
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) is progressing rapidly in healthcare and has the potential to revolutionize the way medical care is provided.Resource optimization and patient crowding in the emergency department is a challenging issue. Resource requirement forecasting is essential to reduce the rising healthcare cost by optimizing the use and availability of healthcare resources. [4]Yousefi et al., utilized machine learning and the genetic algorithm (GA) to determine optimal resource allocation in emergency departments. Yousefi et al., constructed a meta-model, with three power machine learning approaches (adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system, feed forward neural network and recurrent neural network) using the bootstrap aggregating (bagging) and adaptive boosting (AdaBoost) ensemble algorithm. When applied to an emergency department, the GA algorithm was able to reduce the average length of stay by 15%. [5]Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform the patient experience by improving healthcare access, quality, and efficiency. Here are some examples of how AI is being used to enhance the patient experience.Artificial Intelligence (AI), has been playing a vital and growing role in the world in the past few decades. In fact, many people do not realize the form in which artificial intelligence can present itself in their daily life. When logging into email accounts, shopping using online platforms, requesting for car riding services, etc., all these uses artificial intelligence algorithms to improve user experience. But the most important field where AI is growing rapidly in the medical field, especially in treatment management and diagnostic. [6]Overall, AI has the potential to significantly improve the patient experience by providing personalized care, improving healthcare access and efficiency, and enhancing patient engagement and satisfaction.
5. AI in Bed Allocation for In-Patients
- Hospital beds are one of the most critical resources in healthcare institutions. In practice, beds are usually allocated to different departments in advance to accommodate different kinds of patients. Inappropriate decisions in the allocation may lead to the idleness of beds or the high rejection ratio of patients. Hospital managers are under pressure to allocate beds to different departments. High variability in patient arrivals and service times make the allocation problem complex and challenging to solve. To address this problem, a mixed-integer non-linear programming model is formulated, with the objective of minimising the weighted cost of rejecting patients and holding them waiting. To solve this model, a data-driven metamodel simulation optimisation method is proposed, in which metamodels, based on an analytical queuing model and a general function, are proposed and embedded into a general-purpose algorithm Adaptive Hyperbox Algorithm. [7]Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be used to manage bed allocation for patients in hospitals in a more efficient and effective manner. Here are some ways in which AI can be used for bed allocation:Real-time Monitoring: AI algorithms can be used to monitor bed availability in real-time, including the status of each bed, the occupancy rate of each ward, and the expected discharge times of patients. This information can be used to optimize bed allocation and reduce the likelihood of beds being left empty or patients being placed in inappropriate wards. [8]Patient Classification: AI algorithms can be used to analyze patient data, such as medical histories, test results, and vital signs, to classify patients into different categories based on their medical condition and treatment requirements. This information can be used to allocate patients to appropriate wards or units that are equipped to provide the necessary care.Resource Optimization: AI algorithms can be used to optimize the use of hospital resources, such as nursing staff and medical equipment, by allocating them to the areas where they are most needed. This can help to ensure that patients receive the appropriate level of care and that hospital resources are used efficiently.Prediction of Discharge Times: AI algorithms can be used to predict the expected discharge times of patients based on their medical condition and treatment plan. This information can be used to optimize bed allocation and ensure that patients are allocated to the appropriate ward or unit based on their expected length of stay. [9], [10]Automated Alerts: AI algorithms can be used to automatically send alerts to healthcare providers when a bed becomes available or when a patient is ready to be discharged. This can help to optimize bed allocation and reduce the amount of time that patients spend waiting for a bed or for discharge.Overall, the use of AI for bed allocation can help to optimize hospital resources, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the patient experience by ensuring that patients are allocated to appropriate wards or units based on their medical condition and treatment requirements.Use of Markov Chain for Bed AllocationMarkov chain is a mathematical model that is used to analyze and predict the behavior of a system that changes over time. It has been applied to various fields, including healthcare. In the context of bed allocation, Markov chain can be used to predict the availability of beds in different wards or units based on historical data.Through simulation experiments and data analysis, the effectiveness of the Markov chain model is evaluated in terms of bed occupancy rates, patient wait times, and overall resource utilization. The results demonstrate that the proposed model offers significant improvements over traditional bed allocation methods, resulting in reduced patient wait times, optimized bed occupancy, and better overall management of hospital resources.Markov chain can be a useful tool for predicting the availability of beds in different wards or units and optimizing the bed allocation system to improve the patient experience and reduce the cost of healthcare.Overcrowding of hospital wards is a well-known and often revisited problem in the literature, yet it appears in many different variations. In this study, mathematical model to solve the problem of ensuring sufficient beds to hospital wards by re-distributing beds that are already available to the hospital is put forward. Patient flow is modeled using a homogeneous continuous-time Markov chain and optimization is conducted using a local search heuristic. [11]
6. What is Markov Chain Algorithm
- Markov chain is a mathematical algorithm that is used to model the behavior of a system that changes over time. It is based on the principle that the future behavior of the system depends only on its current state, and not on its past states.Use of Markov Chain Algorithm in Bed AllocationMarkov chain can be used in bed allocation for inpatients to predict the availability of beds in different wards or units based on historical data. The algorithm can help hospital administrators and staff to optimize the bed allocation process and improve the overall patient experience.Here are some ways Markov chain can be used in bed allocation for inpatients:1. State representation: In the context of bed allocation, the states represent the availability of beds in each ward or unit. For example, a state could be "Ward A has two vacant beds".2. Probability matrix: Once the states are defined, a probability matrix is created to represent the probabilities of transitioning from one state to another. The entries in the matrix represent the probability of moving from one state to another. For example, the entry in row 1 and column 2 could represent the probability of moving from "Ward A has two vacant beds" to "Ward B has three vacant beds".3. Simulation: The probability matrix can be used to simulate the behavior of the bed allocation system over time. The simulation starts from an initial state and moves from one state to another based on the probabilities in the matrix. The simulation can be run multiple times to generate different scenarios and predict the availability of beds in each ward or unit.4. Optimization: The results of the simulation can be used to optimize the bed allocation system by adjusting the number of beds in each ward or unit or by changing the admission and discharge policies.Overall, Markov chain can be a powerful tool for predicting the availability of beds in different wards or units and optimizing the bed allocation system to improve the patient experience and reduce the cost of healthcare.What is Markov chain algorithmMarkov chains are named after Prof. Andrei A. Markov (1856–1922). He was born on June 14, 1856 in Ryazan, Russia and died on July 20, 1922 in St. Petersburg, Russia. Markov enrolled at the University of St. Petersburg, where he earned a master’s degree and a doctorate degree. [12]
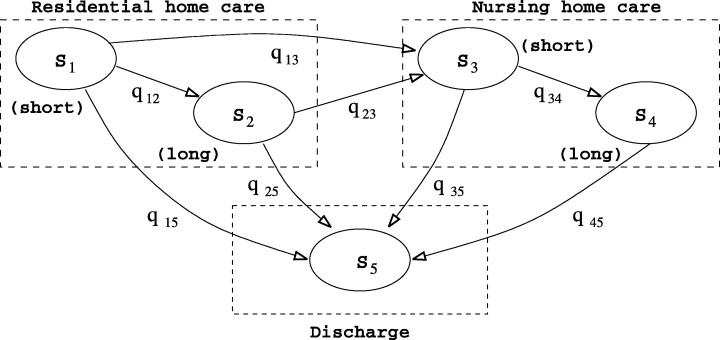 | Figure 1 |
 Calculating the first-passage time (Cox and Miller, 1965) [15] leads to the probability density function (PDF) of the sojourn time in a class, say class R (Colquhoun and Hawkes, 1981). [16]The actual states of the Markov model are not observable but only observe which type of care a person is in. For example, at any time, its observed that a person is in residential home care but do not know whether patient is in a short-stay (S1) or long-stay (S2) state. This is an aggregated Markov process, i.e. a Markov process in which system states are aggregated into a number of classes (Fredkin and Rice, 1986). [17] There are three classes in the model that is outlined in Fig. 1, namely residential home care, nursing home care and discharge (denoted by R, N and D respectively). The partition Markov chain is a mathematical model that is used to analyze and predict the behavior of a system that changes over time. It has been applied to various fields, including healthcare. In the context of bed allocation, Markov chain can be used to predict the availability of beds in different wards or units based on historical data. matrix Q according to the class structure of the model, i.e
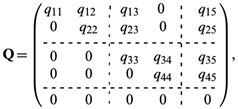
Calculating the first-passage time (Cox and Miller, 1965) [15] leads to the probability density function (PDF) of the sojourn time in a class, say class R (Colquhoun and Hawkes, 1981). [16]The actual states of the Markov model are not observable but only observe which type of care a person is in. For example, at any time, its observed that a person is in residential home care but do not know whether patient is in a short-stay (S1) or long-stay (S2) state. This is an aggregated Markov process, i.e. a Markov process in which system states are aggregated into a number of classes (Fredkin and Rice, 1986). [17] There are three classes in the model that is outlined in Fig. 1, namely residential home care, nursing home care and discharge (denoted by R, N and D respectively). The partition Markov chain is a mathematical model that is used to analyze and predict the behavior of a system that changes over time. It has been applied to various fields, including healthcare. In the context of bed allocation, Markov chain can be used to predict the availability of beds in different wards or units based on historical data. matrix Q according to the class structure of the model, i.e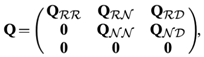 where the submatrices correspond to those delimited by broken lines in equation and the subscripts represent system classes. For instance, QRN is the submatrix of transition rates from states in R to states in N, and QRR that of transition rates between states within R. [18]The theory of aggregated Markov processes has been motivated by and applied to the modelling of ion channels in neurophysiological applications (Colquhoun and Hawkes, 1981, 1982; Fredkin et al., 1985) [18]. Generalization and parameter estimation have been investigated by various researchers, including Ball and Sansom (1989) [19], Fredkin and Rice (1986) and Qin et al. (1997) [20]. Adapt and modify approach that was taken by these researchers to suit the modelling needs and to deal with the existence of an absorbing state and censored observations.A continuous time Markov model which captures the flow of elderly people within and between residential and nursing home care. Using the framework of aggregated Markov processes, derived a procedure for fitting the model to observed data. By modelling the system of long-term care as a whole, it captured the movements between facilities and estimated parameters by using the overall joint likelihood function. [21]
where the submatrices correspond to those delimited by broken lines in equation and the subscripts represent system classes. For instance, QRN is the submatrix of transition rates from states in R to states in N, and QRR that of transition rates between states within R. [18]The theory of aggregated Markov processes has been motivated by and applied to the modelling of ion channels in neurophysiological applications (Colquhoun and Hawkes, 1981, 1982; Fredkin et al., 1985) [18]. Generalization and parameter estimation have been investigated by various researchers, including Ball and Sansom (1989) [19], Fredkin and Rice (1986) and Qin et al. (1997) [20]. Adapt and modify approach that was taken by these researchers to suit the modelling needs and to deal with the existence of an absorbing state and censored observations.A continuous time Markov model which captures the flow of elderly people within and between residential and nursing home care. Using the framework of aggregated Markov processes, derived a procedure for fitting the model to observed data. By modelling the system of long-term care as a whole, it captured the movements between facilities and estimated parameters by using the overall joint likelihood function. [21]7. Mathematical Model for Markov Chain
- Simplified mathematical model for in-patient bed allocation using a Markov chain approach:1. Define the StatesLet S = {S1, S2, S3, ..., Sn} represent the set of states, where each state represents a specific bed status or occupancy level. For example, S1 can represent an empty bed, S2 can represent a bed with a low acuity patient, S3 can represent a bed with a moderate acuity patient, and so on. The last state Sn can represent a bed with a high acuity patient or a fully occupied bed.2. Define the Transition ProbabilitiesDefine a transition probability matrix P = [p_{ij}], where p_{ij} represents the probability of transitioning from state Si to state Sj. These transition probabilities can be estimated based on historical data, patient characteristics, length of stay distributions, and bed availability information. The probabilities should sum to 1 for each row of the matrix.3. Define the Initial State DistributionLet π = [π_1, π_2, π_3, ..., π_n] represent the initial state distribution vector, where π_i represents the probability of starting in state Si. This distribution can be based on the current bed occupancy levels or other relevant factors.4. Calculate the Steady-State DistributionCalculate the steady-state distribution π* = [π_1, π_2, π_3, ..., π_n] by solving the equation π* = π*P. This represents the long-term equilibrium distribution of bed occupancy levels in the hospital.5. Perform Analysis and Decision MakingUse the steady-state distribution to analyze bed occupancy rates, patient wait times, and other performance metrics. Evaluate different scenarios by adjusting transition probabilities or initial state distributions. Utilize the results to make informed decisions regarding bed allocation strategies, capacity planning, and resource utilization optimization.The model can be further refined by incorporating additional factors, such as patient demographics, disease severity, and hospital-specific policies.
8. Analytics View on Markov Chain Model
- The analytical view of using a Markov chain model for in-patient bed allocation offers several advantages and insights for optimizing bed allocation processes in healthcare facilities.Probability-Based Analysis: The Markov chain model allows for a probabilistic analysis of bed occupancy and patient flow dynamics. By assigning transition probabilities between different bed occupancy states, the model provides a quantitative understanding of the likelihood of patients moving between different states over time. This probability-based analysis helps hospitals estimate bed availability, predict patient demand, and make data-driven decisions regarding bed allocation.Performance Metrics Evaluation: The Markov chain model enables the evaluation of key performance metrics related to bed allocation. By analyzing the steady-state distribution of bed occupancy levels, hospitals can assess metrics such as bed occupancy rates, patient wait times, and resource utilization. This analytical view provides insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of the current bed allocation process, identifies areas for improvement, and facilitates the measurement of the impact of different bed allocation strategies.Scenario Analysis and Optimization: The model allows for scenario analysis and optimization by adjusting transition probabilities or initial state distributions. Hospitals can evaluate different bed allocation strategies and assess their impact on performance metrics. This analytical approach facilitates optimization efforts to minimize patient wait times, maximize bed occupancy rates, and improve overall resource utilization. By exploring various scenarios, decision-makers can identify optimal bed allocation policies and make informed decisions.Resource Planning and Capacity Management: The analytical view provided by the Markov chain model assists in resource planning and capacity management. Hospitals can analyze bed occupancy patterns, predict future bed requirements, and plan for capacity expansions or adjustments based on anticipated patient demand. This analytical perspective helps optimize resource utilization, prevent bottlenecks, and improve overall operational efficiency.Decision Support and Policy Evaluation: The Markov chain model can serve as a decision support tool by providing insights and recommendations for bed allocation decisions. Hospitals can utilize the model's outputs, such as steady-state distributions and performance metrics, to evaluate the effectiveness of existing policies and propose improvements. This analytical view empowers decision-makers with quantitative evidence to support strategic decision-making and policy evaluation.Overall, using a Markov chain model for in-patient bed allocation offers a systematic and quantitative approach to understand and optimize bed allocation processes. It enables probability-based analysis, performance metrics evaluation, scenario analysis, resource planning, and decision support, contributing to more efficient and effective bed allocation strategies and improved patient care in healthcare facilities.
9. Benefits to Providers
- Markov Chain is a mathematical model that is useful for modeling a variety of systems with sequential decision-making processes. In the context of in-patient bed allocation, Markov Chain can be used to model the movement of patients between beds over time, and to make predictions about future bed occupancy. Similarly for doctors, how much care time he/she is giving on specific day/date and for specific services. [22]Some of potential benefits of using Markov Chain for in-patient bed allocation are:1. Improved bed allocation: Markov Chain can be used to optimize the allocation of beds to patients based on factors such as expected length of stay and patient acuity. By analyzing patterns of patient movement and predicting future bed occupancy, Markov Chain can help hospitals allocate beds more efficiently, reducing wait times and improving patient outcomes.2. Cost savings: Efficient bed allocation can help hospitals reduce costs by minimizing the number of empty beds and avoiding overcapacity. This can also help reduce the need for expensive temporary beds or facilities, such as overflow units.3. Improved patient experience: By reducing wait times and ensuring that patients are assigned to appropriate beds based on their needs, Markov Chain can help improve the overall patient experience. This can lead to higher patient satisfaction scores and improved patient outcomes.4. Better resource utilization: Markov Chain can help hospitals optimize the use of their resources, such as staff and equipment, by predicting future bed occupancy and adjusting staffing levels accordingly. This can help hospitals operate more efficiently and reduce waste.5. Enhanced decision-making: Markov Chain can help hospital administrators make informed decisions about bed allocation and resource allocation. By providing data-driven insights about future bed occupancy and patient flow, Markov Chain can help hospital administrators allocate resources more effectively and efficiently.6. Accurate forecasting: Markov Chain can be used to forecast bed occupancy rates and patient flow over time, which can be helpful for hospital administrators in making long-term planning decisions. Accurate forecasting can also help hospitals prepare for surges in demand and allocate resources appropriately.7. Improved communication: By providing a clear picture of bed occupancy rates and patient flow, Markov Chain can help improve communication between hospital staff and departments. This can lead to more effective collaboration and better patient outcomes.8. Reduced errors and mistakes: Markov Chain can help reduce errors and mistakes in bed allocation by providing a systematic approach to decision-making. By taking into account factors such as patient acuity and expected length of stay, Markov Chain can help ensure that patients are assigned to appropriate beds and receive the care they need.
10. Future Scope
- The future scope of using Markov chain models for in-patient bed allocation is promising and offers several potential avenues for further research and development. Here are some future directions to consider:Enhanced Data Integration: As electronic health records and data collection systems continue to advance, there is an opportunity to integrate more comprehensive and real-time data into the Markov chain models.Dynamic and Adaptive Models: Developing dynamic and adaptive Markov chain models can account for the evolving nature of patient flow and resource availability.Optimization Algorithms: Integrating optimization algorithms with Markov chain models can further improve bed allocation decisions. These algorithms can consider multiple objectives, such as minimizing patient wait times, maximizing bed occupancy rates, and minimizing resource wastage.Predictive Analytics: Expanding the capabilities of Markov chain models to include predictive analytics can help hospitals forecast future bed requirements and plan resource allocation accordingly.Integration with Decision Support Systems: Integrating Markov chain models with decision support systems can provide real-time recommendations and decision-making support to healthcare administrators and bed management teams.Validation and Real-World Implementation: Further research is needed to validate the effectiveness and feasibility of implementing Markov chain models in real-world hospital settings.The Markov chain models for in-patient bed allocation lies in incorporating more comprehensive data, developing dynamic and adaptive models, integrating optimization algorithms, leveraging predictive analytics, integrating with decision support systems, and validating their effectiveness in real-world healthcare settings. By advancing these areas, the field can make significant strides in improving bed allocation processes, optimizing resource utilization, and enhancing the quality of patient care.
11. Conclusions
- To sum up In conclusion, Markov Chain is a powerful tool for in-patient bed allocation that can help hospitals optimize their bed allocation processes, reduce costs, and improve patient outcomes. By modeling patient movement and predicting future bed occupancy, Markov Chain can provide hospitals with data-driven insights to improve decision-making and resource allocation.Additionally, Markov Chain can help hospitals improve communication, reduce errors and mistakes, and enhance the overall patient experience. With accurate forecasting and improved planning, hospitals can prepare for surges in demand and allocate resources more effectively.Overall, using Markov Chain for in-patient bed allocation can help hospitals operate more efficiently and deliver better care to their patients.By analyzing patterns of patient movement and predicting future bed occupancy, Markov Chain can help hospitals allocate beds more efficiently, reducing wait times and improving patient outcomes. This can lead to improved patient satisfaction scores and better patient experiences.Additionally, Markov Chain can help hospitals reduce costs by minimizing the number of empty beds and avoiding overcapacity. By optimizing resource utilization, hospitals can reduce waste and operate more efficiently.Moreover, the use of Markov Chain can lead to better decision-making, accurate forecasting, and improved communication among hospital staff and departments. This can result in reduced errors and mistakes in bed allocation and better collaboration between hospital staff.Overall, the use of Markov Chain for in-patient bed allocation has the potential to provide numerous benefits to hospitals, including improved patient outcomes, reduced costs, and enhanced operational efficiency. By leveraging the power of data-driven insights, hospitals can optimize their bed allocation processes and deliver better care to their patients.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML