-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Signal Processing
p-ISSN: 2165-9354 e-ISSN: 2165-9362
2012; 2(5): 92-97
doi: 10.5923/j.ajsp.20120205.02
Mixed Language Speech Recognition without Explicit Identification of Language
Kiran Bhuvanagirir , Sunil Kumar Kopparapu
TCS Innovation Labs, Mumbai, Tata Consultancy Services, Thane (West), 400601, India
Correspondence to: Sunil Kumar Kopparapu , TCS Innovation Labs, Mumbai, Tata Consultancy Services, Thane (West), 400601, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Use of mixed language in day to day spoken speech is becoming common and is accepted as being syntactically correct. However machine recognition of mixed language spoken speech is a challenge to a conventional speech recognition engine. There are studies on how to enable recognition of mixed language speech. At one end of the spectra is to use acoustic models of the complete phone set of the mixed language to enable recognition while on the other end of the spectra is to use a language identification module followed by language dependent speech recognition engines to do the recognition. Each of this has its own implications. In this paper, we approach the problem of mixed language speech recognition by using available resources and show that by suitably constructing an appropriate pronunciation dictionary and modifying the language model to use mixed language, one can achieve a good recognition accuracy of spoken mixed language.
Keywords: Speech Recognition, Mixed-language Speech, Language Identification, Phoneme Set
Cite this paper: Kiran Bhuvanagirir , Sunil Kumar Kopparapu , "Mixed Language Speech Recognition without Explicit Identification of Language", American Journal of Signal Processing, Vol. 2 No. 5, 2012, pp. 92-97. doi: 10.5923/j.ajsp.20120205.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Mixed language, also termed as code switching in literature, arises through the fusion of two or more, usually distinct, mixed source languages, normally in situations of thorough bilingualism, so that it is not possible to classify the resulting language as belonging to either of the language families that were its source[17],[1],[2]. With urbanisation and geography shift of people the ability to converse in many languages is becoming common. A very large number of people, especially urban youth, use mixed language in everyday conversation without actually being aware of it. Though mixed language is defined as a mixture of two distinct languages in equal proportion without giving away as to which language is mixed into which; at least in the Indian context, the non-native language (generally English words) is mixed into the native language. As shown in Fig. 1 the native language (Hindi) is the primary language and the non-native English language is the secondary language. Primary language can be defined as that language in the mixed language which is spoken in majority. One can observe that the words uttered in the secondary language are very often keywords or foreign words or phrases which are colloquially used. Subsequently, the rate of language change or shift is very frequent in mixed language. Thus recognition of mixed language speech requires, in our opinion, an entirely different approach.
 | Figure 1. Mixed Language sentence |
2. Existing Approaches
- Recognition of mixed language speech is still in its initial stages of research. There are two approaches reported in literature. One being multi pass framework[4] and other is the one pass framework[3]. However, multilingual speech recognition is another area of research which has close relationship with ML-ASR. In multilingual speech recognition, the spoken speech is not a mix of two languages unlike ML-ASR, however the main challenge is that one does not know a priori the identity of the language. So the first task in multi lingual ASR is to identify the language. This problem of identifying language is well addressed in literature[5]. Language identification using LPC based acoustic features was proposed by Cimarusti et al[5]. They were able to identify eight different languages with reasonable success. In another work, Foil[7] used prosodic features for language identification and Naratil et. al.[10] successfully used phonotactic-acoustic features. Later Yan [9] applied a combination of acoustic, phonotactic and prosodic information for language identification. Nagawaka[8] compared four different methods to identify languages and concluded that continuous hidden Markov model (HMM) based method works best. Many recognizers like Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM), single language phone recognition followed by language modelling (PRLM), parallel PRLM (PPRLM), GMM tokenization[6] and Gaussian Mixture Bi-gram Model (GMBM)[11] have also been studied in literature for multi lingual speech recognition.In order to use the multilingual approaches in mixed language speech recognition, one needs to identify the exact time instants at which switching from one language to another occurs and follow it up with language identification. Automatic segmentation of different languages within a speech utterance had been addressed by Wu et al.[4] who use Bayesian information criteria (BIC) on Delta-MFCC (Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients). In another related work, Chi-Jiun et al.[12] use statistical approach to segment and identify language in a speech utterance. They use maximum a posterior (MAP) estimate to find the boundary segments to do language identification.
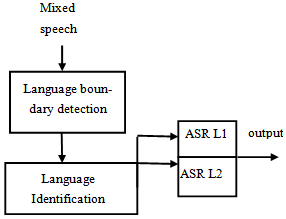 | Figure 2. Multi pass approach for mixed language ASR |
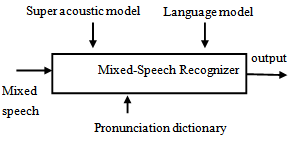 | Figure 3. One pass approach for mixed language ASR |
3. Proposed Approach
- We have worked on a specific language mix, namely, Hindi-English whose usage is very common in the Indian subcontinent. Specifically Hindi being the native language is spoken majority of time compared to the non-native language English. In our corpus, a little more than two thirds of the total spoken words in the corpus were spoken in Hindi and the rest, namely, one third, being either English words or proper nouns. Overall, our corpus consisted of 46 different speakers (with sufficient gender and age variability) from different metros in India. Each of the speakers uttered three to five different sentences, which had a mix of Hindi-English, of which at least one sentence, uttered by the speaker was elicited speech. The elicited speech gave an indication of the actual mix of the language as spoken in everyday conversation. In all there were 213 unique spoken sentences consisting of 1946 words. All the experimental results reported in this paper are based on these word utterances. During data collection, the speakers were supplied a speaker sheet (in Hindi script) and were asked to call from a quite environment and the recording was done using a telephony card, specifically we used a Dialogic CTI card. The speech was recorded at 11 kHz and 8 bits per sample using a home grown data collecting application.Our approach retains the framework of a one pass method with the use of appropriate PL. The use of a modified PL enables us (a) avoid building an AM for the mixed language (note that mixed language speech corpus is difficult to collect) and (b) further recognition can be performed with ASR of one of the languages. We used the public domain speech recognition engine, Sphinx[15], with the HUB4 (English phones) AM in one set of experiments and in another set of experiments we used the readily available Hindi ASR[20] AM (Hindi phones). The reason for using these AM instead of AM for mixed language was (a) these AMs were readily available for use and (b) building acoustic models for mixed language was too cumbersome requiring actual on the field collection of a large amount of speech corpus to which we did not have access. It should be noted that a Hindi ASR has 59 phonemes while English has only 39 phonemes. When using English acoustic models we approximate those phonemes (mainly occurring in Hindi words) which are not in English by replacing the phoneme in Hindi by a combination of two or more English phonemes[13]. The PL that supports the ASR is constructed in the usual way by using the CMU language toolkit[14] for all the English words in the corpus. However, all the Hindi words are first transliterated into English and the pronunciation of this English word is obtained using[14] or approximate phoneme mapping (APM).
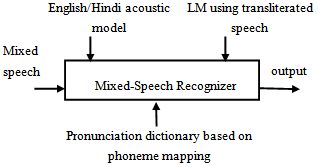 | Figure 4. Proposed approach |
4. Results and Discussion
- We conducted, in all, a set of nine different experiments to evaluate the performance of our approach for ML-ASR. In the first set of experiments we used the English AM’s while in the second set of experiment we used the Hindi language AM’s.In all our experiments we used the Sphinx ASR[15] and the well-known n-gram LM created using the mixed language speech corpus that we collected (Section 2). In each of these experiments the manner of construction of PL was different. The distribution of the Hindi, English and proper noun words in the corpus was 62%, 28% and 10% respectively. For the first set of eight experiments done using English AMs, we used two different methods of PL construction for the three different types of words, namely, English words, Hindi words and proper nouns. The first method of PL creation is based on the CMU toolkit[14] and the second method is based on approximate phoneme mapping (APM). In APM method of lexicon creation, a word is first transliterated and the equivalent Hindi phonemes are generated; each of these Hindi phonemes is then replaced by one or more equivalent English phonemes. For example the Hindi word मत्स्यगंध (Matsyagandha) is represented using the CMU tool kit as M AE TH S AY AH G AH N D (see Fig 5(a)). While the equivalent pronunciation representation using Hindi phoneme set is M A T A S Y A G A N DH A (see Fig 5(b)). Using APM the same word मत्स्यगंध is represented as म (M AH) त् (TH AH) स् (S) य (Y AH) गं (G AH N )ध (DH HH AH) (see Fig 5(c)). Note that in APM, a Hindi phoneme is replaced by one or more equivalent English phonemes. For example the phone DH, occurring only in Hindi is substituted by the phones “DH HH” in English (see Fig 5). For example, the English word “Identification” (आइडेंटीफिकशन) can be transliterated similarly as “aidentiphikation” and equivalent pronunciation using Hindi phoneme set is EI D E N: T: I PH I K EI SH A N A (see Fig 5(b)). Using APM, it is represented as AY D EH N T IY F IY K EY SH AH N (see Fig 5(c)). In the ninth experiment, we represented every word in the PL using both the alternative phonetic representations (see Fig 5(d)), namely using CMU and APM. Table 1 shows experiment number and the method used to construct the PL. For example, in “Expt 6” APM was used to construct the English and the Hindi words however CMU was used to construct the proper nouns. Pronunciation using CMU toolkit is denoted as CMU while, approximate phoneme mapping is denoted as APM
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
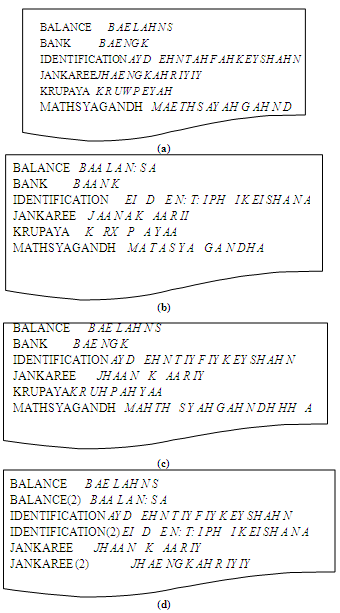 | Figure 5. Sample lexicon constructions. (a) using CMU tool kit. (b) using Hindi phoneme set (c) using APM (from Hindi to English) (d) Both (CMU and APM) phonetic representations in same lexicon |
5. Conclusions
- Mixed language automatic speech recognition (ML-ASR) is gaining increasing popularity because of its wide spread use in everyday conversations and more importantly because of its acceptance in the society. While the best approach to build a ASR to recognize mixed language is to treat the mixed language as a language in itself and build AM, LM and PL as is done for a language specific ASR. This would involve an expensive and time consuming task of collecting a large amount of mixed language speech and text corpus and using this corpus to build AM, LM and PL for mixed language. Note that separate speech and text corpus has to be collected for each mixed language pair. In this paper we have shown an usable novel approach to enable mixed language speech recognition by making use of the available resources (English acoustic models, Hindi acoustic models but not the English-Hindi mixed acoustic models) and (a) carefully constructing a PL for the mixed language words and (b) constructing a LM from a small mixed language text corpus. The advantage of our approach is that (a) there is no actual need to segment speech and identify the language which in most conversational speech is very difficult because in mixed speech the switch from one language to another is very fast, (b) it does not require one to collect extensive speech corpus or data to construct the acoustic models to enable mixed language recognition. It should be noted that this approach can be applied to any other Indian language taking the place of Hindi; this would only require an appropriate mapping of the phones in that language to English phoneset.
References
| [1] | CHIEN-LIN Huang and CHUNG-HSIEN Wu., “Generation of phonetic units for mixed language speech recognition based on acoustic and contextual analysis”. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 56:1225–1233, 2007. |
| [2] | PO-YI Shih, JHING-FA Wang, HSIAO-PING Lee, HUNG-JEN Kai, HUNG-TZU Kao, and YUAN- NING Lin. “Acoustic and phoneme modeling based on confusion matrix for ubiquitous mixed language speech recognition”, In SUTC ’08: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Sensor Networks, Ubiquitous, and Trustworthy Computing, pages 500–506, Washington, DC, USA, 2008. |
| [3] | DAU-CHENG Lyu, REN-YUAN Lyu, YUANG-CHIN Chiang and CHUN-NAN Hsu, “Speech recognition on code-switching among the Chinese dialects”, of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Toulouse, France, May. 2006 |
| [4] | CHUNG-HSIEN Wu, YU-HSEIN Chie, CHI JIUN Shia, CHUN-YU Lin , “Automatic segmentation and identification of mixed language speech using Delta-BIC and LSA based GMMs”, ICASSP 06, vol 14, No 1, 266-276. |
| [5] | CIMARUSTI, D., Ives, R. B. “Development of an automatic identification system of spoken languages: Phase 1”. Proc. ICASSP’82, pp. 1661-1664, May 1982. |
| [6] | P. A. TORRES-CARRASQUILLO, ELLIOT singer, MARS A Kohler, RICHARD J Greene, DOUGLAS A Reynolds, and J R DELLER JR, “Approaches to language identification using Gaussian mixture models and shifted delta Ceptral features”, in Proc. ICSLP’02, 2002, pp. 89–92. |
| [7] | FOIL, J.T. “Language identification using noisy speech”, Proc. ICASSP’86, pp. 861-864, April 1986. |
| [8] | NAKAGAWA, S., UEDA, Y., SEINO, T. “Speaker-independent, text-independent language identification by HMM”, Proc. ICSLP’92, pp. 1011-1014, October 1992. |
| [9] | YAN, Y, “Development of an approach to language identification based on language dependent phone recognition.”, PhD thesis, Oregon Graduate Institute of Science and Technology, October 1995. |
| [10] | NAVRÁTIL, J. “Spoken language recognition - A step Toward Multilinguality in Speech Processing”, IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Processing, vol. 9, pp. 678-685, September 2001. |
| [11] | W. H. TSAI and W.-W. CHANG, “Discriminative training of Gaussian mixture bi-gram models with application to Chinese dialect identification”, Speech Comm., vol. 36, pp. 317–326, 2002. |
| [12] | CHI JIUN shia, YU-HIEN Chiu, JIA-HIN Hieh, CHUNG-HSIEN Wu, “Language boundary detection and identification of mixed language speech based on MAP estimation”, ICASSP 04, vol 1, 381-384. |
| [13] | NILOY Mukherjee, NITENDRA Rajput, L V SUBRAMANIAM, ASISH Verma, “On deriving a phoneme model for new language”, proc ICSLP, 2000, pages 850-852. |
| [14] | http://www.speech.cs.cmu.edu/cgi-bin/cmudict (last accessed Aug 2010) |
| [15] | http://cmusphinx.sourceforge.net/ (last accessed Aug 2012) |
| [16] | Sunil Kumar KOPPARAPU,” Voice based Self-Help System: User Experience Vs Accuracy”, International Conference on Systems, Computing Sciences and Software Engineering: pages 101-105, 2008. |
| [17] | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mixed_language (last accessed Aug 2012) |
| [18] | Kiran Kumar BHUVANAGIRI, Sunil KOPPARAPU, “An approach to mixed language automatic speech recognition”, Oriental COCOSDA 2010, Nepal. |
| [19] | Imseng David, Bourlard Herve, Magimai-Doss Matthew, “Towards mixed language speech recognition systems”, Proceedings of Interspeech, Sept 2010, Pages 278-281, Japan. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML