-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Organic Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-1271 e-ISSN: 2163-1301
2018; 8(2): 17-25
doi:10.5923/j.ajoc.20180802.01

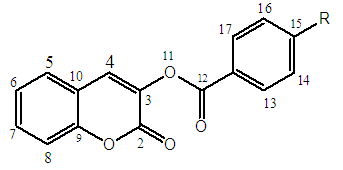
(Coumarin-3-yl)-benzoates as a Series of New Fluorescent Compounds: Synthesis, Characterization and Fluorescence Properties in the Solid State
Sosso Siaka1, Jules Yoda1, 2, Abdoulaye Djandé1, Bruno Coulomb3
1Laboratory of Molecular Chemistry and Materials, Organic Chemistry and Phytochemistry Team, University Ouaga I Pr Joseph KI-Zerbo, Burkina Faso
2Department of Medicine, Traditional Phamacopees and Pharmacy, Institute for Health Sciences Research, Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso
3Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry, Department of Chemistry, UMR 7376, Team TRAME, Aix-Marseille University, France
Correspondence to: Abdoulaye Djandé, Laboratory of Molecular Chemistry and Materials, Organic Chemistry and Phytochemistry Team, University Ouaga I Pr Joseph KI-Zerbo, Burkina Faso.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

(Coumarin-3-yl)-benzoates, a series of coumarin derivatives were designed, synthesized and characterized as fluorescent compounds. The structural assignments of these compounds were examined based on their corresponding FT-IR, ESI-MS, and 1H- and 13C-NMR spectral data in addition to their crystal structures determined by X-ray diffractometry. The fluorescence spectra, recorded in the solid state, have been investigated. The effects of various substituents R on fluorescence properties were examined. As a result, compound 2c with an electron-donating substituent (R = t-Bu) exhibited the strongest fluorescence intensity whereas compound 2f with an electron-withdrawing group (R = CN) presented the weakest one.
Keywords: (Coumarin-3-yl)-benzoates, Synthesis, Characterization, Fluorescence, Solid state, Substituents R
Cite this paper: Sosso Siaka, Jules Yoda, Abdoulaye Djandé, Bruno Coulomb, (Coumarin-3-yl)-benzoates as a Series of New Fluorescent Compounds: Synthesis, Characterization and Fluorescence Properties in the Solid State, American Journal of Organic Chemistry, Vol. 8 No. 2, 2018, pp. 17-25. doi: 10.5923/j.ajoc.20180802.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Fluorescent compounds play an important role in solid state lighting, solar energy conversion and as biomarkers in the life sciences [1-6]. As an important group of organic heterocycles, coumarin derivatives have been found to possess a wide range of pharmacological and biological activities, which can display among others, insecticidal [7], antibacterial [8], anti-HIV [9, 10], anticancer [11, 12], anticoagulant [13] and antioxidant [14] activities.Furthermore, coumarin derivatives, possessing a heterocyclic skeleton with a ring oxygen on a carbonyl group, are well-known fluorescence dyes for their high photoluminescence quantum efficiencies. A number of coumarins have been synthesized and explored the possibility of their application to electro-optic materials, such as laser dyes, fluorescent probes or labels, solar collector systems, organic scintillators and photoelectronic sensitizers. [15-19] In the current work described here, synthesis and structural analysis of six 3-substituted coumarin derivatives, presenting at that position an ester function (compounds 2), were undertaken. Fluorescence properties of these (coumarin-3-yl)-benzoates, in the solid state, were then reported. So, the title compounds were synthesized according to a described convenient method, in satisfactory yields, from chroman-2,3-dione and acyl chloride in the presence of triethylamine (TEA). Their molecular structures were characterized by the means of FT-IR, 1H and 13C NMR and ESI-MS spectrometries and were additionally determined by X-ray diffractometry.The fluorescence spectra were recorded in solid-state, in order to examine the unique effects of different substitutions on fluorescence emission.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Compounds 2
2.1.1. Synthesis
- (Coumarin-3-yl)-benzoates were synthesized from chroman-2,3-dione, the ketone tautomeric form of 3-hydroxycoumarin, by O-acylation with acyl chlorides in the presence of TEA as shown below. (Scheme 1). We used HSAB theory of Pearson [20] in the choice of TEA as base. According to this principle, to obtain best yields with hard acids like benzoyl chlorides, it is necessary to use a hard base like triethylamine (TEA). Further, the preferable solvents were ethers: diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (THF), at reflux.
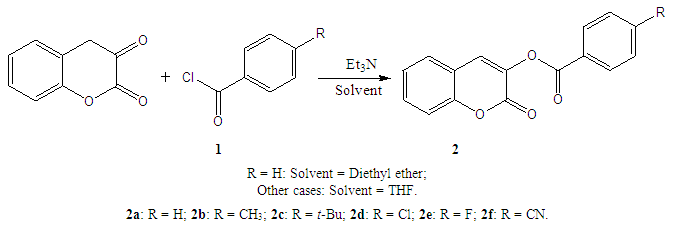 | Scheme 1. Preparation of (coumarin-3-yl)-benzoates |
2.1.2. Materials and Measurement
- Melting points were determined in capillary tubes on a Stuart SMP 11 apparatus and are uncorrected.IR spectra were recorded on a Bruker IFS 66 / S Fourier Transform Infrared spectrometer (FT-IR), driven by the OPUS 6.5 software and using the ATR (Attenuated Total Reflection) technique. 1H and 13C (+ DEPT 135) NMR spectra were recorded on a BRUKER AMX spectrometer at 400 or 600 MHz and 100 MHz respectively, using TMS as internal standard (chemical shifts in δ values, J in Hz). Mass spectra were obtained on a 3200 QTRAP (Applied Biosystems SCIEX) spectrometer equipped with a pneumatically assisted air pressure ionization (API) source.All the compounds were analyzed by X-ray diffractometry. In this study, we highlight the crystallographic data that justify their 3D structures. Data were collected by the X scan technique at 293 and 298 K on an Agilent SuperNova Dual diffractometer with an Atlas S2 detector, using CuKα radiation (λ = 1.54184 Å) and MoKα (λ = 0.71073 Å), and were corrected for Lorentz and polarization effects. The structures were solved by direct methods which revealed the positions of all non-hydrogen atoms, and were refined on F2 by a full-matrix least-squares procedure using anisotropic displacement parameters. The program used to solve structure was SHELXS97 [21]. The program used to refine the structures was SHELXL2013 [22]. All hydrogen atoms were located from difference Fourier maps and were refined isotropically. Molecular graphics were generated with Platon [23]. Finally, the software used to prepare material for publications was publCIF [24].A summary of the crystals data, experimental details, and refinements results is given below in the crystal structure Determination.It’s the occasion for us to signalize that the crystal structures of compounds 2a, 2c, 2d, 2e have previously been published by our research team [25-28] and the crystal structure of compound 2b by M J Matos and al. [29], but in this last case data were measured on a Bruker APEX2 [26] at 100 K using radiation (λ = 0.71073Å).
2.1.3. Characterization
2.1.3.1. (Coumarin-3-yl)-benzoate (2a)
- Yield: 84%; 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6; 400 MHz): 7.43 (t, 1H, J = 8 Hz, H-15); 7.50 (d, 1H, J = 8 Hz, H-8); 7.65 (d, 3H, J = 8 Hz, H-5; H-14 and H-16); 7.77 (t, 2H, J = 8 Hz, H-6 and H-7); 8.13 (d, 2H, J = 4 Hz, H-13 and H-17); 8.21 (s, 1H, H-4). 13C-NMR ( DMSO-d6; 100 MHz): 116.24 (C-8); 118.30 (C-10); 125.14 (C-4); 127.58 (C-12); 128.51 (C-6); 129.12 (C-14 et C-16); 129.94 (C-13 and C-17); 131.60 (C-5); 132.09 (C-7); 134.59 (C-15); 135.48 (C-3); 151.61 (C-9); 156.08 (C-11); 163.59 (C-2). DEPT 135°: 116.24 (C-8); 125.14 (C-4); 128.51 (C-6); 129.12 (C-14 and C-16); 129.94 (C-13 et C-17); 131.60 (C-5); 132.09 (C-7); 134.59 (C-15). IR (cm-1): 1742.3 (C=O, ester); 1728.4 (C=O, lactone); 1607 (C=C); 3046.5 (C-H, aromatic ring); 1250.5 (C−O, ester); 1098.3 (C−O, lactone). ESI-MS [M+H]+: 267.Crystal structure Determination (2a)Chemical formula: C16H10O4; Formula weight: 266.24; Crystal description: prism, yellow; Melting point (K): 423- 426; Crystal system: Triclinic; space group: P1; Temperature (K): 298; Wavelength (Å): 0.71073; Unit cell dimensions: a = 6.9243 (6) Å, b =7.7262 (8) Å, c = 11.8168 (6) Å, α = 84.550 (6)°, β = 81.852 (6)°, γ = 83.023 (8)°; Volume (Å3): 619.22 (9); Z = 2; Radiation type: MoKα; Absorption coefficient (mm-1): 0.10; Density (Mg m−3): 1.428; F(000): 276; Crystal size (mm): 0.34 x 0.12 x 0.06; 7628 measured reflections; 2283 independent reflections; Rint = 0.039; R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051; wR (F2) = 0.159; S = 1.04; 2283 reflections; 221 parameters.
2.1.3.2. (Coumarin-3-yl)-4-mehylbenzoate (2b)
- Yield: 93%; 1H-NMR (CDCl3; 400 MHz): 2.47 (s, 3H, CH3); 7.33 (d, 2H, J = 7,5 Hz, H-6 and H-8); 7.37 (d, 1H, J = 7.4 Hz, H-7); 7.43 (d, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz, H-5); 7.52 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, H-14 and H-16); 7.66 (s, 1H, H-4); 8.1 (d, 2H, J = 8.2 Hz, H-13 and H-17). 13C-NMR (CDCl3; 100 MHz): 21.82 (C-18); 116.71 (C-8); 118.61 (C-10); 124.9 (C-4); 125.41 (C-12); 127.86 (C-6); 129.41 (C-14 and C-16); 130.61 (C-13 and C-17); 130.96 (C-5); 131.14 (C-7); 136.54 (C-3); 145.17 (C-15) ; 152.12 (C-9); 156.73 (C-11); 164.09 (C-2). DEPT135°: 21.82 (C-18); 116.71 (C-8); 124.9 (C-4); 127.86 (C-6); 129.41 (C-14 and C-16); 130.61 (C-13 and C-17); 130.96 (C-5); 131.14 (C-7). IR (cm-1): 1744.3 (C=O, ester); 1726.4 (C=O, lactone); 1611.2 (C=C); 3054.9 (C-H, aromatic ring); 2960 (C-H, aliphatic); 1248.7 (C−O, ester); 1097.8 (C−O, lactone). ESI-MS: [M+H]+: 281.
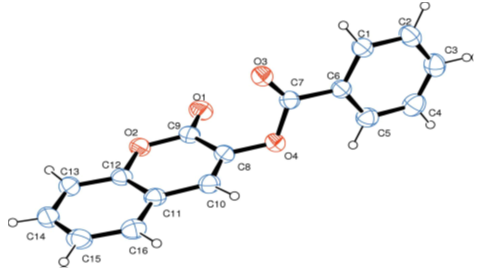 | Figure 1. Molecular structure of compound 2a. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are shown as spheres of arbitrary radius |
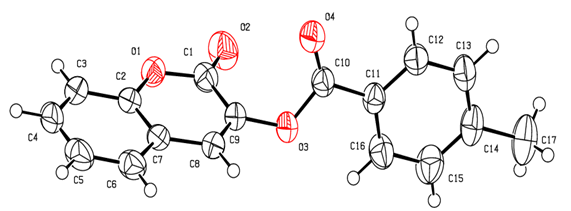 | Figure 2. Molecular structure of compound 2b with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level |
2.1.3.3. (coumarin-3-yl)-4-tertiobutylbenzoate (2c)
- Yield: 84%; 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6; 600 MHz):1.2019 (s, 9H, 3CH3); 7.4229 (d, 1H, J = 6.6 Hz, H-7); 7.44855 (d, 1H, J = 9.9 Hz, H-5); 7.5001 (d, 2H, J = 7.92 Hz, H-6 and H-8); 7.6457 (d, 2H, J = 7.44 Hz, H-14 and H-16); 7.8154 (d, 2H, J = 7.08 Hz, H-13 and H-17); 8.0473 (s, 1H, H-4). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6; 400 MHz): 30.73 (CH3); 39.04 (C-18); 116.39 (C-8); 118.36 (C-10); 124.87 (C-12); 125.34 (C-4); 126.02 (C-14 and C-16); 128.54 (C-6); 130.49 (C-13 and C-17); 131.61 (C-5); 132.07 (C-7); 135.56 (C-3); 151.74 (C-9); 156.15 (C-11); 157.90 (C-15); 163.53 (C-2). DEPT 135°: 30.73 (CH3); 116.39 (C-8); 125.34 (C-4); 126.02 (C-14 and C-16); 128.54 (C-6); 130.49 (C-13 and C-17); 131.61 (C-5); 132.07 (C-7). IR (cm-1): 1726.6 (C=O, ester); 1705.3 (C=O, lactone); 1603.1 (C=C); 3046.4 (C-H, aromatic ring); 2913.8 (C-H, aliphatic); 1269.4 (C−O, ester), 1091.8 (C−O, lactone). ESI-MS: [M+H]+: 323.Crystal structure Determination (2c)Chemical formula: C20H18O4; Formula weight: 322.34; Crystal description: Prism, colorless; Melting point (K): 410-413 K; Crystal system: Monoclinic; space group: C2/c; Temperature (K): 298; Wavelength (Å): λ = 0.71073; Unit cell dimensions: a = 22.8977 (5) Å, b = 5.9947 (1) Å, c = 24.0352 (7)Å; β = 93.297 (2)°; Volume (Å3): 3293.73(13); Z = 8; Radiation type: MoKα; Absorption coefficient (mm-1): 0.09; Density (Mg m−3): 1.300; F(000): 1360; Crystal size (mm): 0.34 x 0.12 x 0.06; 19994 measured reflections; 3005 independent reflections; Rint = 0.031; R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048; wR(F2) = 0.127; S = 1.12; 3005 reflections; 290 parameters.
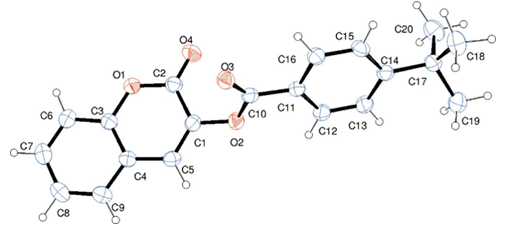 | Figure 3. Molecular structure of compound 2c with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level |
2.1.3.4. (Coumarin-3-yl)-4-chlorobenzoate (2d)
- Yield: 70%; 1H-NMR (Acetone-d6; 400 MHz): 7.32 (d, 2H, J = 7.95 Hz, H-6 and H-8); 7.44 (d, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz, H-7); 7.52 (d, 2H, J = 8.2 Hz, H-14 and H-16); 7.63 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, H-5); 7.91 (s, 1H, H-4); 8.07 (d, 2H, J = 8.4 Hz, H-13 and H-17). 13C-NMR (Acetone-d6; 100 MHz): 116.35 (C-8); 116.67 (C-10); 125.05 (C-4); 127.16 (C-12); 128.47 (C-6); 128.68 (C-5); 129.25 (C-14 and C-16); 131.82 (C-13 and C-17); 136.25 (C-3); 140.14 (C-15); 151.5 (C-7); 152.3 (C-9); 157.5 (C-11); 162.92 (C-2). DEPT135°: 116.35 (C-8); 125.05 (C-4); 128.47 (C-6); 128.68 (C-5); 129.25 (C-14 and C-16); 131.82 (C-13 and C-17); 151.5 (C-7). IR (cm-1): 1746.4 (C=O, ester), 1724.9 (C=O, lactone), 1592 (C=C); 3052.7 (C-H, aromatic ring); 1249.4 (C−O, ester); 1092.1 (C−O, lactone); 750 (C-Cl). ESI-MS [M+H]+: 301.Crystal structure Determination (2d)Chemical formula: C16H9ClO4; Formula weight: 300.68; Crystal description: Prism, colourless; Melting point (K): 478-479; Crystal system: Triclinic; space group: P1; Temperature (K): 293; Wavelength (Å): λ = 1.54184; Unit cell dimensions: a = 6.7866 (4) Å; b = 7.1789 (3)Å, c = 14.0981 (5) Å; α = 94.098 (3)°; β = 93.461 (4)° ;γ = 106.154 (4)°; Volume (Å3): 655.75 (5); Z = 2; Radiation type: CuKα; Absorption coefficient (mm-1): 2.72; Density (Mg m−3): 1.523; F(000): 308; Crystal size (mm): 0.12 × 0.12 × 0.08; 7634 measured reflections; 2409 independent reflections; Rint = 0.022; R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039; wR (F2) = 0.106; S = 1.05; 2409 reflections; 190 parameters.
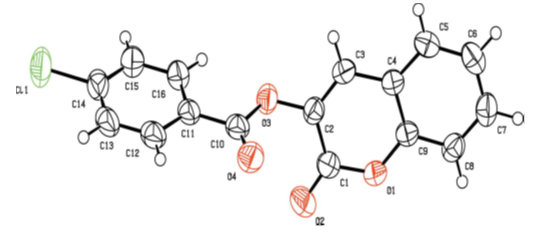 | Figure 4. Molecular structure of compound 2d with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level |
2.1.3.5. (Coumarin-3-yl)-4-fluorobenzoate (2e)
- Yield: 80%; 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6; 600MHz): 7.43125 (d, 1H, J = 7.26 Hz, H-8); 7.4716 (t, 1H, J = 8.82 Hz, H-6); 7.51165 (d, 2H, J = 8.34 Hz, H-14 and H-16); 7.6645 (t, 1H, J = 8.58 Hz, H-7); 7.76295 (d, 1H, J = 9 Hz, H-5); 8.1940(s,1H,H-4); 8.2088 (d, 2H, J = 8.76 Hz, H-13 and H-17). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6; 100 MHz): 116.36 (C-14 and C-16); 116.50 (C-8); 118.28 (C-10); 125.21 (C-4); 128.57 (C-6); 131.7 (C-5); 132.19 (C-7); 133.10 (C-13 and C-17); 135.39 (C-12); 151.63 (C-3); 156.07 (C-9); 162.66 (C-11); 165.00 (C-2); 166.88 (C-15). DEPT 135°: 116.36 (C-14 and C-16); 116.50 (C-8); 125.21 (C-4); 128.57 (C-6); 131.7 (C-5); 132.19 (C-7); 133.10 (C-13 and C-17). IR (cm-1): 1746.4 (C=O, ester); 1724.0 (C=O, lactone); 1604.4 (C=C); 3059.5 (C-H, aromatic); 1245.4 (C−O, ester); 1099.1 (C−O, lactone); 1151 (C-F). ESI-MS: [M+H]+: 285.Crystal structure Determination (2e)Chemical formula: C16H9FO4; Formula weight: 284.23; Crystal description: prism, colourless; Melting point (K): 452-454; Crystal system: Triclinic; space group: P1; Temperature (K): 293; Wavelength (Å): λ = 1.54184; Unit cell dimensions: a = 6.8116 (2) Å, b = 7.2402 (2) Å, c = 13.4826 (3) Å, α = 96.943 (2)°, β = 90.862 (2)°, γ = 106.139 (2)°; Volume (Å3): 633.21 (3); Z = 2; Radiation type: CuKα; Absorption coefficient (mm-1): 1.00; Density (Mg m−3): 1.491; F(000): 292; Crystal size (mm): 0.36 × 0.26 × 0.16; 12676 measured reflections; 2358 independent reflections; Rint = 0.017; R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036; wR(F2) = 0.100; S = 1.09; 2358 reflections; 191 parameters.
2.1.3.6. (Coumarin-3-yl)-4-cyanobenzoate (2f)
- Yield: 67%; 1H-NMR (CDCl3; 400MHz): 7.32 (d, 1H, J = 7.7 Hz, H-8); 7.39 (d, 1H, J = 7.92 Hz, H-6); 7.51 (d, 1H, J = 7.98 Hz, H-7); 7.60 (d, 1H, J = 8.01 Hz, H-5); 7.68 (s, 1H, H-4); 7.80 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, H-14 and H-16); 8.3 (d, 2H, J = 8.2 Hz, H-13 and H-17). 13C-NMR (CDCl3; 100 MHz): 114.7 (C15); 116.87 (C-8); 117.85 (C-18); 125.09(C-4); 127.99(C-6); 128.44(C-10); 130.97(C-5); 131.17 (C-13 and C-17); 131.59 (C-7); 132.46 (C-14 and C-16); 133.99 (C-12); 137.30 (C-3); 151.06 (C-9); 159.34 (C-11); 161.46 (C-2). DEPT135°: 116.87 (C-8); 125.09(C-4); 127.99(C-6); 130.97(C-5); 131.17(C-13 and C-17); 131.59 (C-7); 132.46 (C-14 and C-16). IR (cm-1): 1745.8 (C=O, ester); 1722.7 (C=O, lactone); 1606.2 (C=C); 3064 (C-H, aromatic ring); 1239.6 (C−O, ester); 1106.0 (C−O, lactone); 2236 (CN). ESI-MS [M+H]+: 292.
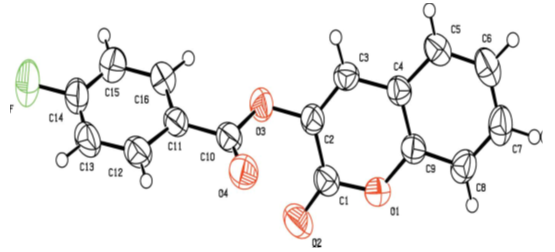 | Figure 5. Molecular structure of compound 2e with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level |
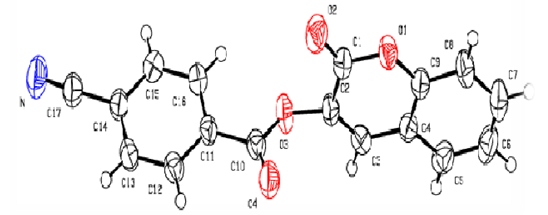 | Figure 6. Molecular structures of compound 2f with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50 % probability level |
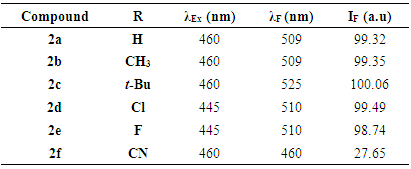
2.2. Fluorescence Spectra
- The fluorescence spectra of compounds 2 were recorded in the solid state on a SAFAS Xenius fluorimeter equipped with a temperature controlled 10-cell auto sampler for liquid analysis and an optic nose for solid analysis. Spectra acquisition were performed in 2D (Excitation-Emission Matrices). The fluorescence spectra were recorded using excitation into the maximum of the longest wavelength absorption band program. All compounds were excited at their respective maximum excitation wavelength.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
- Compounds 2 were prepared in high to acceptable yields (65% – 91%), by an O-acylation reaction of chroman-2,3-dione (tautomer of 3-hydroxycoumarin) with the corresponding benzoyl chloride (Scheme 1). Examination of the information obtained from the NMR spectra enabled us to assign the chemical shifts of the different protons and carbons for all compounds. The FT-IR spectra of compounds 2 showed their main characteristic absorption bands (C=O, lactone); (C=O, ester); (C=C); (C-H Aromatic ring); (C−O, lactone); (C−O, ester)…The molecular structures of all compounds were resolved by X-ray diffractometry and are shown in the different ORTEP structures obtained, with the atomic numbering scheme used.As it can be observed, all the molecules under study adopted some similar aspects in the conformation of the crystal. Coumarin nucleus and aromatic ring attached to the ester bridge in each molecule are planar, as expected. The main difference between the molecular structures of compounds 2 is the dihedral angle between coumarin ring system and the benzene ring: 2a: 83.58(9)°; 2b: 79.64(5)°; 2c: 57.55(9)°; 2d: 73.95(8)°; 2e: 70.18(6)°; 2f: 87.35(5)°. For all compounds, the C-O-C-C torsion angle and the dihedral angles between the coumarin cycle and the benzoate group also vary with steric hindrance.In the different structures, intramolecular bonds, valence bonds and stacking modes (C-H ... π; π ... π) have been observed, connecting the molecules in a three-dimensional supramolecular framework [25-28]. The analysis of the crystallographic data provides further evidence on the results of the structural characterization of the compounds 2.
3.2. Fluorescence Properties
- The different bands are characterized by the position of the maximum emission, analyzed through the wavelength (λF) and the fluorescence intensity (IF). The results are reported in the table below (table 2).
|
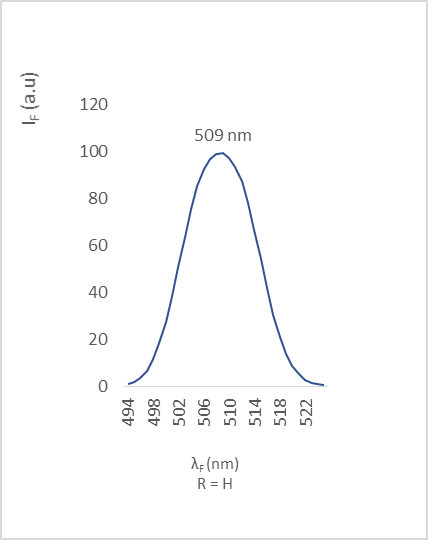 | Figure 7. Fluorescence emission of compound 2a |
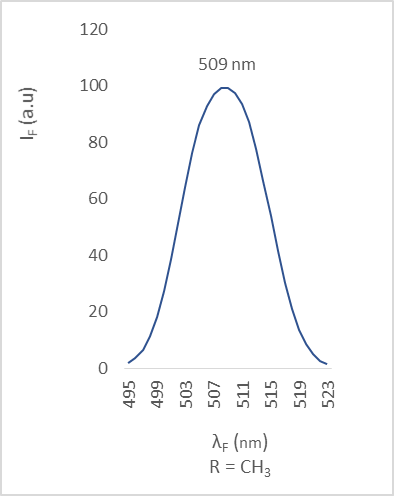 | Figure 8. Fluorescence emission of compound 2b |
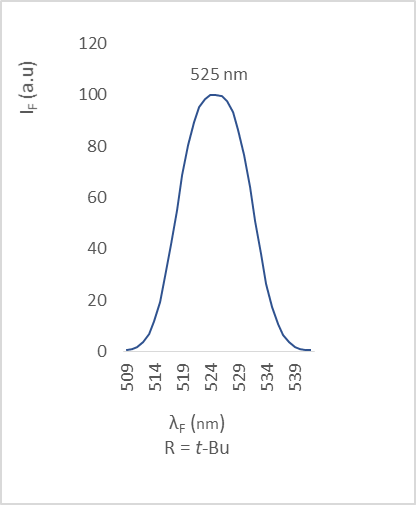 | Figure 9. Fluorescence emission of compound 2c |
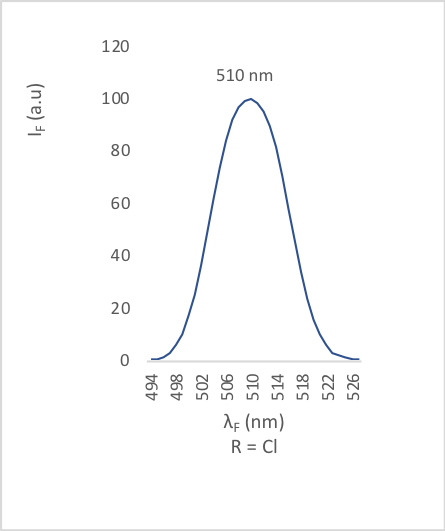 | Figure 10. Fluorescence emission of compound 2d |
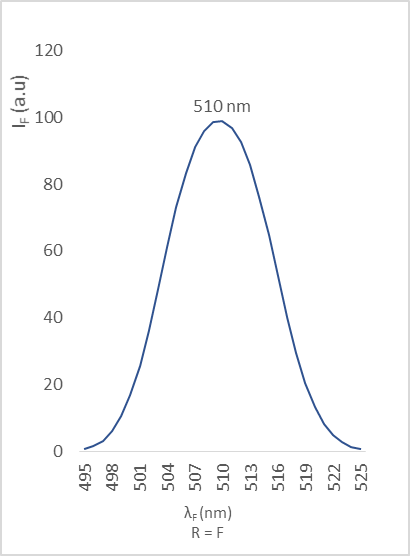 | Figure 11. Fluorescence emission of compound 2e |
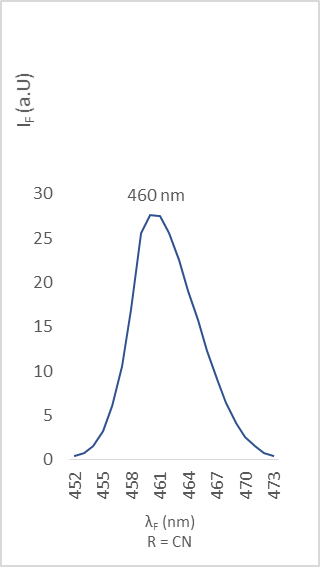 | Figure 12. Fluorescence emission of compound 2f |
4. Conclusions
- A series of 3-substituted coumarin derivatives (compounds 2a-2f) were successfully synthesized and the proposed structures were determined by spectral analysis performed by IR, NMR, and ESI-MS and confirmed by X-ray diffractometry.Fluorescence properties of these (coumarin-3-yl)-benzoates were studied in the solid state. The fluorescence emission was influenced by the electronic nature of the substituting group R. In summary, all the compounds exhibited intense fluorescence except compound 2f, due to the great electron-withdrawing ability of its substituent cyano (R = CN).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We are indebted to the Spectropole Service of the Federation of Chemical Sciences (Aix-Marseille University, France) for its help with the whole structural analysis. The authors also thank the Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry (Department of Chemistry, Aix-Marseille University, France) for recording fluorescence spectra.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML